Abstract
Acute respiratory infections (ARIs) continue to pose a major global health threat, particularly among vulnerable populations. These infections often present with similar clinical symptoms, complicating accurate diagnosis and facilitating unmonitored transmissions. Genomic surveillance has emerged as an invaluable tool for pathogen identification and monitoring of such infectious pathogens; however, its implementation is frequently limited by high costs. The widespread use of high-throughput sequencing during the COVID-19 pandemic has created an opportunity to repurpose existing genomic platforms for broader respiratory virus surveillance. In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of adapting the Illumina COVIDSeq assay—initially designed for SARS-CoV-2 whole-genome sequencing—for use with Influenza A/B, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), and Rhinovirus. Positive control samples were processed using two approaches for library preparation: four virus-specific multiple workflows and a combined rapid workflow. Both workflows incorporated pathogen-specific primers for amplification and followed the Illumina COVIDSeq protocol for library preparation and sequencing. Sequencing quality metrics were analysed, including Phred scores, read length distribution, and coverage depth. The study did not identify significant differences in genome coverage and genetic diversity metrics between workflows. Genome Detective consistently identified the correct species across both methods. The findings of this study demonstrate that the COVIDSeq assay can be effectively adapted for multi-pathogen genomic surveillance and that the combined rapid workflow can offer a cost- and labour-efficient alternative with minimal compromise to data quality.
1. Introduction
Acute respiratory infections (ARIs) pose a significant burden on global public health, accounting for an estimated 2.7 million deaths annually worldwide [1]. They have been associated with diverse pathogens, with viruses widely recognised as the predominant etiological agents in humans [2]. The major viral agents in ARIs include Influenza A and Influenza B (FluA, FluB), Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Parainfluenza viruses (PIVs), Human Rhinovirus (HR), and adenovirus (ADV), among others [3]. These infections cause clinical symptoms ranging from mild, cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress, especially among populations with heightened vulnerability, such as infants and older adults [4]. The non-specific nature of symptoms associated with respiratory infections makes distinguishing between viral and other respiratory pathogens difficult without laboratory confirmation [5]. As a result, studies have found that mismanagement and misdiagnosis of respiratory tract infections and otitis media have contributed significantly to the global escalation in antimicrobial resistance due to excessive antibiotic use.
The prevalence and distribution of these agents vary substantially with geography and time [6]. Respiratory viruses commonly affect the upper [7,8] and lower [9] respiratory tracts. In South Africa, the illnesses often peak during autumn and winter, resulting in 60,000–118,000 deaths from just the lower respiratory tract infection alone [10]. In addition, studies indicated that HIV infection increases susceptibility to certain respiratory viruses: HIV-infected children in South Africa experience higher risks of hospitalisation for RSV-related acute lower respiratory infections (ALRIs) and exhibit differential prevalence patterns of other viruses [6,11]. The National Institute for Communicable Diseases (NICD) has surveillance programmes such as the Pneumonia Surveillance Programme (PSP) and influenza-like illness (ILI) initiatives that are in place to monitor Influenza, RSV, Bordetella pertussis, and SARS-CoV-2 at sentinel sites, as these are commonly occurring in this region [10]. This is crucial, as it elucidates the pathogen’s genomic nature and informs the epidemiological implications vital for prevention and control strategies, particularly in developing regions where the burden of ARIs remains disproportionately high [12].
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) has emerged as an essential tool for viral characterisation, genomic surveillance, therapeutic decision-making, and discovering new pathogens [13,14,15,16,17]. In the Influenza H1N1 pandemic in 2009, WGS played a crucial role in revealing the zoonotic origins of this strain while the pandemic was ongoing, facilitating the practical value of robust viral genomics pipelines [18]. Furthermore, systematic genomic monitoring of Influenza A viruses over the years has been crucial for the World Health Organisation (WHO) in forecasting antigenic changes and refining vaccine selection [19]. The global sequencing capacity significantly increased in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, both internationally [20] and locally [21]. This presented an unprecedented opportunity to develop and sustain genomic surveillance for other clinically relevant respiratory viruses [20]. However, routine genomic sequencing faces challenges, such as the high cost of sequencing and the lack of standardised protocols. The advent of the COVID-19 pandemic led to an exponential use of and therefore reduced cost of sequencing to identify SARS-CoV-2 [22]. Maintaining post-COVID-19 pandemic infrastructure offers the prospect of supporting global genomic monitoring for pathogens that pose a pandemic threat with minimal adjustments to those infrastructures [23,24]. Countries can efficiently adapt sequencing workflows to various viral pathogens by employing modular approaches and standardised bioinformatic pipelines, facilitating sustainable, cost-effective surveillance. Therefore, this study aims to perform whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 using the Illumina COVIDSeq Assay and to adapt this protocol for other common respiratory viruses in a single rapid library preparation workflow.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Commercially available positive control RNA samples (n = 5) were included, two of which were Influenza controls: Influenza A with a viral load of 1.41 × 105 and Influenza B with a viral load of 1.70 × 105. One RSV sample: RSV A with a viral load of 3.16 × 106. Lastly, two Rhinovirus controls, Rhinovirus A1 with a viral load of 1.43 × 105 and Rhinovirus A16 with a viral load of 1.41 × 105 were utilised in this study. These were purchased from SepSci (Separations Scientific SA, Johannesburg, South Africa). In addition, two SARS-CoV-2 positive clinical remnant samples (n = 2) with cycle threshold values 16.64 for the E12 and 23.31 were included as positive controls, bringing the total number of controls to 7.
