- Article
A Vision-Based Deep Learning Framework for Monitoring and Recognition of Chemical Laboratory Operations
- Chuntao Guo,
- Jing Lin and
- Yunlin Chen
- + 3 authors
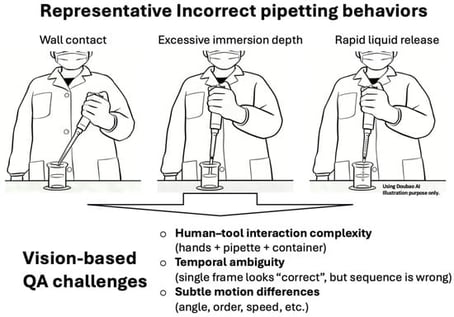
Standardized operating procedures are essential for ensuring safety and reproducibility in chemical laboratory experiments. However, real-time monitoring of manual laboratory operations, such as pipetting, remains challenging due to complex human–tool interactions, temporal dependencies between procedural steps, and operator variability. In this study, we propose a vision-based deep learning framework that leverages spatiotemporal features for automated monitoring of pipetting operations using non-contact visual sensing. Briefly, human poses and pipette interactions are extracted from video recordings using a YOLO-based perception model, while temporal execution patterns are captured through bidirectional long short-term memory networks. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach can reliably distinguish between standard and non-standard pipetting behaviors across multiple predefined error categories and shows improved robustness compared with static or frame-level analysis. Overall, this work demonstrates the feasibility of vision-based AI systems for objective and scalable monitoring of laboratory pipetting operations, with potential applicability to other manual laboratory procedures.
8 February 2026