- Review
Vitamin D in Obesity: Mechanisms and Clinical Impact
- Jitka Jirků,
- Zuzana Kršáková and
- Jarmila Křížová
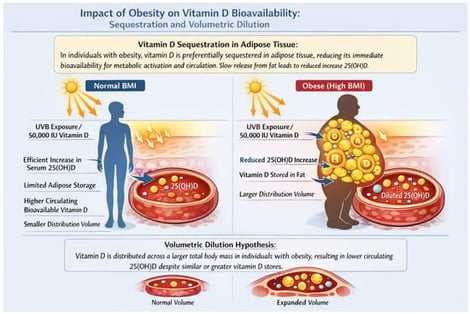
Obesity is a major global health challenge that substantially affects vitamin D metabolism and status. Numerous studies have consistently demonstrated an inverse relationship between body fat and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentrations. Emerging evidence suggests that lower serum 25(OH)D in obesity largely reflects altered distribution and metabolism rather than a uniform state of true functional deficiency. Adipose tissue functions both as a storage compartment and as a metabolically active organ capable of modulating vitamin D handling. Mechanisms include the sequestration of vitamin D in fat, volumetric dilution across a larger body mass, and the local expression of enzymes involved in vitamin D metabolism. As a result, obese individuals typically exhibit a blunted increase in serum 25(OH)D in response to supplementation, consistent with altered pharmacokinetics and increased distribution volume. Weight loss, particularly the reduction in visceral fat, is associated with modest increases in circulating 25(OH)D, further supporting a distribution-based mechanism. Although low 25(OH)D levels in obesity have been linked to insulin resistance, inflammation, and metabolic syndrome, randomized controlled trials have not consistently demonstrated that supplementation improves clinically relevant outcomes in this population. Meta-analyses confirm that the increase in serum 25(OH)D after supplementation is smaller in obese individuals, indicating that higher doses are often required to achieve comparable levels to those in normal-weight subjects. Obesity thus represents a major determinant of vitamin D deficiency, highlighting the need for individualized supplementation strategies alongside weight management. Understanding the mechanistic basis for low 25(OH)D in obesity is essential for distinguishing true deficiency from altered distribution, informing clinical decisions, and optimizing interventions to maintain adequate vitamin D status and support metabolic health.
6 February 2026