Integration of Silicon PIN Detectors and TENGs for Self-Powered Wireless AI Intelligent Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
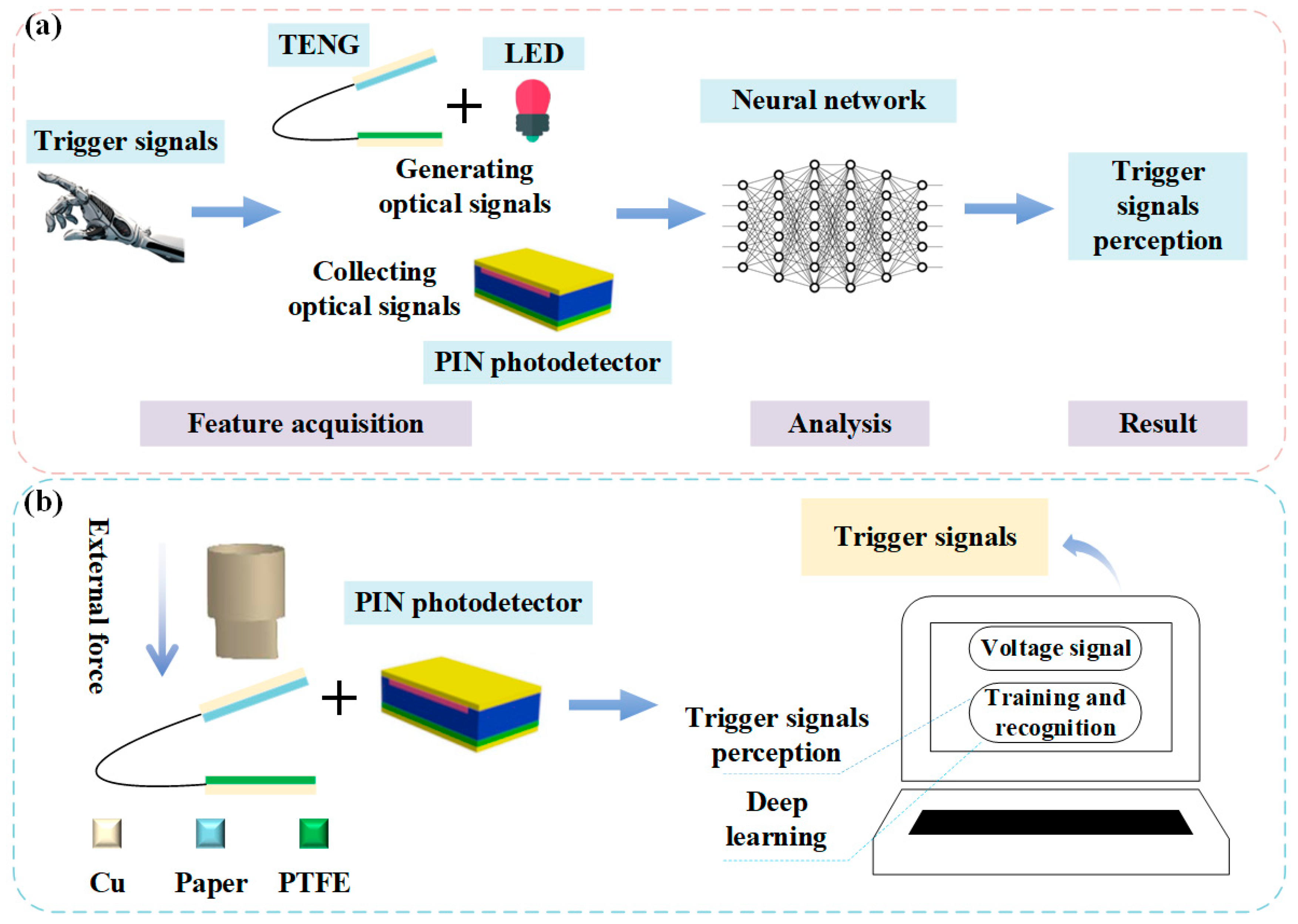
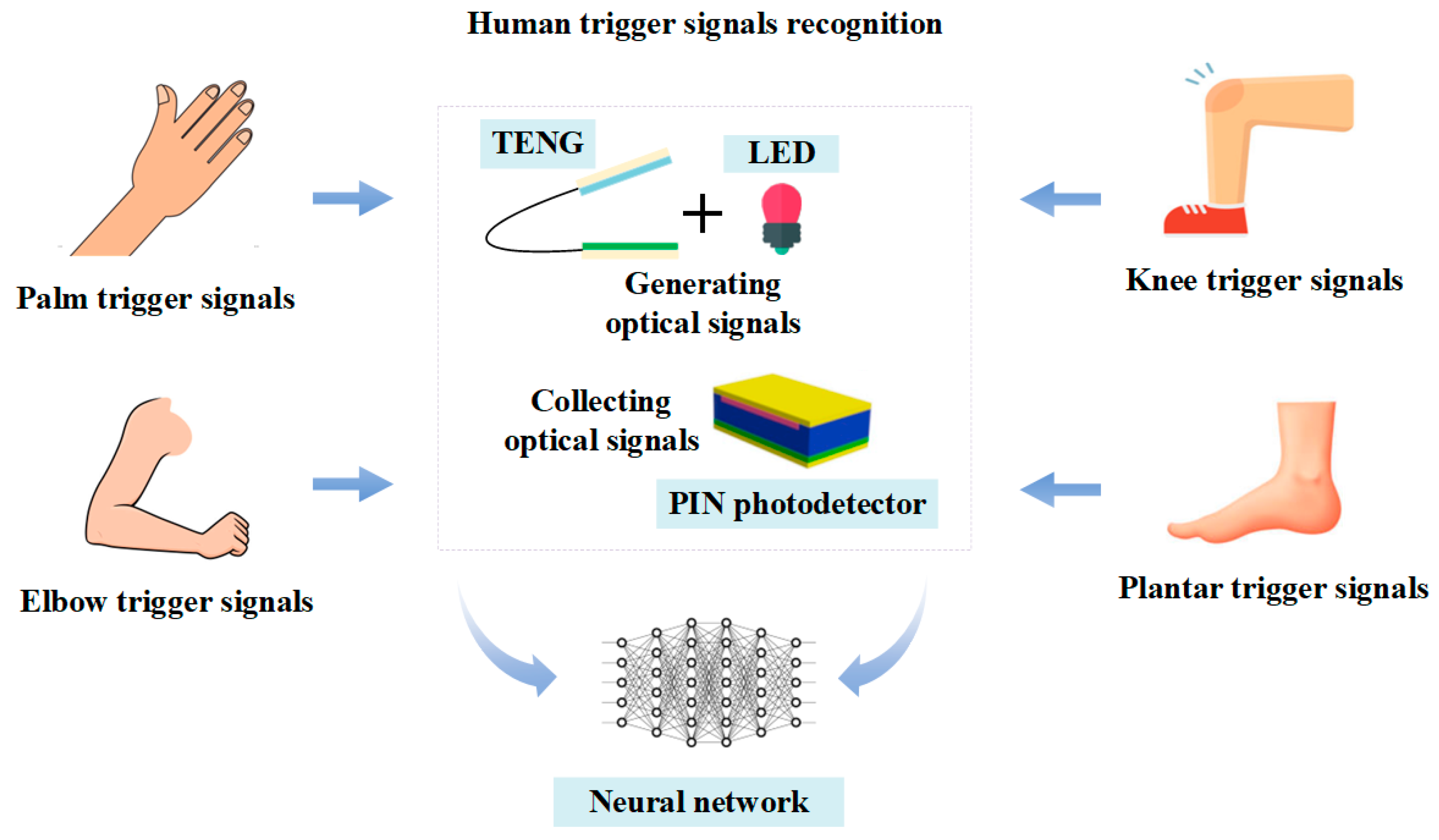
2. System Structure Design
3. Device Fabrication
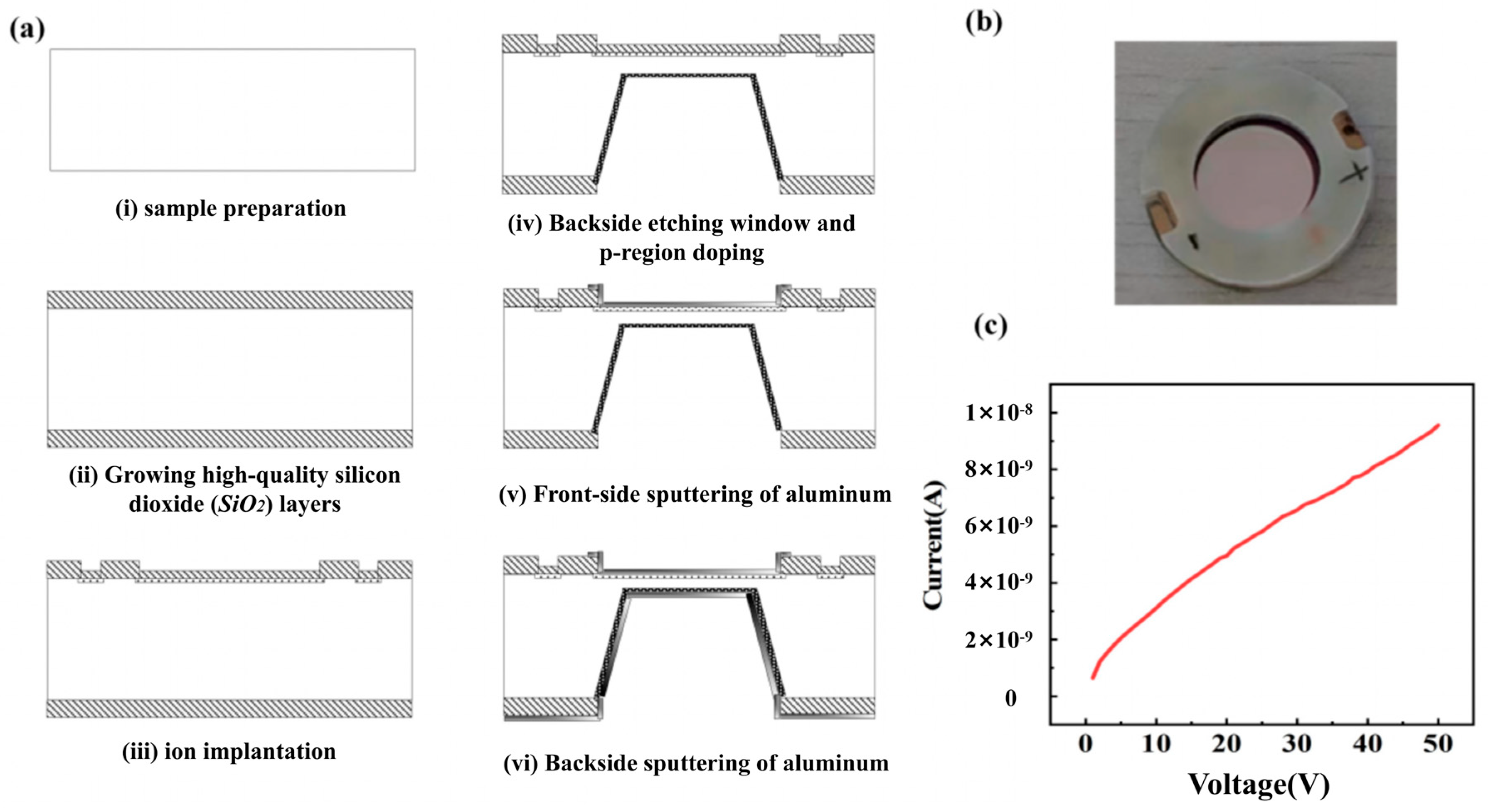
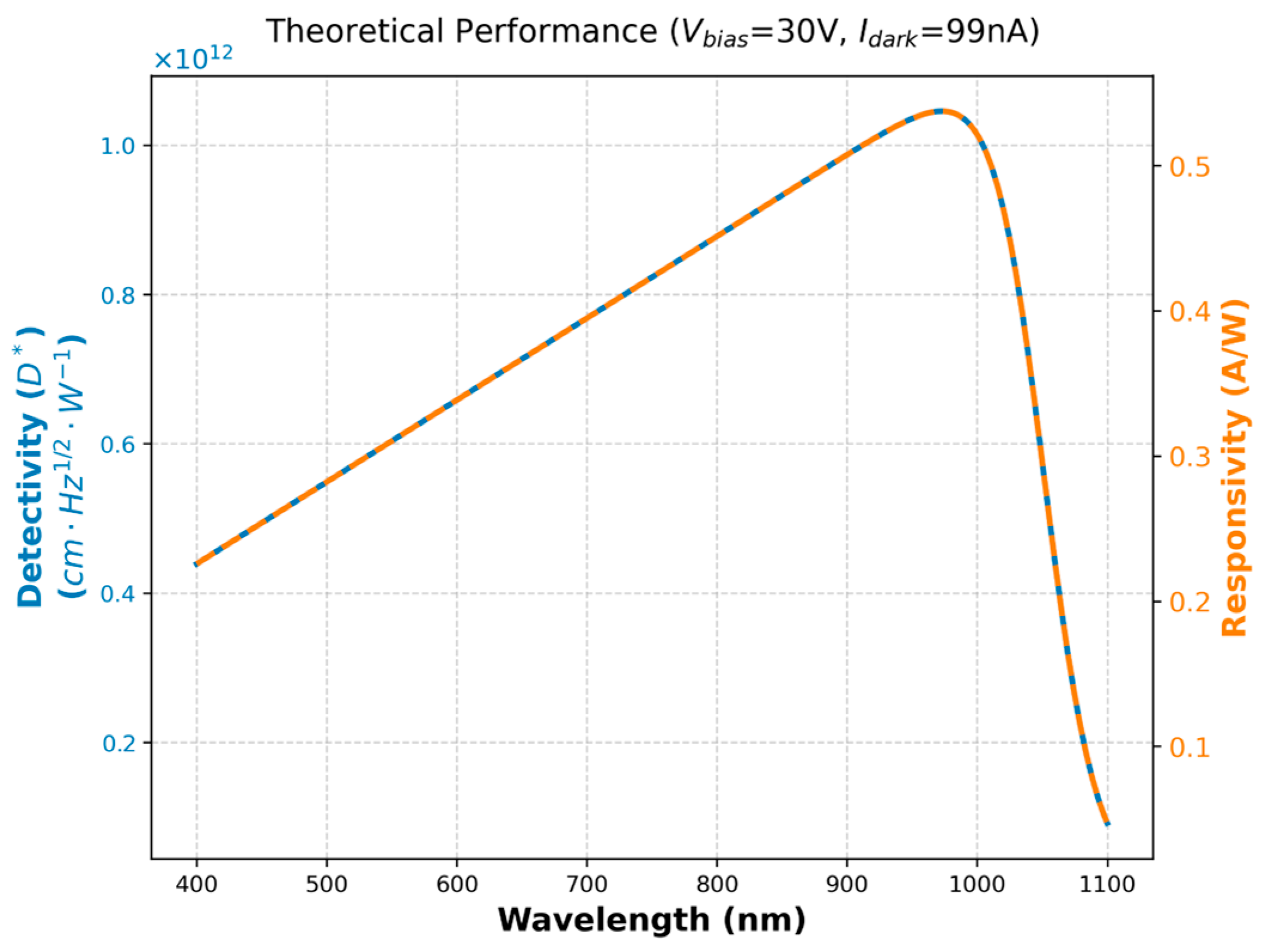
3.1. Fabrication of Silicon PIN Detector
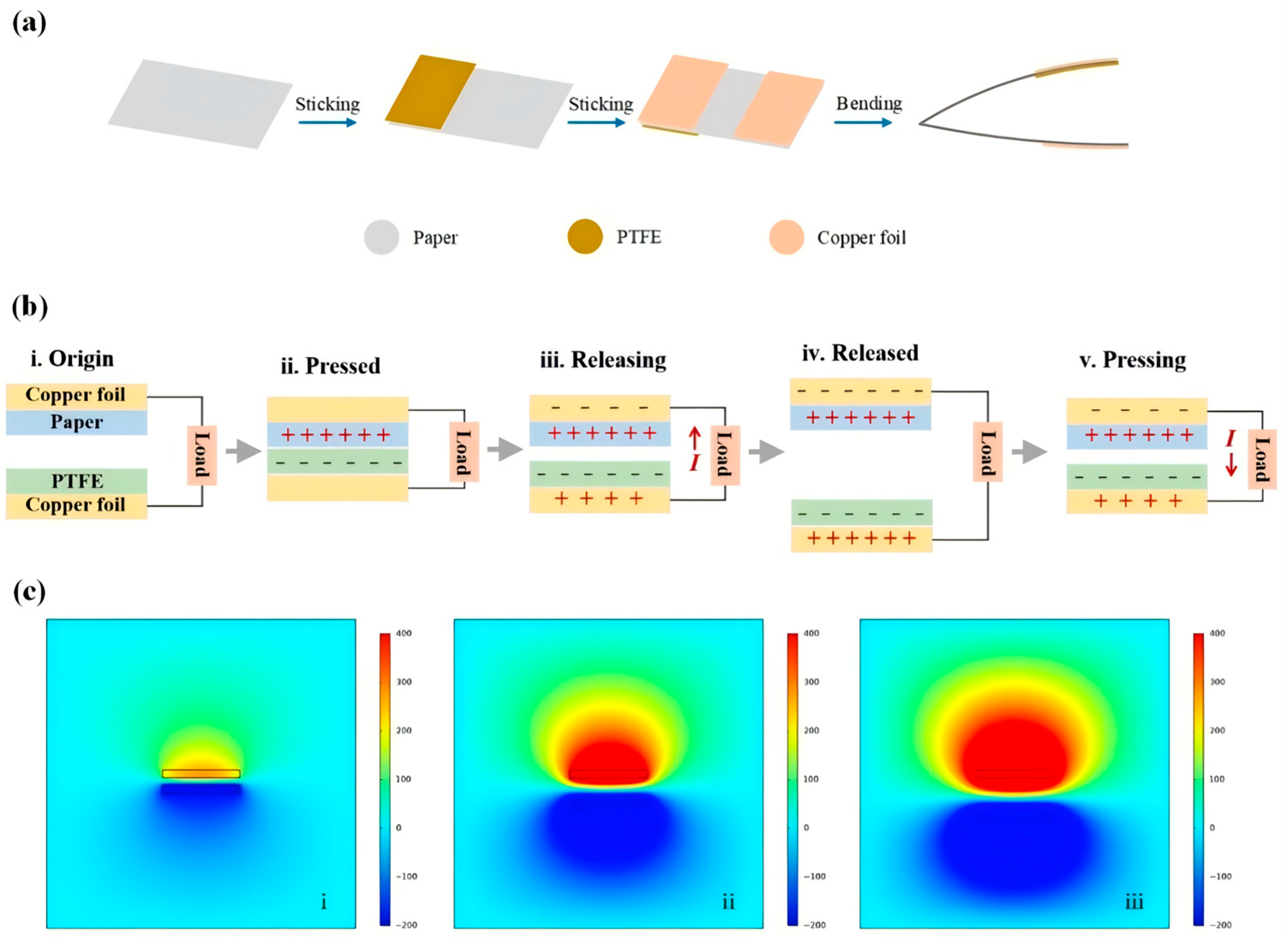
3.2. Preparation of TENG
3.3. TENG Output Performance
4. Triggered Signals Recognition Based on Self-Powered Sensing System and Neural Network
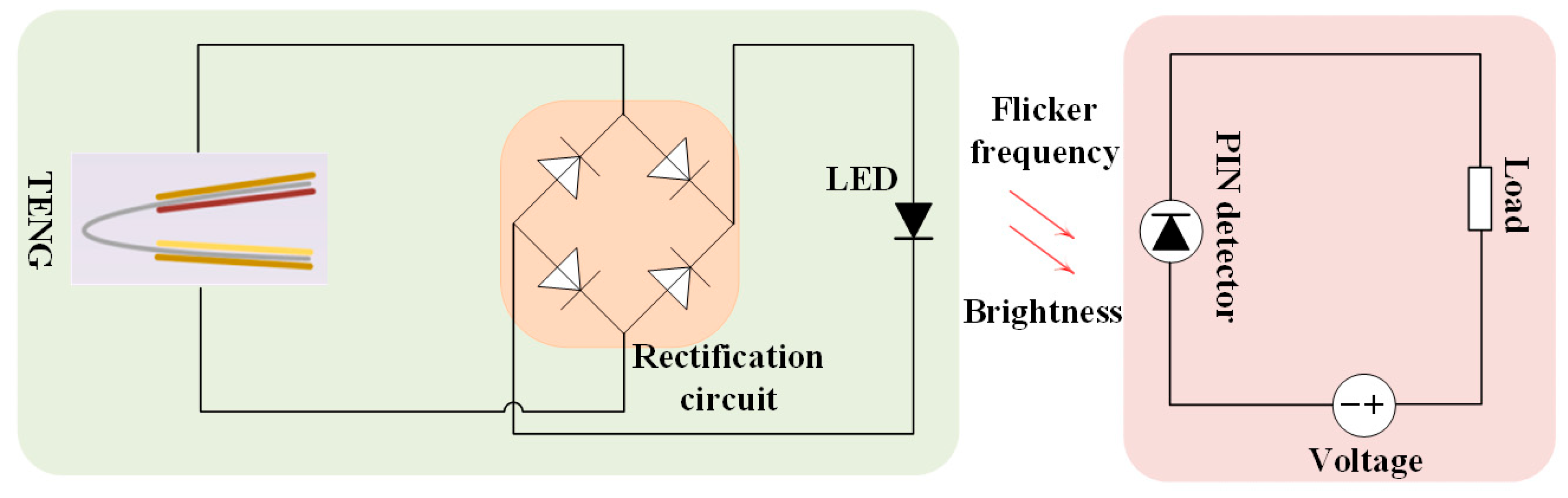
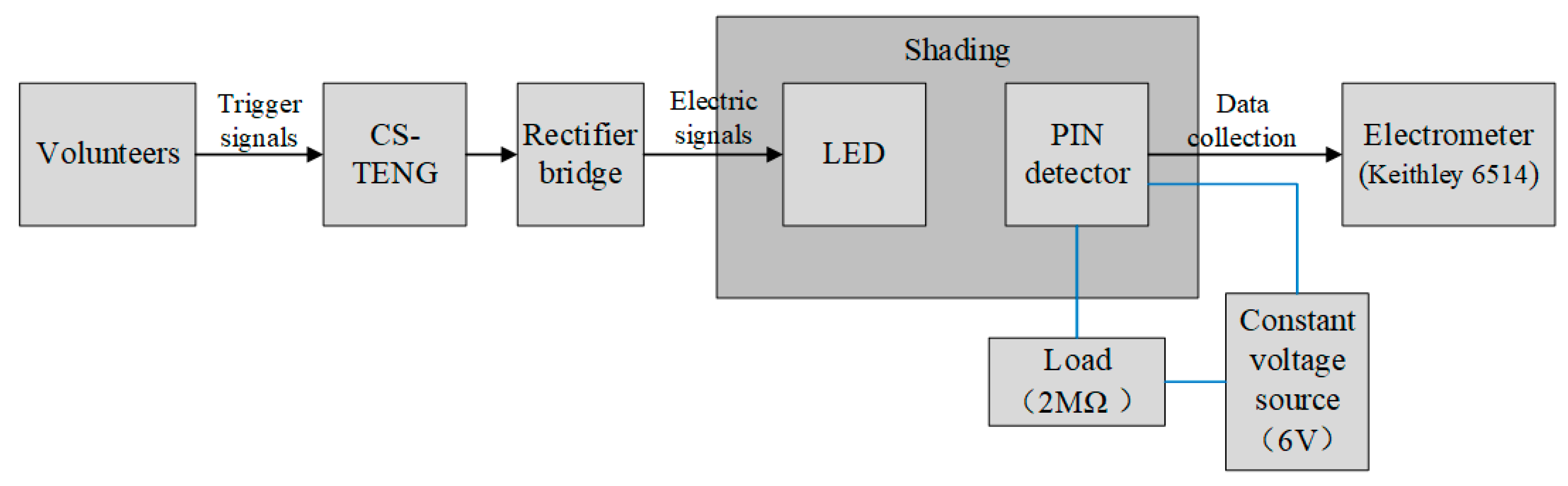
4.1. The Self-Powered Sensing System Based on TENG and Silicon PIN Detector
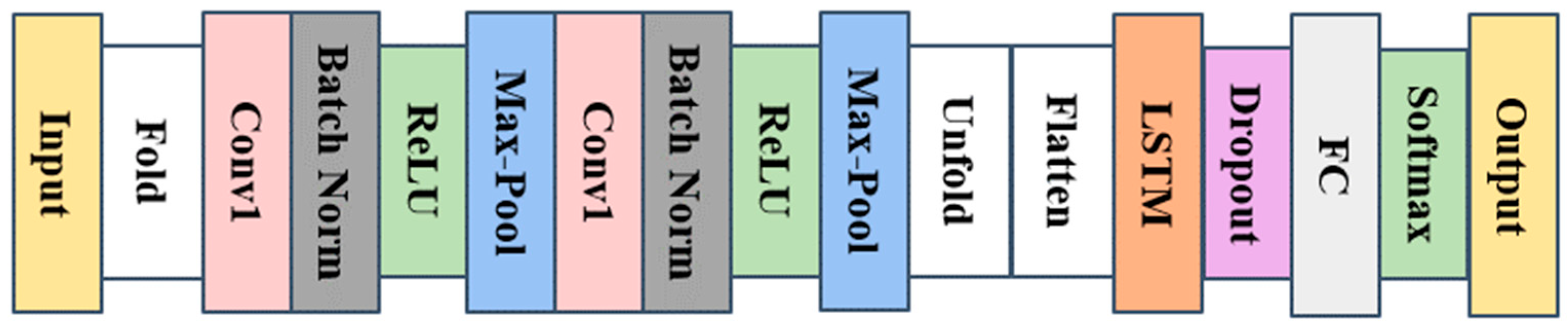
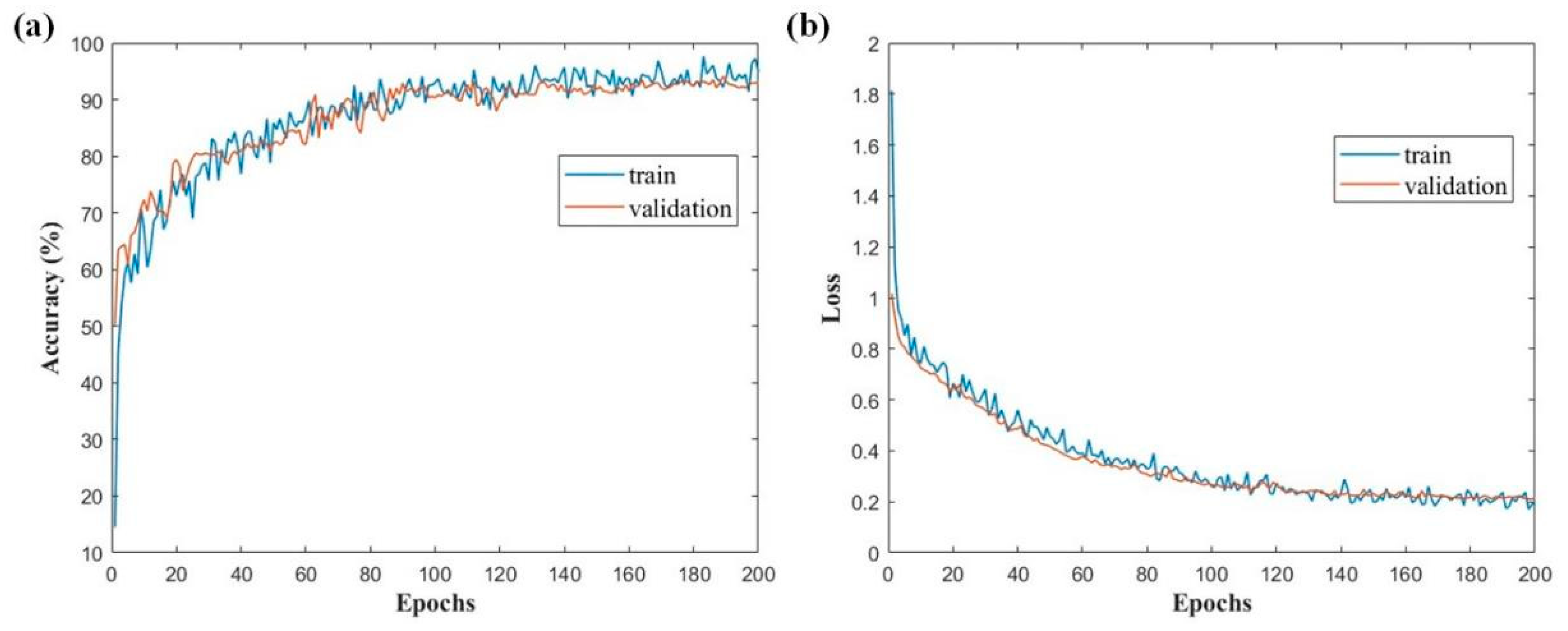
4.2. Neural Network Model
5. Experiment and Result Analysis
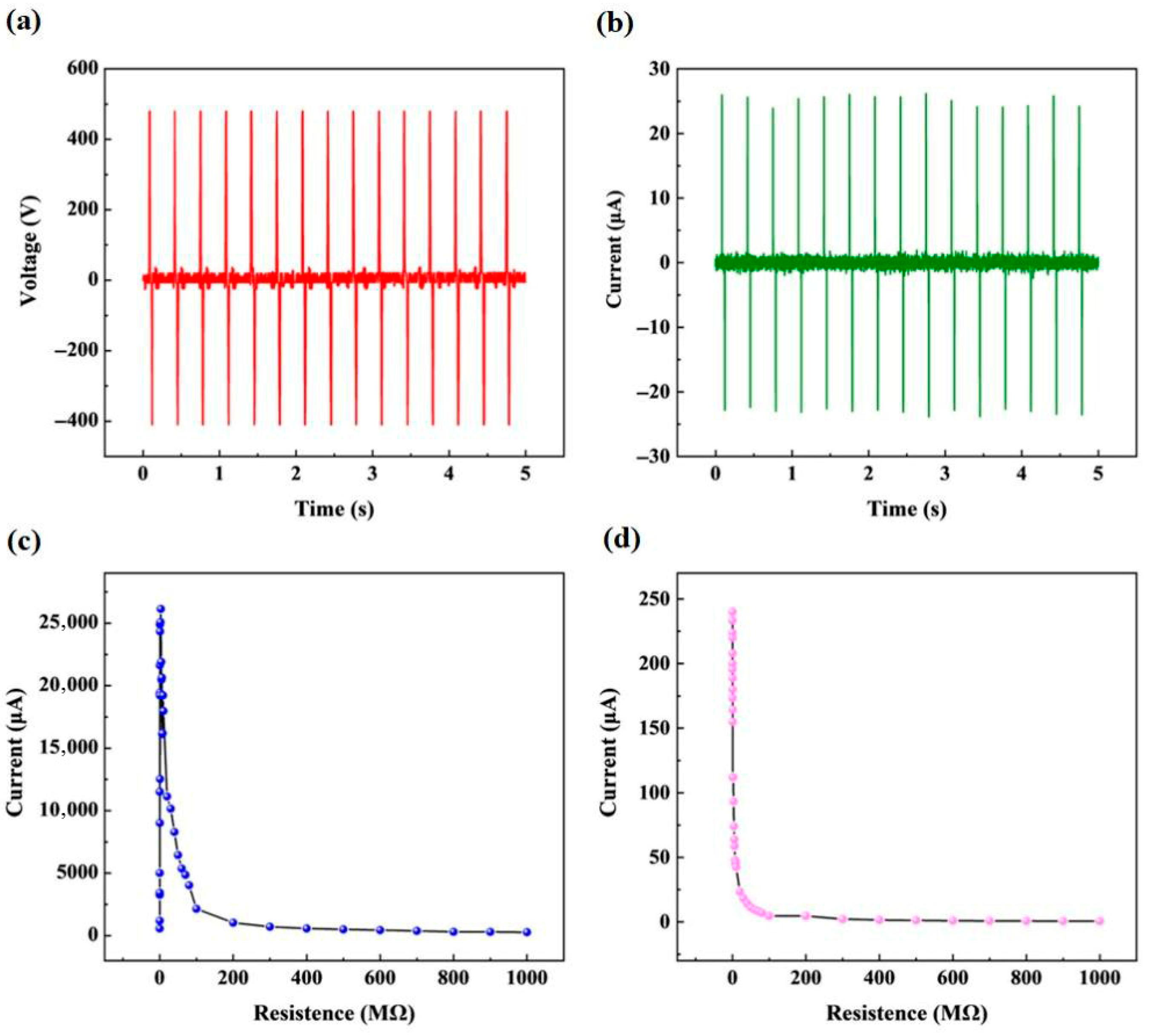
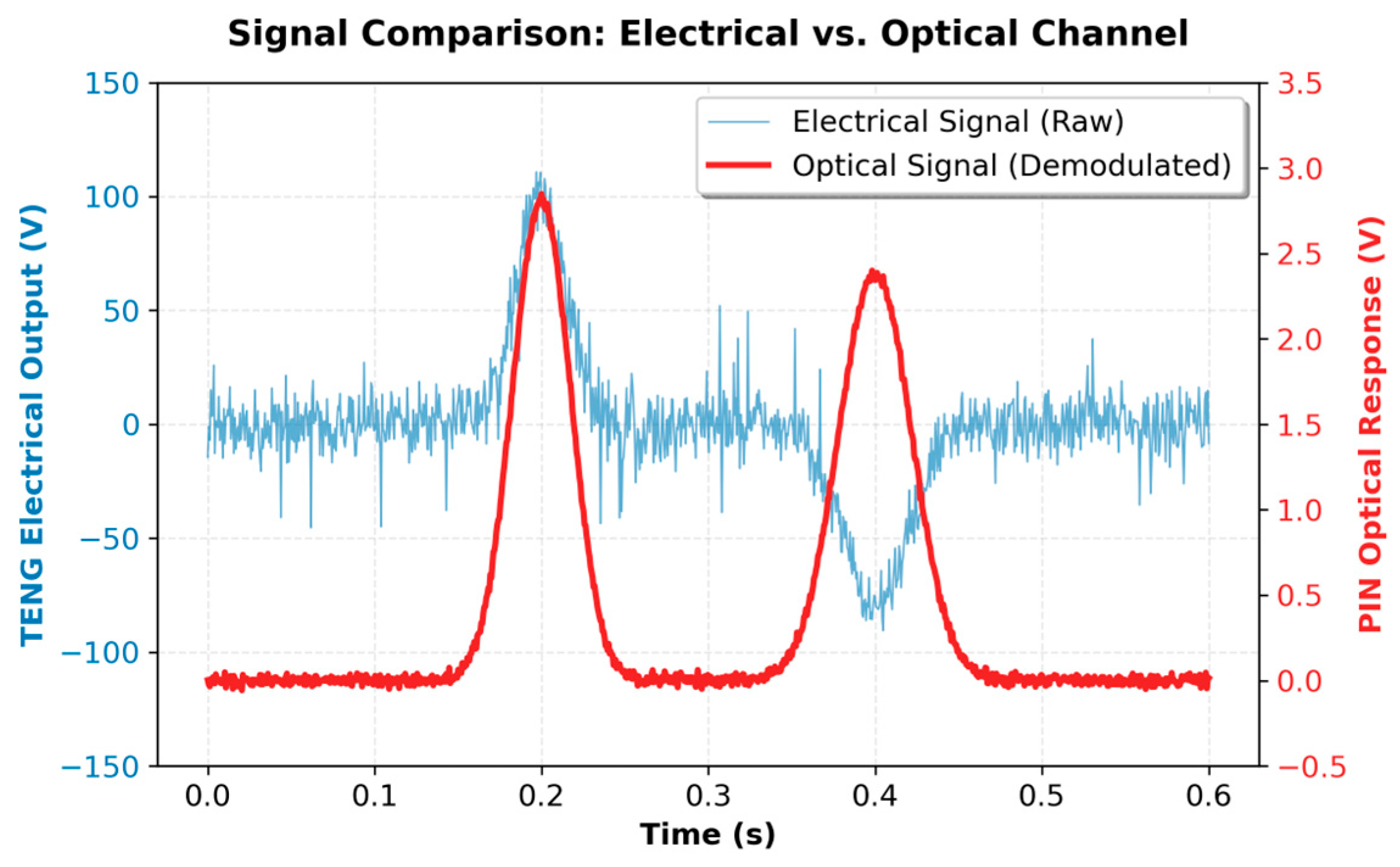
5.1. Experimental Data Collection and Mechanism Analysis
5.2. Data Processing
5.3. Analysis of Results
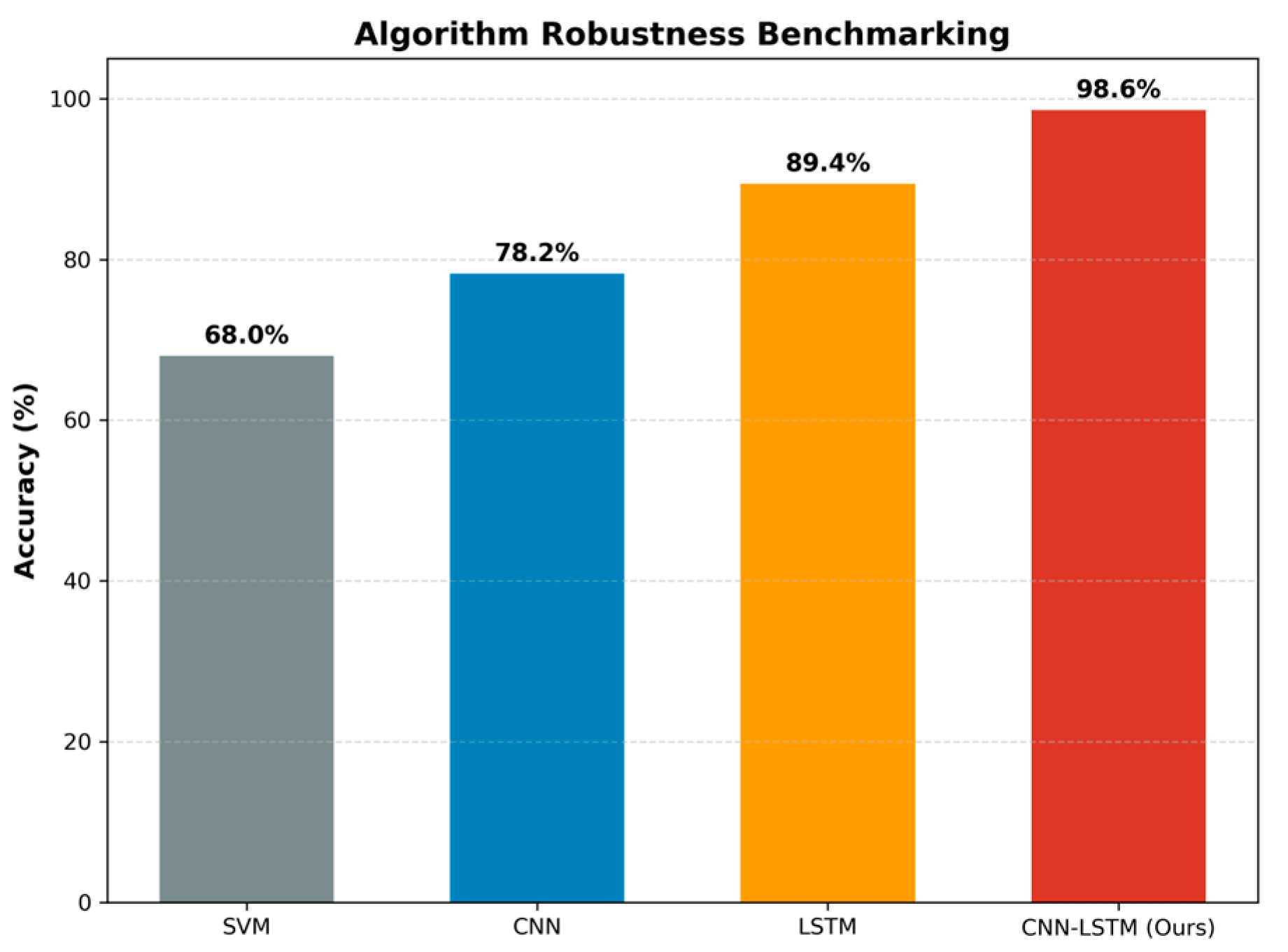
5.4. Performance Comparison and System Advantages
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z.; Pu, M.; Jiang, M.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Tang, J. Bonding Processing and 3D Integration of High-Performance Silicon PIN Detector for ΔE-E telescope. Processes 2023, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhao, K.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Process effects on leakage current of Si-PIN neutron detectors with porous microstructure. Phys. Status Solidi 2017, 214, 1600900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Li, Z.K.; Wang, F.C.; Han, R.; Zhu, H.B. Application