A Humanized Anti-IL-4Rα Monoclonal Antibody Improves Aural Fullness
Abstract
1. Introduction
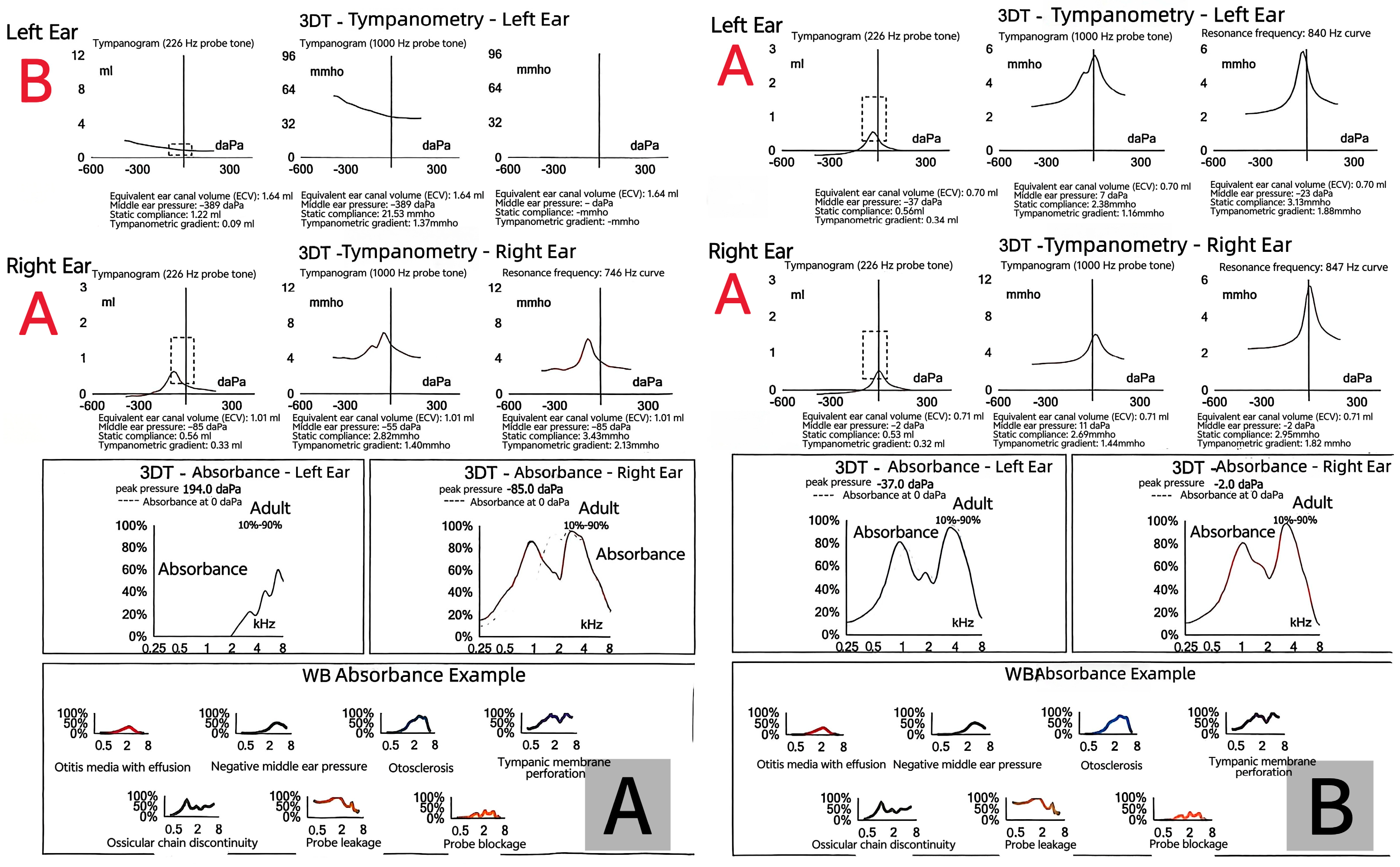
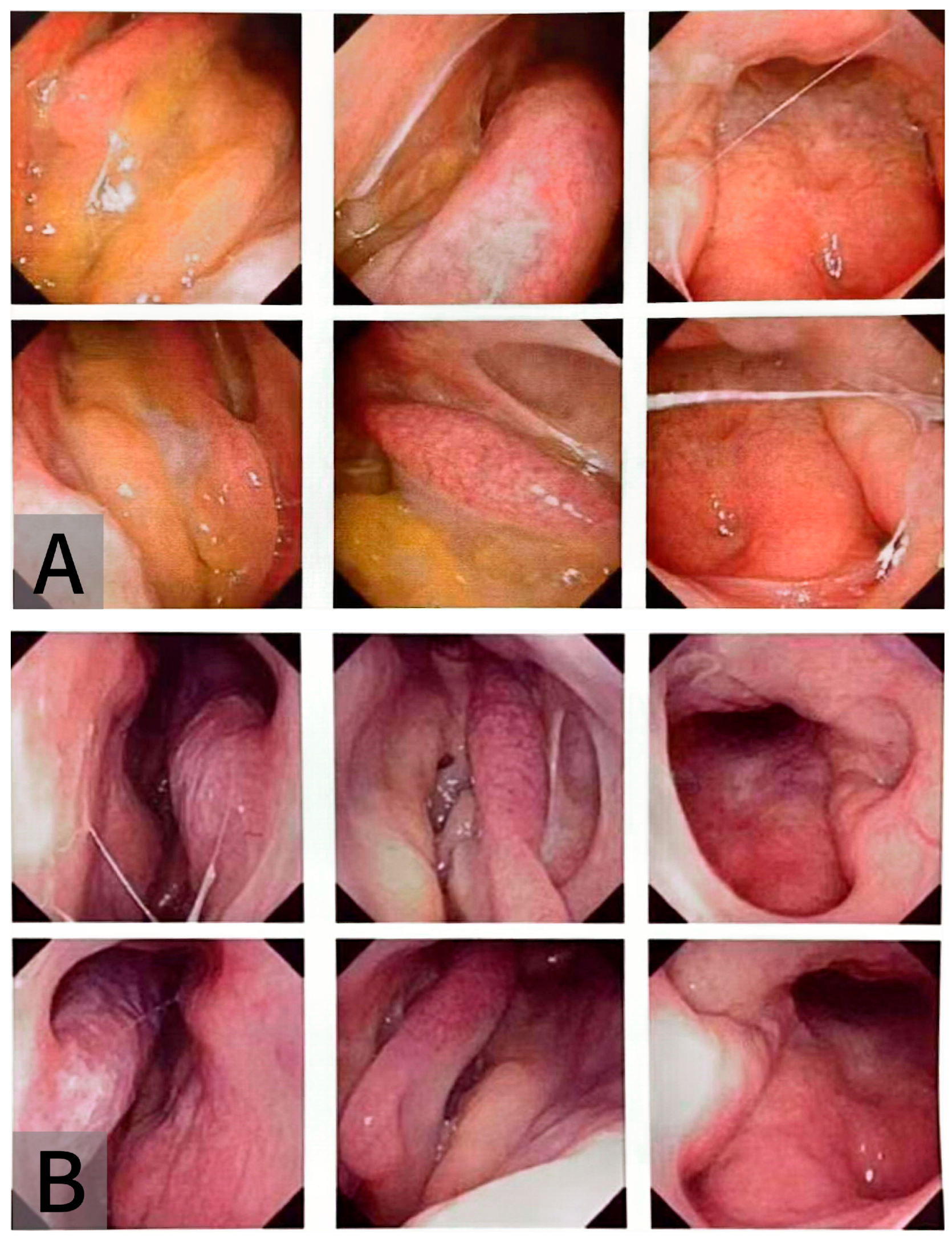
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OME | Otitis Media with Effusion |
| CRSwNP | Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps |
| AD | Atopic Dermatitis |
| SAR | Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis |
References
- Lautermann, J.; Begall, K.; Hilger, G.; Wilhelm, T.; Mir-Salim, P.; Kaschke, O.; Zahnert, T. Leitlinie seromukotympanum—Langfassung. HNO 2012, 60, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, L.; Brough, H.A.; Arasi, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bergmann, C.; Jutel, M.; Bousquet, J.; Hox, V.; Gevaert, P.; Tomazic, P.V.; et al. Otitis media with effusion (OME) and eustachian tube dysfunction: The role of allergy and immunity—An EAACI position paper. Allergy 2025, 80, 2429–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farboud, A.; Skinner, R.; Pratap, R. Otitis media with effusion (glue ear). BMJ 2011, 343, d3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karyanta, M.; Satrowiyoto, S.; Wulandari, D.P. Prevalence ratio of otitis media with effusion in laryngopharyngeal reflux. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 2019, 7460891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Kim, W.J. Interaction between allergy and middle ear infection. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantzi, F.M.; Kafetzis, D.A.; Bairamis, T.; Avramidou, C.; Paleologou, N.; Grimani, I.; Apostolopoulos, N.; Papadopoulos, N.G. IgE sensitization, respiratory allergy symptoms, and heritability independently increase the risk of otitis media with effusion. Allergy 2006, 61, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.N.; Hellings, P.W.; Rotiroti, G.; Scadding, G.K. Allergic rhinitis. Lancet 2011, 378, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikan, Z. Audiometric changes in chronic secretory otitis media due to nasal allergy. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo-Sáenz, J.G.; Galván-Aguilera, A.A.; Martínez-Ordaz, V.A.; Velasco-Rodríguez, V.M.; Nieves-Rentería, A.; Rincón-Castañeda, C. Eustachian tube dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Floc’h, A.; Allinne, J.; Nagashima, K.; Scott, G.; Birchard, D.; Asrat, S.; Bai, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Martin, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Yan, B.; Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Cao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Stapokibart for moderate-to-severe seasonal allergic rhinitis: A randomized phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovers, M.M.; Schilder, A.G.; Zielhuis, G.A.; Rosenfeld, R.M. Otitis media. Lancet 2004, 363, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddineni, S.; Ahmad, I. Updates in eustachian tube dysfunction. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 55, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, E.; Seppä, J. Results of bone conduction following surgery for chronic ear disease. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1997, 254, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordzij, J.P.; Dodson, E.E.; Ruth, R.A.; Arts, H.A.; Lambert, P.R. Chronic otitis media and sensorineural hearing loss: Is there a clinically significant relation? Am. J. Otol. 1995, 16, 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Wiatr, M.; Składzień, J.; Wiatr, A.; Tomik, J.; Stręk, P.; Medoń, D. Postoperative bone conduction threshold changes in patients operated on for chronic otitis media: Analysis. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2015, 69, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproat, R.; Burgess, C.; Lancaster, T.; Martinez-Devesa, P. Eustachian tube dysfunction in adults. BMJ 2014, 348, g1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yao, W.; Sun, Y. Occlusion of the lateral semicircular canal through the external ear canal: A case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, NP447–NP450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, H.; Matsubara, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Ohta, N.; Izuhara, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Abe, T.; Takeda, I.; Shinkawa, H. The role of periostin in eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, Y.; Tada, Y.; Okano, M.; To, M.; To, Y. Dupilumab remarkably improved eustachian tube obstruction: A case of mepolizumab-resistant eosinophilic otitis media. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 33, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M. Stapokibart: First approval. Drugs 2025, 85, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Sánchez, H.; Vallejo, L.A. Eosinophilic otitis media. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Suzuki, S.; Iino, Y. Clinical efficacy of mepolizumab and dupilumab for eosinophilic otitis media: Analysis of patient clinical characteristics. Allergol. Int. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, D.; Nakayama, T.; Minagawa, S.; Adachi, T.; Mitsuyama, C.; Shida, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Haruna, S.I.; Matsuwaki, Y. Dupilumab improves eosinophilic otitis media associated with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, Y. Eosinophilic otitis media: State-of-the-art diagnosis and treatment. Auris Nasus Larynx 2023, 50, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| System Organ Class | Frequency | Adverse Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Infections and infestations | Common | Conjunctivitis |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Common | Injection site reaction * |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Common | Arthralgia (Joint pain) |
| Eye disorders | Common | Dry eye |
| Uncommon | Blepharitis (Eyelid inflammation) | |
| Uncommon | Keratitis (Corneal inflammation) | |
| Immune system disorders | Rare | Hypersensitivity reaction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Y. A Humanized Anti-IL-4Rα Monoclonal Antibody Improves Aural Fullness. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2025, 6, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020021
Zhang Y, Shi M, Zhou Y, Chen J, Li H, Sun Y. A Humanized Anti-IL-4Rα Monoclonal Antibody Improves Aural Fullness. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine. 2025; 6(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiyun, Mengwen Shi, Yan Zhou, Jianjun Chen, Huabin Li, and Yu Sun. 2025. "A Humanized Anti-IL-4Rα Monoclonal Antibody Improves Aural Fullness" Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine 6, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020021
APA StyleZhang, Y., Shi, M., Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Li, H., & Sun, Y. (2025). A Humanized Anti-IL-4Rα Monoclonal Antibody Improves Aural Fullness. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine, 6(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020021







