- 2.8Impact Factor
- 5.5CiteScore
- 15 daysTime to First Decision
Advances in Genomics and Epigenetics of Hearing Loss
This special issue belongs to the section “Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
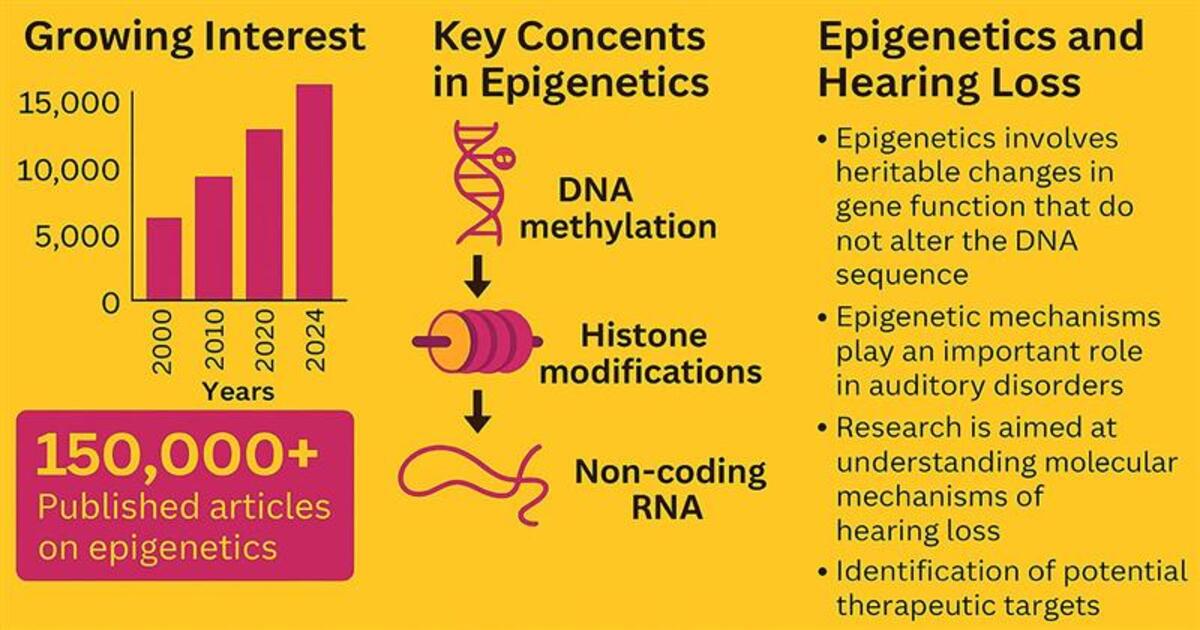
In recent years, the treatment and understanding of hearing loss have evolved significantly, largely due to advances in genetics and epigenetics. Many types of hearing loss that were once considered "idiopathic" now have clear genetic explanations. At the same time, it has become increasingly clear that epigenetic mechanisms—such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and the regulation of gene expression by non-coding RNAs—play an important role in the development and progression of auditory dysfunction.
This Special Issue aims to highlight current research exploring the genetic and epigenetic foundations of hearing loss. Our goal is to gather studies that improve our understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind hearing impairment and to foster discussion on future directions in diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment.
We welcome a wide range of submissions, including both basic and clinical research. Studies involving human subjects, animal models, or in vitro systems are all suitable. We also encourage the submission of review articles, case series, and opinion pieces.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Newly identified gene mutations causing syndromic or non-syndromic hearing loss;
- Regulation of gene expression in the inner ear;
- Age-related epigenetic changes in the auditory system;
- The role of microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in hair cell function, degeneration, and regeneration;
- Genetic studies of inherited hearing loss using family-based or population-based data;
- Applications of cochlear organoids, iPSC models, or CRISPR-based technologies;
- Gene therapy and other experimental approaches targeting specific genetic defects;
- Epigenetic markers as potential tools for diagnosis and prognosis;
- Multi-omics approaches combining genomics, transcriptomics, methylomics, and more;
- Interdisciplinary research connecting genetics, audiology, and neuroscience.
Although this field is advancing rapidly, many important questions remain. What are the most effective strategies to correct or compensate for defective genes? Are epigenetic changes in the cochlea reversible? Can we predict which patients will respond to gene- or RNA-based therapies—and to what extent?
We believe that progress in this area requires collaboration across disciplines, involving geneticists, audiologists, molecular biologists, and clinicians. With this Special Issue, we hope to provide a platform for sharing new insights and for accelerating advances in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hearing loss.
We warmly invite you to contribute.
Dr. Alessandro Castiglione
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Genes is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- genetics
- hearing loss
- inner ear
- epigenetics
- auditory system
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.

