Abstract
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune skin disease with current treatments often causing significant side effects. This study systematically evaluated the therapeutic potential and mechanisms of polyphenolic compounds in psoriasis treatment. Following PRISMA guidelines, we searched PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect databases between January 2008 and September 2023. Studies investigating polyphenolic effects on psoriasis through in vitro, animal, or clinical models were included. Twenty-five studies met inclusion criteria: nine in vitro studies, eleven animal studies, and five clinical trials. Curcumin was most extensively studied, demonstrating 30–60% reductions in inflammatory markers (TNF-alpha, IL-17, IL-22) and significant PASI score improvements. Mechanistic analysis revealed polyphenols primarily target NF-kappaB pathway inhibition and IL-17/Th17 axis suppression, addressing fundamental inflammatory processes in psoriatic pathophysiology. However, limited clinical evidence represents a significant implementation barrier. Polyphenols show potential as adjunctive therapies to conventional topical and systemic treatments. Future research should prioritize large-scale randomized controlled trials with standardized formulations and combination therapy investigations to establish clinical efficacy and overcome bioavailability challenges.
1. Introduction
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease that represents a wide clinical spectrum—from skin manifestations to joint involvement—such as psoriatic arthritis, dactylitis, enthesitis, axial spondyloarthritis, and nail disease [1]. It affects an estimated 2–3% of the global population, with prevalence reaching 8–11% in certain Northern European regions [2].
The past two decades have seen significant advances in understanding the pathobiology of the disease. This has led to the adoption of biologic therapies based on key cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin (IL)-23, and IL-17A, which have transformed disease management [3]. Current treatment modalities encompass topical therapies (corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs), systemic conventional drugs (methotrexate, cyclosporine), biologic agents (anti-TNF, anti-IL17, anti-IL23), and phototherapy, each with distinct efficacy and limitation profiles [4,5]. Topical treatments achieve 60–70% symptom improvement in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis but face adherence challenges and skin atrophy risks [6,7]. Systemic therapies provide 60–75% psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) improvements but carry significant organ toxicity concerns requiring careful monitoring [8]. Biologics demonstrate superior efficacy with PASI 75 response rates ranging from 43–72% for anti-TNF agents to 65–73% for newer IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors but present substantial barriers including annual costs ranging from USD 39,000–USD 79,000, increased infection risks, and treatment discontinuation affecting 15–32% of patients within the first year [9,10,11].
Despite these therapeutic advances, significant unmet needs persist, including treatment resistance, cost-related discontinuation affecting 25–40% of biologic users, and the need for safer, more accessible alternatives that can address the multifactorial nature of psoriatic inflammation [12,13].
The rationale for investigating polyphenolic compounds extends beyond monotherapy applications to their potential as adjunctive treatments that could enhance conventional therapy outcomes while minimizing adverse effects. This adjunctive approach could address current treatment limitations including high costs and systemic toxicity while leveraging the multi-target anti-inflammatory mechanisms of polyphenols to complement conventional therapies [14,15]. Polyphenolic interventions may offer particular value in combination with existing treatments, potentially allowing for dose reduction in conventional therapies while maintaining or improving clinical efficacy, an approach that has shown promise in other inflammatory conditions [16].
The etiology of psoriasis is characterized as multifactorial, resulting from both genetic predisposition and environmental exposure factors [17]. This immune dysregulation leads to the activation of T helper (Th)-1 and Th-17 T cells, ultimately resulting in an overproduction of inflammatory cytokines, notably interleukins (IL) IL-1, IL-6, IL-23, IL-22, IL-17, IL-33, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). These cytokines drive inflammation, hyper-proliferation, and angiogenesis through a cascade of events. This manifests as the hallmark skin lesions and can also extend to the articular involvement observed in psoriatic arthritis [18].
Polyphenols are ubiquitously present in the plant kingdom. They are mainly plant secondary metabolites and are well known for their antioxidant properties, which hold significant relevance in mitigating oxidative stress an underlying factor in the pathophysiology of numerous diseases [19]. Associated health-promoting properties include anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, anti-angiogenic, anti-metastatic, and pro-apoptotic effects, influencing various signaling pathways [16]. These versatile properties potentially render phenolic compounds as promising candidates for managing multifactorial diseases, including psoriasis [20]. The rationale for investigating polyphenolic compounds stems from their superior safety profiles compared to conventional systemics, multi-target therapeutic mechanisms addressing inflammation and keratinocyte hyperproliferation simultaneously, cost-effectiveness potential, and opportunities for combination therapy to reduce conventional treatment doses while maintaining efficacy [14,15].
A range of plant polyphenols, including resveratrol, curcumin, epigallocatechin gallate, and others exhibit the ability to inhibit inflammatory pathways activated by TNF-alpha both in vitro and in vivo [21]. This suggests their potential therapeutic value in addressing inflammatory disorders such as psoriasis, where TNF-alpha assumes a pivotal role [22,23,24].
1.1. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a relapsing skin disease characterized by cutaneous irritation, enlarged epidermal growth, hyperkeratosis, angiogenesis, and peculiar keratinization with T cell infiltration into inflamed skin tissue. It affects up to 2–3% of the worldwide population or more than 125 million people [25]. Psoriasis is more common in people living in cold climates than in people living in the tropics. The disease affects 0.6–6.5% of people in Europe and is more common in northern countries [26].
Psoriasis can occur at any age but is most common between the ages of 50 to 69 years. The most commonly affected areas are the fingernail, toenails, trunk, elbows, knees and scalp, or other cutaneous surfaces [27]. The most common form of the disease, psoriasis vulgaris, is characterized by almost symmetrical red and scaly plaques and papules covered with white or silver scales, especially on the surfaces of the limb extensors, scalp, and lumbosacral region [28]. Additional symptoms include itching, joint pain, eye irritation, skin injuries, skin cracks, and small flaky skin patches in babies [29]. Irritation and angiogenesis correspond to the pathophysiology of psoriasis and promote uncontrolled keratinocyte growth. Phototherapies and medications with antiproliferative effects that inhibit keratinocyte growth are the primary treatment options for psoriasis [30]. However, current treatments can aggravate symptoms and trigger phototoxicity, hypersensitivity, organ damage, malignant growth, and systemic immunosuppression [31]. Consequently, identifying natural treatment options represents a vital alternative.
The etiology of psoriasis is unclear, but the leading causes are the imbalance in genetic, immunological, and environmental factors and the involvement of oxidative stress. There is also evidence that psoriasis develops by external and internal triggers [32]. Many research studies have shown that factors that trigger psoriasis include mild trauma, sunburn, infections, systemic medications, stress, smoking, air pollution, physical damage, and biological agents that can lead to damage to keratinocytes [33]. Additionally, over the past few years, numerous studies have shown evidence that reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) synthase are involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Redox imbalance and increased levels of inducible NOS are responsible for the generation of oxidative stress [26].
