Brewer’s Spent Yeast Cell Wall Polysaccharides as Vegan and Clean Label Additives for Mayonnaise Formulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BSY Extracts Composition
2.2. Emulsifying Properties of BSY Extracts
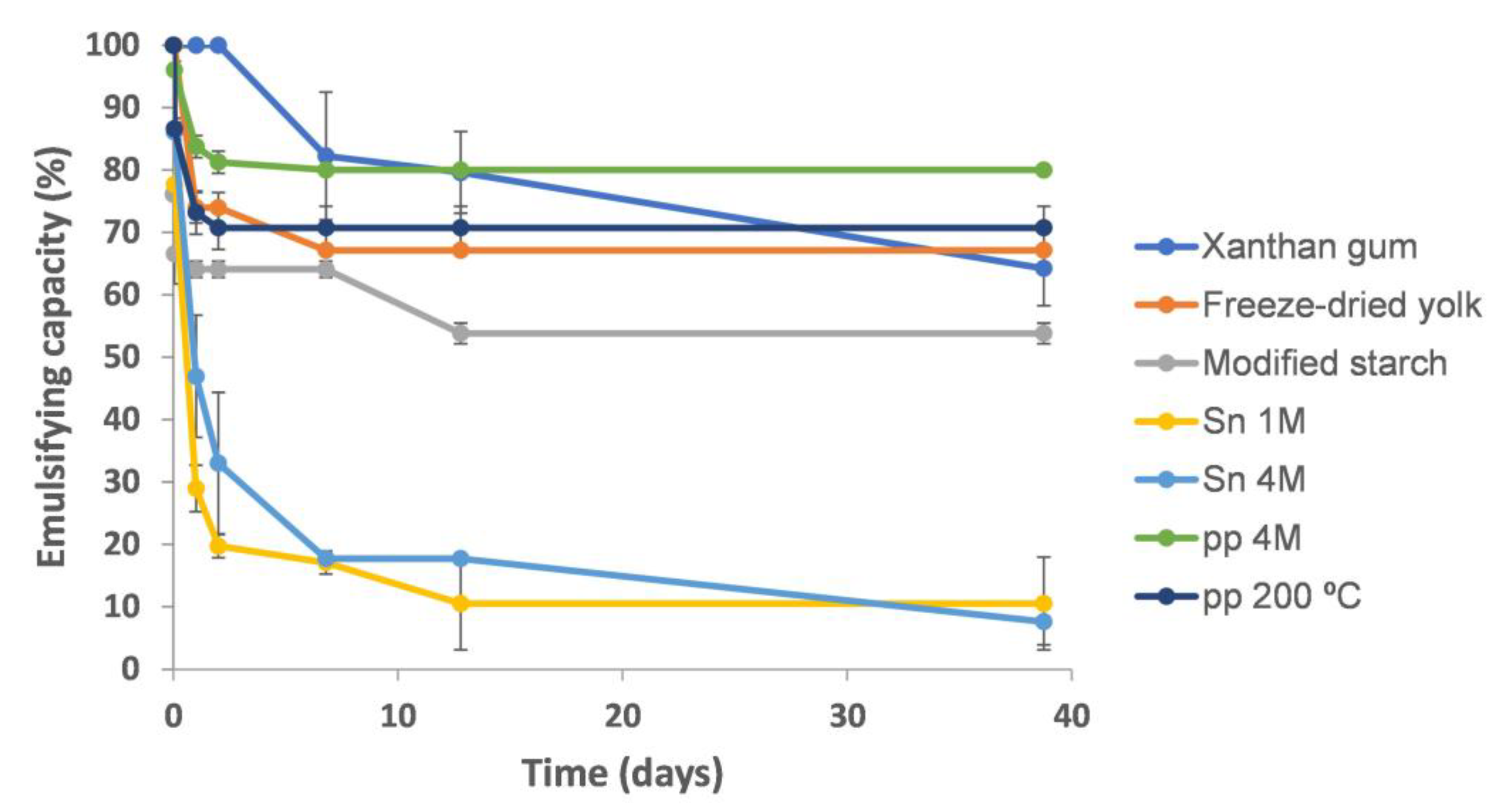
2.2.1. Emulsifying Capacity and Stability
2.2.2. Emulsifying Polysaccharides of BSY Extract’s Emulsions
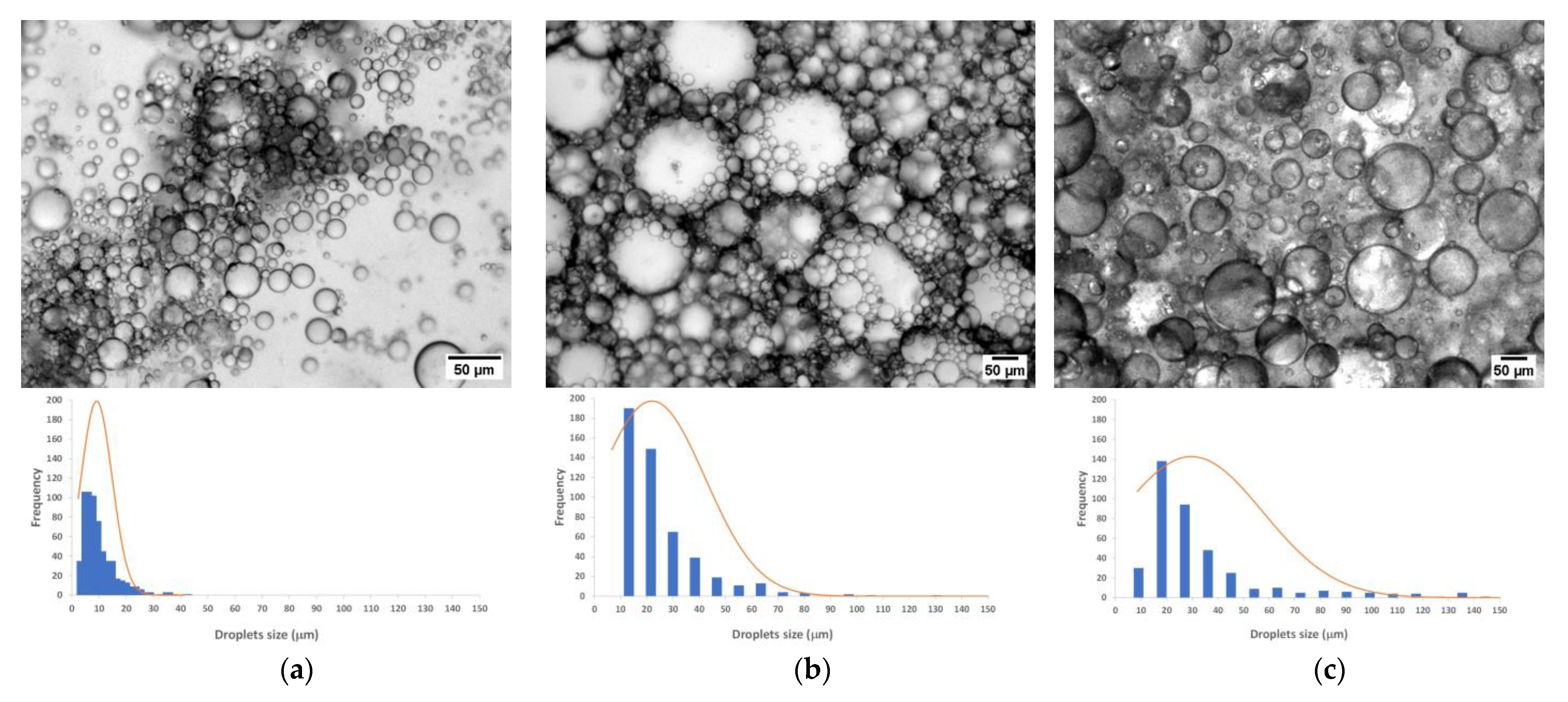
2.2.3. Emulsions Droplet Size Distribution
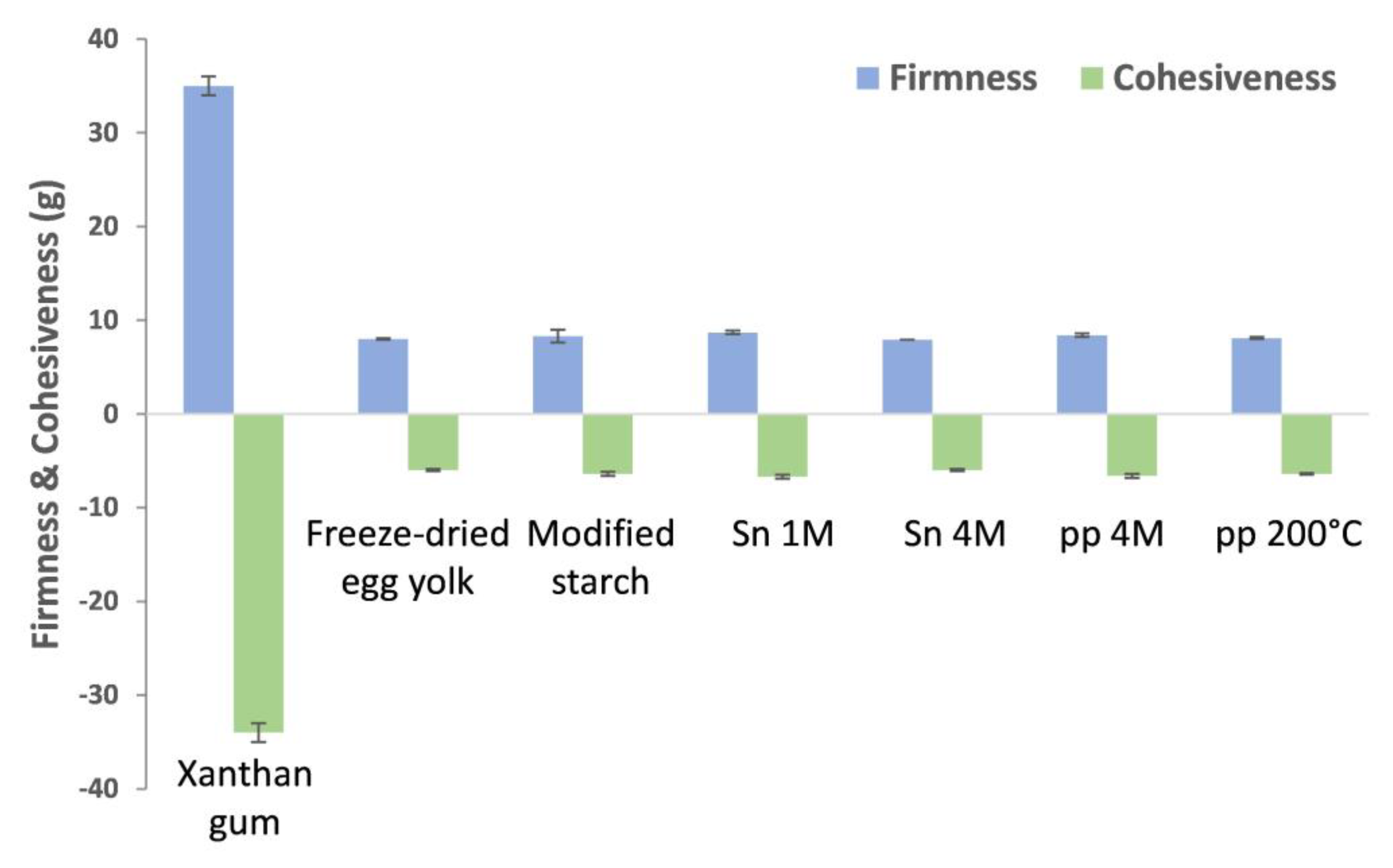
2.3. Emulsifying Properties of Mayonnaise Emulsion Models with Addition of BSY Extracts
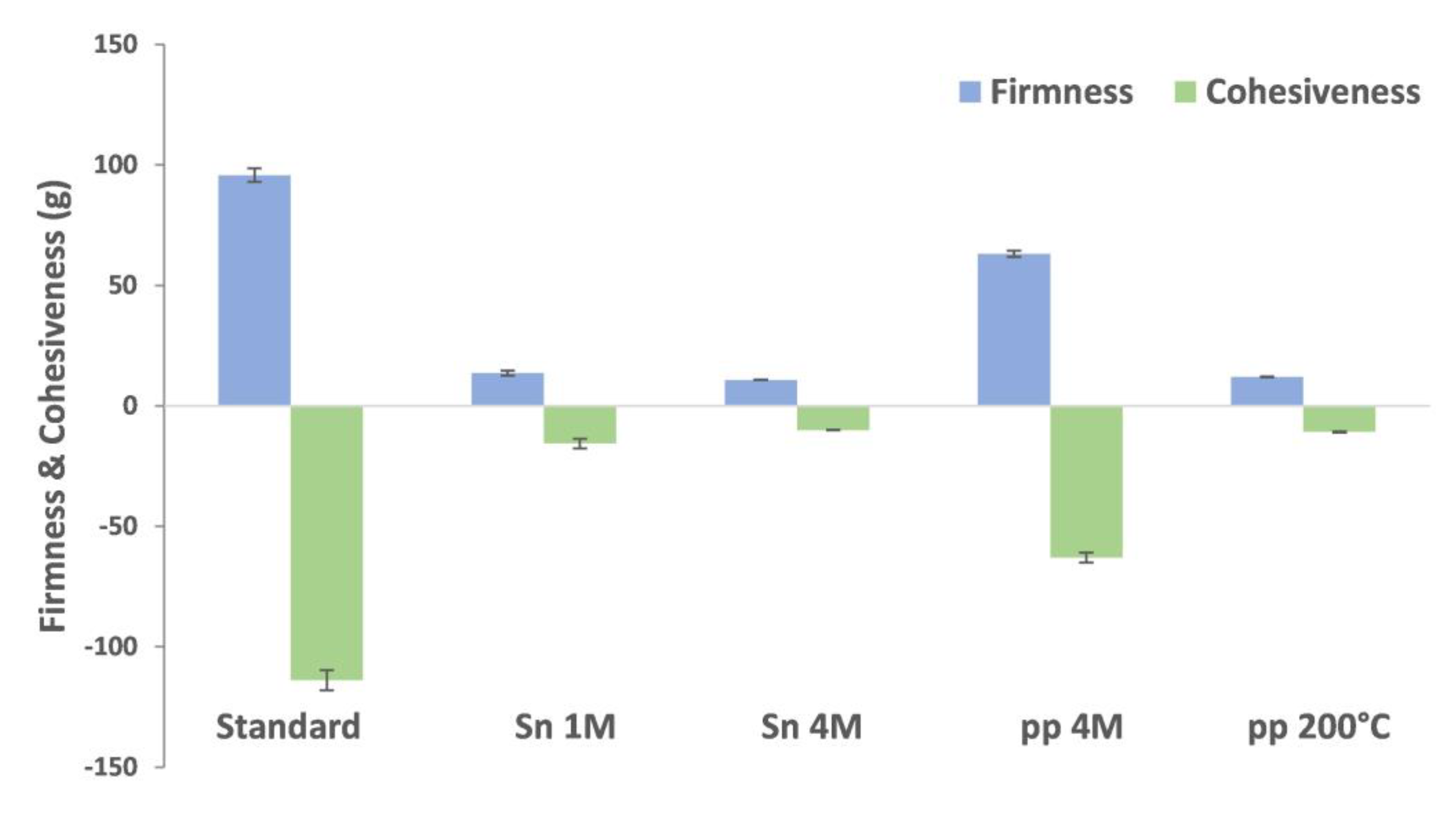
2.4. Mayonnaises Formulation Using BSY Extracts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Brewer’s Spent Yeast (BSY) Extracts
4.2.1. BSY Alkaline Extracts
4.2.2. BSY Subcritical Water Extracts
4.3. Chemical Composition Analysis of BSY Extracts
4.4. Emulsifying Properties of BSY Extracts
4.4.1. Emulsifying Capacity and Stability
4.4.2. Polysaccharide Composition of Emulsions
4.4.3. Widefield Fluorescence Microscopy
4.5. Texture Analysis of Mayonnaise Models with BSY Extracts Addition
4.6. Mayonnaises Formulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780429154034. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, B.; Argin, S.; Ozilgen, M.; McClements, D.J. Formation and Stabilization of Nanoemulsion-Based Vitamin E Delivery Systems Using Natural Surfactants: Quillaja Saponin and Lecithin. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Bai, L.; Chung, C. Recent Advances in the Utilization of Natural Emulsifiers to Form and Stabilize Emulsions. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 205–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstonošić, V.; Dokić, L.; Nikolić, I.; Milanović, M. Influence of Xanthan Gum on Oil-in-Water Emulsion Characteristics Stabilized by OSA Starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Feng, J.; Sun, P.; Xiang, N.; Lu, B.; Qiu, D. Recent Advances in Improving Stability of Food Emulsion by Plant Polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, K.; Bouhallab, S.; Croguennec, T.; Renard, D.; Lechevalier, V. Recent Trends in Design of Healthier Plant-Based Alternatives: Nutritional Profile, Gastrointestinal Digestion, and Consumer Perception. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachie, C.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Aryee, A.N.A. Trends and Innovations in the Formulation of Plant-Based Foods. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2023, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.R.; Cooper, D.G.; Neufeld, R.J. The Mannoprotein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Is an Effective Bioemulsifier. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iseppi, A.; Marangon, M.; Lomolino, G.; Crapisi, A.; Curioni, A. Red and White Wine Lees as a Novel Source of Emulsifiers and Foaming Agents. LWT 2021, 152, 112273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karboune, S. Characterization of the Composition and the Techno-Functional Properties of Mannoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast Cell Walls. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerome, S.; Onishi, M.; Saito, D.; Mizobuchi, A.; Ando, T.; Daira, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Ojima, Y.; Azuma, M. Cell Surface Changes That Advance the Application of Using Yeast as a Food Emulsifier. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlean, P. Architecture and Biosynthesis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cell Wall. Genetics 2012, 192, 775–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, R.; Oliveira, P.G.