- Case Report
Beyond the Ordinary: Diagnosing a Case with Urinothorax
- Tarneem M. Alghamdi,
- Mohammed M. Mergani and
- Mahmoud I. Mahmoud
- + 4 authors
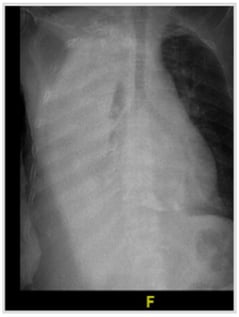
Urinothorax, the presence of urine in the pleural space, is an exceptionally rare cause of pleural effusion, with fewer than 100 cases described in the literature. It most often follows trauma or urological procedures, though obstructive uropathy is also a recognized mechanism. We report an 83-year-old man with chronic kidney disease and benign prostatic hyperplasia who presented with acute dyspnea and a massive right-sided pleural effusion. Thoracentesis yielded clear yellow fluid with an ammonia-like odor, while imaging revealed chronic bladder outlet obstruction with bilateral hydroureteronephrosis. Despite inconclusive scintigraphy, the effusion resolved completely after urinary decompression with Foley catheterization, confirming the diagnosis. This case underscores the diagnostic challenges of urinothorax, which may be overlooked due to its rarity and variable biochemical profile, and highlights the importance of correlating clinical, radiologic, and pleural fluid findings. Early recognition is crucial, as timely relief of urinary obstruction provides both definitive diagnosis and curative treatment.
3 February 2026