1.2. Categorizing Polyphenols
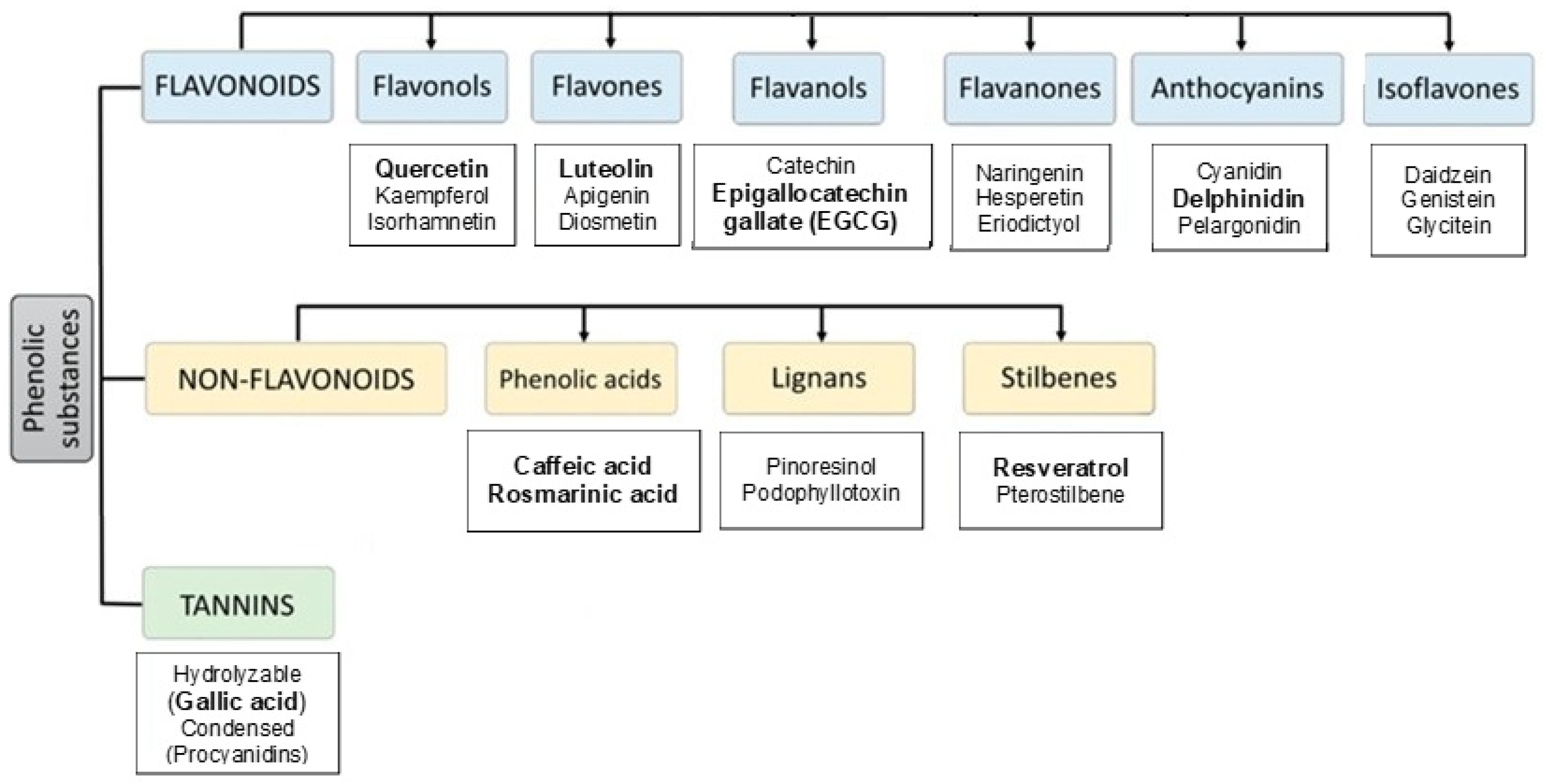
Polyphenolic compounds are a large group of secondary metabolites with antioxidant properties that protect the tissues in the human body from the harmful effects of oxidative stress. Phenolic compounds can be obtained from different sources such as fruits, vegetables, herbs, and nuts [19]. Polyphenols are a large group of bioactive plant compounds with a wide variety of diverse structures, classified into two main groups: non-flavonoids and flavonoids (Figure 1).
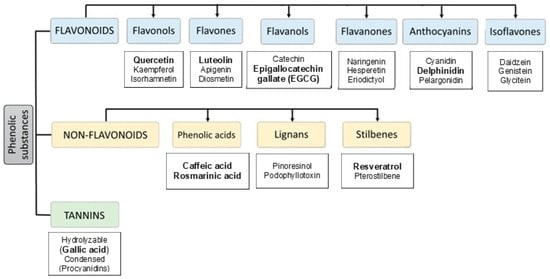
Figure 1.
Classification of dietary phenolic compounds, with reviewed polyphenols in bold.
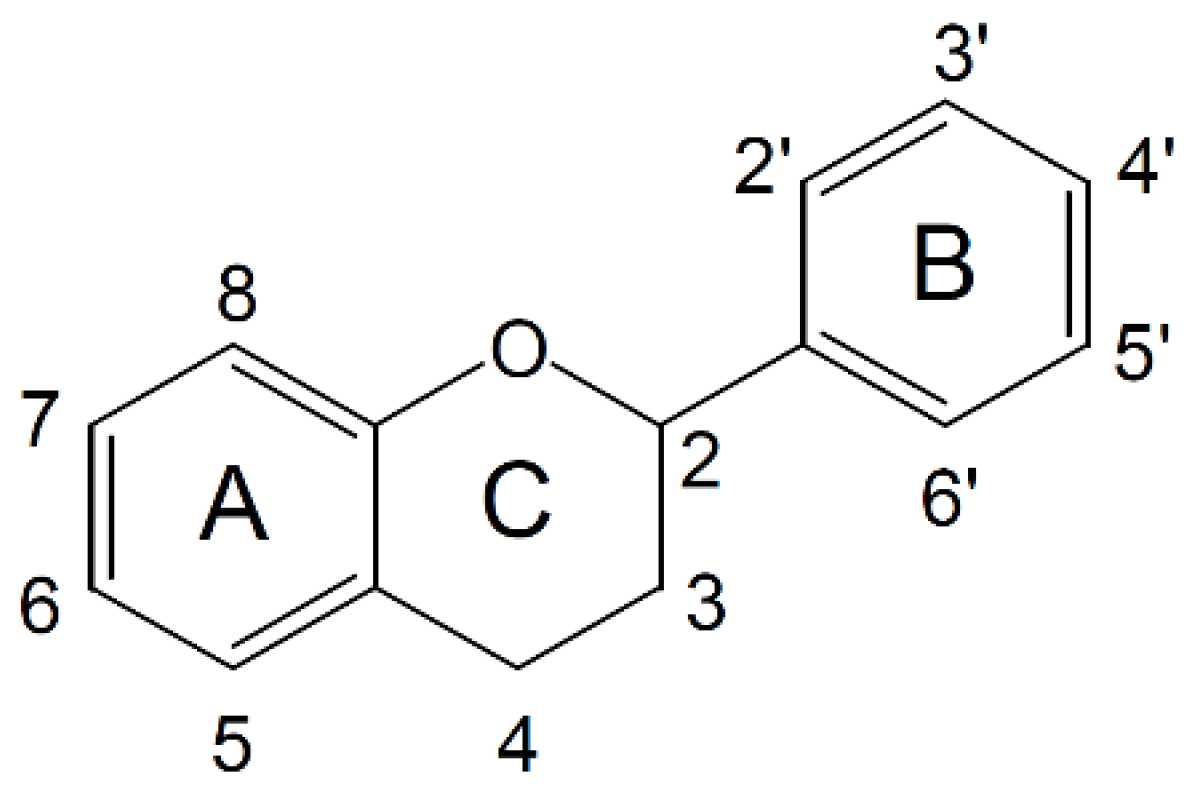
The flavonoid class is defined by a basic C6-C3-C6 skeleton structure (Figure 2). In this structure, two aromatic rings are linked by a heterocyclic ring, whose degree of oxidation leads to further subclassification into flavones, flavonols, isoflavones, flavanones, anthocyanins, and flavanols (or catechins) [34]. In plant-based foods, polyphenols are primarily present in conjugated forms, either linked to acid-alcohol derivatives or glycosides. Additionally, they can exist as oligomeric and polymeric structures, commonly referred to as tannins. Tannins are generally categorized into two types: hydrolysable tannins and condensed tannins [35].
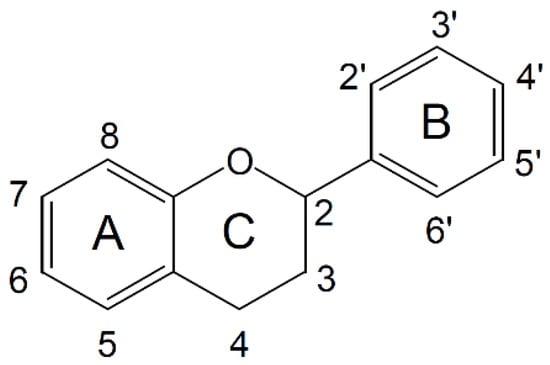
Figure 2.
Basic flavonoid structure. Numbers indicate carbon positions in the flavonoid backbone, with rings designated as A, B, and C.
This study summarizes the effects of selected polyphenols such as rosmarinic acid, gallic acid, curcumin, resveratrol, apigenin, delphinidin, genistein, luteolin, and quercetin as promising anti-psoriatic agents. The use of phenolic compounds for many therapeutic purposes due to their versatile effects may direct future research. This systematic literature review focuses on reported in vitro, in vivo, and clinical trial studies regarding the potential and underlying mechanisms of polyphenolic compounds in the treatment of psoriasis.