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F.; Coimbra, M.A.; Coelho, E. Brewer’s Yeast Polysaccharides—A Review of Their Exquisite Structural Features and Biomedical Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.; Coelho, E.; Nunes, A.; Brandão, T.; Coimbra, M.A. Valuation of Brewers Spent Yeast Polysaccharides: A Structural Characterization Approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Iseppi, A.; Lomolino, G.; Marangon, M.; Curioni, A. Current and Future Strategies for Wine Yeast Lees Valorization. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautério, G.V.; Silvério, S.I.D.C.; Egea, M.B.; Lemes, A.C. β-Glucan from Brewer’s Spent Yeast as a Techno-Functional Food Ingredient. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1074505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, R.; Coelho, E.; Coimbra, M.A. Modifications of Saccharomyces pastorianus Cell Wall Polysaccharides with Brewing Process. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.R.; Le Bourvellec, C.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Nunes, F.M.; Bastos, R.; Coelho, E.; Wessel, D.F.; Coimbra, M.A.; Cardoso, S.M. Revisiting the Chemistry of Apple Pomace Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.F.; Messias, S.; Bastos, R.; Martins, V.J.; Correia, V.G.; Pinheiro, B.A.; Silva, L.M.; Palma, A.S.; Coimbra, M.A.; Coelho, E. Structural Differences on Cell Wall Polysaccharides of Brewer’s Spent Saccharomyces and Microarray Binding Profiles with Immune Receptors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhao, G.; Liu, J. Effect of Preparation Methods on Physiochemical and Functional Properties of Yeast β-Glucan. LWT 2022, 160, 113284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikit, P.; Methacanon, P.; Visessanguan, W.; H-kittikun, A.; Maneerat, S. Characterization of an Unexpected Bioemulsifier from Spent Yeast Obtained from Thai Traditional Liquor Distillation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, M.; Ueda, M.; Saito, D.; Takata, M.; Ojima, Y.; Azuma, M. Identification of Yeast-Derived Emulsification Proteins through Analyses of Proteins Distributed into the Emulsified Phase. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Xia, C.; Liu, L.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Structural Characterization and Emulsifier Property of Yeast Mannoprotein Enzymatically Prepared with a β-1,6-Glucanase. LWT 2022, 168, 113898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajhosseini, A.; Doroud, D.; Sharifan, A.; Eftekhari, Z. Stress Response and Characterization of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized with Kluyveromyces marxianus Mannoprotein. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Kakuda, Y.; Cui, W. Hydrocolloids in Emulsions: Particle Size Distribution and Interfacial Activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabizadeh, H.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Tehrani, H. Preparation and Characterisation of Bioemulsifier From Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Its Application in Food Products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 29, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Araújo, V.B.D.; de Melo, A.N.F.; Costa, A.G.; Castro-Gomez, R.H.; Madruga, M.S.; de Souza, E.L.; Magnani, M. Followed Extraction of β-Glucan and Mannoprotein from Spent Brewer’s Yeast (Saccharomyces uvarum) and Application of the Obtained Mannoprotein as a Stabilizer in Mayonnaise. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 23, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, A.N.F.; de Souza, E.L.; da Silva Araújo, V.B.; Magnani, M. Stability, Nutritional and Sensory Characteristics of French Salad Dressing Made with Mannoprotein from Spent Brewer’s Yeast. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, S.; Kasuga, A.; Aoyagi, Y.; Sugahara, T. Nitrogen-to-Protein Conversion Factors for Some Common Edible Mushrooms. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, M.A.; Delgadillo, I.; Waldron, K.W.; Selvendran, R.R. Isolation and Analysis of Cell Wall Polymers from Olive Pulp. In Plant Cell Wall Analysis; Linskens, H.F., Jackson, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 19–44. ISBN 978-3-642-60989-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ciucanu, I.; Kerek, F. A Simple and Rapid Method for the Permethylation of Carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 131, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.M.; Guo, S.D. Rheological, Texture and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Mayonnaise with Different Fat Mimetics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Extraction | Samples | Yield (%) | Carbohydrates (mol%) | Total Carbohydrates (%) | Protein (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Man | Glc | ||||||
| Autolysis Precipitate | 100 | 30 ± 1 | 70 ± 1 | 30 ± 4 | ---- | ||
| Alkaline | 1M KOH | Sn | 12 | 66 ± 2 | 34 ± 2 | 69 ± 2 | 23 ± 1 |
| pp | 3 | 12 ± 2 | 88 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | 27 ± 1 | ||
| Sn_FR | 3 | 57 ± 0 | 43 ± 0 | 60 ± 2 | 14 ± 1 | ||
| 4M KOH | Sn | 17 | 77 ± 0 | 23 ± 0 | 45 ± 3 | 14 ± 2 | |
| pp | 13 | 12 ± 3 | 88 ± 3 | 21 ± 4 | 73 ± 0 | ||
| Sn_FR | 4 | 10 ± 2 | 90 ± 2 | 79 ± 5 | 23 ± 1 | ||
| SWE | 180 °C | Sn | 8 | 50 ± 3 | 50 ± 3 | 15 ± 1 | 32 ± 0 |
| pp | 24 | 48 ± 1 | 52 ± 1 | 69 ± 7 | 32 ± 0 | ||
| 200 °C | Sn | 20 | 29 ± 1 | 71 ± 1 | 38 ± 0 | 32 ± 0 | |
| pp | 22 | 43 ± 1 | 57 ± 1 | 79 ± 9 | 32 ± 0 | ||
| Glycosidic Linkage | Alkaline Extracts | SWE Extracts | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn 1M | pp 1M | Sn_FR 1M | Sn 4M | pp 4M | Sn_FR 4M | Sn 180 °C | pp 180 °C | Sn 200 °C | pp 200 °C | |