of stratified implantation for silicon micro-strip detectors. Chin. Phys. C 2015, 39, 066005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, M.W.; Spector, S.J.; Grein, M.E.; Fu, J.; Lennon, D.M.; Yoon, J.U.; Liederman, T.M. CMOS-compatible all-Si high-speed waveguide photodiodes with high responsivity in near-infrared communication band. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2007, 19, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehme, M.; Werner, J.; Kasper, E.; Kibbel, H. High bandwidth Ge pin photodetector integrated on Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 071117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel, N.S.; Pallon, J.; Ros, L.; Elfman, M.; Nilsson, P.; Kröll, T. Characterizations of new ΔE detectors for single-ion hit facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2014, 318, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, R.; Alinia, P.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Fortino, G. Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 2017, 35, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y. Multi-sensor filtering fusion with parametric uncertainties and measurement censoring: Monotonicity and boundedness. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2021, 69, 5875–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Magnetoelectrics for magnetic sensor applications: Status, challenges and perspectives. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Davis, L.S. A general method for sensor planning in multi-sensor systems: Extension to random occlusion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 76, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Intelligent manufacturing production line data monitoring system for industrial internet of things. Comput. Commun. 2020, 151, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, M. An industrial Wireless Sensor Networks framework for production monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Istanbul, Turkey, 1–4 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1442–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, H.; Griffiths, T.; Brennan, D.; Lewis, R. The state-of-the-art of sensors and environmental monitoring technologies in buildings. Sensors 2019, 19, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mois, G.; Folea, S.; Sanislav, T. Analysis of three IoT-based wireless sensors for environmental monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Khan, K.; Zou, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Recent advances in emerging 2D material-based gas sensors: Potential in disease diagnosis. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1901329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, J.; Choi, S.W.; Tewari, M. Real-time, personalized medicine through wearable sensors and dynamic predictive modeling: A new paradigm for clinical medicine. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2020, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu-Perez, J.; Leff, D.R.; Ip, H.M.D.; Yang, G.Z. From wearable sensors to smart implants—Toward pervasive and personalized healthcare. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2750–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Mittal, S.; Lee, X.H.; Chuang, C.H.; Hu, Z. From personalized medicine to population health: A survey of mHealth sensing techniques. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15413–15434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yi, Z.; Yang, B.; Lee, C. Making use of nanoenergy from human–Nanogenerator and self-powered sensor enabled sustainable wireless IoT sensory systems. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Yao, G.; Yan, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, S.; Ding, W.; Zhu, G. Self-powered, wireless, remote meteorologic monitoring based on triboelectric nanogenerator operated by scavenging wind energy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32649–32654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Gan, B.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, A.; Yuan, H.; Chen, N.; Sun, C.; Wang, Z.L. Nanopillar arrayed triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered sensitive sensor for a sleep monitoring system. Acs Nano 2016, 10, 8097–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Hu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.L. Investigation of contact electrification between 2D MXenes and MoS2 through density functional theory and triboelectric probes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered electrodeposition system for Sub-10-Nm silver nanoparticles with high-efficiency antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 6721–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; He, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.L. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator based on theoretical analysis and ferroelectric nanocomposites and its high-voltage applications. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120074. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Cheng, G.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.L. A Hybridized Power Panel to Simultaneously Generate Electricity from Sunlight, Raindrops, and Wind around the Clock. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, J.; Han, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, F.; Tang, W.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; et al. Stimulation of ambient energy generated electric field on crop plant growth. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Ding, Y.; Nie, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Xiang, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z.L. Environmental Energy Harvesting Adapting to Different Weather Conditions and Self-Powered Vapor Sensor Based on Humidity-Responsive Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6143–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; He, M.; Jing, Q.; Fan, W.; Xie, L.; Zhu, K. Angle-shaped triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting environmental wind energy. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Leaves based triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) and TENG tree for wind energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, U.; Hwang, H.; Kim, S.W. Triboelectric Nanogenerators: High Permittivity CaCu3Ti4O12 Particle-Induced Internal Polarization Amplification for High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2070040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Cheng, G.; Lin, L.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. Water–solid surface contact electrification and its use for harvesting liquid-wave energy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12545–12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Su, Y.