- Article
Predictors and Trends of Hepatitis B Virus Transmissions in Selected Regions of Kenya
- Missiani Ochwoto,
- Raphael O. Ondondo and
- Damaris Matoke-Muhia
- + 11 authors
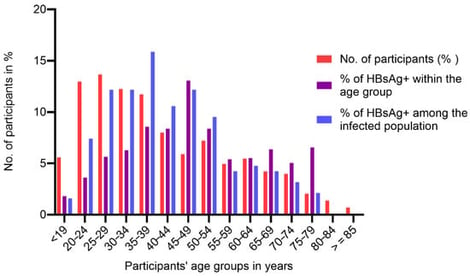
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a silent epidemic; many infected people are asymptomatic and not aware of the infection. In 2022, it was reported that approximately 254 million people were living with chronic HBV infection globally, majority being in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia. In Kenya, the national HBV prevalence is estimated to be 3.5%. Our study was aimed at identifying key predictors and transmission trends that could inform the development of sustainable prevention models needed to address existing gaps in the national framework towards HBV elimination. We targeted participants seeking health services in Baringo and Kisumu county health facilities and conducted community mass testing in the two counties. Participants were interviewed using a study questionnaire and were tested for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) using an HBsAg rapid test. Venous blood was collected from participants who tested HBsAg+ for further infection confirmation and linkage to care. Logistic regression was performed to assess factors correlated with HBV infection. Out of 3034 participants, 192 tested positive for HBsAg and the prevalence of HBV infection was 6.3% (95% CI = 0.055–0.072). Intrafamilial infections in Baringo were 15.0%. HBV infection prevalence exceeded 10% among those aged 25–49 years, peaking at 13.1% in the 45–49-year age group and lowest at 1.8% in the 16–19-year age group. Overall, males had a higher prevalence in younger ages, while females above 60 years old were more affected. In multivariable logistic regression, individuals residing in Baringo (aPR = 8.1; 95% CI = 2.2–29.4), users of other injectable drugs (aPR = 6.7; 95% CI = 1.3–204.0), those traditionally circumcised (aPR 1.02; 95% CI = 0.56, 1.88), and staying >5 km from a health care facility (aPR = 10.4; 95% CI = 2.2–49.4) had significantly higher prevalence ratios of being infected with HBV. These different infection predictors underscore the need for different care and prevention approach models.
2 February 2026



![Flow diagram according to PRISMA 2020 [28].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/labmed/labmed-03-00004/article_deploy/html/images/labmed-03-00004-g001-550.jpg)