2.2. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Extraction
All four respiratory viruses were ribonucleic acid in nature. Therefore, RNA was extracted using the QIAamp RNA Mini kit (QIAGEN, Catalogue no. 74104, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s recommendation, and once extracted, it was stored at −80 °C. The extracted RNA was quantified using the Qubit RNA High Sensitivity assay kit on a Qubit 4.0 instrument (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. cDNA Synthesis and Amplification
Complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis was performed on all the samples (n = 7) using the Illumina COVIDSeq Kit (Catalogue No. 20065135, San Diego, CA, USA). The protocol was adapted for the different viruses by substituting primers: Influenza [25], RSV [26], and SARS-CoV-2 [27]. Primers for Rhinovirus were designed on Primal Scheme (https://primalscheme.com/) to generate 400 base pair (bp) amplicons with 70 bp overlaps, covering the 7200 bp Rhinovirus genome. Consensus FASTA sequences obtained from NCBI were first compiled and subjected to multiple sequence alignment using MUSCLE. The resulting alignment was then analysed using the Primal Scheme tool, and these were subsequently synthesised by Inqaba Biotech (Inqaba Biotech, Pretoria, South Africa). The PCR products for all the viruses were purified using 80% ethanol as per the protocol and quantified using the Qubit double-strand DNA (dsDNA) High Sensitivity assay kit on a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer instrument (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The fragment sizes of the amplicons were visualised using the E-Gel Power Snap electrophoresis device and run according to the manufacturer’s protocol using an E-Gel EX 1–2% cassette (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.4. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4.1. Multiple Workflows on Positive Controls
Using the Illumina COVIDSeq Kit (Catalogue No. 20065135, San Diego, CA, USA) library preparation reagents, DNA amplicons were tagmented with bead-linked transposomes. The tagmentation reaction was stopped with a tagmentation stop buffer before proceeding to the post-tagmentation purification, using the tagmentation wash buffer. This step was followed by amplifying the tagmented DNA with an enhanced PCR mix, and Illumina UD index adapters (set B) were used. The libraries were then pooled into four tubes according to their viral types. Five microlitres (5 μL) of the two Influenza samples were pooled into one tube, and the same was performed for the remaining three virus types, resulting in four libraries as indicated in Figure 1A. The four pooled libraries were then purified using IPB, followed by two ethanol washes with each library eluted in 13.0 μL of resuspension buffer (RSB). Libraries were then quantified using the Qubit dsDNA High Sensitivity assay kit on a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer instrument (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The library fragment size was then visualised using the E-Gel Power Snap electrophoresis device, run according to the manufacturer’s protocol on an E-Gel EX 1–2% cassette (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The four libraries were diluted to 4 nm using RSB before quantification, using the Takara qPCR Library Quantification Kit (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). Based on the qPCR quantifications, the four libraries were normalised and pooled. The pooled library was then diluted to 650 pM and spiked with 1% PhiX control before sequencing on the Illumina NextSeq2000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA), using a NextSeq P1 flow cell Kit (300 cycles) at the KwaZulu-Natal Research Innovation and Sequencing Platform (KRISP) in South Africa.
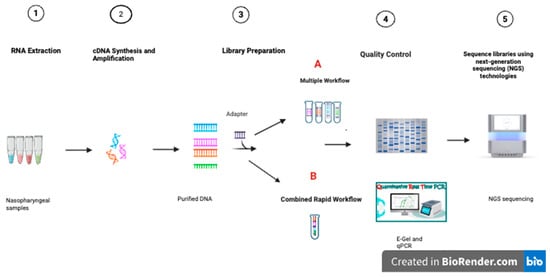
Figure 1.
Sample preparation and sequencing of multiple respiratory viruses in multiple workflows, indicated by four tubes, and a combined rapid library preparation workflow, indicated by one tube, the different colours indicating different viruses. (A) indicates the multiple library preparation workflow. (B) indicates the rapid combined library preparation workflow.
2.4.2. Rapid Combined Workflow on Positive Controls
Using the same kit and positive control samples described above in Section 2.4.1, library preparation was performed; however, before the post-indexing purification, instead of pooling only the viruses of the same kind into one tube, all seven libraries were pooled into one tube as indicated in Figure 1B, purified using IPB and eluted in 13.0 μL of resuspension buffer (RSB). The one pooled library was quantified using the Qubit dsDNA High Sensitivity assay kit on a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer instrument (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The fragment size of the library was then visualised using the E-Gel Power Snap electrophoresis instrument, run according to the manufacturer’s protocol on an E-Gel EX 1–2% cassette (Thermosfisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The library was then diluted to 4 nm using RSB before quantification using the Takara qPCR Library Quantification Kit (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). The combined library was then normalised to 650 pM. It was spiked with 1% PhiX control and sequenced on an Illumina NextSeq2000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA), using a NextSeq P1 flow cell Kit (300 cycles) at KRISP.
2.5. Sequence Quality Metrics
The quality of sequenced reads was assessed using FastQC version 0.12.0 (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 30 March 2025), generating individual reports for each FASTQ file. MultiQC version 1.29 [28] summarised these results across the multiple workflows and the rapid combined library preparation workflows, assessing whether the adapted, rapid workflow impacted the fragment integrity or base-calling accuracy compared to the original, numerous viral-specific workflows by evaluating parameters such as per-sequence quality scores and length distribution.
2.6. Genome Coverage
Genome percentage coverage and species classification were all obtained from Genome Detective version 2.89 (https://www.genomedetective.com/app/typingtool/virus/ (accessed on 30 March 2025)) [29]. A Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test was used to analyse whole genome coverage percentage in R version 4.4.1 [30]
2.7. Mutation Analysis
Mutations were computed by analysing consensus sequences obtained from Genome Detective in Nextclade Web version 3.12.0 for all the viruses except Rhinovirus A. Nextclade CLI was used to analyse Rhinovirus A using default parameters [31]. Sequence mutation outputs were then analysed.
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Quality Metrics
A total of seven positive control paired-end sequences were returned by the Illumina instrument. Two sequencing quality metrics were assessed: mean sequence quality (Phred score) and sequence length distribution. The Phred scores are indicated in Figure 2A and Figure 2B for multiple workflows and the rapid combined workflow, respectively. Samples that had a Phred score <35 were in the lower range of 0–0.5 M and 0–0.2 M reads, while samples that had a Phred score >35 had a read count that went up to 4 M and 1.2 M for the multiple workflows and a rapid combined workflow library preparation approach, respectively. Sequence length distribution obtained using multiple workflows, as indicated in Figure 3A, shows a line graph with all the samples (read one and read 2) depicting the sequence length. At <140 bp, read count is low, ranging from 0–0.5 M, and when the sequence length is >140 bp, read count goes up to 3.5 M. A similar observation is also made in the rapid combined workflow in Figure 3B. When the sequence length is <140 bp, the read count is low, 0–0.2 M; when the sequence length is >140 bp, the read count shoots to 1.2 M.
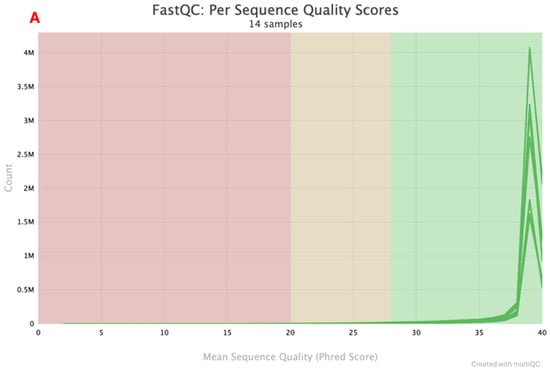
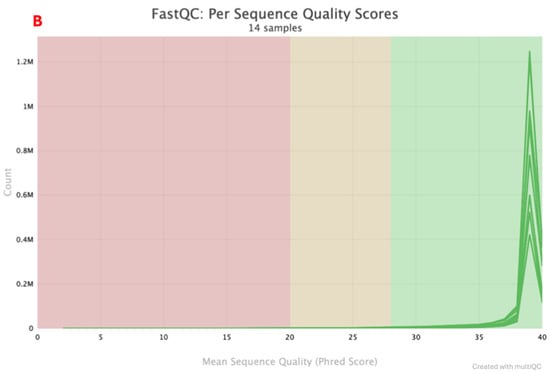
Figure 2.
