Rutin Attenuates H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the AMPK/NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
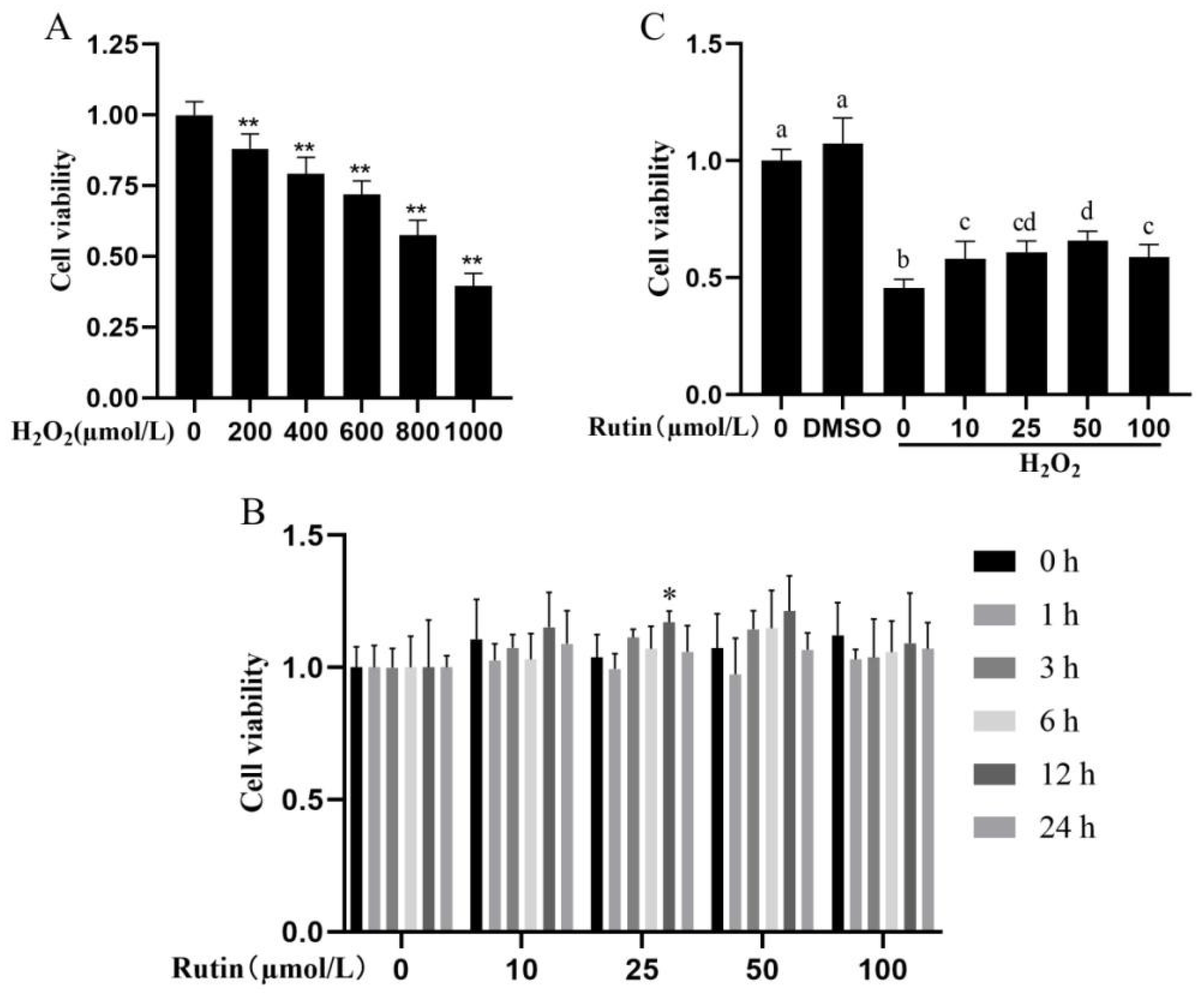
2.1. Impacts of H2O2 and Rutin on Cell Viability
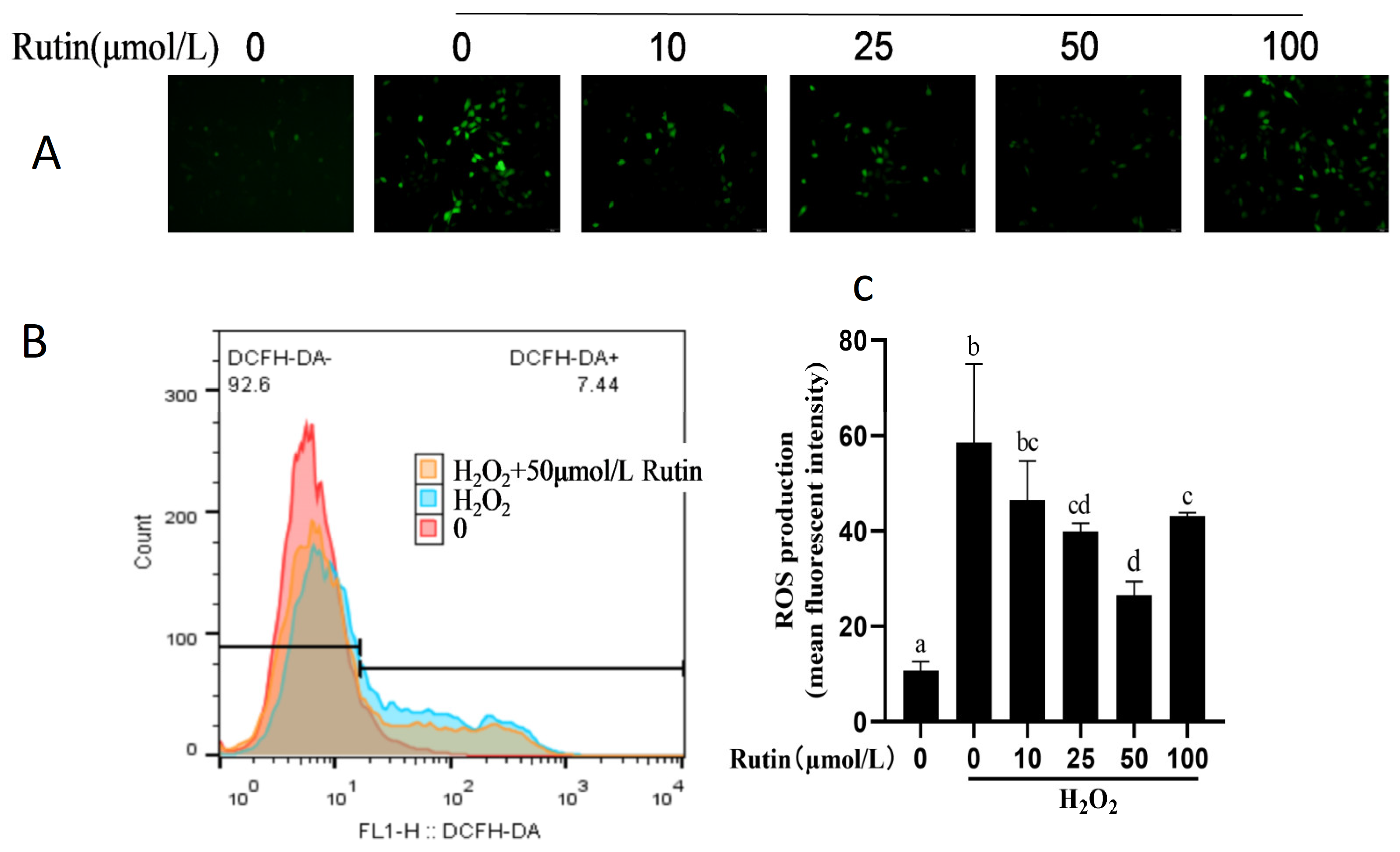
2.2. Effect of H2O2 and Rutin on ROS in BMEC
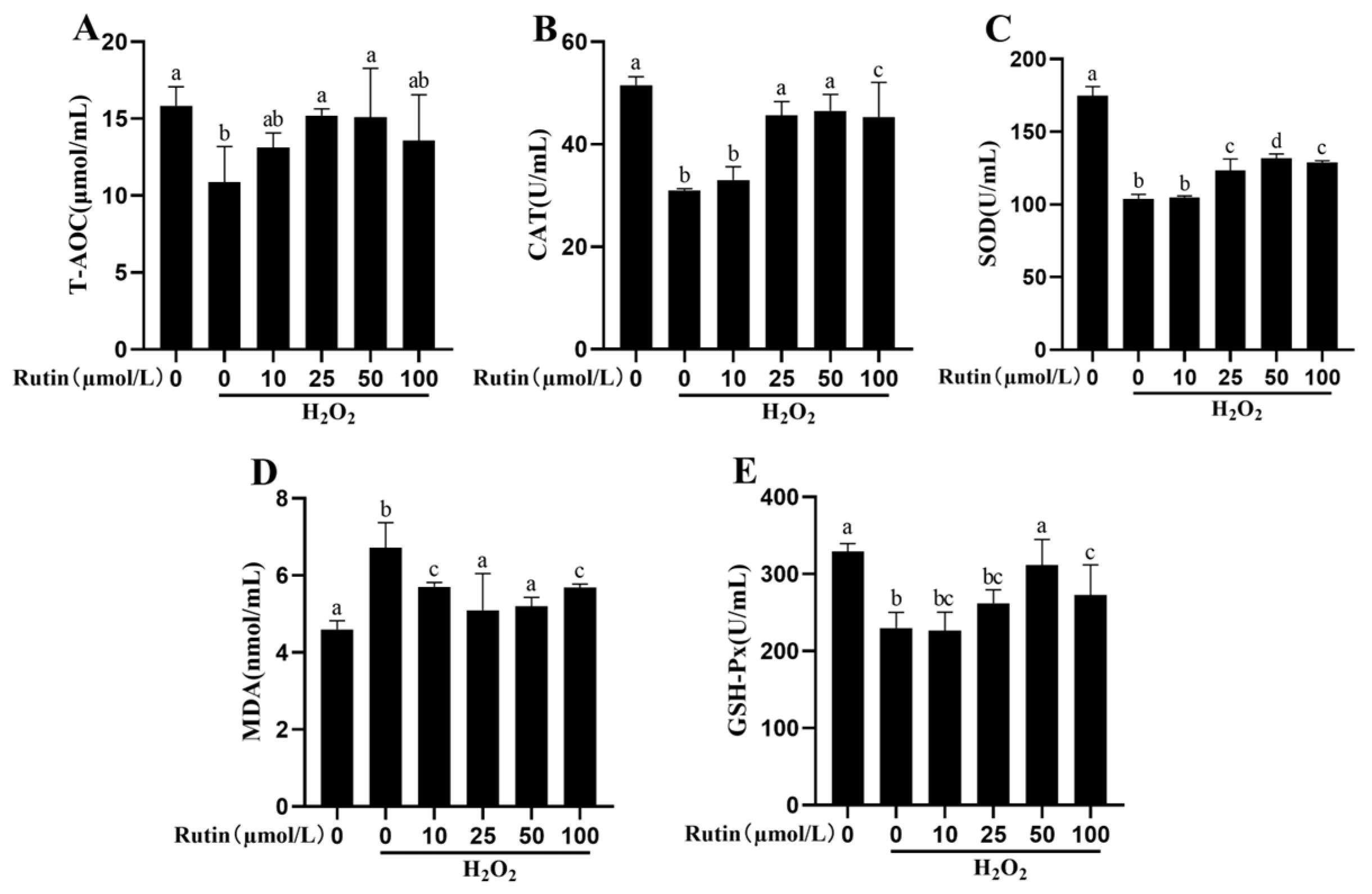
2.3. Rutin Mitigated Oxidative Stress Induced by H2O2
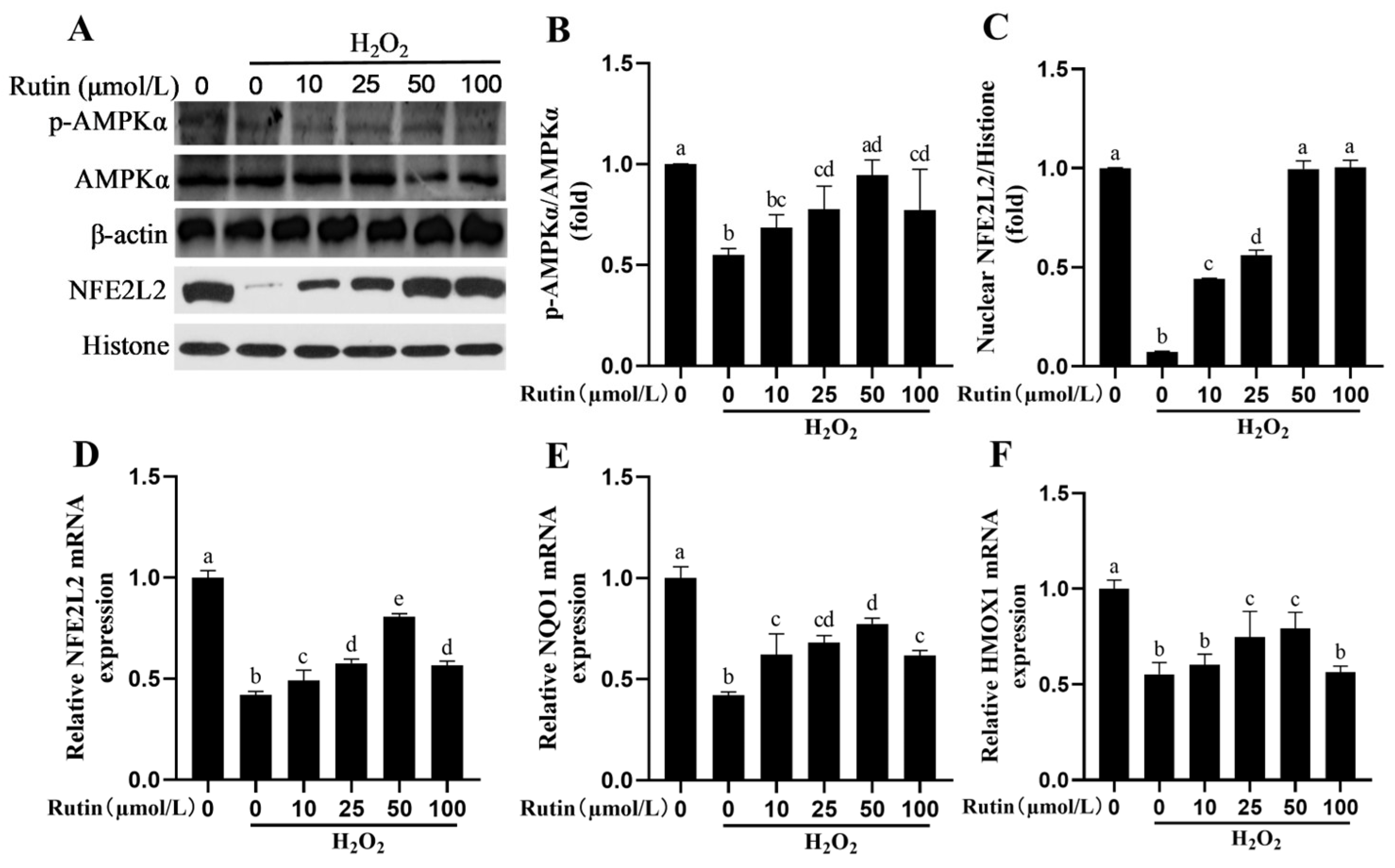
2.4. Rutin Caused Activation of the AMPK/NFE2L2 Pathway
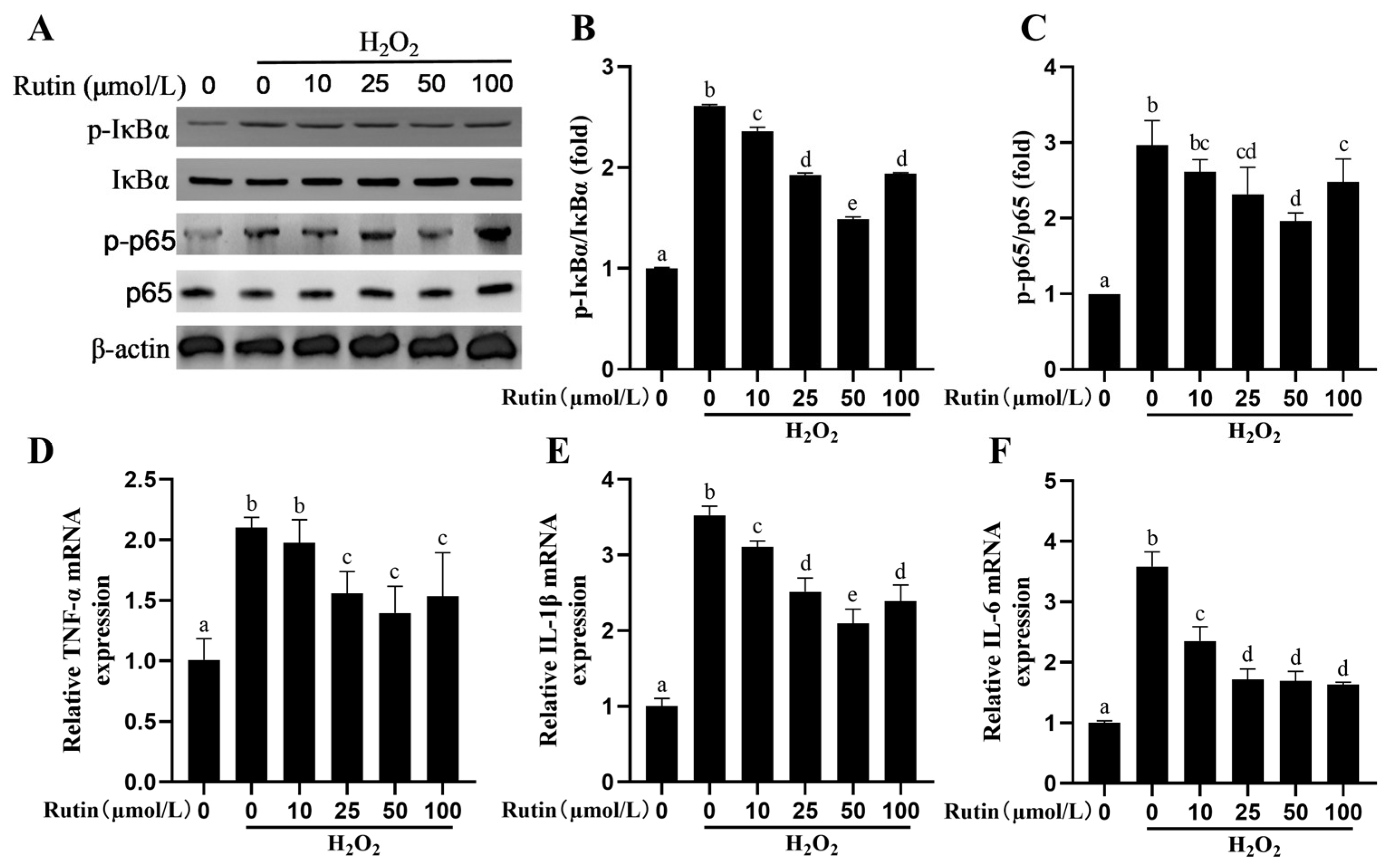
2.5. Rutin Rescued the Activity of the NF-kB Signaling Pathway Elicited by H2O2
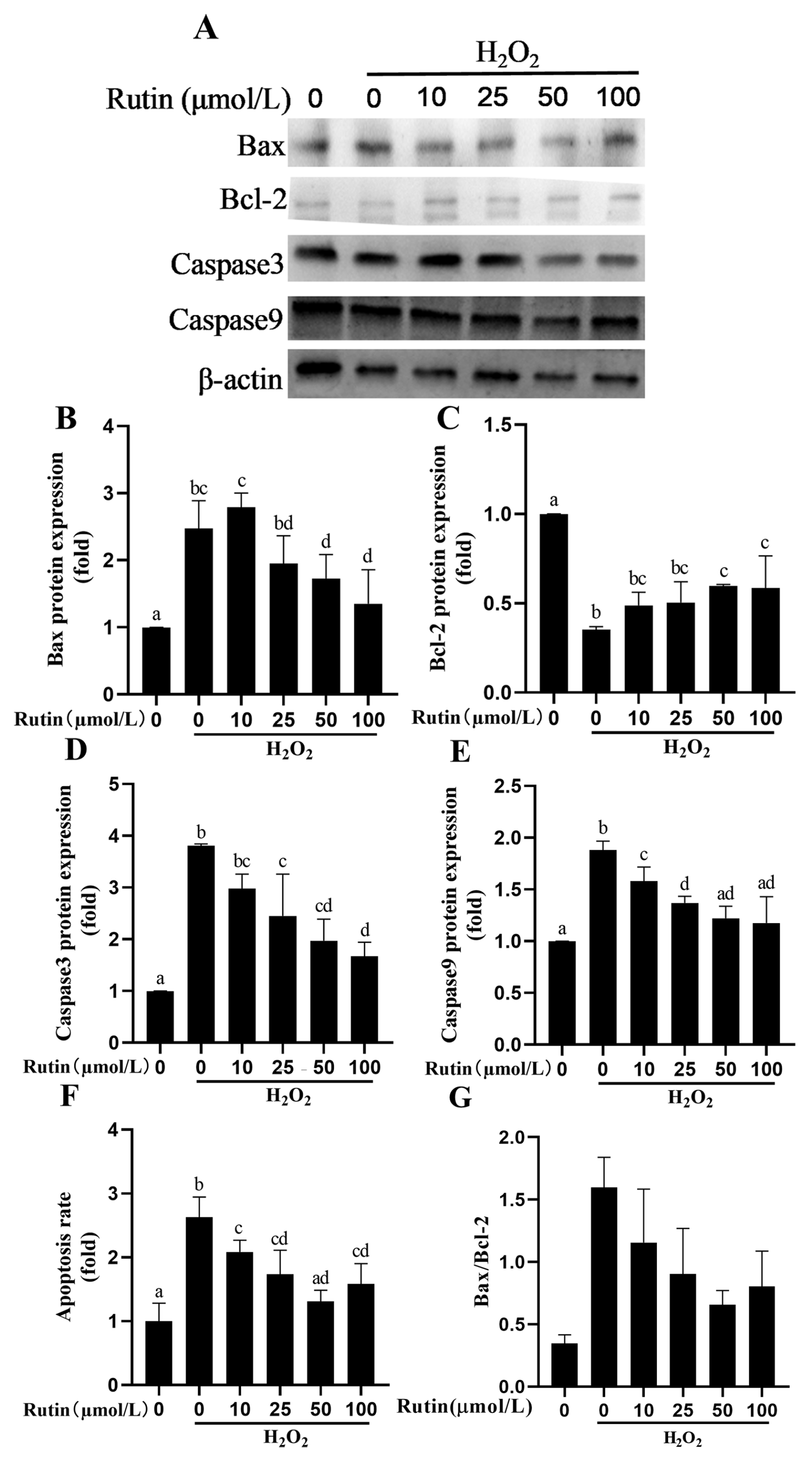
2.6. Rutin Prevented H2O2-Mediated Caspase Pathway Activation and Apoptosis
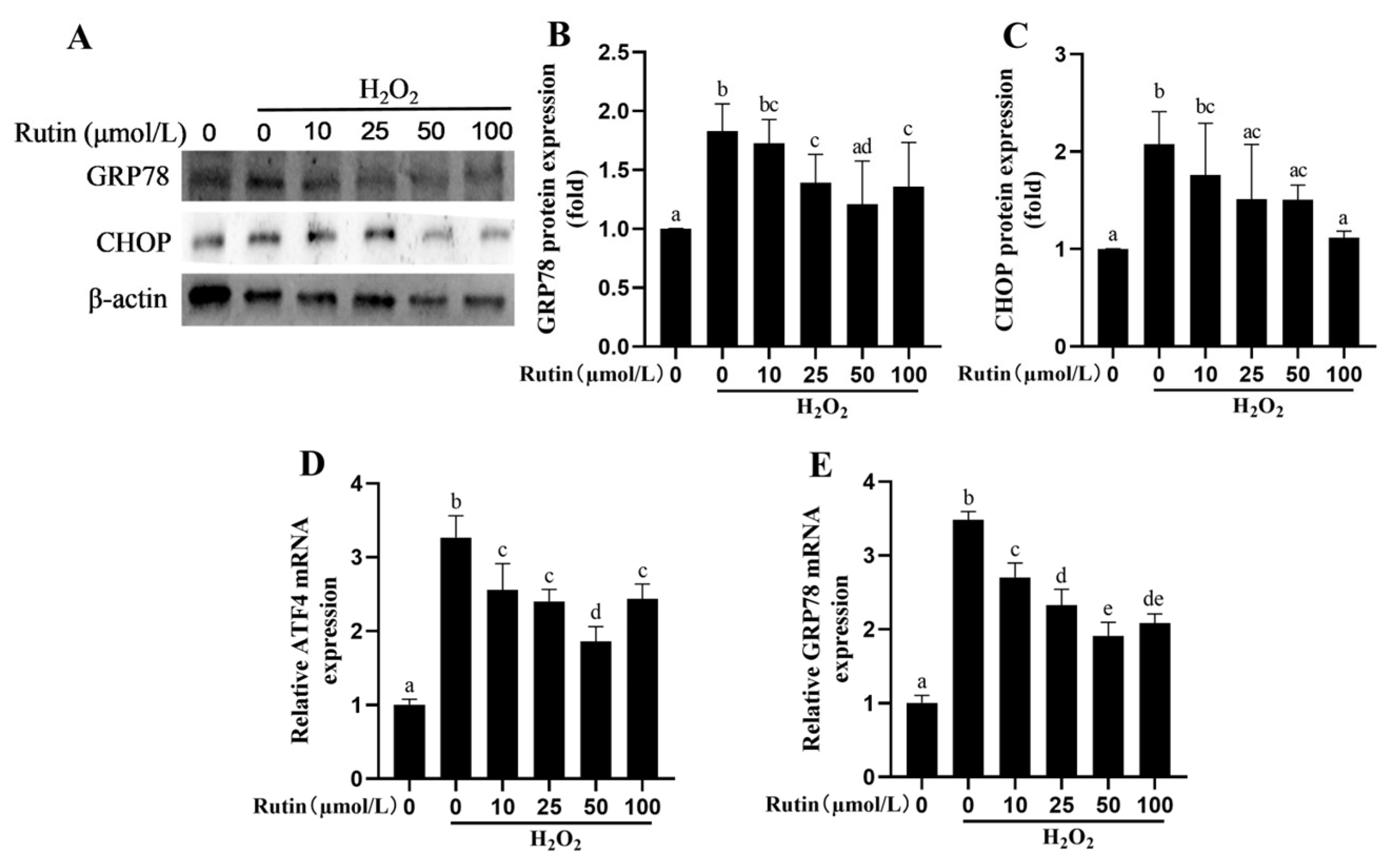
2.7. Rutin Attenuated H2O2-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress (ERS)
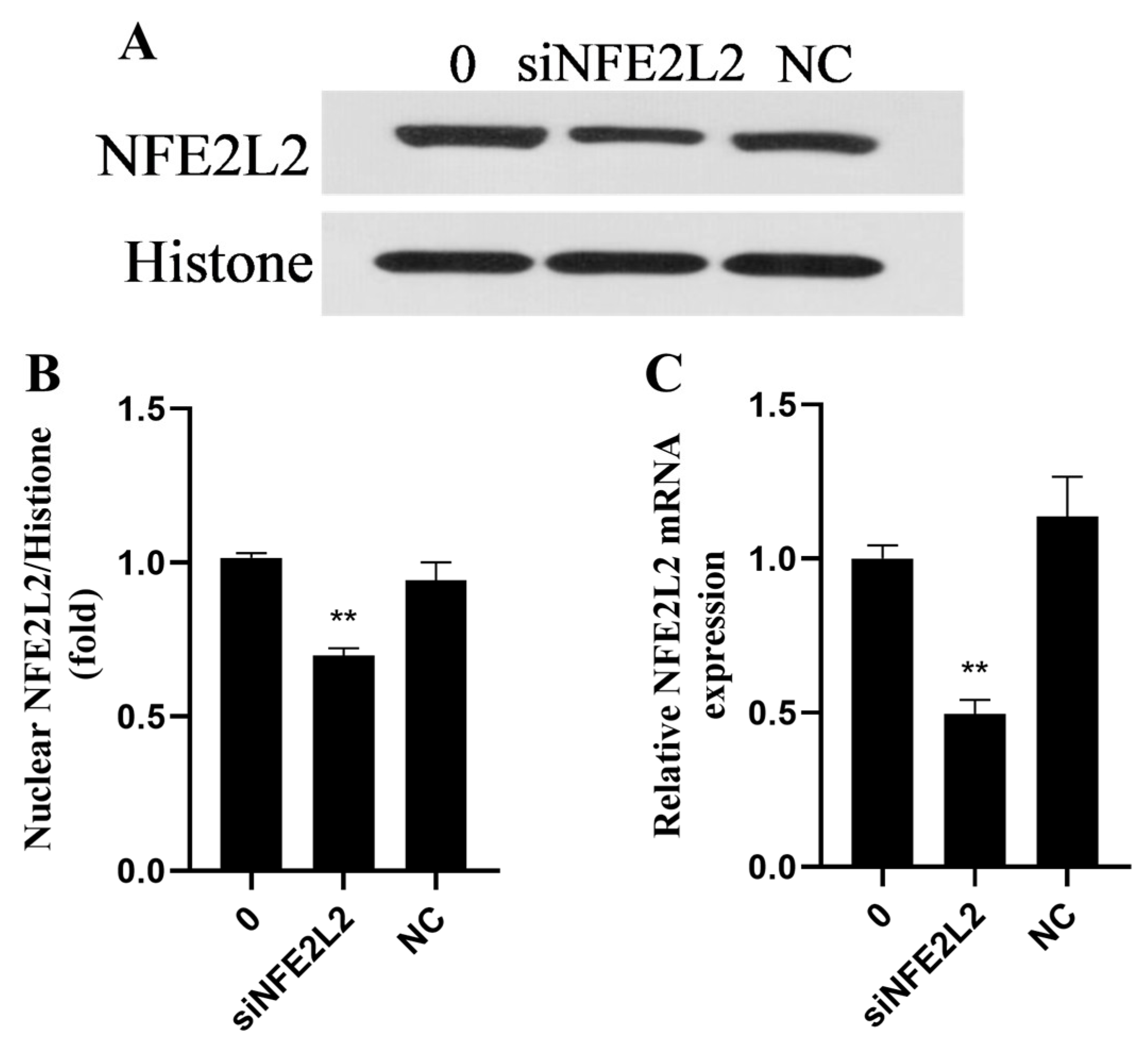
2.8. Rutin Upregulated the NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway in BMEC Through AMPK
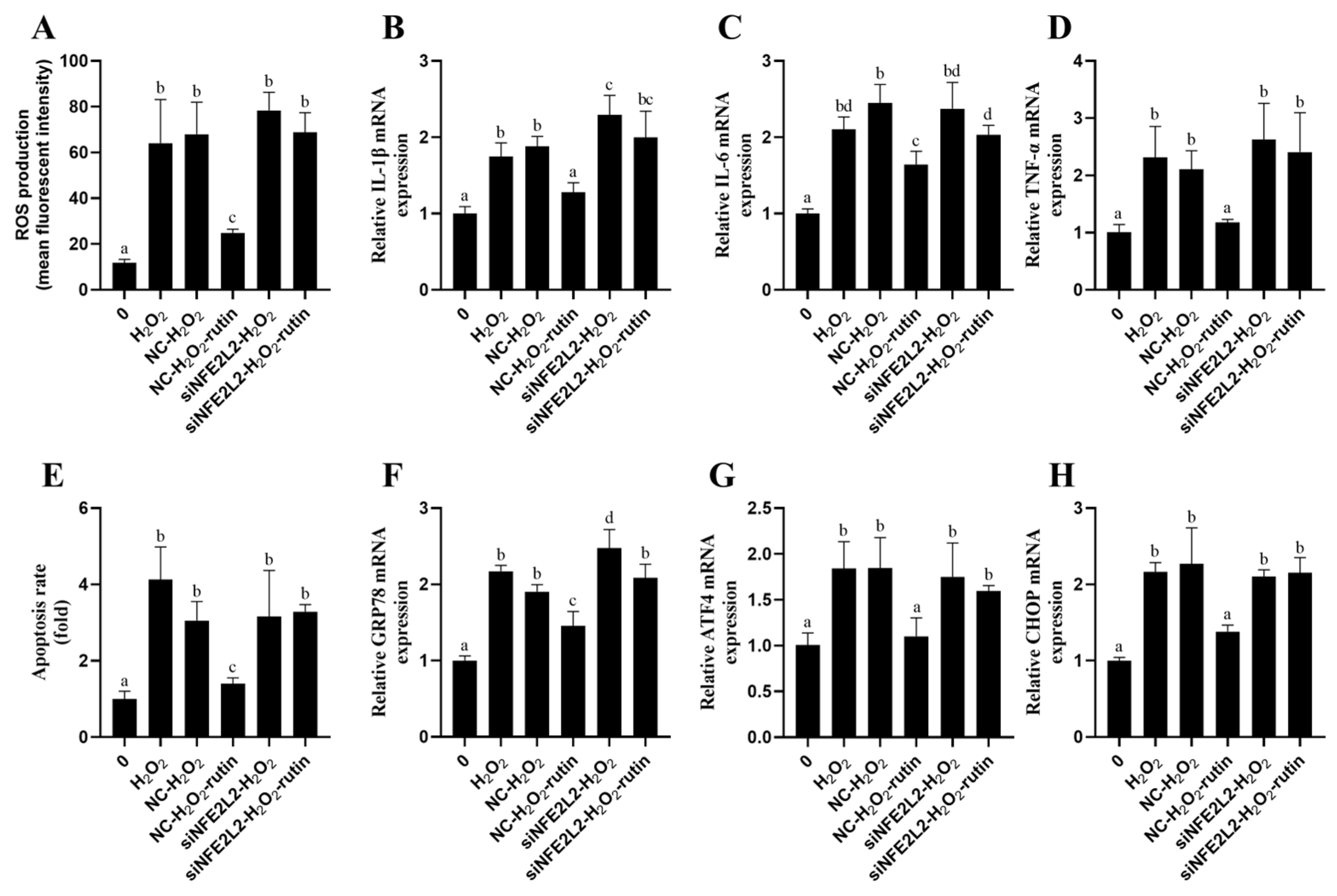
2.9. Rutin Exploited NFE2L2 to Alleviate Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Responses, Apoptosis, and ERS Induced by H2O2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Culture and Treatment of Cells
4.2. Assay on Cell Viability
4.3. Small Interference RNA Infection
4.4. Determination of ROS Level
4.5. Oxidative Stress Assay
4.6. Cell Apoptosis Determination
4.7. RNA Isolation Plus Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.8. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Activities of catalase |
| GST | Glutathione-S-transferase |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| IκBα | Nuclear Factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cell inhibitor alpha |