| t-Man | 36.9 | 6.7 | 29.2 | 29.5 | 6.4 | 7.4 | 26.3 | 25.2 | 5.1 | 23.6 |
| 2-Man | 16.1 | 3.9 | 8.9 | 17.3 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 25.8 | 12.5 | 3.8 | 9.8 |
| 3-Man | 5.5 | 1.4 | 4.0 | 8.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 3.5 | ---- | 2.5 |
| 6-Man | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | ---- | 0.8 |
| 2,6-Man | 11.4 | 4.0 | 3.3 | 20.12 | 3.3 | 3.8 | 0.8 | 8.8 | ---- | 6.2 |
| 3,6-Man | ---- | ---- | 0.2 | 2.0 | ---- | ---- | 0.3 | ---- | ----- | ---- |
| 2,3,4,6-Man | 0.3 | 0.4 | ---- | ---- | 0.2 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 3.4 | 0.2 |
| Total | 70.6 | 17.4 | 46.2 | 78.5 | 14.2 | 15.8 | 56.1 | 51.5 | 12.3 | 43.1 |
| t-Glc | 3.5 | 9.5 | 5.2 | 1.8 | 9.1 | 9.2 | 10.5 | 6.7 | 13.4 | 9.2 |
| 3-Glc | 0.9 | 17.7 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 6.2 | 0.1 | 6.2 | 3.2 | 21.8 | 18.0 |
| 4-Glc | 23.3 | 48.1 | 45.4 | 17.3 | 64.0 | 70.4 | 20.5 | 34.2 | 43.6 | 23.8 |
| 6-Glc | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 4.8 | 3.1 | ---- | 2.8 |
| 3,6-Glc | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 1.2 |
| 4,6-Glc | 0.8 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| 2,3,4,6-Glc | 0.2 | 0.7 | ---- | ---- | 0.9 | 0.3 | ---- | ---- | 4.2 | 0.8 |
| Total | 29.4 | 82.5 | 53.5 | 21.3 | 85.6 | 84.2 | 43.6 | 48.5 | 87.7 | 56.9 |
| Emulsion | Hand-Shaken | Ultraturrax | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsion Phase | Aqueous Phase | Emulsion Phase | Aqueous Phase | |||
| LLE_Water | LLE_Hexane | LLE_Water | LLE_Hexane | |||
| Sn 1M | 21 | 0 | 79 | 21 | 19 | 60 |
| Sn 4M | 26 | 0 | 74 | 22 | 25 | 53 |
| pp 4M | 55 | 25 | 20 | 41 | 39 | 20 |
| pp 200 °C | 13 | 0 | 87 | 30 | 35 | 35 |
