- Systematic Review
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature
- Raffaella Lucchini,
- Rodrigo Cartes and
- Marta Scorsetti
- + 8 authors
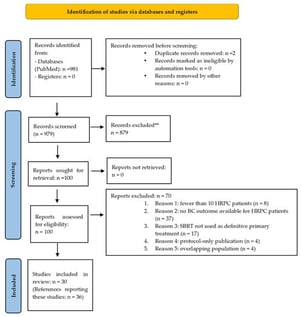
Background/Objectives: Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is increasingly used for localized prostate cancer (PCa), but evidence supporting its use in high-risk PCa (HRPC) remains limited. Standard management continues to favor conventional or moderately hypofractionated radiotherapy combined with long-course androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). This systematic review aimed to synthesize current data on SBRT biochemical outcomes, toxicity, and technical aspects in localized HRPC. Methods: A systematic PubMed search was conducted on 1 May 2024, following PRISMA 2020 guidelines (PROSPERO ID CRD420251235649). Studies reporting biochemical control (BC) for HRPC treated definitively with SBRT, with or without ADT, were included. Studies not meeting these criteria or including ≤10 HRPC patients were excluded. Risk of bias was assessed through qualitative appraisal of study methodology. Substantial heterogeneity across study design, SBRT schedules, cohort composition, and ADT integration precluded a meta-analysis; data were synthesized descriptively. Results: Thirty studies contributed biochemical control data after prostate SBRT for 1354 patients meeting inclusion criteria. SBRT was delivered using diverse platforms and dose-fractionation schemes, frequently in combination with ADT. Across studies, BC was generally favorable, though follow-up duration varied widely. Toxicity profiles were acceptable, with most reports describing predominantly grade 1–2 events and low rates of severe toxicity. Marked variability was observed in target volume definition, focal-boost strategies, urethra-sparing techniques, and the use of rectal spacers. Conclusions: Although current evidence is heterogeneous and largely derived from non-randomized studies, BC and toxicity outcomes are consistently promising, supporting SBRT as a potentially effective strategy for localized HRPC. Randomized prospective trials are needed to confirm these findings and refine optimal SBRT regimens and the role of ADT. This review received no funding.
4 February 2026