- Article
Effect of Ag/AgCl Paste Composition on the Performance of Screen-Printed Flexible Ag/AgCl Biomedical Electrodes
- Wei Li,
- Qingyue Luo and
- Junpeng Li
- + 7 authors
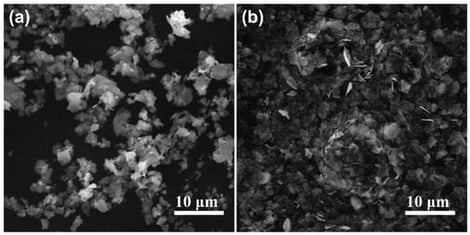
This study focused on the flexible Ag/AgCl biomedical electrode fabricated by screen printing. It systematically investigated the influence of the Ag/AgCl paste on its performance. By adjusting the type of silver powder and the mass ratio of Ag to AgCl, multiple groups of Ag/AgCl pastes were prepared, and their conductivity, microstructure, electrochemical properties, and mechanical stability were systematically characterized. The research results indicated that the specific surface area of the silver powder and the ratio of Ag to AgCl significantly affected the resistivity of the paste and the interface structure of the electrode. When using high specific surface area sheet-like silver powder H and an Ag:AgCl ratio of 5:5, the prepared electrode exhibited the best comprehensive performance: a lower resistivity (2.16 × 10−7 Ω·m), stable open-circuit voltage, good redox reversibility, and an impedance lower than that of commercial electrocardiogram electrodes. Further verification through an electrocardiogram detection system confirmed that this electrode could clearly and stably collect human electrocardiogram signals, meeting the practical requirements of electrocardiogram detection. This study provided an important theoretical and experimental basis for the development of high-performance and low-cost screen-printed Ag/AgCl flexible electrodes.
7 February 2026