FastQC graph reporting on Per Sequence Quality Scores for the multiple library preparation workflow indicated by (A,B)’s rapid combined library preparation workflow. (A) indicates multiple workflows per Sequence Quality Score FastQC report. (B) indicates the rapid combined workflow per sequence Quality Score FastQC report.  means the sequence results are significantly outside of acceptable ranges. This usually indicates a serious issue with data quality.
means the sequence results are significantly outside of acceptable ranges. This usually indicates a serious issue with data quality.  means the sequence results are outside the ideal range, but not necessarily a serious problem.
means the sequence results are outside the ideal range, but not necessarily a serious problem.  means the sequence results for that module are within expected/acceptable ranges.
means the sequence results for that module are within expected/acceptable ranges.
 means the sequence results are significantly outside of acceptable ranges. This usually indicates a serious issue with data quality.
means the sequence results are significantly outside of acceptable ranges. This usually indicates a serious issue with data quality.  means the sequence results are outside the ideal range, but not necessarily a serious problem.
means the sequence results are outside the ideal range, but not necessarily a serious problem.  means the sequence results for that module are within expected/acceptable ranges.
means the sequence results for that module are within expected/acceptable ranges.
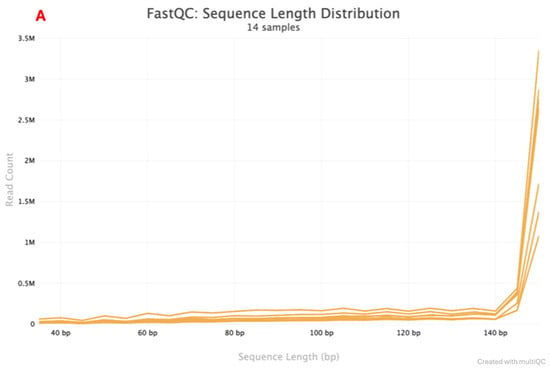
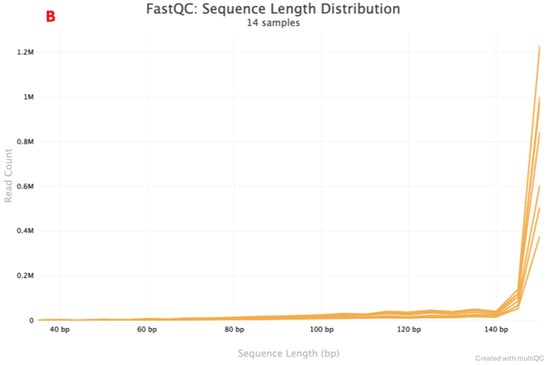
Figure 3.
FastQC graph reporting on the Sequence Length Distribution for multiple. The library preparation workflow indicated by (A,B)’s rapid combined library preparation workflow. (A) indicates the Multiple workflows Sequence length Distribution report. (B) indicates the rapid combined workflow Sequence Length Distribution report.
3.2. Genome Coverage
There was near full genome coverage depicted in Figure 4, genome coverage (%) for the multiple and rapid workflow. SARS-CoV-2 (1) exhibited near-complete genome coverage of 99.7% in the multiple workflow and 98.9% in the rapid workflow. SARS-CoV-2 (2) followed with 95.2% and 91.9% coverage. Rhinovirus A16 showed similar genome coverage between workflows—94.6% for multiple and 94.3% for rapid. Rhinovirus A1 maintained equal genome coverage of 98.9% across both workflows. RSV A had the lowest genome coverage overall, with 90.3% in the multiple workflow and 89.3% in the rapid workflow—the Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test between the multiple and rapid combined workflows (W = 29.5, p = 0.5631).
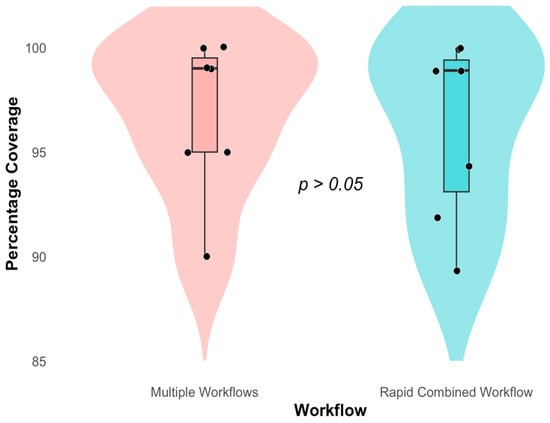
Figure 4.
Whole Genome Coverage (%) of viruses Rhinovirus A1 and A16, RSV A and B, SARS-CoV-2, and Influenza A and B in multiple and a single rapid Workflow. Red indicates the Genome Coverage for respiratory viruses prepared in Multiple workflows. Blue indicates the Genome Coverage for respiratory viruses prepared in a rapid combined workflow.
3.3. Species Assignment
Species assignments in Table 1 using Genome Detective were consistent across both methods for Influenza A (Alphainfluenzavirus H1N1), Influenza B (Betainfluenzavirus), RSV A (Bovine orthopneumovirus), Rhinovirus A16, and Rhinovirus A1 (Rhinovirus A, HRV-A1), and for the two samples of SARS-CoV-2 (Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2, Omicron (BA.2 21L) and Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2, International A_B Diversity).

Table 1.
Species Assignment of respiratory viruses taken through the Multiple and Rapid Combined Workflows.
3.4. Mutation Analysis
Statistical comparisons in Table 2 indicated no significant differences in genetic variability between workflows for substitutions (W = 27.5, p = 1), deletions (W = 28, p = 1), insertions (W = 28.5, p = 1), nucleotide missing (W = 24, p = 0.6477), and amino acids unknown (W = 25, p = 0.7441).

Table 2.
Wilcoxon test on the Genetic Diversity Variable in the library preparation workflows obtained from NextClade.
