Novel Nanosystems Composed of Amphiphilic Copolymers: Synthesis, Properties and Some Applications
A special issue of Materials (ISSN 1996-1944). This special issue belongs to the section "Polymeric Materials".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (1 December 2023) | Viewed by 8962
Special Issue Editors
Interests: nanomedicine; polymer micelles; cancer therapy; gene delivery; NMR spectroscopy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. LAQV-REQUIMTE, Galenic and Pharmaceutical Technology Laboratory, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Coimbra, 3000-548 Coimbra, Portugal
3. Faculty of Medicine, Institute for Clinical and Biomedical Research (iCBR) Area of Environment Genetics and Oncobiology (CIMAGO), University of Coimbra, 3000-548 Coimbra, Portugal
Interests: nanomedicine; nanotoxicology; nutraceuticals; oncobiology; toxicology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: polymeric micelles; micelleplexes; controlled release; gene therapy; cancer; nanotechnology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
Amphiphilic copolymers are versatile tools with a wide range of practical applications, e.g., in the environment, cosmetics, pharmacy, and medicine, among others.
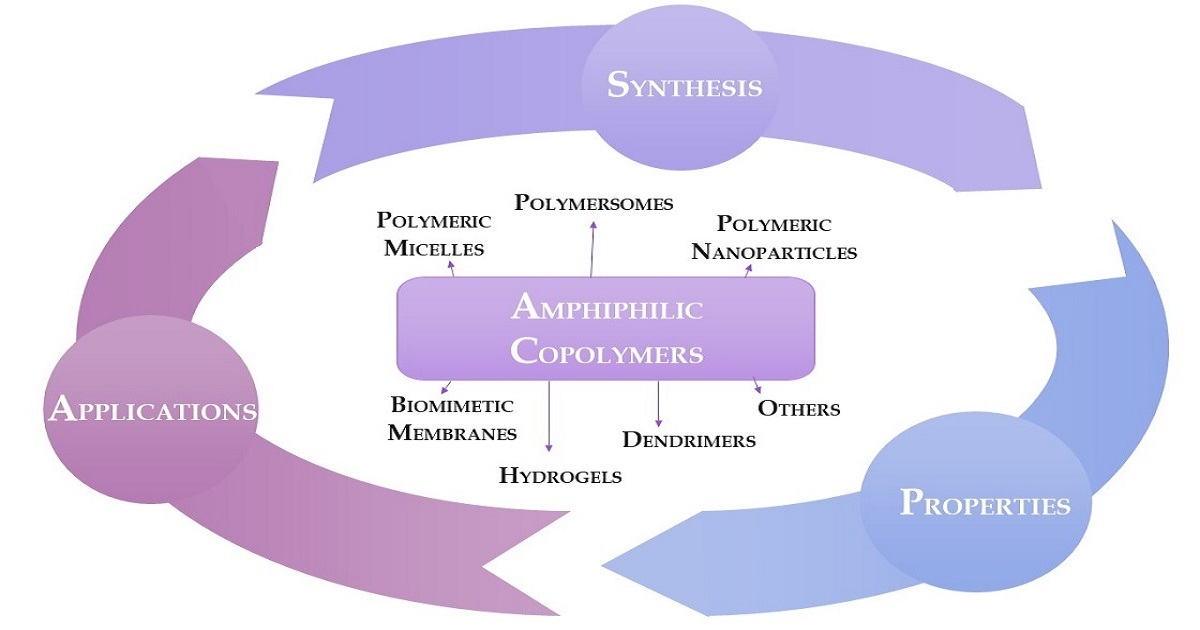
Particularly, they have revealed interesting properties to be used for the repurposing of drug design and development for medicinal purposes, from a patient-centric perspective. In fact, amphiphilic copolymers have been interestingly applied for the development of innovative nanosystems, namely polymeric micelles, polymersomes, hydrogels, and dendrimers, to develop artificial biomimetic membranes. Most of the amphiphilic copolymers that have been studied for medicinal purposes have been advantageously recognized to be biocompatible with the potential to be modified for a targeted/triggering release to the disease site.
This Special Issue aims to compile the most recent advances in the synthesis, characterization, and applications of amphiphilic copolymers for medicinal purposes, taking into consideration a sustainable and safety-by-design.
Therefore, we cordially invite researchers to contribute with original research work or review articles that present up-to-date data on the use of amphiphilic copolymers for the prevention and management of human health.
Dr. Ivana Jarak
Dr. Cátia Domingues
Dr. Ana Figueiras
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- amphiphilic copolymers
- nanomedicine
- polymeric micelles
- polymersomes
- biomimetic membranes
- dendrimers
- green synthesis
- safety-by-design
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.








