A Whole-Body Physiology Model to Investigate Respiratory Function During Exercise Across Different Age Cohorts
Abstract
1. Introduction
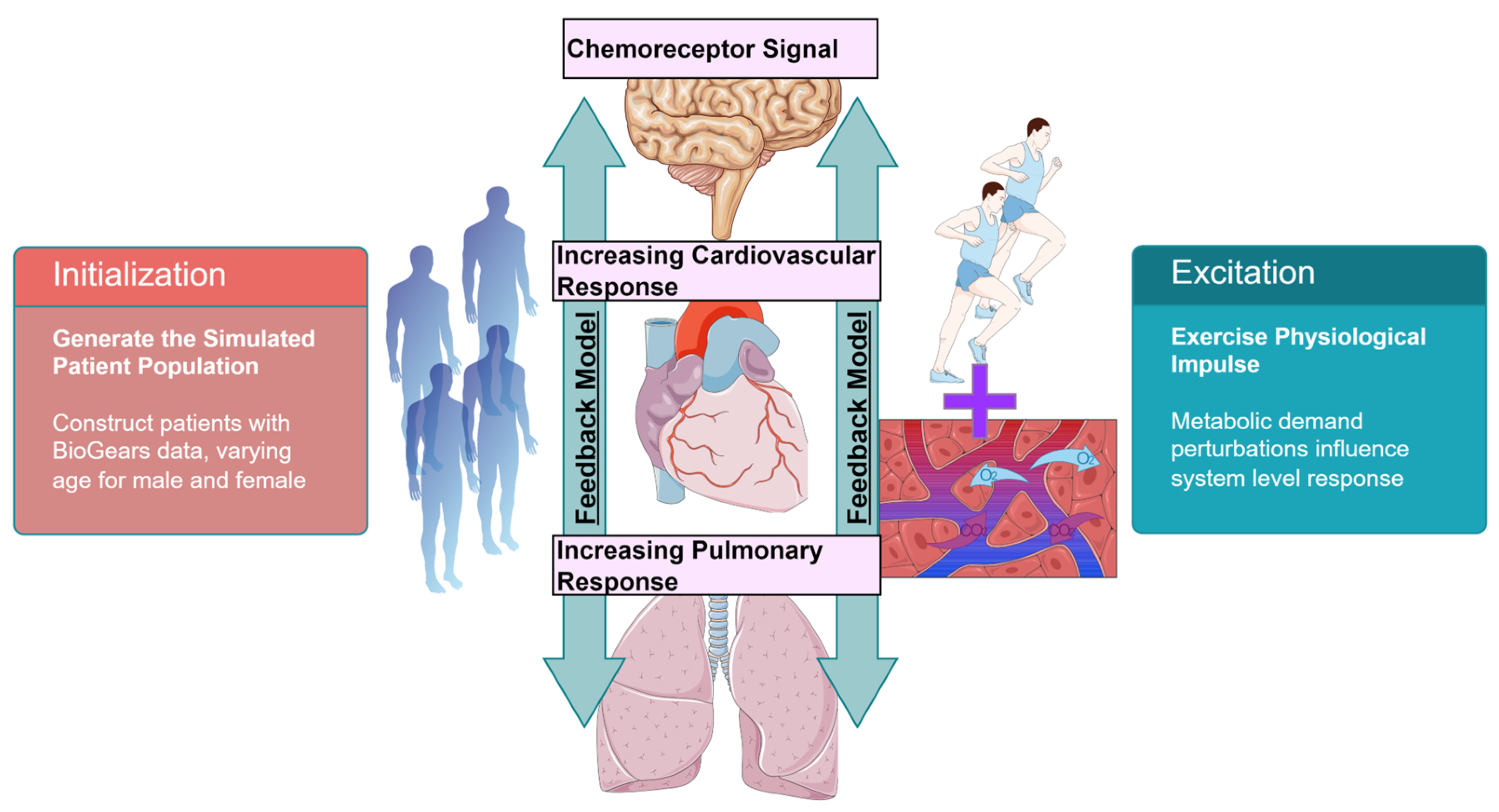
2. Materials and Methods
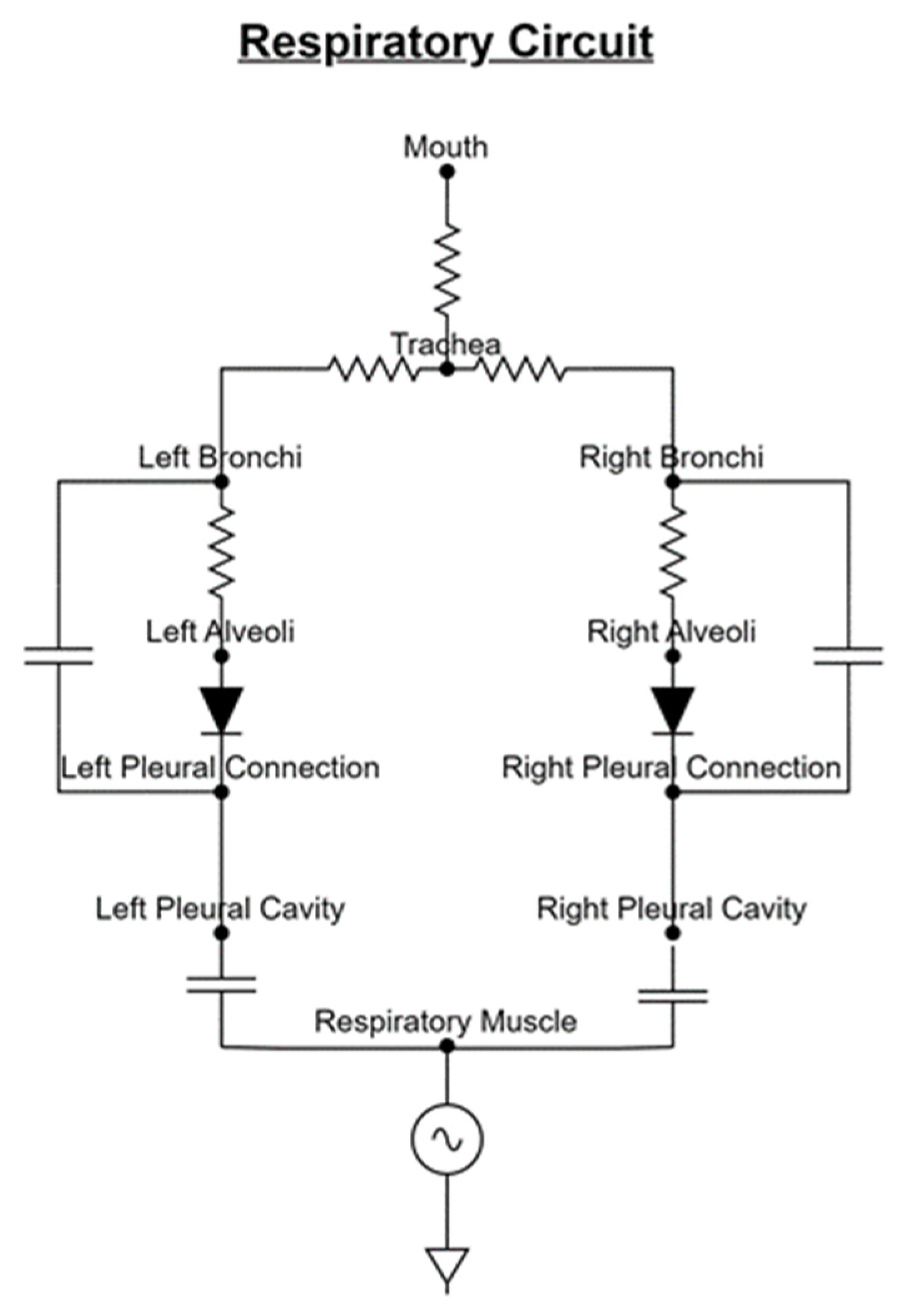
2.1. Respiratory Mechanics
2.2. Respiratory Control
2.3. Patient Variability
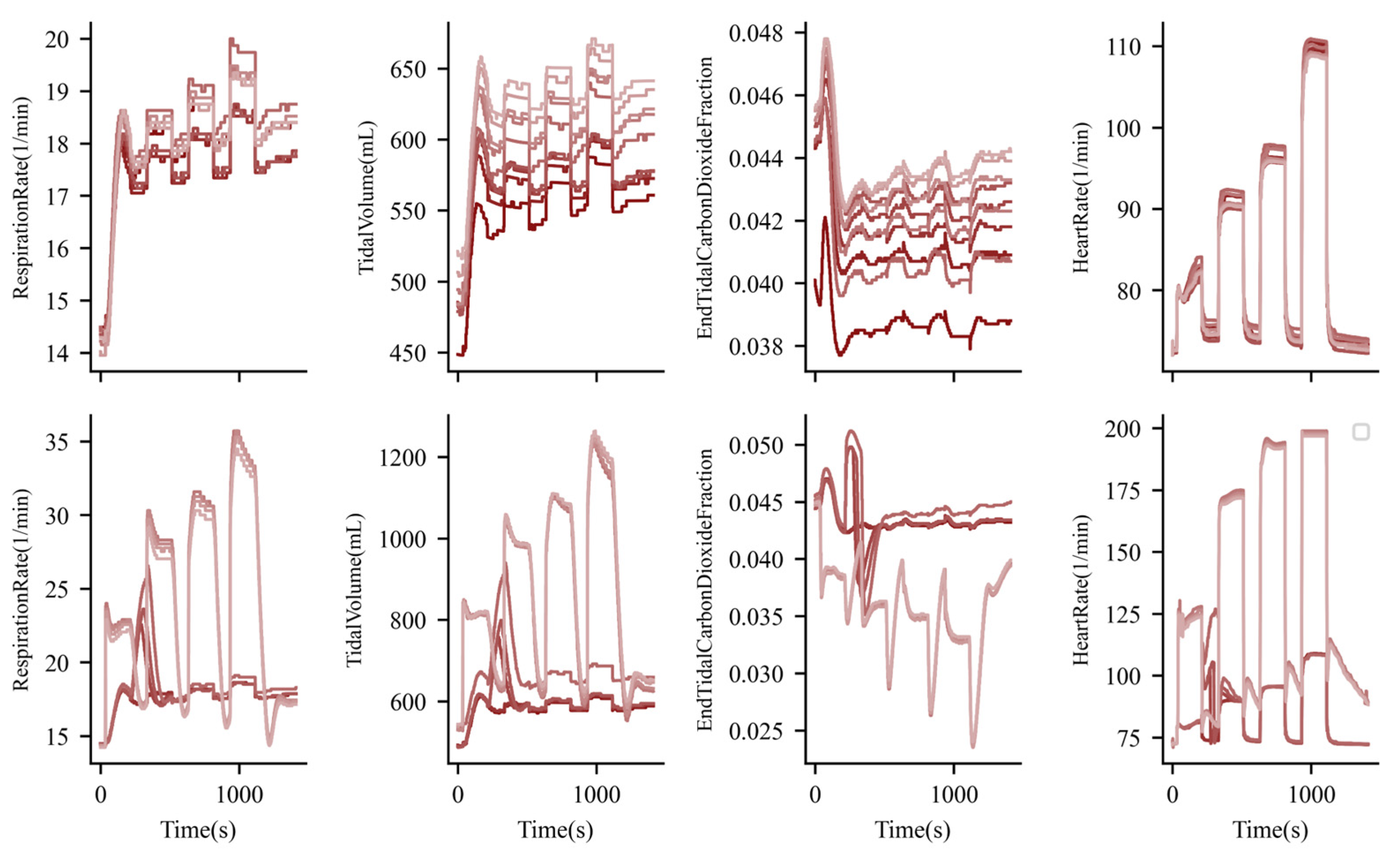
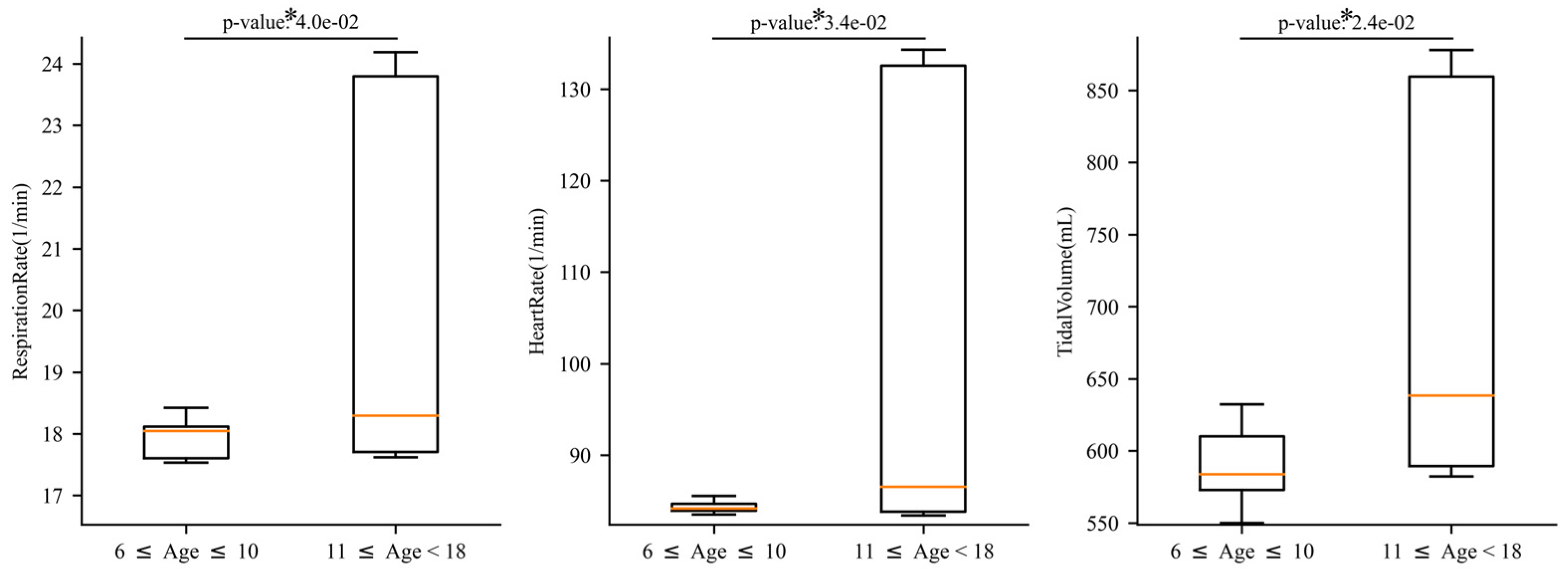
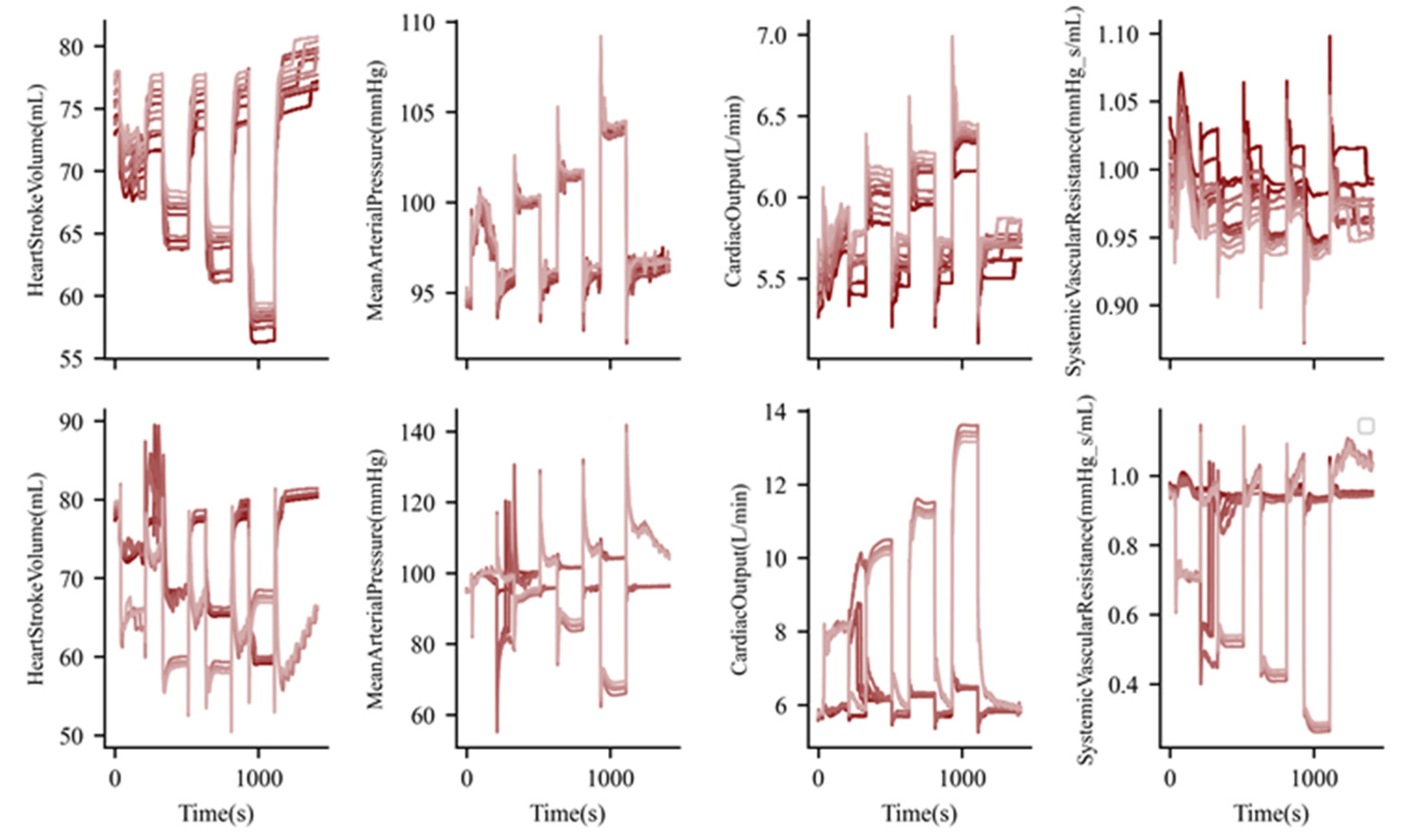
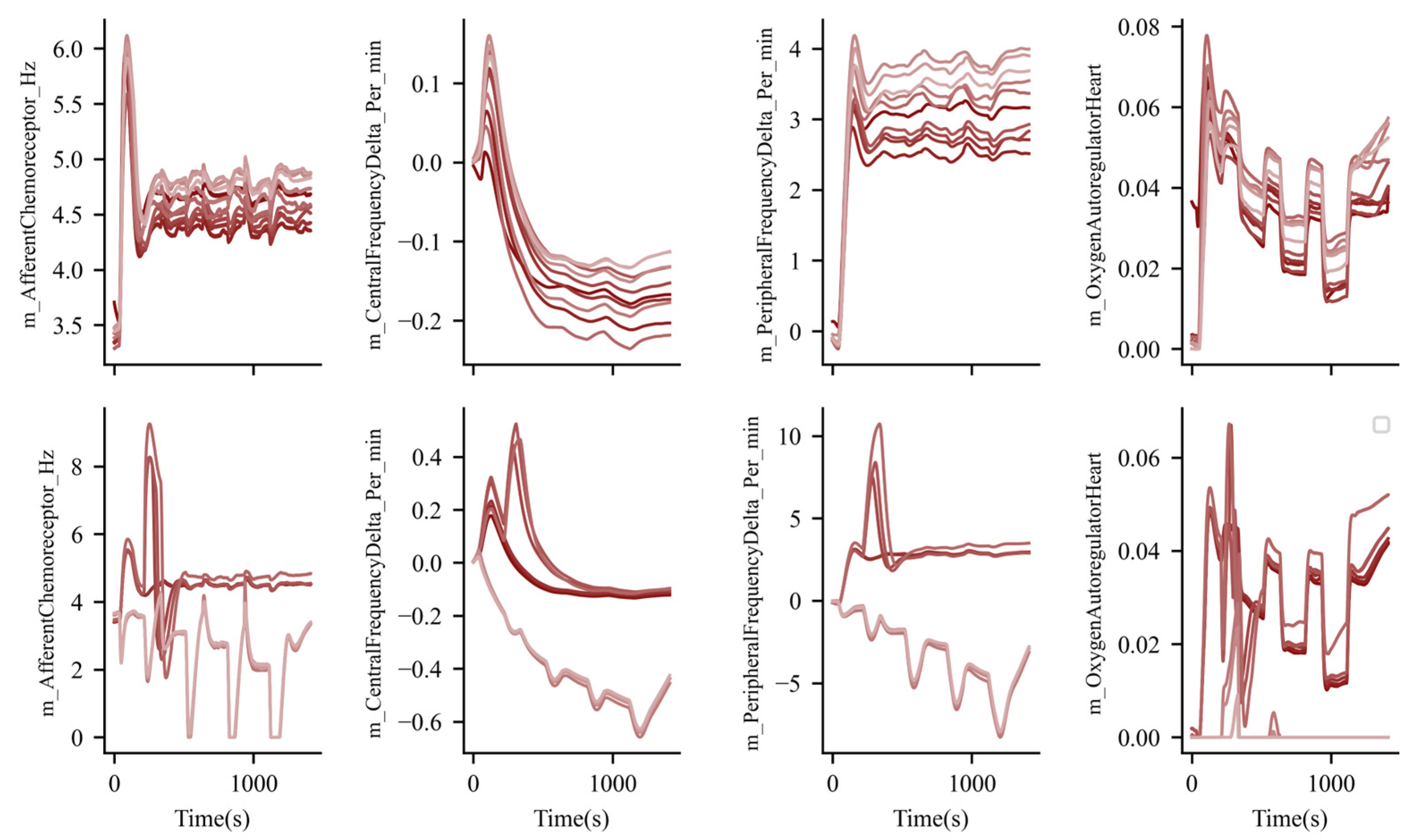
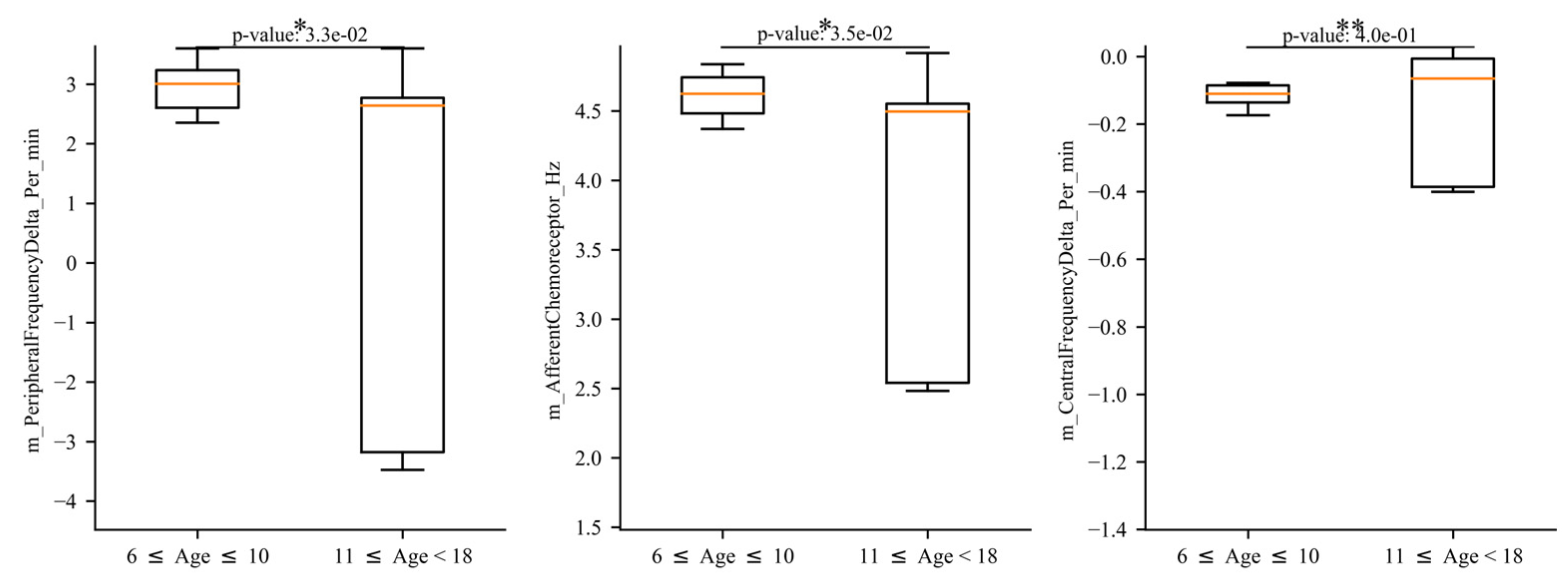
3. Results
3.1. Exercise and Cardiopulmonary Function
3.2. Exercise and Nervous System Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Visaria, R. Lumped Parameter Modeling of Human Respiratory System. In Theory and Applications of Heat Transfer in Humans; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, Nj, USA, 2018; pp. 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, Y.; Smith, N.T. Interactions among ventilation, the circulation, and the uptake and distribution of halothane—Use of a hybrid computer multiple model: I. The basic model. Anesthesiology 1981, 54, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, S.; Xin, Y.; Gaver, D.P.; Cereda, M.; Rizi, R.; Smith, B.J.; Avazmohammadi, R. Computational lung modelling in respiratory medicine. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawhai, M.H.; Hunter, P.J. Characterising respiratory airway gas mixing using a lumped parameter model of the pulmonary acinus. Respir. Physiol. 2001, 127, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Cheng, L.; Ursino, M.; Chbat, N.W. An integrated mathematical model of the human cardiopulmonary system: Model development. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H899–H921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaminos-Barroso, A.; Reina-Tosina, J.; Roa-Romero, L.M.; Ortega-Ruiz, F.; Márquez-Martín, E. Computational modeling of the control mechanisms involved in the respiratory system. In Control Applications for Biomedical Engineering Systems; Azar, A.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 325–357. [Google Scholar]
- Magosso, E.; Ursino, M. A mathematical model of CO2 effect on cardiovascular regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 281, H2036–H2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, N.; Hristovski, R.; Almarcha, M.; Garcia-Retortillo, S.; Ivanov, P.C. Network Physiology of Exercise: Vision and Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 611550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Retortillo, S.; Abenza, Ó.; Vasileva, F.; Balagué, N.; Hristovski, R.; Wells, A.; Fanning, J.; Kattula, J.; Ivanov, P.C. Age-related breakdown in networks of inter-muscular coordination. GeroScience 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, P.C.; Liu, K.K.L.; Bartsch, R.P. Focus on the emerging new fields of network physiology and network medicine. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, R.P.; Liu, K.K.L.; Bashan, A.; Ivanov, P.C. Network Physiology: How Organ Systems Dynamically Interact. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, A.; Bartsch, R.P.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Havlin, S.; Ivanov, P.C. Network physiology reveals relations between network topology and physiological function. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åstrand, P.-O.; Cuddy, T.E.; Saltin, B.; Stenberg, J. Cardiac output during submaximal and maximal work. J. Appl. Physiol. 1964, 19, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noakes, T.D. Fatigue is a Brain-Derived Emotion that Regulates the Exercise Behavior to Ensure the Protection of Whole Body Homeostasis. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, E.R.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Kalman, D.; Kreider, R.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; Taylor, L.; Willoughby, D.; Stout, J.; Graves, B.S.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.M.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, S.; Rona, R.J. Height and age adjustment for cross sectional studies of lung function in children aged 6–11 years. Thorax 1992, 47, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kassim, Z.; Greenough, A.; Rafferty, G.F. Effect of caffeine on respiratory muscle strength and lung function in prematurely born, ventilated infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, C.A.; Hernández, A.M.; Serna, L.Y.; Mañanas, M.Á. An integrated mathematical model of the cardiovascular and respiratory response to exercise: Model-building and comparison with reported models. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H1235–H1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, M.; Keller, J.M.; White, S.; Baird, A. A Whole-Body Mathematical Model of Sepsis Progression and Treatment Designed in the BioGears Physiology Engine. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, E.D.; Deutsch, T. A physiological model of glucose-insulin interaction in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 14, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, M.; Carter, J.; Keller, J.M.; White, S.A.; Baird, A. Open Source Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Framework: Tutorial on the BioGears Engine. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2019, 8, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, W.A.; Wiechert, L.; Comerford, A.; Rausch, S. Towards a comprehensive computational model for the respiratory system. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2010, 26, 807–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molkov, Y.I.; Rubin, J.E.; Rybak, I.A.; Smith, J.C. Computational models of the neural control of breathing. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2017, 9, e1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, L.Y.; Mañanas, M.A.; Hernández, A.M.; Rabinovich, R.A. An Improved Dynamic Model for the Respiratory Response to Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Thomson, D.; Seto, I.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Curtis, S.; Constantin, E.; Batmanabane, G.; Hartling, L.; Klassen, T.; et al. Standard 6: Age Groups for Pediatric Trials. Pediatrics 2012, 129, S153–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitzky, M.G. Pulmonary Physiology; LANGE Physiology Series; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.-W.; Ruehli, A.; Brennan, P. The modified nodal approach to network analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1975, 22, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.E., Jr.; Mikail, M.S. Clinical Anesthesiology, 2nd ed.; Appleton & Lange: Norwalk, CT, USA, 1996; p. 881. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, A.; McDaniel, M.; White, S.A.; Tatum, N.; Marin, L. BioGears: A C++ library for whole body physiology simulations. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, S.A.; Smith, D.L. Exercise Physiology for Health Fitness and Performance; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, M.; Gube, M.; Chaabene, H.; Prieske, O.; Zenon, A.; Broscheid, K.-C.; Schega, L.; Husmann, F.; Weippert, M. Fatigue and Human Performance: An Updated Framework|Sports Medicine. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40279-022-01748-2 (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Furrer, R.; Hawley, J.A.; Handschin, C. The molecular athlete: Exercise physiology from mechanisms to medals. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 1693–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, S.; Stocks, J.; Stanojevic, S.; Wade, A.; Robinson, P.; Gustafsson, P.; Brown, M.; Aurora, P.; Subbarao, P.; Hoo, A.; et al. Age and height dependence of lung clearance index and functional residual capacity. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.M. Best practice in statistics: Use the Welch t-test when testing the difference between two groups. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 58, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.; Schell, L. Human Growth and Development; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, M.D. Physical changes of puberty. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. 1991, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, A.; White, S.A.; Das, R.; Tatum, N.; Bisgaard, E.K. Whole body physiology model to simulate respiratory depression of fentanyl and associated naloxone reversal. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, T.; Hehre, D.; Feller, R.; Reifenberg, L.; Bancalari, E. Pulmonary mechanics in normal infants and young children during first 5 years of life. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1987, 3, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigen, H.; Bieler, H.; Grant, D.; Christoph, K.; Terrill, D.; Heilman, D.K.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Tepper, R.S. Spirometric Pulmonary Function in Healthy Preschool Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Filippo, P.; Giannini, C.; Attanasi, M.; Dodi, G.; Scaparrotta, A.; Petrosino, M.I.; Di Pillo, S.; Chiarelli, F. Pulmonary Outcomes in Children Born Extremely and Very Preterm at 11 Years of Age. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 635503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.; Serio-Melvin, M.; Hackett, M.; Clover, M.; McDaniel, M.; Rowland, M.; Williams, A.; Wilson, B. BurnCare tablet trainer to enhance burn injury care and treatment. BMC Emerg. Med. 2020, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, D.; Aggarwal, R.; Rush, R.M.; Lee, G.; Blair, P.G.; Hananel, D.; Park, Y.S.; Sweet, R.M.; Wisbach, G.G.; Sachdeva, A.K. Advanced Modular Manikin and Surgical Team Experience During a Trauma Simulation: Results of a Single-Blinded Randomized Trial. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2021, 233, 249–260e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, E.M.; Caglar, D.; Ackley, S.H.; Umoren, R. Virtual Reality Simulation in Pediatric Resuscitation for Pre-hospital Providers. Cureus 2024, 16, e56090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.; Baird, A.; Sawyer, T.; James, J.; DeBroux, T.; Bartlett, M.; Krick, J.; Umoren, R. Increasing Realism and Variety of Virtual Patient Dialogues for Prenatal Counseling Education Through a Novel Application of ChatGPT: Exploratory Observational Study. JMIR Med. Educ. 2024, 10, e50705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, R.A.; Schmölzer, G.M. Virtual simulations for neonatal education. Semin. Perinatol. 2023, 47, 151826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, R.A.; Gray, M.M.; Chitkara, R.; Josephsen, J.; Lee, H.C.; Strand, M.L.; Sawyer, T.L.; Ramachandran, S.; Weiner, G.; Zaichkin, J.G.; et al. Impact of virtual simulation vs. Video refresher training on NRP simulation performance: A randomized controlled trial. J. Perinatol. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, R.; Bucher, S.; Hippe, D.S.; Ezenwa, B.N.; Fajolu, I.B.; Okwako, F.M.; Feltner, J.; Nafula, M.; Musale, A.; Olawuyi, O.A.; et al. eHBB: A randomised controlled trial of virtual reality or video for neonatal resuscitation refresher training in healthcare workers in resource-scarce settings. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezenwa, B.N.; Umoren, R.; Fajolu, I.B.; Hippe, D.S.; Bucher, S.; Purkayastha, S.; Okwako, F.; Esamai, F.; Feltner, J.B.; Olawuyi, O.; et al. Using Mobile Virtual Reality Simulation to Prepare for In-Person Helping Babies Breathe Training: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial (the eHBB/mHBS Trial). JMIR Med. Educ. 2022, 8, e37297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baird, A.; Umoren, R.A.; White, S.A.; Gray, M.; Sawyer, T.L. A Whole-Body Physiology Model to Investigate Respiratory Function During Exercise Across Different Age Cohorts. J. Respir. 2025, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5010001
Baird A, Umoren RA, White SA, Gray M, Sawyer TL. A Whole-Body Physiology Model to Investigate Respiratory Function During Exercise Across Different Age Cohorts. Journal of Respiration. 2025; 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaird, Austin, Rachel A. Umoren, Steven A. White, Megan Gray, and Taylor L. Sawyer. 2025. "A Whole-Body Physiology Model to Investigate Respiratory Function During Exercise Across Different Age Cohorts" Journal of Respiration 5, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5010001
APA StyleBaird, A., Umoren, R. A., White, S. A., Gray, M., & Sawyer, T. L. (2025). A Whole-Body Physiology Model to Investigate Respiratory Function During Exercise Across Different Age Cohorts. Journal of Respiration, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor5010001