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting water wave energy by asymmetric screening of electrostatic charges on a nanostructured hydrophobic thin-film surface. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6031–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Jing, Q.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Pradel, K.C.; Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Networks of triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting water wave energy: A potential approach toward blue energy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Miao, L.; Wan, J.; Xu, C.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, H. Wearable and Self-Cleaning Hybrid Energy Harvesting System based on Micro/Nanostructured Haze Film. Nano Energy 2019, 67, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Han, K.; Cui, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, X. Energy conversion analysis of multilayered triboelectric nanogenerators for synergistic rain and solar energy harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Fang, Y.; Jing, Q.; Hu, N.; Lin, K.; Pan, Y.; Xu, L.; Gao, H.; Yuan, M. A portable triboelectric spirometer for wireless pulmonary function monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 187, 113329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Jing, T. An electrospun nanowire-based triboelectric nanogenerator and its application in a fully self-powered UV detector. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7842–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zheng, H.; Yang, F.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, M.; Yang, J.; Qin, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Managing and maximizing the output power of atriboelectric nanogenerator by controlled tip–electrode air-discharging and application for UV sensing. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Peng, M.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Lei, H.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L.; Sun, X.; et al. Self-driven photodetection based on impedance matching effect between a triboelectric nanogenerator and a MoS2 nanosheets photodetector. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xia, K.; Li, T.; Yin, C.; Yin, Z.; Xu, Z. Self-powered silicon PIN photoelectric detection system based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Multidimensional force sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerators for electronic skin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56320–56328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yin, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.L. A fully self-powered vibration monitoring system driven by dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerators. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Shu, S.; Yang, W. A self-powered vector angle/displacement sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Micromachines 2021, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zheng, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; Yao, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Flexible triboelectric nanogenerator for human motion tracking and gesture recognition. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106601–106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, B.; Zhao, E.; Pu, M.; Yu, B.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Niu, H. Self-powered silicon PIN neutron detector based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Layers | Types | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input | - |