This systematic review adopts a mechanistic-to-clinical translational framework to evaluate polyphenolic compounds as emerging therapeutic agents for psoriasis. The review examines three core parameters: (1) convergent anti-inflammatory mechanisms across NF-kappaB, IL-17/Th17, and oxidative stress pathways demonstrated in preclinical models; (2) comparative therapeutic efficacy from laboratory studies through clinical applications, with particular focus on curcumin, quercetin, and resveratrol; and (3) critical translational barriers including bioavailability challenges, formulation strategies, safety considerations, and clinical implementation gaps. Through this conceptual approach, we provide mechanistic insights for researchers investigating natural anti-inflammatory compounds while offering practical guidance for clinicians considering polyphenolic interventions as adjunctive therapies to enhance conventional treatment outcomes or as alternative therapies in psoriasis management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol Registration
This systematic review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [36] (Supplementary Material S1). The review protocol was prospectively registered on the Open Science Framework (OSF) and is publicly accessible at: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/7M6AU (accessed on 8 July 2025).
2.2. Data Sources and Search Strategy
Electronic searches for eligible studies were conducted using the databases PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect between January 2008 and September 2023. The 15-year timeframe was selected to ensure comprehensive coverage of both foundational mechanistic studies and recent clinical investigations in this specialized field. This extended period was necessary due to the limited research volume in polyphenols for psoriasis treatment; a more restrictive timeframe would have substantially reduced the number of available studies, potentially compromising the review’s depth and reliability. The timeframe allows for charting the evolution of polyphenol research in psoriasis from early mechanistic investigations to advanced molecular and clinical studies.
The search strategy used expanded terms including “polyphenol” or “phenolic compounds” AND “psoriasis”, as well as specific polyphenol names including “curcumin”, “resveratrol”, “quercetin”, “luteolin”, “gallic acid”, “rosmarinic acid”, “EGCG”, “delphinidin”, “astilbin”, “apigenin”, “genistein”, and “baicalin” each combined with “psoriasis”. Additional keywords related to study types were included: “clinical trial”, “animal model”, “in vitro”, “randomized controlled trial”, and “research” to capture relevant study designs.
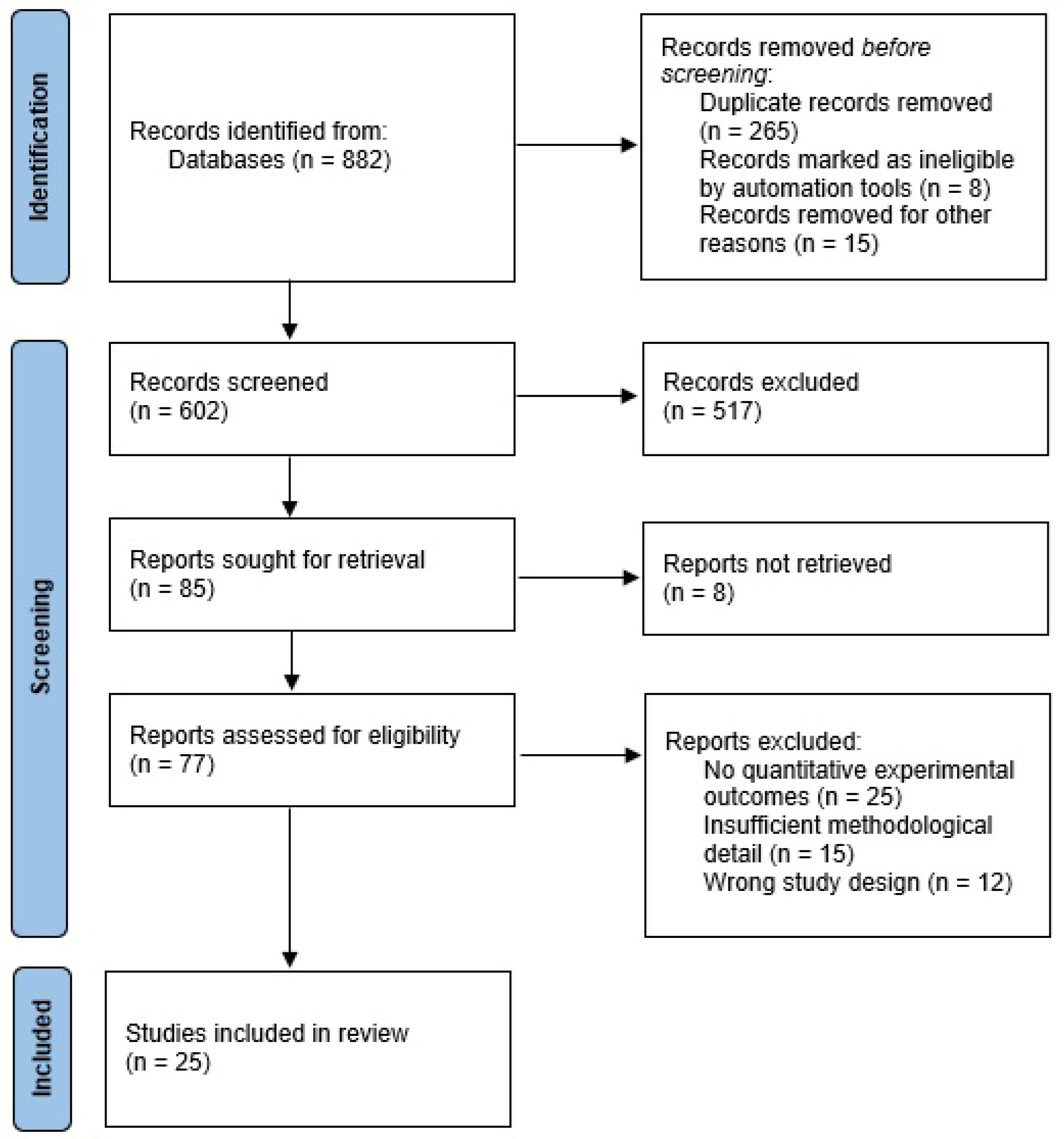
The search was limited to articles that were published in English. Following the initial search, titles and abstracts were examined for relevance, and studies that did not report experimental data (reviews, commentaries, case reports without experimental components) were excluded. The complete study selection process is detailed in the PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 3).
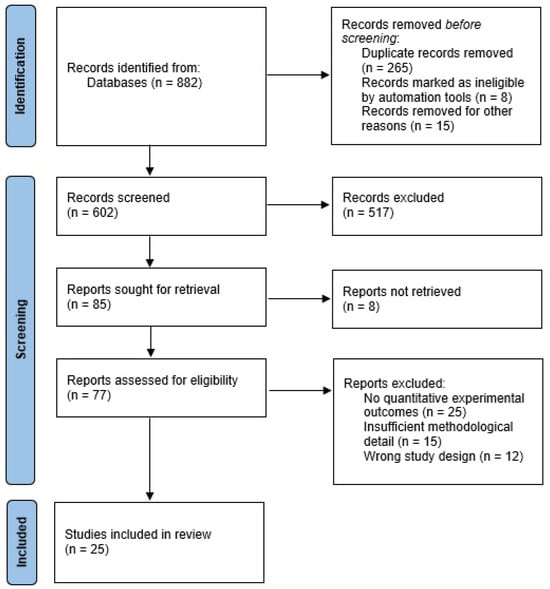
Figure 3.
PRISMA flow diagram.
2.3. Study Selection and Data Acquisition
Studies were included if they met the following criteria: (1) investigated the effects of identified polyphenolic compounds on psoriasis or psoriatic inflammation; (2) included in vitro studies using relevant cell models (keratinocytes, immune cells), animal studies with psoriasis-like models, or clinical trials in psoriatic patients; (3) reported quantitative outcomes related to inflammatory markers, disease severity, or mechanistic endpoints; and (4) were published in peer-reviewed journals.
Randomized studies comparing the use of polyphenol supplements in the treatment of psoriasis with placebo or control groups without polyphenol supplements as well as mechanistic studies elucidating anti-psoriatic pathways were prioritized for inclusion in the systematic review.
Study selection and data extraction were conducted independently by two reviewers (S.P. and M.R.), with extracted data organized into a comprehensive matrix. Study quality was assessed qualitatively by two reviewers (S.A. and M.R.) based on study design, sample size, methodology, and reporting quality. Conflicts were resolved through consultation with a third reviewer (T.A.A.). Data extraction captured both general study characteristics (including author details, publication year, and study design) and specific information regarding polyphenolic interventions, experimental methodologies, outcome measurements, and therapeutic mechanisms.
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics and Quality Assessment
The 25 included studies comprised 9 in vitro studies (36%), 11 in vivo animal studies (44%), and 5 clinical trials (20%) (Figure 3). The studies were published between 2010 and 2023, with the majority (60%) published after 2015, reflecting increased scientific interest in polyphenolic anti-psoriatic research.
