- Article
The Longitudinal Impact of Bone Anchored Hearing Aid Adoption on Resting-State Functional Connectivity Using fNIRS: A Multiple Single-Case Experimental Approach
- Cassandra Cowan,
- Amberley V. Ostevik and
- Jacqueline Cummine
- + 4 authors
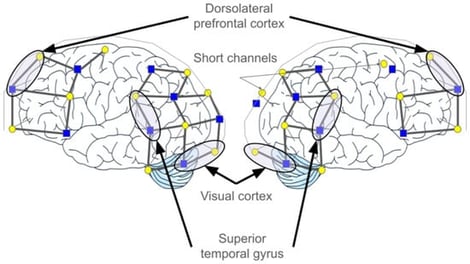
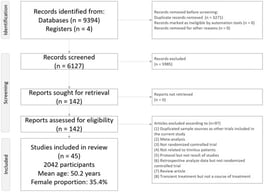
Background/Objectives: Three types of neuroplasticity that have been reported following hearing aid uptake include: cross-modal reorganization, homologue shifts, and neighbouring region restructuring. However, such evidence primarily stems from cochlear implants and conventional air-conduction hearing aids, leaving a notable gap in research on the neural and neuroplastic consequences of percutaneous bone-anchored hearing aids. The following study aimed to investigate three types of neuroplasticity associated with the integration of bone-conduction hearing aids and resting-state functional connectivity. Methods: Participants (n = 8) came to the lab nine times (i.e., five pre-treatment and four post-treatment), and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) was employed to capture functional brain connectivity between the bilateral superior temporal gyrus (STG), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and visual cortex (VC). Results: Across participants, evidence for cross-modal reorganization (between STG and VC) was evident in the left hemisphere. While the presence of homologue shifts and neighbouring region restructuring was detected, these forms of neuroplasticity were much more individualistic. Conclusions: These findings highlight both shared and individualized patterns of neuroplasticity following the uptake of bone-conduction hearing aids, underscoring the importance of considering heterogeneous neural adaptation in auditory rehabilitation research.
9 February 2026



![Illustration of Capnic Challenge Test Protocol across time. Created in BioRender (biorender.com, accessed on 29 December 2025). Kingsbury, H. (2025). Modified from Stepanek (2025) [5].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/ohbm/ohbm-07-00006/article_deploy/html/images/ohbm-07-00006-g001-550.jpg)