- Article
Spatial-Multiplexed Four-Channel Optical Amplification via Multiple Four-Wave Mixing in a Double-Λ Atomic System
- Xin Li,
- Dan Song and
- Jun-Xiang Zhang
- + 5 authors
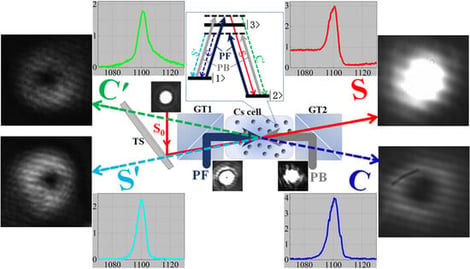
Optical amplification and spatial multiplexing technologies have important applications in quantum communication, quantum networks, and optical information processing. In this paper, based on the non-reciprocal amplification of a pair of co-propagating conjugate four-wave mixing (FWM) signals induced by a one-way pump field in a double-Λ-type hot atomic system, we demonstrate spatially multiplexed multiple FWM processes by introducing a counter-propagating collinear pump field. This configuration enables simultaneous amplification of bidirectional four-channel FWM signals. Furthermore, when the injected signal and pump beams are modulated to Laguerre–Gaussian beams carrying different optical orbital angular momentum (OAM), the OAM of the pump beam is transferred to each amplified field. Through the tilted lens method, we experimentally demonstrate that the OAM of the amplified signal light remains identical to that of the original injected signal light. In contrast, the OAM of the other three newly generated FWM fields is governed by the angular momentum conservation law of their respective FWM processes, which enables the precise manipulation of the OAM for the other generated amplified fields. Theoretical analysis of the dynamical transport equation for the density operator in light–matter interaction processes fully corroborates the experimental results. These findings establish a robust framework for developing OAM-compatible optical non-reciprocal devices based on complex structured light.
29 January 2026