Clinical trials included two randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with curcumin, two RCTs with plant polyphenol extracts (olive polyphenols, silver fir), and one observational study with Pycnogenol®. Sample sizes ranged from 30 to 63 participants, with treatment durations varying from 4 to 12 weeks. Both curcumin trials demonstrated significant improvements in PASI scores and inflammatory markers.
Most animal studies (8/11, 73%) utilized BALB/c mice with imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis models, which are widely regarded as the gold standard for psoriatic inflammation research [37]. Treatment durations ranged from 1 to 12 weeks, with 64% (7/11) utilizing topical administration routes, reflecting clinical application preferences.
In vitro studies employed various cell models, with human adult low calcium temperature (HaCaT) keratinocytes used in 44% (4/9) of studies, normal human keratinocytes in 33% (3/9), and T cells from psoriatic patients in 22% (2/9). Polyphenol concentrations tested ranged from 1 to 100 uM, with most effective concentrations falling between 10 and 50 uM, indicating therapeutic windows consistent with achievable tissue concentrations.
3.2. Polyphenol Distribution
Curcumin was the most extensively studied polyphenol (eight studies, 32%), reflecting its established safety profile, commercial availability, and promising preliminary results. Quercetin and resveratrol each appeared in two studies. Single studies investigated gallic acid, rosmarinic acid, luteolin, delphinidin, astilbin, baicalin, and various plant polyphenol extracts. This distribution pattern highlights the need for expanded research on lesser studied but potentially efficacious compounds.
3.3. Study Characteristics and Therapeutic Outcomes
The review identified a limited number of studies that met the inclusion criteria. A total of 25 research articles were included in the qualitative synthesis. Research articles that suggested various anti-psoriatic mechanisms of polyphenols included nine in vitro studies, eleven in vivo studies, and five clinical trial-based studies. These studies varied in terms of design, sample size, and polyphenol types (e.g., curcumin, resveratrol) used as interventions. The outcomes measured included psoriasis severity scores, symptom improvement, and quality of life. The study characteristics and therapeutic outcomes of the 25 studies selected for inclusion in the systematic review are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Studies on polyphenols for psoriasis treatment.
3.4. Dose–Response Relationships and Bioavailability Considerations
Critical to understanding clinical translation potential, dose–response relationships and bioavailability considerations varied significantly across polyphenolic compounds (Table 2). These pharmacokinetic parameters directly determined which compounds successfully progressed from laboratory studies to clinical applications.

Table 2.
Pharmacokinetic and dosing parameters for polyphenolic compounds in psoriasis treatment.
The reviewed studies revealed considerable variability in effective dosing regimens across polyphenolic compounds, with disparities between laboratory concentrations and clinically achievable levels.
Administration route significantly influenced therapeutic outcomes, with clear distinctions observed between topical and systemic applications. Topical formulations target local inflammatory processes directly at psoriatic lesions, offering advantages for localized disease with minimal systemic exposure and reduced risk of systemic adverse effects. Examples include 1% EGCG cream and 5% baicalin cream, which achieved direct dermal delivery that circumvented systemic bioavailability limitations while providing localized anti-inflammatory effects at the site of application.
Conversely, systemic oral formulations provide comprehensive immunomodulation suitable for extensive or severe psoriasis, targeting both cutaneous and potential systemic inflammatory components. These formulations required bioavailability enhancement strategies, such as curcumin’s Meriva® phospholipid complexation, to achieve therapeutic plasma concentrations sufficient for systemic immunomodulatory effects.
Curcumin demonstrated dose–response data spanning in vitro concentrations of 10–50 µM to clinical doses of 1000–2000 mg daily. Clinical trials utilized bioavailability enhancement approaches, including phospholipid complexation (Meriva®) and standardized extracts for oral administration, while topical applications were employed for compounds like EGCG (1% cream) and baicalin (5% cream) through direct dermal delivery.
3.5. Structure–Activity Relationships of Major Polyphenols
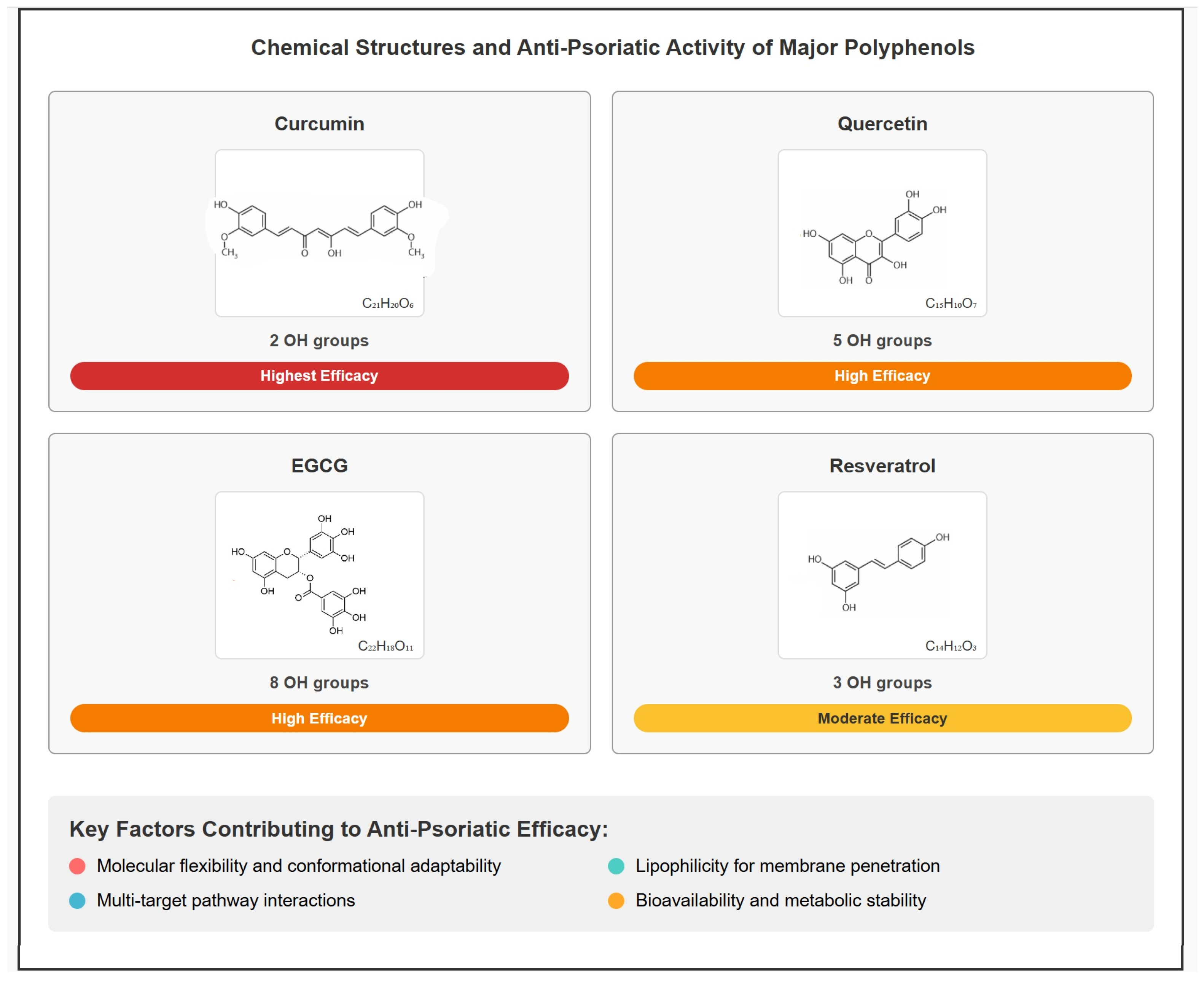
Among the 25 included studies, four polyphenolic compounds were most extensively investigated: curcumin (eight studies), quercetin (two studies), resveratrol (two studies), and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) (one study). These compounds demonstrate varying levels of anti-psoriatic efficacy that correlate with their structural features (Figure 4).
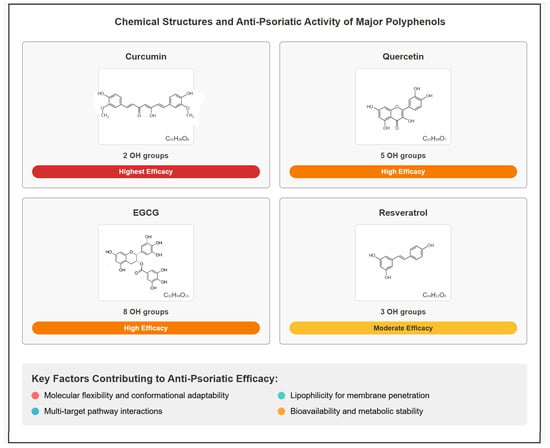
Figure 4.