| Glycosidic Linkage | Sn 1M | Sn 4M | pp 4M | pp 200 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsion | Aqueous | Emulsion | Aqueous | Emulsion | Aqueous | Emulsion | Aqueous | |
| t-Man | 54 | 57 | 42 | 36 | 6 | 7 | 24 | 26 |
| 2-Man | 16 | 19 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| 3-Man | 4 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | tr | 2 | 2 |
| 6-Man | 1 | 1 | ---- | 1 | ---- | ---- | 1 | 1 |
| 2,6-Man | 3 | 6 | ---- | 4 | tr | tr | 5 | 5 |
| 2,3,4,6-Man | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | tr | ---- | ---- |
| Total | 78 | 88 | 51 | 56 | 9 | 9 | 41 | 45 |
| t-Glc | 4 | 3 | 10 | 6 | 13 | 18 | 11 | 11 |
| 3-Glc | 6 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 5 | ---- | 12 | 11 |
| 4-Glc | 7 | 6 | 39 | 35 | 65 | 65 | 27 | 24 |
| 6-Glc | tr | tr | ---- | tr | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| 3,6-Glc | tr | tr | ---- | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 4,6-Glc | 1 | 1 | ---- | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| 2,3,4,6-Glc | 3 | 1 | ---- | tr | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 22 | 12 | 49 | 44 | 91 | 91 | 59 | 54 |
| Glycosidic Linkage | Sn 1M | Sn 4M | pp 4M | pp 200 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsion | Aqueous | Emulsion | Aqueous | Emulsion | Aqueous | Emulsion | Aqueous | |
| t-Man | 63 | 54 | 55 | 46 | 18 | 16 | 51 | 42 |
| 2-Man | 21 | 24 | 17 | 20 | 5 | 8 | 17 | 22 |
| 3-Man | 7 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| 6-Man | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ---- | tr | 1 | 3 |
| 2,6-Man | 5 | 11 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 16 |
| 2,3,4,6-Man | tr | tr | tr | tr | ---- | tr | tr | tr |
| Total | 95 | 96 | 81 | 81 | 25 | 32 | 77 | 89 |
| t-Glc | 1 | tr | 4 | 2 | 18 | 12 | 4 | 1 |
| 3-Glc | 1 | ---- | tr | ---- | 16 | ---- | 13 | 7 |
| 4-Glc | 2 | 2 | 12 | 13 | 35 | 42 | 1 | 1 |
