Photocatalysis for a Green Future: Breaking Barriers in Energy, Environment, and Healthcare
A special issue of Materials (ISSN 1996-1944). This special issue belongs to the section "Catalytic Materials".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (20 September 2025) | Viewed by 2662
Special Issue Editor
Interests: nanomaterials; microspheres; sol-gel; polymer gels; semiconductors; catalysis; photocatalysis; environmental remediation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
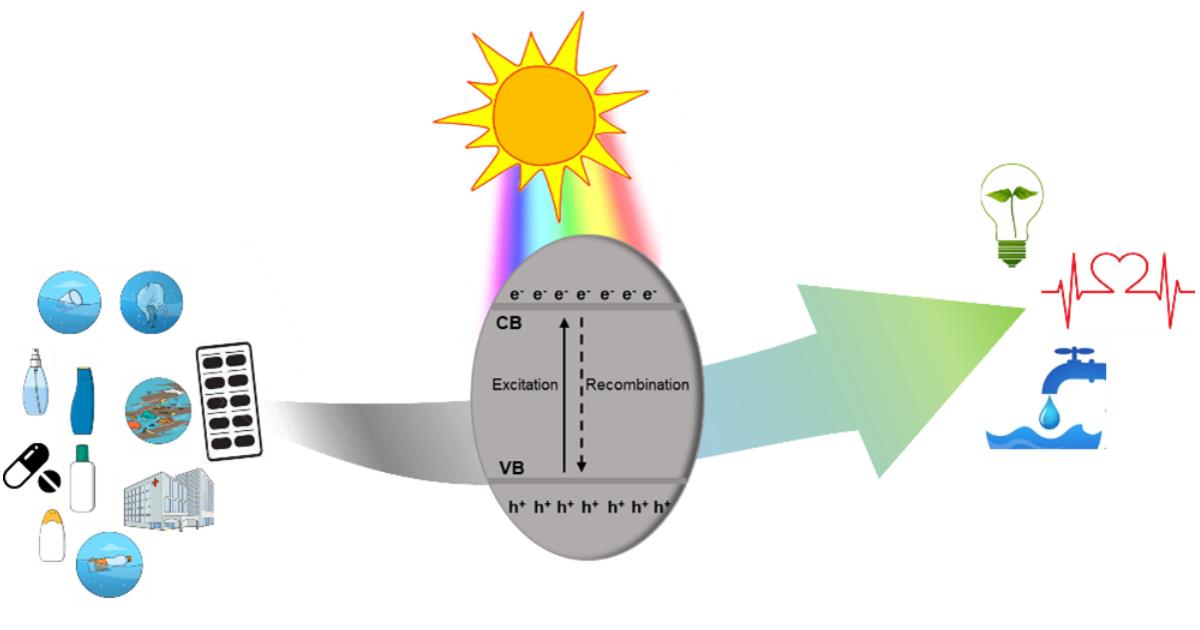
Photocatalysis is a revolutionary process leveraging light energy to expedite chemical reactions; it presents a multitude of advantages, including environmental sustainability, energy efficiency, and the capacity to decompose pollutants. Its applications range widely, encompassing water purification, air quality enhancement, self-cleaning surfaces, advanced medical treatments, and even energy generation. This versatile technology not only addresses contemporary challenges but also contributes significantly to sustainable solutions across diverse domains.
The primary drawback of this method lies in the selection of semiconductor materials. Numerous semiconductors exhibit limitations, including a high rate of recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs within the semiconductor and a low absorption of radiation in the visible range. Consequently, the quest for novel semiconductor materials with enhanced properties has garnered the attention of researchers, leading to the exploration of innovative solutions.
In this context, this Special Issue, “Photocatalysis for a Green Future: Breaking Barriers in Energy, Environment, and Healthcare” will compile recent developments in the field of new semiconductor materials for several photocatalytic applications.
The articles presented in this Special Issue will cover various topics, such as the following:
- The synthesis and characterization of novel photocatalysts;
- The photocatalytic synthesis of organic and inorganic compounds;
- Photocatalytic materials to address specific sustainability challenges;
- Applications of photocatalysts in different areas:
- Wastewater and air treatment;
- Energy conversion;
- Drug delivery;
- others;
- Critical reviews and perspectives on photocatalyst applications.
Dr. Beatriz Trindade Barrocas
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- novel photocatalysts
- semiconductor
- photocatalysis
- environmental applications
- water splitting
- wastewater treatment
- air purification
- pollutants photocatalytic removal
- energy conversion
- drug delivery
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