Chemical structures and anti-psoriatic efficacy of major polyphenolic compounds based on systematic review evidence.
Curcumin showed the highest therapeutic efficacy with two completed RCTs demonstrating 30–60% reductions in inflammatory markers. The compound features four phenolic hydroxyl groups within its beta-diketone structure.
Quercetin and EGCG demonstrated high efficacy in animal studies, with quercetin containing five hydroxyl groups in its flavonol structure and EGCG containing eight hydroxyl groups in its catechin–gallate structure.
Resveratrol showed moderate anti-psoriatic activity in preclinical studies, containing three hydroxyl groups within its stilbene framework.
Common structural features observed across effective anti-psoriatic polyphenols include multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups (3–8), aromatic ring systems, and conjugated double bond systems (Figure 4).
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanistic Analysis of Polyphenolic Anti-Psoriatic Effects
Plant polyphenols demonstrate anti-psoriatic properties through multiple interconnected mechanisms, primarily involving the inhibition of pro-inflammatory pathways that drive psoriatic pathophysiology [27]. The evidence reveals several key therapeutic targets that are consistently modulated across different polyphenolic compounds.
4.1.1. NF-kappaB Pathway Modulation: A Central Mechanism
The NF-kappaB pathway emerges as the most consistently targeted mechanism across multiple polyphenolic compounds, with seven different polyphenols (curcumin, resveratrol, luteolin, gallic acid, lignans, astilbin, and rosmarinic acid) demonstrating significant inhibitory activity. This convergence suggests that NF-kappaB represents a critical therapeutic node for polyphenolic interventions in psoriasis.
Curcumin exhibited the most comprehensive NF-kappaB inhibition, with studies demonstrating reduced expression of both NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2 subunits and downstream inflammatory mediators. The compound’s dual action on multiple NF-kappaB pathways, as demonstrated by Saelee et al. [44], suggests broad-spectrum inflammatory suppression rather than pathway-specific effects.
Luteolin demonstrated particular selectivity for TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation, specifically reducing mRNA expression of NFKB1 and RELA genes [53]. This selectivity is therapeutically significant given TNF-alpha’s central role in psoriatic inflammation and the success of anti-TNF biologics in clinical practice [59].
Resveratrol’s NF-kappaB inhibition correlated with clinical improvements in animal models, suggesting this pathway’s therapeutic relevance [45]. The consistent targeting of this pathway across structurally diverse polyphenols indicates its fundamental importance in anti-psoriatic mechanisms.
4.1.2. IL-17/Th17 Axis Suppression: Targeting Adaptive Immunity
The IL-17/Th17 pathway represents another critical therapeutic target, with five polyphenols (curcumin, astilbin, rosmarinic acid, gallic acid, and resveratrol) demonstrating significant suppressive effects on this axis that drives psoriatic inflammation.
Curcumin showed the broadest spectrum of IL-17 pathway inhibition, reducing IL-17 production by 30–60% in T cell studies [24] and suppressing Th17-related cytokines (IL-17A, IL-22, IL-23) across multiple experimental models [24,40]. Importantly, these effects occurred without compromising T cell viability, suggesting selective immunomodulation rather than generalized immunosuppression [41].
Astilbin’s mechanism involves direct inhibition of Th17 cell differentiation through modulation of the Janus kinase 3 (JAK3)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway [50], representing a more upstream intervention compared to curcumin’s broader cytokine suppression. This specificity may offer advantages in terms of reduced systemic effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Rosmarinic acid, by contrast, exerts its effects through a more nuanced mechanism—suppressing Th17 differentiation via inhibition of the retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORgammat) and modulation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling [54]. This suggests that rosmarinic acid operates through multi-level intervention along the Th17 differentiation cascade.
4.1.3. Keratinocyte Proliferation Control: Addressing Hyperproliferation
Keratinocyte hyperproliferation, a pathognomonic feature of psoriatic lesions [60], was effectively controlled by six polyphenols through distinct but complementary mechanisms.
Quercetin demonstrated the most pronounced anti-proliferative effects, significantly reducing epidermal thickness while increasing orthokeratotic regions in animal models [46]. This dual action suggests that quercetin not only inhibits abnormal proliferation but also promotes normal differentiation processes essential for healthy skin architecture.
Curcumin enhanced skin barrier function through upregulation of differentiation markers including involucrin and filaggrin [42], addressing both hyperproliferation and barrier dysfunction. This dual mechanism may explain curcumin’s consistent clinical efficacy across multiple trials and diverse patient populations.
Delphinidin uniquely promoted keratinocyte differentiation markers (caspase-14, filaggrin, involucrin, and loricrin) while simultaneously reducing proliferation [61]. This pattern supports a primary pro-differentiation mechanism, substantiated by studies in flaky skin mice and 3D human epidermal models demonstrating enhanced differentiation without apoptosis [52,61].
4.1.4. Oxidative Stress Reduction: Addressing Fundamental Pathophysiology
Oxidative stress represents a fundamental pathophysiological component driving both inflammatory cascades and keratinocyte dysfunction in psoriasis [62,63]. Multiple polyphenolic compounds demonstrate significant antioxidant properties that correlate directly with their therapeutic effects.
EGCG exhibits particularly robust antioxidant activity through enhancement of key enzymes including superoxide dismutase and catalase [55] while simultaneously activating Nrf2-mediated antioxidant pathways [64,65]. This dual mechanism creates synergistic effects where reduced oxidative burden enhances anti-inflammatory signaling, as demonstrated in preclinical models of psoriasiform inflammation [55,66].
Gallic acid demonstrates complementary antioxidant properties through its unique phenolic structure, which enables efficient electron donation and metal chelation [67,68]. Gallic acid demonstrates therapeutic effects in stressed keratinocytes through its ability to upregulate antioxidant defenses and protect against oxidative damage, as evidenced by enhanced wound healing and increased expression of antioxidant genes [69].
Pine bark polyphenols comprise complex mixtures of proanthocyanidins and tannins that exhibit synergistic antioxidant effects. Similarly, oak bark polyphenols are rich in both condensed and hydrolyzable tannins, contributing to their potent antioxidant activity [70]. These compounds act through both enzymatic and non-enzymatic pathways, offering a broad-spectrum protective effect against oxidative cellular damage [64].
The black spruce polyphenolic extract demonstrated the most potent antioxidant capacity among tested compounds [58], with 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity significantly exceeding that of individual polyphenols. This enhanced activity correlated directly with the extract’s superior ability to suppress inflammatory mediator production in cultured psoriatic keratinocytes [22], suggesting that antioxidant potency may serve as a predictive marker for anti-inflammatory therapeutic potential. These findings suggest that oxidative stress reduction may serve as a primary therapeutic mechanism rather than merely a secondary benefit [62].
4.1.5. Multi-Target vs. Single-Target Approaches: Mechanistic Comparison
Analysis of the mechanistic data reveals two distinct approaches: multi-target compounds (curcumin, resveratrol) and more selective agents (luteolin, astilbin) [24,45,50,53].
Curcumin demonstrated the broadest mechanistic profile, simultaneously targeting NF-kappaB, IL-17/Th17, keratinocyte proliferation, and NOD-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome pathways [24,38,41]. For example, in imiquimod-induced psoriasis models, curcumin not only reduced inflammatory cytokine production but also normalized keratinocyte differentiation markers [24,42]. This multi-target approach may explain its consistent efficacy across diverse study models and its successful translation to clinical trials [38,39].
Specialized compounds like astilbin (JAK3/STAT3 selective) [50] and luteolin (TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB selective) [53] showed potent but narrower effects. For instance, astilbin specifically inhibited Th17 cell differentiation without affecting other immune pathways [50] while luteolin primarily targeted keratinocyte activation through NF-kappaB suppression [53]. While potentially offering reduced side effects, their clinical translation may require combination approaches to achieve comprehensive anti-psoriatic effects [30,31].