| ATF4 | Activating Transcription Factor 4 |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta. |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| NQO1 | NADH dehydrogenase quinone 1 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| NFE2L2 | Nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2 |
| HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| AMPKα | AMP-activated protein kinase alpha subunit |
References
- Reczek, C.R.; Chandel, N.S. ROS-dependent signal transduction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 33, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4350965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Aitken, S.L. Impact of oxidative stress on the health and immune function of dairy cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, W.; Xu, D.; Cheng, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fu, S. Myricetin protects against H2O2-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 2684–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.; Bhandari, B. Gelation properties of myofibrillar protein under malondialdehyde-induced oxidative stress. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelo, A.; Hernández, J.; Benedito, J.L.; Castillo, C. The importance of the oxidative status of dairy cattle in the periparturient period: Revisiting antioxidant supplementation. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelo, A.; Hernández, J.; Benedito, J.L.; Castillo, C. Oxidative stress index (OSi) as a new tool to assess redox status in dairy cattle during the transition period. Animal 2013, 7, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G.; Ross, F.A.; Hawley, S.A. AMPK: A nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hybertson, B.M.; Gao, B.; Bose, S.K.; McCord, J.M. Oxidative stress in health and disease: The therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activation. Mol. Asp. Med. 2011, 32, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Zhao, L.; Coleman, D.N.; Gao, M.; Loor, J.J. Tea polyphenols protect bovine mammary epithelial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in vitro by activating NFE2L2/HMOX1 pathways. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Wu, Z.H.; Gao, M.; Loor, J.J. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-antioxidant activation through the action of ataxia telangiectasia-mutated serine/threonine kinase is essential to counteract oxidative stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5317–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Y.A.; Ahmed, O.M.; Soliman, H.A.; Abdel-Gabbar, M.; Al-Dossari, M.; El-Gawaad, N.S.A.; El-Nahass, E.-S.; Ahmed, N.A. Rutin and Hesperidin Alleviate Paclitaxel-Induced Nephrocardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats via Suppressing the Oxidative Stress and Enhancing the Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2023, 2023, 5068304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Shi, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J. Rutin attenuates H2O2-induced oxidation damage and apoptosis in Leydig cells by activating PI3K/Akt signal pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, V.; Brown, L.; Gobe, G.C. The flavonoid rutin improves kidney and heart structure and function in an adenine-induced rat model of chronic kidney disease. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoldt, A.-K.; Derno, M.; Das, G.; Weitzel, J.M.; Wolffram, S.; Metges, C.C. Effects of rutin and buckwheat seeds on energy metabolism and methane production in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jia, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Xu, C. Lycopene alleviates H2O2 induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells via the NFE2L2 signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6276–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.M.; Stelwagen, K.; Dobson, J.; Henderson, H.V.; Davis, S.R.; Farr, V.C.; Singh, K. Transcriptome Profiling of Streptococcus Uberis-induced Mastitis Reveals Fundamental Differences Between Immune Gene Expression in the Mammary Gland and in a Primary Cell Culture Model. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Pu, X.; Loor, J.J.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, J.; Shen, T.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Lei, L.; Du, X.; et al. Impaired autophagy aggravates oxidative stress in mammary gland of dairy cows with clinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 6030–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Luo, S.; Jia, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Liang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Shao, G.; et al. Oxidative stress, NF-κB signaling, NLRP3 inflammasome, and caspase apoptotic pathways are activated in mammary gland of ketotic Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, Q.-C.; Wang, J.-P.; Ren, Q.-Q.; Wang, X.-P.; Luoreng, Z.-M.; Wei, D.-W.; Ma, Y. RNA-Seq Reveals the Role of miR-29c in Regulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress of Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 865415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, A. Mechanisms of antidiabetic effects of flavonoid rutin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enogieru, A.B.; Haylett, W.; Hiss, D.C.; Bardien, S.; Ekpo, O.E. Rutin as a Potent Antioxidant: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6241017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Adewole, D.; Yu, L.; Sid, V.; Wang, B.; O, K.; Yang, C. Rutin attenuates inflammatory responses induced by lipopolysaccharide in an in vitro mouse muscle cell (C2C12) model. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2756–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Ku, S.-K.; Baek, Y.-D.; Bae, J.-S. Anti-inflammatory effects of rutin on HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muvhulawa, N.; Dludla, P.V.; Ziqubu, K.; Mthembu, S.X.H.; Mthiyane, F.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E. Rutin ameliorates inflammation and improves metabolic function: A comprehensive analysis of scientific literature. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Xia, A.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Shi, T.; Cai, C.; Jin, W.; Zhou, M.; Liao, Y.; et al. Rutin Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Upregulating miRNA-877-3p Expression. Molecules 2022, 27, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Sghaier, M.; Pagano, A.; Mousslim, M.; Ammari, Y.; Kovacic, H.; Luis, J. Rutin inhibits proliferation, attenuates superoxide production and decreases adhesion and migration of human cancerous cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-L.; Yu, M.