Metacognition, Learning Strategies, and Self-Regulated Learning to Promote Sustained Learning
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Education and Approaches".
Viewed by 133067Editor
Interests: learning sciences; educational psychology; education; metacognition; self-regulated learning; motivation; cognition; quantitative research methods/statistics; measurement
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
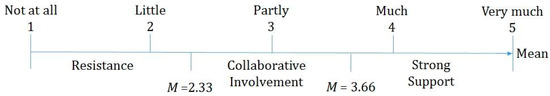
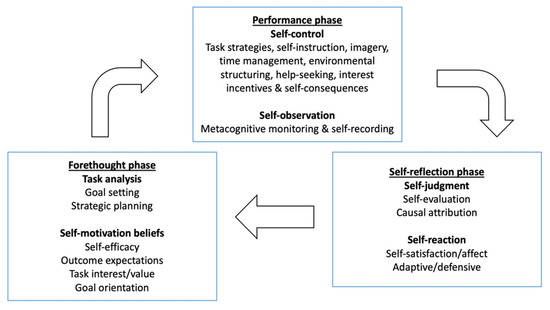
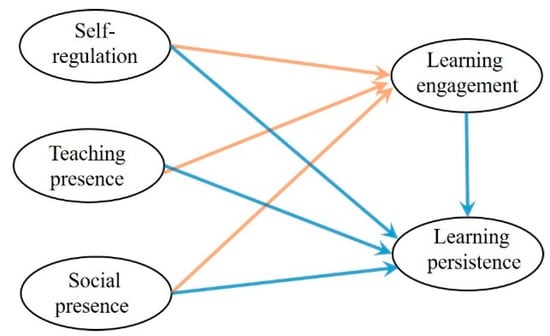
Self-regulated learning (SRL) theory posits that SRL encompasses cognition, metacognition, and motivation. Several theoretical accounts of SRL have been proposed in the literature (see Panadero, 2017, for a review). For instance, Zimmerman’s cyclical phases model (CPM) (Zimmerman and Moylan, 2009) describes SRL as a cyclical process involving three parts: (1) forethought (e.g., goal setting, strategic planning, self-efficacy beliefs, and intrinsic motivation); (2) performance and volitional control (e.g., attention focusing, self-instruction, and self-monitoring); and (3) self-reflection (e.g., self-evaluation, attributions, and self-reactions). Similarly, Winne and Hadwin (2008) developed a metacognitive perspective model (MPM) of SRL in which metacognitive processes play a central role. According to the tenets of this model, learners are perceived as being active, involved self-regulated individuals who control their own learning through the implementation of metacognitive monitoring and strategy use and motivational factors such as self-efficacy and task value. Even though all these models vary regarding labels and what aspects to include, they all converge on the conclusion that learning is regulated by a variety of dynamic interacting and cyclical cognitive, metacognitive, and motivational factors (Butler and Winne, 1995; Panadero, 2017).
Thus, the purpose of this Topical Collection is to publish the latest research on the dynamic relation between metacognition, learning strategies, and self-regulated learning in academic and non-academic settings. It is my hope that research that emerges from this Topical Collection will not only contribute to sustainable education practices through components of SRL theory, but also to the advancement of sustained, enduring learning both within and beyond the classroom. To this end, research studies on these topics employing quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods research designs are welcome.
Reference:
- Ernesto, P. A Review of Self-regulated Learning: Six Models and Four Directions for Research. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 422, doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00422
- Zimmerman, B.J.; Moylan, A.R. Self-regulation: Where metacognition and motivation intersect. In Handbook of metacognition in education; Hacker, D.J., Dunlosky, J., Graesser, A.C., Eds. Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group: Oxford, England, 2009; pp. 299–315.
- Winne, P.H.; Hadwin, A.F. The weave of motivation and self-regulated learning. In Motivation and self-regulated learning: Theory, research, and applications. D. H. Schunk, D.H., Zimmerman, B.J., Eds. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 297–314.
- Butler, D.L.; Winne, P.H. Feedback and Self-Regulated Learning: A Theoretical Synthesis. Rev. Educ. Res. 1995, 65, 245–281.
Dr. Antonio P. Gutierrez de Blume
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- learning strategies
- metacognition
- self-regulated learning
- sustained learning