4.1.6. Structure–Activity Considerations
The structure–activity analysis reveals that therapeutic efficacy correlates with molecular features beyond simple hydroxyl group count (Figure 4). Curcumin’s superior clinical translation, despite containing only two hydroxyl groups compared to quercetin (five) or EGCG (eight), suggests that structural factors including molecular flexibility, lipophilicity, and bioavailability characteristics play crucial roles in determining clinical success [38,39,71]. The compound’s beta-diketone structure enables conformational adaptability and enhanced cellular penetration, potentially explaining its multi-target activity across NF-kappaB, IL-17/Th17, and keratinocyte proliferation pathways observed in our systematic review [24,38,41,42].
Conversely, compounds with higher hydroxyl group counts demonstrate excellent antioxidant activity in preclinical studies but face bioavailability challenges that may limit clinical translation. This structure–efficacy relationship provides insights for optimizing polyphenolic formulations and delivery strategies to enhance therapeutic potential [71,72].
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Polyphenol Efficacy
Among the polyphenols studied, curcumin demonstrated the most robust and consistent anti-psoriatic effects across all study designs [24,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. Eight studies investigating curcumin showed significant reductions in inflammatory markers (TNF-alpha, IL-17, IL-22) and improvements in PASI scores [38,39,41]. The compound’s multi-target approach, simultaneously affecting NF-kappaB, IL-17/Th17, keratinocyte proliferation, and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways, may explain its superior clinical translation compared to more selective compounds.
Quercetin and resveratrol showed promising results in preclinical models, particularly in reducing epidermal pathology and immune cell infiltration [45,46]. Resveratrol ameliorated imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice [45], while quercetin demonstrated anti-psoriatic activity with significant antiproliferative effects in keratinocytes [48]. However, the limited clinical trial data for these compounds represent a significant research gap that should be prioritized in future investigations.
The dose-dependent effects observed with luteolin [53] and the clinical improvements seen with olive polyphenols [47] highlight the therapeutic potential of both individual compounds and complex plant extracts. The variability in effective concentrations—from micromolar levels for pure compounds to hundreds of micrograms per milliliter for extracts—underscores the importance of standardized formulations and optimized delivery systems.
4.3. Dose–Response Relationships and Bioavailability
The dose–response analysis reveals critical translational challenges that explain the limited clinical adoption of polyphenolic interventions despite promising preclinical results. The concentration gap between effective in vitro doses (10–50 µM for most compounds) and achievable plasma concentrations through standard oral administration represents a fundamental barrier to therapeutic efficacy [24,41,42,51]. Curcumin’s successful clinical translation correlates directly with enhanced bioavailability strategies, particularly the Meriva® phospholipid complexation that achieved therapeutic plasma levels matching effective laboratory concentrations [37]. This formulation–efficacy relationship demonstrates that bioavailability enhancement is not merely advantageous but essential for clinical success [71,73].
The superior performance of topical applications for compounds like EGCG and baicalin suggests that direct dermal delivery circumvents systemic bioavailability limitations while achieving localized therapeutic concentrations [51,55]. This route-dependent efficacy pattern indicates that delivery method selection should be guided by compound-specific pharmacokinetic properties rather than conventional dosing approaches [39,74]. The variability in effective concentrations across different polyphenols—from micromolar levels for pure compounds to hundreds of milligrams for complex extracts—underscores the critical need for individualized formulation strategies and dosing optimization in future clinical investigations [47,48,72].
The reviewed studies revealed significant variability in dosing regimens and formulations across polyphenolic compounds, highlighting the complex relationship between dose, delivery method, and therapeutic efficacy. Curcumin studies employed concentrations ranging from 10 to 50 µM in vitro [24,41,42], with clinical trials using oral formulations at doses of 1000–2000 mg daily [38,39]. The bioavailability challenges associated with many polyphenols, particularly curcumin’s poor water solubility and rapid metabolism [73], suggest that formulation strategies may be crucial for clinical efficacy [30,31]. The Meriva® formulation used by Antiga et al. [38], which utilizes phospholipid complexation to enhance absorption [71], demonstrated superior clinical outcomes compared to standard curcumin preparations.
Topical applications showed promise for several compounds, potentially circumventing systemic bioavailability issues while providing localized effects through enhanced skin penetration and dermal bioavailability [74]. The turmeric tonic used by Bahraini et al. [41] achieved significant clinical improvements in scalp psoriasis with minimal systemic exposure. Similarly, the 5% baicalin cream demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in animal models [51], while olive polyphenol formulations showed clinical efficacy when applied topically [47].
Dose-dependent responses were particularly evident with plant polyphenol extracts. Black spruce extract demonstrated optimal anti-inflammatory effects at 500 µg/mL [22,58], while silver fir polyphenolic extract achieved 40% improvement rates in clinical psoriasis [48]. The variability in effective concentrations across different polyphenols—ranging from micromolar levels for pure compounds to hundreds of micrograms per milliliter for complex extracts—underscores the importance of standardized formulations and advanced delivery systems such as nanoencapsulation for bioavailability enhancement [72].
4.4. Safety Considerations and Clinical Implementation
Among the clinical trials reviewed, specific safety data were limited but generally favorable. Antiga et al. [38] reported only 1 adverse event in 31 patients receiving oral curcumin (Meriva®) 2 g daily for 12 weeks, consisting of diarrhea that was likely associated with viral gastroenteritis rather than the study product. Bahraini et al. [39] found no adverse effects from turmeric tonic in patients treated twice daily for 9 weeks. Herrera Acosta et al. [47] reported no side effects in 30 participants receiving olive polyphenol-based nutraceutical over 12 weeks. Starbek Zorko et al. [48] found silver fir polyphenolic extract was well tolerated in 61 patients over 12 weeks, with only one participant experiencing allergic contact dermatitis to the active ingredient.
However, comprehensive safety assessment remains limited due to small sample sizes (30–63 participants per study), short follow-up periods (4–12 weeks), and lack of standardized safety monitoring protocols across studies. No studies reported laboratory safety parameters, drug interaction profiles, or long-term safety data beyond 12 weeks.
The safety profile of polyphenols is generally favorable, with minimal adverse effects reported [38,39,47,48,57]. However, long-term safety data remain limited, particularly for concentrated formulations and novel delivery systems. The positive results from clinical trials, especially with curcumin (Meriva®) [38,39] and olive polyphenols [47], provide encouraging evidence for expanded human studies. The transition from in vitro and animal studies to clinical applications requires careful consideration of formulation, dosing, and potential drug interactions. Advanced formulation strategies, including the phospholipid complexation used in successful curcumin trials [38], demonstrate the importance of delivery system optimization for clinical efficacy.
4.5. Limitations and Research Gaps
The current evidence base exhibits notable constraints that warrant careful consideration. The limited clinical evidence represents the most significant barrier to therapeutic implementation, with only five human studies providing clinical data. This substantial gap between promising preclinical results and proven clinical efficacy limits confidence in therapeutic applications and prevents development of evidence-based treatment guidelines for dermatological practice.
Study heterogeneity emerges as a primary concern, with considerable variation in experimental approaches, assessment metrics, and therapeutic dosing complicating meaningful comparisons between polyphenolic interventions. The concentration gap between effective laboratory doses (10–50 uM) and clinically achievable tissue levels raises questions about therapeutic feasibility, particularly given poor bioavailability of many polyphenols.
Clinical evidence remains limited, with only five human studies encompassing modest sample sizes of 30–63 participants. While these trials employ appropriate randomization and controls, the absence of standardized polyphenolic preparations challenges establishing consistent therapeutic guidelines.
Methodological concerns affect both preclinical and clinical investigations. Animal studies predominantly use IMQ-induced psoriasis models in BALB/c mice, which may not fully recapitulate human pathophysiology, with significant variation in treatment durations affecting result reproducibility. In vitro studies show inconsistency in culture conditions, polyphenol concentrations, and exposure times, while reliance on HaCaT cells may not represent the complex cellular interactions in psoriatic lesions.
Research focus has concentrated on NF-kappaB and cytokine pathways, leaving other therapeutic mechanisms underexplored. Most investigations employ brief observation periods, providing insufficient insight into sustained benefits or extended safety profiles. The inconsistent use of biomarkers across studies hampers identification of treatment response predictors and development of personalized therapeutic strategies.
These constraints collectively explain the current disconnect between laboratory promise and limited clinical adoption, highlighting the need for comprehensive, rigorously controlled trials with standardized methodologies and clinically relevant endpoints to establish therapeutic value in psoriasis management.