-M.; Liu, Y.-C.; Gao, Y.-L.; Chen, X.-S.; Shou, S.-T.; Chai, Y.-F. Rutin Inhibits Cardiac Apoptosis and Prevents Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 834077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Yeh, K.-L.; Huang, F.-M.; Su, N.-Y.; Kuan, Y.-H. Protective Effect of Rutin on Triethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate-Induced Toxicity through the Inhibition of Caspase Activation and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Körner, H.; Wu, H.; Wei, W. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in autoimmune diseases. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardic, S.; Gumrukcu, A.; Cekic, O.G.; Erdem, M.; Kose, G.D.R.; Demir, S.; Kose, B.; Yulug, E.; Mentese, A.; Turedi, S. The value of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers (GRP78 and CHOP) in the diagnosis of acute mesenteric ischemia. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Yao, Z. Rutin alleviates cardiomyocyte injury induced by high glucose through inhibiting apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Ming, P.; Huang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ding, H.; Feng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Rutin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.-L.; Shen, H.-T.; Su, C.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Huang-Liu, R.; Chen, C.-J.; Chen, S.-P.; Kuan, Y.-H. Nerolidol Suppresses the Inflammatory Response during Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the Modulation of Antioxidant Enzymes and the AMPK/Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9605980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-x.; Zeng, S.; Wan, B.