3.5. Comparison of the Cost of Quality Control Reagents Between the Rapid and the Multiple Workflow in USD
The cost comparison of quality control reagents between the rapid and multiple workflows in Table 3 below shows a reduction in the cost of quality reagents between the two approaches, as the rapid workflow library preparation results in one library and the multiple workflows with four libraries. The TAKARA Library Quantification Kit, priced at $972.54 (500 reactions), as of the 11 March 2025, resulted in $1.94 for the single library with the rapid workflow approach and $7.78 for the four libraries using the multiple workflows approach. The Qubit 1X dsDNA HS Kit, costing $102.59 (100 reactions), as of the 20 February 2025, contributed $1.03 for the single library, the rapid workflow, $4.10 for four libraries in the multiple workflows. For the E-Gel EX Gels (1%), with a kit cost of $119.05 (10 packs), as of 21st of February 2025, the rapid workflow incurred $11.91 for the single library, compared to $47.62 for four libraries in the multiple workflows. Overall, the total quality control cost per sample was $14.88 for processing seven samples for the rapid workflow and $59.50 for processing seven samples for the multiple workflows, highlighting a more cost-effective solution with the rapid method.

Table 3.
The cost of quality control reagents: Takara library Quantification kit, Qubit DSDNA HS kit, and E-Gel EX Gels, 1% in USD when executing multiple workflows and a combined workflow.
3.6. Comparison Between the Processing Time Using the Multiple and Rapid Workflows
The processing time of both workflows is described in Table 4 below. An equal amount of time was taken for the amplification step (4 h and 30 min), as separate amplification is required for each pathogen. The Multiple workflows, repeated individual runs for four different assays, resulted in an extended time: Purification required 40 min (10 min per assay), which included multiple waiting periods in each assay. Library preparation totalled 3 h and 20 min (50 min per assay), including multiple thermal cycle runs. Post-library preparation purification took an additional 1 h (15 min per assay). E-Gel Visualisation accumulated to 1 h (15 min per assay), as there were multiple runs, while Qubit Quantification required 32 min (8 min per assay). Finally, qPCR Quantification required 7 h (1 h and 45 min per assay). Collectively, these steps led to a total workflow duration of approximately 18 h and 2 min. The Combined workflow considerably reduced processing time through simultaneous assay handling. Purification was completed in 15 min, library preparation in 1 h, additional purification in 15 min, E-Gel Visualisation in 15 min, and Qubit Quantification in 8 min. Finally, qPCR Quantification required only 1 h and 45 min. The total processing duration for the Combined workflow was approximately 8 h, representing a significant reduction of roughly 10 h compared to the Multiple workflows.

Table 4.
Total processing time between the Multiple and Combined workflows.
4. Discussion
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) has evolved significantly in recent years, with cost, speed, and accuracy [32,33,34] improvements. Its routine application in public health and clinical settings has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic [21,35,36], with over 15 million SARS-CoV-2 sequences uploaded to the GISAID database over the past 6 years [37]. The urgent need for rapid identification and monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 variants led to widespread adoption and innovation in sequencing technologies. This study adapted and optimised an existing high-throughput sequencing workflow, the Illumina COVIDSeq™ Assay (Illumina, Inc.: San Diego, USA,) developed initially for rapid whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2, for use in sequencing other prevalent respiratory viruses, including Influenza, RSV, and Rhinovirus. The COVIDSeq Assay was an invaluable tool in the whole genome sequencing and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 [38,39,40]. Supporting different sample types, from nasopharyngeal (NP), oropharyngeal (OP) and nasal swabs to wastewater samples [41]. It has high sensitivity, repeatability, and reproducibility and can effectively sequence samples with cycle threshold values up to approximately 31 [42]. A study by Lowry et al. (2023), addressing the question of sequencing sensitivity of this assay on SARS-CoV-2 low-viral-load samples, sequenced samples with cycle threshold scores ranging between 30 and 35 [40], demonstrating the assay’s capability of sequencing low-viral-load samples. By replacing SARS-CoV-2-specific primers with pathogen-specific primers in the amplification stage, we were able to sequence whole genomes of all seven positive control samples successfully.
The described workflow is streamlined and adaptable, incorporating an initial amplification step that facilitates rapid protocol modification for a broad range of viral pathogens across all Illumina sequencing platforms. Its versatility has been demonstrated in various studies: for dengue virus on the NovaSeq [43], the NextSeq 6000 [44], the MiSeq [37], and the iSeq [45]; for chikungunya virus on the MiSeq [46,47,48]; for HIV drug resistance monitoring [49]; for monkeypox [50]; and for hepatitis A virus on the MiSeq [51,52] and hence can be adapted for a range of pathogens provided the use of highly sensitive primers which can then be run on any Illumina platform. Studies have shown that adaptation of sequencing protocols improves cost-effectiveness and operational simplicity [21,53]; however, maintaining sequencing quality is imperative. Our findings indicate that adapting this protocol for other respiratory viruses did not reduce the data quality. This is supported by the comparable Phred scores (>30) observed for both SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory samples that were library prepared using the COVIDSeq assay, reflecting an error rate of 1 in 1000 base calls, or a base call accuracy of 99.9% [54]. Similar Phred score thresholds (>30) have also been accepted in respiratory virus studies focusing on Influenza [55,56]. Furthermore, this assay was compatible with other respiratory viruses, as we obtained read lengths suggested by the Illumina COVIDSeq Kit (Catalogue No. 20065135, San Diego, CA, USA) for all respiratory samples. Other studies have also successfully adapted COVIDSeq for respiratory viruses like RSV, obtaining high-quality genomes [57] and enabling researchers to explore the genetic variability of the seasonal viruses [23]. These standardisation attempts of NGS technology and protocols are essential, as they will allow application in clinical laboratories for routine practice at an affordable cost and play a vital role in diagnosing respiratory diseases, developing more appropriate treatment, and keeping surveillance of emerging viruses in the near future [12].
A streamlined, rapid workflow was attempted, simultaneously enabling a single library preparation approach for all four viruses. This effectively reduced the number of samples for the post-indexing purification step and downstream quantification by qPCR and Qubit, as well as library fragment visualisation using an E-gel. Here, we reduced the cost of quality control reagents by 4-fold and total run time by 2.25-fold. The combined workflow may be ideal for large-scale sequencing in a public laboratory or genomic surveillance. An approach such as this is particularly advantageous when handling full plates of varying viral samples, as it enables a larger sample number to be processed, reducing not only turnaround time and costs of reagents but also repetitive pipetting, which can introduce variability [58,59]. The reduction of cost and time in genome sequencing over time translated to more laboratories being able to access these technologies [36,60] and set up surveillance programmes, utilising protocols like the COVIDSeq assay routinely for influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and Bordetella pertussis, which had been facilitated [10]. This is important, as it ensures standardisation of existing protocols and swift response in outbreaks for laboratories sequencing routinely. The combined approach is enabled by an indexing step in the workflow, which gives each sample a unique ID, allowing for combining all of the samples after this step without losing them. In the current study, both workflows yielded comparable quality scores (Phred). They read lengths, underscoring that sequencing quality was not compromised in the rapid combined workflow and that the library read lengths produced by the kit were not affected by the combined purification step. The difference in the whole genome coverage percentages between the workflows was also not significantly different, indicating that “pooling”, or combining all the viruses at the final purification step and taking a single sample through the final quality control steps and sequencing, did not impair the ability to retrieve the whole genome of respiratory viruses: Influenza, Rhinovirus, RSV, and SARS-CoV-2.