5. Conclusions and Future Applications
This systematic review demonstrates that polyphenolic compounds show significant therapeutic potential for psoriasis management through convergent anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Curcumin emerges as the most promising candidate, with seven studies showing consistent reductions in inflammatory markers (TNF-alpha, IL-17, IL-22) by 30–60% and clinical improvements in PASI scores. Mechanistic analysis reveals that polyphenols primarily target NF-kappaB signaling inhibition and IL-17/Th17 axis suppression, addressing fundamental inflammatory processes in psoriatic pathophysiology. Additional compounds including quercetin, resveratrol, luteolin, and gallic acid demonstrated anti-proliferative effects on keratinocytes and selective pathway targeting, though with more limited clinical evidence.
Despite promising preclinical results, significant research gaps limit clinical translation, including scarcity of human studies (only 5 of 25 reviewed), small sample sizes, methodological heterogeneity, and bioavailability challenges. To address these limitations, future research should prioritize large-scale randomized controlled trials with standardized formulations, extended follow-up periods, and investigation of combination therapies leveraging synergistic polyphenolic effects. Integration of pharmacogenomic approaches, predictive biomarkers, and novel delivery systems including nanoparticle formulations may optimize therapeutic responses and overcome current limitations.
Specifically, clinical investigations should focus on studying polyphenolic compounds in combination with standard-of-care treatments, including topical corticosteroids, biologics, and phototherapy, to establish evidence-based protocols for adjunctive therapy that may improve patient outcomes while reducing treatment-related adverse effects and healthcare costs. Additionally, research should also define optimal selection criteria for topical versus systemic polyphenolic interventions based on disease severity, extent, and patient-specific factors.
In conclusion, the convergent mechanisms identified across multiple polyphenols provide a strong foundation for developing evidence-based polyphenolic interventions as adjunctive or alternative therapies in psoriasis management, positioning these natural compounds as promising candidates for next-generation psoriasis therapeutics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nutraceuticals5030024/s1, Supplementary Material S1: PRISMA checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P. and T.A.A.; methodology, R.A.; validation, S.A., M.R. and T.A.A.; formal analysis, S.P.; investigation, S.P.; resources, S.P.; data curation, M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A., T.A.A. and S.P.; writing—review and editing, S.A., M.R. and T.A.A.; visualization, R.A.; supervision, S.P.; project administration, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data analyzed in this systematic review are available in the published studies cited in the reference list. No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gottlieb, A.; Merola, J.F. Psoriatic Arthritis for Dermatologists. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 662–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Karimkhani Aksut, C.; Wu, D.; Alicandro, G.; McGonagle, D.; Guo, C.; Dellavalle, R.; Grada, A.; Wong, P.; et al. The Global, Regional, and National Burden of Psoriasis: Results and Insights From the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 743180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres-Ejarque, R.; Ale, H.B.; Grys, K.; Tosi, I.; Solanky, S.; Ainali, C.; Catak, Z.; Sreeneebus, H.; Saklatvala, J.; Dand, N.; et al. Author Correction: Enhanced NF-ΚB Signaling in Type-2 Dendritic Cells at Baseline Predicts Non-Response to Adalimumab in Psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmets, C.A.; Lim, H.W.; Stoff, B.; Connor, C.; Cordoro, K.M.; Lebwohl, M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Davis, D.M.R.; Elewski, B.E.; Gelfand, J.M.; et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology–National Psoriasis Foundation Guidelines of Care for the Management and Treatment of Psoriasis with Phototherapy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 775–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menter, A.; Strober, B.E.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kivelevitch, D.; Prater, E.F.; Stoff, B.; Armstrong, A.W.; Connor, C.; Cordoro, K.M.; Davis, D.M.R.; et al. Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of Care for the Management and Treatment of Psoriasis with Biologics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1029–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.R.; Mason, J.; Cork, M.; Dooley, G.; Hancock, H. Topical Treatments for Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD005028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, S.K.; McEleney, M. Topical Corticosteroids: Choice and Application. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, A.; Korman, N.J.; Elmets, C.A.; Feldman, S.R.; Gelfand, J.M.; Gordon, K.B.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Koo, J.Y.M.; Lebwohl, M.; Lim, H.W.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: Section 4. Guidelines of Care for the Management and Treatment of Psoriasis with Traditional Systemic Agents. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 451–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.B.; Gooderham, M.; Burge, R.; Zhu, B.; Amato, D.; Liu, K.H.; Shrom, D.; Guo, J.; Brnabic, A.; Blauvelt, A. Comparison of Cumulative Clinical Benefits of Biologics for the Treatment of Psoriasis over 16 Weeks: Results from a Network Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egilman, A.C.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Avorn, J.; Raymakers, A.J.N.; Rome, B.N. Use of Efficiency Frontiers to Align Prices and Clinical Benefits of Biologic Therapies for Plaque Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, S.; Zhuo, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, Q.; Chen, X.; Bao, Y.; Dhanda, D.; Priya, L.; Wu, J.J. Real-World Treatment Patterns and Healthcare Costs in Patients with Psoriasis Taking Systemic Oral or Biologic Therapies. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2023, 34, 2176708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.A.; Takeshita, J.; Pinto, L.; Li, P.; Yu, X.; Rao, P.; Viswanathan, H.N.; Gelfand, J.M. Biologic Therapy Adherence, Discontinuation, Switching, and Restarting among Patients with Psoriasis in the US Medicare Population. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 1057–1065.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, M. Challenges and Future Trends in the Treatment of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M. The Promising Role of Polyphenols in Skin Disorders. Molecules 2024, 29, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladu, A.F.; Ficai, D.; Ene, A.G.; Ficai, A. Combination Therapy Using Polyphenols: An Efficient Way to Improve Antitumoral Activity and Reduce Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, A.; Afzali, S.; Amirzargar, A.; Mohaghegh, P.; Salehi, S.; Mansoori, Y. Potential Roles of Inflammasomes in the Pathophysiology of Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 161, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsimbri, P.; Korakas, E.; Kountouri, A.; Ikonomidis, I.; Tsougos, E.; Vlachos, D.; Papadavid, E.; Raptis, A.; Lambadiari, V. The Effect of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capacity of Diet on Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Phenotype: Nutrition as Therapeutic Tool? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; Gonçalves, S.; Romano, A. Mediterranean Diet: The Role of Phenolic Compounds from Aromatic Plant Foods. Foods 2023, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez, M.E.; Kasangana, P.B.; Stevanovic, T. Bioactive Polyphenols for Diabetes and Inflammation in Psoriasis Disease. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2017, 52, 231–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Deshmukh-Taskar, P.; Hinojosa, M.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Downregulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Other Proinflammatory Biomarkers by Polyphenols. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 559, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pérez, M.E.; Allaeys, I.; Rusu, D.; Pouliot, R.; Janezic, T.S.; Poubelle, P.E. Picea Mariana Polyphenolic Extract Inhibits Phlogogenic Mediators Produced by TNF-α-Activated Psoriatic Keratinocytes: Impact on NF-ΚB Pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, K.M.; Itankar, P.R.; Joshi, A.; Prasad, S.K. Anti-Psoriatic Potential of Solanum xanthocarpum Stem in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriatic Mice Model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Jiang, W.; Lu, Q.; Rong, M.; Lai, R. Curcumin Shows Excellent Therapeutic Effect on Psoriasis in Mouse Model. Biochimie 2016, 123, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yin, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Sun, Q. CircOAS3 Regulates Keratinocyte Proliferation and Psoriatic Inflammation by Interacting with Hsc70 via the JNK/STAT3/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Perlak, M.; Szpadel, K.; Jabłońska, I.; Pizon, M.; Woźniak, M. Promising Strategies in Plant-Derived Treatments of Psoriasis-Update of In Vitro, In Vivo, and Clinical Trials Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, G.W.; Lebwohl, M. Psoriasis: Overview and Diagnosis. In Evidence-Based Psoriasis; Bhutani, T., Liao, W., Nakamura, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisondi, P.; Bellinato, F.; Girolomoni, G. Topographic Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: Challenges and Tricks. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Simard, M.; Lorthois, I.; Bélanger, A.; Maheux, M.; Duque-Fernandez, A.; Rioux, G.; Simard, P.; Deslauriers, M.; Masson, L.C.; et al. In Vitro Models of Psoriasis. In Skin Tissue Models; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, H.; Deng, X.; Yue, P.; Lin, J.; Yang, M.; Han, L.; Zhang, D.K. Advances in the Application of Natural Products and the Novel Drug Delivery Systems for Psoriasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 644952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Alam, K.