| 6-Glc | ---- | tr | tr | 1 | ---- | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3,6-Glc | tr | tr | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | tr | 1 |
| 4,6-Glc | tr | tr | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | tr | tr |
| 2,3,4,6-Glc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Total | 5 | 4 | 19 | 19 | 75 | 68 | 23 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis, S.F.; Fernandes, P.A.R.; Martins, V.J.; Gonçalves, S.; Ferreira, L.P.; Gaspar, V.M.; Figueira, D.; Castelo-Branco, D.; Mano, J.F.; Coimbra, M.A.; et al. Brewer’s Spent Yeast Cell Wall Polysaccharides as Vegan and Clean Label Additives for Mayonnaise Formulation. Molecules 2023, 28, 3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083540
Reis SF, Fernandes PAR, Martins VJ, Gonçalves S, Ferreira LP, Gaspar VM, Figueira D, Castelo-Branco D, Mano JF, Coimbra MA, et al. Brewer’s Spent Yeast Cell Wall Polysaccharides as Vegan and Clean Label Additives for Mayonnaise Formulation. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083540
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis, Sofia F., Pedro A. R. Fernandes, Vítor J. Martins, Sara Gonçalves, Luís P. Ferreira, Vítor M. Gaspar, Diogo Figueira, Diogo Castelo-Branco, João F. Mano, Manuel A. Coimbra, and et al. 2023. "Brewer’s Spent Yeast Cell Wall Polysaccharides as Vegan and Clean Label Additives for Mayonnaise Formulation" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083540
APA StyleReis, S. F., Fernandes, P. A. R., Martins, V. J., Gonçalves, S., Ferreira, L. P., Gaspar, V. M., Figueira, D., Castelo-Branco, D., Mano, J. F., Coimbra, M. A., & Coelho, E. (2023). Brewer’s Spent Yeast Cell Wall Polysaccharides as Vegan and Clean Label Additives for Mayonnaise Formulation. Molecules, 28(8), 3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083540