While rapid diagnostic methods, such as antigen-based assays and some multiplex PCR methods, offer faster turnaround times, they often compromise on sensitivity, resolution, or depth of pathogen detection [61,62]. PCR remains the gold standard for influenza subtyping due to its high specificity and sensitivity [63,64], with WHO advising against using rapid tests for influenza diagnosis [65]. Similarly, Rhinovirus C detection relies on RT-PCR followed by species-specific assays or sequencing for subtype resolution. Fidelity multiplex PCR systems (e.g., BioFire® FilmArray®, Verigene® RV+, and Prodesse assays) provide accurate and clinically useful data for early identification of respiratory viruses such as Influenza A, Influenza B, and RSV, albeit at a higher cost [66,67]. However, these do not provide the comprehensive genomic information for surveillance, and their applicability is restricted to pathogen identification and limited subtyping. Viral identification using whole genome sequencing of respiratory viruses proved superior, as it not only identifies the species but also plays a crucial role in nosocomial outbreaks and tracking [68,69], as well as vaccine efficacy [70,71]. Therefore, yielding a sufficient data sequence is imperative when optimising protocols. This study’s rapid combined and multiple workflows yielded sufficient data, consistently characterising the same species between the workflows. SARS-CoV-2 exhibited substitutions, deletions, and nucleotide gaps; Rhinovirus A had substitutions and insertions; Influenza B showed minimal variation; and Influenza A had a high substitution rate; however, there were no significant differences in mutation types between workflows.
Benchmarking whole-genome sequencing approaches against standard-of-care diagnostics is essential to assess their clinical applicability. Standard-of-care tests such as Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) and rapid antigen tests are widely used for clinical diagnosis due to their affordability, speed, and ease of use without requiring specialised personnel. However, studies show that these rapid tests often have reduced sensitivity [62]. One study found that the PanBio™ rapid antigen test (Abbott Diagnostics, Brisbane, Australia) shows variable sensitivity between 74.4 and 86.8% [72,73], and another study found that the BinaxNOW test underperforms compared to what the manufacturer claims (91.84% vs. 97.1%) [74]. Furthermore, their application is limited only to pathogen identification. Despite these limitations, rapid tests are practical for situations requiring fast results. While our findings on a combined NGS approach suggest a reduced turnaround time and cost, with in-depth pathogen insights and 100% sensitivity. Its applicability as a standard-of-care test is still an area under extensive research. A comprehensive review concluded that NGS-based whole genome sequencing methods are not yet suitable for routine diagnostics due to their high cost, time demands, and need for specialised laboratories [12]. Nevertheless, advancing and utilising rapid tests and whole-genome sequencing ensures accurate diagnosis, pathogen identification, and genomic surveillance.
It is essential to acknowledge that this study had several limitations, notably the limited sample size. Since the study’s primary objective was to establish the workflow and validate the functionality of individual primers, cultured positive controls were utilised to minimise any adventitious bias that comes with clinical samples. However, relying on cultured controls restricted the number of replicates, limiting the findings’ statistical power. While the use of positive controls was sufficient to achieve the study’s objectives, it remains essential to apply and evaluate this workflow on a larger scale of samples that will give us statistical relevance in assessing a threshold of the number of samples that can be pooled, yielding viable results. Furthermore, as clinical specimens are known to be variable in viral load and can potentially be degraded [39,75], assessing the range of Ct scores or viral loads for which the method will still produce good results is essential.
Furthermore, primer-based whole-genome amplification targeting multiple pathogens has previously been associated with amplification bias and interspecies competitive effects [76,77]. This method necessitates separate amplification procedures for each pathogen species before library preparation, thus limiting its applicability for sequencing samples with co-infections. Additionally, the assay is only compatible with Illumina sequencing platforms, restricting its adoption in laboratories utilising alternative sequencing technologies.
5. Conclusions
Our findings demonstrated that the Illumina COVIDSeq assay can successfully adapt to other respiratory viruses while maintaining comparable sound quality. The streamlined, rapid combined workflow offers a cost-effective, time-efficient alternative without compromising sequencing performance, making it a promising approach for genomic surveillance. Therefore, future work should validate this approach on more clinical samples to fully assess if the same quality output will be demonstrated and assess thresholds for which the method may not produce good results.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/labmed2040019/s1. File S1: NextClade Diversity Analysis.
Author Contributions
J.G. and S.P. conceived and designed the project; N.M. (Nqobile Mthembu), S.P., and S.J.N., N.Z.M., and T.T. performed the lab work; N.M. (Nokukhanya Msomi), J.G. and T.d.O. contributed towards resources; N.M. (Nqobile Mthembu), H.T.M., B.C.B., and D.T. analysed the data; J.G., S.P. and H.T.M. supervised the work; N.M. (Nqobile Mthembu) wrote the original draft of the manuscript; N.M. (Nqobile Mthembu), S.P., J.G., H.T.M., B.C.B. and D.T. reviewed and edited the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Technology Innovation Agency (TIA): 2021/FUN190/MW, National Research Foundation (NRF): 1504279 (NEP), and the Poliomyelitis Research Foundation (PRF): 24/109.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All protocols were reviewed and approved by the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee (BREC) of the University of KwaZulu-Natal (protocol reference number: BREC/00007092/2024), valid between 14 July 2024 and 13 July 2026.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent for participation was not required as per South Africa’s Department of Health Ethics in Health Research Guidelines (2004/2005), Section 4.1.5b.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in the National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at https://dataview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/object/PRJNA1335216?reviewer=o57oqo8pdt6gsqtumlp1qbj4hp (accessed on 30 March 2025).