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Gupta, G.; Afzal, M.; Akhter, S.; Kazmi, I.; Jyoti; Ahmad, F.J.; Anwar, F. Classical to Current Approach for Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 12, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhawaga, O.Y.; Ellety, M.M.; Mofty, S.O.; Ghanem, M.S.; Mohamed, A.O. Review of Natural Compounds for Potential Psoriasis Treatment. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čižmárová, B.; Hubková, B.; Tomečková, V.; Birková, A. Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Selected Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Cicala, C.; Caiazzo, E.; Izzo, A.A.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Polyphenols: A Concise Overview on the Chemistry, Occurrence, and Human Health. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2221–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, S.; Pilar Francino, M.; Ángel Rufián Henares, J. Why Is It Important to Understand the Nature and Chemistry of Tannins to Exploit Their Potential as Nutraceuticals? Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.A.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.-M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in Mice Is Mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 Axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiga, E.; Bonciolini, V.; Volpi, W.; Del Bianco, E.; Caproni, M. Oral Curcumin (Meriva) Is Effective as an Adjuvant Treatment and Is Able to Reduce IL-22 Serum Levels in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 283634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahraini, P.; Rajabi, M.; Mansouri, P.; Sarafian, G.; Chalangari, R.; Azizian, Z. Turmeric Tonic as a Treatment in Scalp Psoriasis: A Randomized Placebo-Control Clinical Trial. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, H.; Hu, J. Curcumin Relieves TPA-Induced Th1 Inflammation in K14-VEGF Transgenic Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyvalidas, D.; Mavropoulos, A.; Tsiogkas, S.; Dardiotis, E.; Liaskos, C.; Mamuris, Z.; Roussaki-Schulze, A.; Sakkas, L.I.; Zafiriou, E.; Bogdanos, D.P. Curcumin Mediates Attenuation of Pro-Inflammatory Interferon γ and Interleukin 17 Cytokine Responses in Psoriatic Disease, Strengthening Its Role as a Dietary Immunosuppressant. Nutr. Res. 2020, 75, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.R.; Sivaprakasam, T.O.; Mishra, A.; Prabhu, S.; Rafiq, M.; Rangesh, P. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Inflammation in Differentiated Human Keratinocytes: Its Evaluation Using Curcumin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 813, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, W. Curcumin Reduces Inflammation in Mice with the Psoriasis Model by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammatory Bodies. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2021, 67, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saelee, C.; Thongrakard, V.; Tencomnao, T. Effects of Thai Medicinal Herb Extracts with Anti-Psoriatic Activity on the Expression on NF-ΚB Signaling Biomarkers in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Molecules 2011, 16, 3908–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjær, T.N.; Thorsen, K.; Jessen, N.; Stenderup, K.; Pedersen, S.B. Resveratrol Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalakshmi, A.; Ravichandiran, V.; Velraj, M.; Nirmala, S.; Jayakumari, S. Screening of Flavonoid “Quercetin” from the Rhizome of Smilax China Linn. for Anti–Psoriatic Activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera Acosta, E.; Alonso Suárez Pérez, J.; Aguilera Arjona, J.; Visioli, F. An Olive Polyphenol-Based Nutraceutical Improves Cutaneous Manifestations of Psoriasis in Humans. PharmaNutrition 2016, 4, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starbek Zorko, M.; Štrukelj, B.; Švajger, U.; Kreft, S.; Lunder, T. Efficacy of a Polyphenolic Extract from Silver Fir (Abies alba) Bark on Psoriasis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Ren, J.; Huo, J. Amentoflavone Protects against Psoriasis-like Skin Lesion through Suppression of NF-ΚB-Mediated Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 413, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, T.T.; Ruan, Z.T.; Zhao, J.X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. Astilbin Inhibits Th17 Cell Differentiation and Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Skin Lesions in BALB/c Mice via Jak3/Stat3 Signaling Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 32, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, H.; Li, M. Effects of Baicalin Cream in Two Mouse Models: 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Contact Hypersensitivity and Mouse Tail Test for Psoriasis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 2128. [Google Scholar]
- Chamcheu, J.C.; Pal, H.C.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Adhami, V.M.; Ayehunie, S.; Boylan, B.T.; Noubissi, F.K.; Khan, N.; Syed, D.N.; Elmets, C.A.; et al. Prodifferentiation, Anti-Inflammatory and Antiproliferative Effects of Delphinidin, a Dietary Anthocyanidin, in a Full-Thickness Three-Dimensional Reconstituted Human Skin Model of Psoriasis. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Patel, A.B.; Vasiadi, M.; Therianou, A.; Theoharides, T.C. Luteolin Inhibits Human Keratinocyte Activation and Decreases NF-ΚB Induction That Is Increased in Psoriatic Skin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, N.; Cai, R.; Gu, J.; Xie, F.; Wei, H.; Lu, C.; Wu, D. Rosmarinic Acid Protects Mice from Imiquimod Induced Psoriasis-like Skin Lesions by Inhibiting the IL-23/Th17 Axis via Regulating Jak2/Stat3 Signaling Pathway. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4526–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Mei, L.; Wang, H.; Fang, F. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Inhibits Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Inflammation of BALB/c Mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiogkas, S.G.; Apostolopoulou, K.; Mavropoulos, A.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Dardiotis, E.; Zafiriou, E.; Bogdanos, D.P. Gallic Acid Diminishes Pro-Inflammatory Interferon-γ- and Interleukin-17-Producing Sub-Populations in Vitro in Patients with Psoriasis. Immunol. Res. 2023, 71, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belcaro, G.; Luzzi, R.; Hu, S.; Cesarone, M.R.; Dugall, M.; Ippolito, E.; Corsi, M.; Caporale, S. Improvement in Signs and Symptoms in Psoriasis Patients with Pycnogenol® Supplementation. Panminerva Med. 2014, 56, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Pérez, M.E.; Royer, M.; Duque-Fernandez, A.; Diouf, P.N.; Stevanovic, T.; Pouliot, R. Antioxidant, Toxicological and Antiproliferative Properties of Canadian Polyphenolic Extracts on Normal and Psoriatic Keratinocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, A.; Schäkel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Chamcheu, J.C.; Adhami, V.M.; Wood, G.S.; Elmets, C.A.; Mukhtar, H.; Afaq, F. Topical Application of Delphinidin Reduces Psoriasiform Lesions in the Flaky Skin Mouse Model by Inducing Epidermal Differentiation and Inhibiting Inflammation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 172, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleńkowska, J.; Gabig-Cimińska, M.; Mozolewski, P. Oxidative Stress as an Important Contributor to the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.I.; Park, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Piao, M.S.; Suh, M.S.; Lee, J.B.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, S.C. Keratinocytes-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Play an Active Role to Induce Type 2 Inflammation of the Skin: A Pathogenic Role of Reactive Oxygen Species at the Early Phase of Atopic Dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2020, 33, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Modulation of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant and Detoxifying Enzyme Induction by the Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Xing, L.; Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, W.; et al. Metformin Sensitizes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to an Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Treatment by Suppressing the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamcheu, J.C.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Adhami, V.M.; Esnault, S.; Bharali, D.J.; Babatunde, A.S.; Adame, S.; Massey, R.J.; Wood, G.S.; Longley, B.J.; et al. Chitosan-Based Nanoformulated (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Modulates Human Keratinocyte-Induced Responses and Alleviates Imiquimod-Induced Murine Psoriasiform Dermatitis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4189–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Liñán-Atero, R.; Tarahi, M.; Christodoulou, M.C.; Aghababaei, F. The Potential Health Benefits of Gallic Acid: Therapeutic and Food Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee, M.S.; Moeenfard, M.; Farhoosh, R. Kinetics and Stoichiometry of Gallic Acid and Methyl Gallate in Scavenging DPPH Radical as Affected by the Reaction Solvent. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.J.; Moh, S.H.; Son, D.H.; You, S.; Kinyua, A.W.; Ko, C.M.; Song, M.; Yeo, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, K.W. Gallic Acid Promotes Wound Healing in Normal and Hyperglucidic Conditions. Molecules 2016, 21, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geana, E.I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Tamaian, R.; Marinas, I.C.; Gaboreanu, D.M.; Stan, M.; Chitescu, C.L. Antioxidant and Wound Healing Bioactive Potential of Extracts Obtained from Bark and Needles of Softwood Species. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cas, M.D.; Ghidoni, R. Dietary Curcumin: Correlation between Bioavailability and Health Potential. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y. Nanoformulations to Enhance the Bioavailability and Physiological Functions of Polyphenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungmunnithum, D.; Thongboonyou, A.; Pholboon, A.; Yangsabai, A. Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants for Pharmaceutical and Medical Aspects: An Overview. Medicines 2018, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zillich, O.V.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P.; Kerscher, M. Polyphenols as Active Ingredients for Cosmetic Products. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).