-b.; Wang, Y.-y.; Sun, H.-x.; Liu, G.; Gao, Z.-q.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.-q.; Lu, M.-d.; et al. Sophoricoside attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, G.; Liu, J.; Hou, S.; Guo, W.; Kan, X.; Fu, S. Dioscin Improves Pyroptosis in LPS-Induced Mice Mastitis by Activating AMPK/Nrf2 and Inhibiting the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8845521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Huo, R.; Wang, Y.; Ma, N.; Shi, X.; Shen, X.; Chang, G. Lentinan inhibits oxidative stress and alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis of BMECs by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2375–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Dong, J.; Liu, K.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Meloxicam inhibited oxidative stress and inflammatory response of LPS-stimulated bovine endometrial epithelial cells through Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 116, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Yang, W.; Xue, Q.; Gao, L.; Huo, J.; Ren, D.; Chen, X. Rutin ameliorates diabetic neuropathy by lowering plasma glucose and decreasing oxidative stress via Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genes | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Length (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward | CCTGGAGAAGAGCTACGAG | 132 |
| Reverse | AAGGTAGTTTCGTGAATGCC | ||
| TNF-α | Forward | CAAGCCTCAAGTAACAAGCC | 123 |
| Reverse | GTTGTCTTCCAGCTTCACAC | ||
| IL-6 | Forward | AAGGAGACACTGGCAGAAAA | 91 |
| Reverse | AGCAAATCGCCTGATTGAAC | ||
| IL-1β | Forward | GGATCCTATTCTCTCCAGCC | 82 |
| Reverse | TTTCGTTGATGGGTTCAGGT | ||
