- Systematic Review
Post-COVID-19 Cardiovascular Complications: An Updated Systematic Review
- Alexandru Stoichita,
- Beatrice Mahler and
- Adriana Iliesiu Mihaela
- + 11 authors
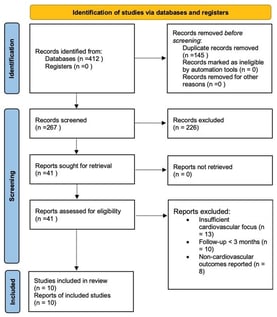
Background: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can cause persistent, multisystem complications collectively termed long COVID. Cardiovascular sequelae are among the most clinically significant yet remain incompletely characterized. This review aimed to synthesize current evidence on objective cardiovascular outcomes in long COVID and explore underlying mechanisms. Methods: A systematic review was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science for studies published between January 2020 and March 2024. Search terms included “COVID-19,” “long COVID,” “post-acute sequelae,” “cardiovascular,” “echocardiography,” “biomarkers,” and “imaging.” Only studies reporting at least one cardiovascular outcome, defined as either objectively measured parameters (e.g., echocardiography, cardiac biomarkers, ECG findings, or vascular function indices) or clinically relevant cardiovascular symptoms during follow-up, were included. From 412 identified records, ten recent, high-quality studies with a primary cardiovascular focus were selected. This systematic review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Results: Long COVID is associated with subclinical myocardial dysfunction, arrhythmias, endothelial injury, vascular stiffness, and a prothrombotic state. Reported findings included reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, impaired global longitudinal strain, increased arterial stiffness, elevated cardiac biomarkers, new-onset hypertension, and persistent ECG changes, even in non-hospitalized patients without prior cardiovascular disease. Proposed mechanisms include myocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system dysregulation, autonomic imbalance, and chronic inflammation. Secondary bacterial and fungal infections were noted in critically ill survivors but did not fully explain the breadth or persistence of symptoms. Conclusions: Long COVID is a heterogeneous entity with substantial cardiovascular implications across all levels of acute disease severity. Early detection through longitudinal monitoring, standardized definitions, and multidisciplinary care is essential to reduce long-term cardiovascular risk.
25 February 2026