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the University of KwaZulu-Natal College of Health Sciences (UKZN CHS), the KwaZulu-Natal Research Innovation and Sequencing Platform (KRISP), and the Distributed Platform in Omics (DIPLOMIC) for providing resources for this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| ADV | Adenovirus |
| ALRI | Acute Lower Respiratory Infection |
| ARI | Acute Respiratory Infection |
| BREC | Biomedical Research Ethics Committee |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| dsDNA | Double-Stranded DNA |
| FluA | Influenza A |
| FluB | Influenza B |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| HR | Human Rhinovirus |
| ILI | Influenza-Like Illness |
| KRISP | KwaZulu-Natal Research Innovation and Sequencing Platform |
| MUSCLE | Multiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NHLS | National Health Laboratory Service |
| NICD | National Institute for Communicable Diseases |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PIV | Parainfluenza Virus |
| PSP | Pneumonia Surveillance Programme |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| RSV | Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| UKZN | University of KwaZulu-Natal |
| WGS | Whole Genome Sequencing |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
References
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Walker, G.J.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Shorter, C.; Honeywill, C.; Wynn, M.; Willenborg, C.; Barnes, P.; Kang, J.; Pierse, N.; Crane, J. Viruses Associated with Acute Respiratory Infection in a Community-based Cohort of Healthy New Zealand Children. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, C.L.; Babady, E.; Ginocchio, C.C.; Hatchette, T.F.; Jerris, R.C.; Li, Y.; Loeffelholz, M.; McCarter, Y.S.; Miller, M.B.; Novak-Weekley, S. Practical Guidance for Clinical Microbiology Laboratories: Viruses Causing Acute Respiratory Tract Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 32, e00042-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvia, R.; Corcioli, F.; Ciccone, N.; Della Malva, N.; Azzi, A. Detection of 12 Respiratory Viruses by Duplex Real Time PCR Assays in Respiratory Samples. Mol. Cell. Probes 2015, 29, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.L.; Baggett, H.C.; Brooks, W.A.; Feikin, D.R.; Hammitt, L.L.; Higdon, M.M.; Howie, S.R.; Knoll, M.D.; Kotloff, K.L.; Levine, O.S. Causes of Severe Pneumonia Requiring Hospital Admission in Children without HIV Infection from Africa and Asia: The PERCH Multi-Country Case-Control Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 757–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.C.; Kuschner, Z.; Rabede, Z.; Madimabe, R.; Van Niekerk, N.; Moloi, J.; Kuwanda, L.; Rossen, J.W.; Klugman, K.P.; Adrian, P.V. Clinical Epidemiology of Bocavirus, Rhinovirus, Two Polyomaviruses and Four Coronaviruses in HIV-Infected and HIV-Uninfected South African Children. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleszko, W.; Marengo, R.; Vieira, A.S.; Ratajczak, K.; Mayorga Butrón, J.L. Immunity-targeted Approaches to the Management of Chronic and Recurrent Upper Respiratory Tract Disorders in Children. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2019, 44, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S. Epidemiology of Viral Pneumonia. Clin. Chest Med. 2017, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferkol, T.; Schraufnagel, D. The Global Burden of Respiratory Disease. Ann. ATS 2014, 11, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis—NICD. Available online: https://www.nicd.ac.za/about-us/respiratory-diseases-and-meningitis/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Moyes, J.; Cohen, C.; Pretorius, M.; Groome, M.; von Gottberg, A.; Wolter, N.; Walaza, S.; Haffejee, S.; Chhagan, M.; Naby, F. Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus–Associated Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Hospitalizations among HIV-Infected and HIV-Uninfected South African Children, 2010–2011. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, S217–S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Scotch, M.; Rawlinson, W.D. Detection of Respiratory Viruses Directly from Clinical Samples Using Next-generation Sequencing: A Literature Review of Recent Advances and Potential for Routine Clinical Use. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houldcroft, C.J.; Beale, M.A.; Breuer, J. Clinical and Biological Insights from Viral Genome Sequencing. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greninger, A.L.; Naccache, S.N.; Messacar, K.; Clayton, A.; Yu, G.; Somasekar, S.; Federman, S.; Stryke, D.; Anderson, C.; Yagi, S.; et al. A Novel Outbreak Enterovirus D68 Strain Associated with Acute Flaccid Myelitis Cases in the USA (2012–14): A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greninger, A.L.; Zerr, D.M.; Qin, X.; Adler, A.L.; Sampoleo, R.; Kuypers, J.M.; Englund, J.A.; Jerome, K.R. Rapid Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing during an Investigation of Hospital-Acquired Human Parainfluenza Virus 3 Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grad, Y.H.; Newman, R.; Zody, M.; Yang, X.; Murphy, R.; Qu, J.; Malboeuf, C.M.; Levin, J.Z.; Lipsitch, M.; DeVincenzo, J. Within-Host Whole-Genome Deep Sequencing and Diversity Analysis of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Reveals Dynamics of Genomic Diversity in the Absence and Presence of Immune Pressure. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7286–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Chen, J. Application of next Generation Sequencing for the Detection of Human Viral Pathogens in Clinical Specimens. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 86, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.J.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Bahl, J.; Lycett, S.J.; Worobey, M.; Pybus, O.G.; Ma, S.K.; Cheung, C.L.; Raghwani, J.; Bhatt, S. Origins and Evolutionary Genomics of the 2009 Swine-Origin H1N1 Influenza A Epidemic. Nature 2009, 459, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.H.; Gostic, K.M.; Pompei, S.; Bedford, T.; Łuksza, M.; Neher, R.A.; Grenfell, B.T.; Lässig, M.; McCauley, J.W. Predictive Modeling of Influenza Shows the Promise of Applied Evolutionary Biology. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Guzman, E.; Simons, L.M.; Dean, T.J.; Agnes, F.; Pawlowski, A.; Alisoltanidehkordi, A.; Nam, H.H.; Ison, M.G.; Ozer, E.A.; Lorenzo-Redondo, R. Deviations in RSV Epidemiological Patterns and Population Structures in the United States Following the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Giandhari, J.; Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Chimukangara, B.; Lessells, R.; Moosa, Y.; Mattison, S.; Gazy, I.; Fish, M. Whole Genome Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2: Adapting Illumina Protocols for Quick and Accurate Outbreak Investigation during a Pandemic. Genes 2020, 11, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, A.M.; Alkhilaiwi, F.A.; Ullah Khan, N. Era of Molecular Diagnostics Techniques before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4769–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davina-Nunez, C.; Perez-Castro, S.; Cabrera-Alvargonzalez, J.J.; Montano-Barrientos, J.; Godoy-Diz, M.; Regueiro, B. The Modification of the Illumina® CovidSeqTM Workflow for RSV Genomic Surveillance: The Genetic Variability of RSV during the 2022–2023 Season in Northwest Spain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Pérez, J.A.; Wong-Arambula, C.; Solis-Hernandez, M.; Becerril-Vargas, E.; Barrera-Badillo, G.; Ahumada-Topete, V.H.; Avila-Rios, S.