| GRP-78 | Forward | GTGCGTTTGAGAGCTCAGTA | 90 |
| Reverse | GTCAGCAGTCAGCTATAGGG | ||
| ATF4 | Forward | GGCTCTCCAAATAAGAGCCT | 106 |
| Reverse | CCTTGACTTTTGCTGCTACC | ||
| NFE2L2 | Forward | TCAGCATGATGGACTTGGAG | 114 |
| Reverse | ATACCTCTCGACTTACCCCA | ||
| HMOX1 | Forward | GTCCTCACACTCAGCTTTCT | 192 |
| Reverse | AGAGAGGGATACAGGGAGAC | ||
| NQO-1 | Forward | ACTTTCAGTATCCTGCCGAG | 193 |
| Reverse | TACTTGTAAGCGAACTCCCC | ||
| CHOP | Forward | GGTCAGAGGCTTGAGTCTAA | 91 |
| Reverse | CTCAGGTTCCGGCTTTGATT | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, H.; Yan, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Feng, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, J.; Wu, D.; et al. Rutin Attenuates H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the AMPK/NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104788
Ding H, Yan W, Zhang D, Wang L, Yang Y, Zhao C, Feng S, Wang X, Tang J, Wu D, et al. Rutin Attenuates H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the AMPK/NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104788
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Hongyan, Weizhe Yan, Daoliang Zhang, Lei Wang, Yue Yang, Chang Zhao, Shibin Feng, Xichun Wang, Jishun Tang, Dong Wu, and et al. 2025. "Rutin Attenuates H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the AMPK/NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104788
APA StyleDing, H., Yan, W., Zhang, D., Wang, L., Yang, Y., Zhao, C., Feng, S., Wang, X., Tang, J., Wu, D., Wu, J., & Li, Y. (2025). Rutin Attenuates H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells via the AMPK/NFE2L2 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104788






