- Article
The Mixed Halogen-Ion Effect in Lead Silicate Glasses: A Correlative Study of Ionic Transport and Optical Spectroscopy in the 45PbO–xPbF2–(20−x)PbCl2–35SiO2 System
- Manar Alenezi,
- Amrit Prasad Kafle and
- Biprodas Dutta
- + 3 authors
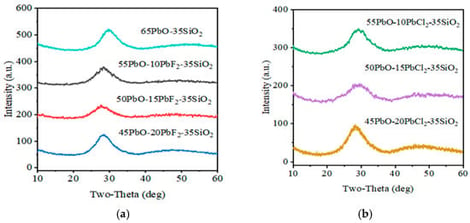
We present a fresh perspective on the mixed halogen-ion effect (MHE) in lead silicate glasses containing a mixture of halogen ions with a correlative study of optical spectroscopy and halogen ion transport. PbO was partially substituted by either PbCl2 or PbF2 in the ternary glass system: (65 − x) − x(PbF2 or PbCl2)-35SiO2 (where 0 ≤ x ≤ 20 mol%) and by a mixture of PbF2 and PbCl2 in the quaternary glass series: 45PbO − xPbF2 − (20 − x)PbCl2–35SiO2 (where 0 ≤ x ≤ 20 mol%). A suite of improved characterization techniques, including 4-probe van der Pauw resistivity measurements, optical absorption spectroscopy, differential thermal analysis, etc., was employed to correlate composition with physical properties. Replacing PbO with small quantities of PbF2 or PbCl2 in binary 65PbO-35SiO2 glass resulted in a dramatic increase in conductivity by 3–4 orders of magnitude, confirming a shift from Pb2+-mediated to halide ion-mediated conduction and, within the mixed-halogen series, a profound MHE was observed. Contrary to previously reported data, the activation energy for conduction and the resistivity both exhibited maxima at the mixed halogen-ion ratio, MHR = (F/(F + Cl), of 0.5. The glass transition temperature (Tg) exhibited a non-monotonic trend, peaking at 506 °C for the MHR = 0.5 composition. Optical absorption measurements have revealed that the MHR = 0.5 glass has the broadest absorption edge and also exhibits certain features in the near IR region of the Urbach tail, which are suggestive of maximum electronic disorder.
5 February 2026