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Mejia-Nepomuceno, F.; Mendoza-Ramirez, E. First Laboratory-Confirmed Human Case of Infection with Influenza A (H5N2) Virus Reported in Mexico. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wentworth, D.E. Influenza A Virus Molecular Virology Techniques. Influenza Virus Methods Protoc. 2012, 865, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, D.M.; Fernandes, G.; Jasim, S.; Williams, T.; Namugenyi, S.; Carr, M.; Meyer, J.R.; Sharma, A.; Marshal, L.; Nunley, B.E.; et al. ARTIC RSV Amplicon Sequencing Reveals Global RSV Genotype Dynamics. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; San, J.E.; Tshiabuila, D.; Naidoo, Y.; Pillay, Y.; Maharaj, A.; Anyaneji, U.J.; Wilkinson, E.; Tegally, H.; Lessells, R.J. Evaluation of Miniaturized Illumina DNA Preparation Protocols for SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize Analysis Results for Multiple Tools and Samples in a Single Report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsker, M.; Moosa, Y.; Nooij, S.; Fonseca, V.; Ghysens, Y.; Dumon, K.; Pauwels, R.; Alcantara, L.C.; Vanden Eynden, E.; Vandamme, A.-M. Genome Detective: An Automated System for Virus Identification from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Aksamentov, I.; Roemer, C.; Hodcroft, E.; Neher, R. Nextclade: Clade Assignment, Mutation Calling and Quality Control for Viral Genomes. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardy, J.L.; Loman, N.J. Towards a Genomics-Informed, Real-Time, Global Pathogen Surveillance System. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, V.; Ngwira, L.G.; Lewis, J.M.; Baker, K.S.; Peacock, S.J.; Jauneikaite, E.; Feasey, N. A Systematic Review of Economic Evaluations of Whole-Genome Sequencing for the Surveillance of Bacterial Pathogens. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 000947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Smurthwaite, K.S.; Nghiem, S.; Cribb, D.M.; Zahedi, A.; Ferdinand, A.D.; Andersson, P.; Kirk, M.D.; Glass, K.; Lancsar, E. Economic Evaluations of Whole-Genome Sequencing for Pathogen Identification in Public Health Surveillance and Health-Care-Associated Infections: A Systematic Review. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e953–e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.; Lee, S.; Park, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Park, M.G.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, D.; Chang, H.; Kim, V.N.; Lee, C.J. Development of a Laboratory-Safe and Low-Cost Detection Protocol for SARS-CoV-2 of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Exp. Neurobiol. 2020, 29, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, S.H.; Gerasimova, A.; Ruiz-Vega, R.; Livingston, K.; Kagan, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Anderson, B.; Owen, R.; Bernstein, L.; Smolgovsky, A. Development and Validation of a High Throughput SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing Workflow in a Clinical Laboratory. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Imran, M.; Khare, K.; Mishra, P.; Mohite, R.; Khan, M.A.; Swaminathan, A.; Yadav, A.; Sinha, S.; Shukla, R. Clinico-Genomic Study Reveals Association of Dengue Virus Genome High Frequency Mutations with Dengue Disease Severity. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.E.; Tamrakar, V.K.; Almas, S.; Brown, E.; Sharma, R. COVIDSeq as Laboratory Developed Test (LDT) for Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOC). Arch. Clin. Biomed. Res. 2022, 6, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoyar, R.C.; Jain, A.; Sehgal, P.; Divakar, M.K.; Sharma, D.; Imran, M.; Jolly, B.; Ranjan, G.; Rophina, M.; Sharma, S.; et al. High Throughput Detection and Genetic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 Using COVIDSeq next-Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, K.; Bauer, M.J.; Buckley, C.; Wang, C.; Bordin, A.; Badman, S.; Harris, P.N.; Mackay, I.; Whiley, D. Evaluation of Illumina® COVIDSeqTM as a Tool for Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Characterisation. J. Virol. Methods 2023, 322, 114827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina, Inc. Illumina Illumina COVIDSeq RUO Kits; Illumina, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.R.; Hardison, M.T.; Houdeshell, H.N.; Vest, A.C.; Whitlock, D.A.; Skola, D.D.; Koble, J.S.; Oberholzer, M.; Schroth, G.P. Evaluation of an Optimized Protocol and Illumina ARTIC V4 Primer Pool for Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 Using COVIDSeqTM and DRAGENTM COVID Lineage App Workflow. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, C.B.; Hill, V.; Breban, M.I.; Chaguza, C.; Paul, L.M.; Sodeinde, A.; Taylor-Salmon, E.; Ott, I.M.; Petrone, M.E.; Dijk, D. DengueSeq: A Pan-Serotype Whole Genome Amplicon Sequencing Protocol for Dengue Virus. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermann, T.; Baethgen, L.F.; Gregianini, T.S.; Godinho, F.; Barcellos, R.B.; Ruivo, A.P.; Bauerman, M.; Selayaran, T.M.; dos Santos, F.M.; Schoerer, J.A. Deep Sequencing of Dengue Virus Genome Reveals Simultaneous Circulation and Coinfection of Dengue Virus in Southern Brazil 2022–2023. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, M.; Katuwal, N.; Shrestha, A.; Madhup, S.K.; Tamrakar, D.; Shrestha, R. Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Dengue Virus in Central Nepal from 2022 to 2023. BMC Glob. Public Health 2025, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padane, A.; Tegally, H.; Ramphal, Y.; Seyni, N.; Sarr, M.; Diop, M.M.; Diedhiou, C.K.; Mboup, A.; Diouf, N.D.; Souaré, A. An Emerging Clade of Chikungunya West African Genotype Discovered in Real-Time during 2023 Outbreak in Senegal. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, A.C.P.; Fonseca, P.L.C.; Alves, H.J.; Bonfim, D.M.; Dutra, J.V.R.; Moreira, F.R.R.; de Brito Mendonça, C.P.T.; Rios, J.S.H.; do Prado Silva, J.; Malta, F.S.V. Retrospective Epidemiologic and Genomic Surveillance of Arboviruses in 2023 in Brazil Reveals High Co-Circulation of Chikungunya and Dengue Viruses. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de La Roque, D.G.L.; Santos, E.V.; Policastro, L.R.; da Costa, P.N.M.; Evaristo, M.; Yamamoto, A.Y.; Giomo, D.B.; Torres, P.M.A.; Gentil, D.C.D.; Minto, E.C.M. Exploring the Chikungunya Virus Landscape in a Dengue-Endemic Brazilian Area. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, N.C.; Yeboah, E.; Tsaknaridis, L.; Makris, V. An NGS Amplicon Tiling Protocol for HIV-1 Drug Resistance Detection Using Illumina® COVIDSeq™ Assay Kit; NGS-Globalhealth APHL Association of Public Health Laboratories: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Brown, J.; Broadhurst, M.J.; Houlihan, C.; O’Toole, Á.; Rambaut, A.; Barrett, J.C.; Goodfellow, I.; Cotten, M. Monkeypox Virus Multiplexed PCR Amplicon Sequencing (PrimalSeq), protocols.io. 2022. Available online: https://www.protocols.io/view/monkeypox-virus-multiplexed-pcr-amplicon-sequencin-5qpvob1nbl4o/v4 (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Sicilia, P.; Fantilli, A.C.; Cuba, F.; Di Cola, G.; Barbas, M.G.; Poklepovich, T.; Re, V.E.; Castro, G.; Pisano, M.B. Hepatitis A Virus Whole Genome Sequencing Strategy Using NGS/Illumina Technology. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicilia, P.; Fantilli, A.C.; Cuba, F.; Di Cola, G.; Barbás, M.G.; Poklepovich, T.; Ré, V.E.; Castro, G.; Pisano, M.B. Novel Strategy for Whole-Genome Sequencing of Hepatitis A Virus Using NGS Illumina Technology and Phylogenetic Comparison with Partial VP1/2A Genomic Region. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GISAID—Gisaid.Org. Available online: https://gisaid.org/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Illumina|technote_Q-Scores.Pdf. Available online: https://www.illumina.com/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Bendall, E.E.; Zhu, Y.; Fitzsimmons, W.J.; Rolfes, M.; Mellis, A.; Halasa, N.; Martin, E.T.; Grijalva, C.G.; Talbot, H.K.; Lauring, A.S. Influenza A Virus Within-Host Evolution and Positive Selection in a Densely Sampled Household Cohort over Three Seasons. Virus Evol. 2024, 10, veae084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoecke, S.; Verhelst, J.; Vuylsteke, M.; Saelens, X. Analysis of the Genetic Diversity of Influenza A Viruses Using Next-Generation DNA Sequencing. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunley, B.E.; Weixler, A.; Kim, H.G.; Xie, H.; Sereewit, J.; Hajian, P.; Ellis, S.; Mills, M.G.; Pérez-Osorio, A.C.; Goya, S. Clinical Performance Evaluation of a Tiling Amplicon Panel for Whole Genome Sequencing of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, K.; Ray, C.A.; Brunner, L.; Wang, J.; Lee, J.W.; DeSilva, B. Strategies to Minimize Variability and Bias Associated with Manual Pipetting in Ligand Binding Assays to Assure Data Quality of Protein Therapeutic Quantification. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrafi, A.A. Preanalytical Errors: A Major Issue in Medical Laboratory. Acta Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 3, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Buermans, H.P.; den Dunnen, J.T. Next Generation Sequencing Technology: Advances and Applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliendo, A.M.; Gilbert, D.N.; Ginocchio, C.C.; Hanson, K.E.; May, L.; Quinn, T.C.; Tenover, F.C.; Alland, D.; Blaschke, A.J.; Bonomo, R.A. Better Tests, Better Care: Improved Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, S139–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisht, V.; Vashisht, A.; Mondal, A.K.; Farmaha, J.; Alptekin, A.; Singh, H.; Ahluwalia, P.; Srinivas, A.; Kolhe, R. Genomics for Emerging Pathogen Identification and Monitoring: Prospects and Obstacles. BioMedInformatics 2023, 3, 1145–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monne, I.; Ormelli, S.; Salviato, A.; De Battisti, C.; Bettini, F.; Salomoni, A.; Drago, A.; Zecchin, B.; Capua, I.; Cattoli, G. Development and Validation of a One-Step Real-Time PCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Subtype H5, H7, and H9 Avian Influenza Viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.E.; Williams, J.V. Emerging Respiratory Viruses in Children. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2018, 32, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations on the Use of Rapid Testing for Influenza Diagnosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.-S.; Tsai, C.-L.; Chang, J.; Hsu, T.-C.; Lin, S.; Lee, C.-C. Multiplex PCR System for the Rapid Diagnosis of Respiratory Virus Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabold, E.; Waggoner, J. Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Infectious Diseases. In CDC Yellow Book, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Traveler’s Health; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, M.; Macori, G.; Mullane, N.; Sutton-Fitzpatrick, U.; Gonzalez, G.; Coughlan, S.; Purcell, A.; Fenelon, L.; Fanning, S.; Schaffer, K. Whole-Genome Sequencing to Track Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Transmission in Nosocomial Outbreaks. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e727–e735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, E.; Schulte, E.C.; Graf, A.; Karollus, A.; Smith, N.H.; Michler, T.; Dvoretskii, S.; Angelov, A.; Sonnabend, M.; Peter, S. Viral Genome Sequencing to Decipher In-Hospital SARS-CoV-2 Transmission Events. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, M.L.; Copin, R.; McCarthy, S.; Coppi, A.; Warner, F.; Ferguson, D.; Duckwall, C.; Borg, R.; Muenker, M.C.; Overton, J. Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing to Estimate the Contribution of Immune Evasion and Waning Immunity on Decreasing COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.; Sjaarda, C.; Rand, B.; Roberts, D.; Tozer, K.; Fattouh, R.; Kozak, R.; Sheth, P. The Molecular Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Ontario, Canada from 2022–2024 Using a Custom Whole Genome Sequencing Assay and Analytics Package. J. Clin. Virol. 2025, 176, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulilete, O.; Lorente, P.; Leiva, A.; Carandell, E.; Oliver, A.; Rojo, E.; Pericas, P.; Llobera, J.; COVID-19 Primary Care Research Group. PanbioTM Rapid Antigen Test for SARS-CoV-2 Has Acceptable Accuracy in Symptomatic Patients in Primary Health Care. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, L.J.; Gaeddert, M.; Tobian, F.; Lainati, F.; Gottschalk, C.; Klein, J.A.; Schnitzler, P.; Kräusslich, H.-G.; Nikolai, O.; Lindner, A.K. The Abbott PanBio WHO Emergency Use Listed, Rapid, Antigen-Detecting Point-of-Care Diagnostic Test for SARS-CoV-2—Evaluation of the Accuracy and Ease-of-Use. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, G.A.; Kamara, H.I.; Strobeck, M.; Mellman, T.A.; Kwagyan, J.; Sullivan, A.; Byrd, A.S.; Shokrani, B.; Mighty, H.E. Diagnostic Accuracy of a Rapid Diagnostic Test for the Early Detection of COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 147, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, S.A. DNA/RNA Preparation for Molecular Detection. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnifro, E.M.; Ashshi, A.M.; Cooper, R.J.; Klapper, P.E. Multiplex PCR: Optimization and Application in Diagnostic Virology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.L.; Kelly, R.P.; Lowell, N.C.; Port, J.A. Indexed PCR Primers Induce Template-Specific Bias in Large-Scale DNA Sequencing Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).