| 2 | Sequence Folding Layer | - |
| 3 | Convolution Layer 1 | 64 2 × 1 convolutions with stride [1 × 1] |
| 4 | Batch Normalization 1 | - |
| 5 | ReLU | - |
| 6 | Max-pool 1 | 2 × 1 pooling kernel with stride [2 × 1] |
| 7 | Convolution Layer 2 | 32 2 × 1 convolutions with stride [1 × 1] |
| 8 | Batch Normalization 2 | - |
| 9 | ReLU | - |
| 10 | Max-pool 2 | 2 × 1 pooling kernel with stride [2 × 1] |
| 11 | Sequence Unfolding Layer | - |
| 12 | Flatten Layer | - |
| 13 | LSTM Layer 1 | LSTM with 32 hidden units |
| 14 | Dropout | 25% dropout |
| 15 | Fully Connected | - |
| 16 | Softmax | - |
| 17 | Classification | - |
| Models | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 88.01 | 88.69 | 88.12 | 87.94 |
| LSTM | 87.53 | 88.24 | 87.64 | 87.64 |
| CNN-LSTM | 92.92 | 93.35 | 93.11 | 92.94 |
| Models | Types | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | M | 97.96 | 96.39 | 97.17 |
| E | 69.71 | 84 | 76.19 | |
| W | 86.44 | 77.27 | 81.60 | |
| R | 97.91 | 97.10 | 97.50 | |
| LSTM | M | 97.37 | 94.47 | 95.90 |
| E | 68.94 | 83.94 | 75.70 | |
| W | 85.71 | 76.83 | 81.03 | |
| R | 98.10 | 97.73 | 97.91 | |
| CNN-LSTM | M | 95.18 | 95.56 | 95.37 |
| E | 86.46 | 90.83 | 88.59 | |
| W | 92.16 | 87.85 | 89.95 | |
| R | 97.88 | 99.14 | 98.51 |
| Ref. | System Type | Data Transmission | Processing Method | Anti-EMI Capability | Target Recognition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | TENG + PIN | Direct Circuit | Circuit Model Analysis | Low | Light Intensity |
| [44] | Flexible TENG | Electrical (Wired) | Signal Statistics/Filtering | Low | Motion States |
| [36] | Wireless Spirometer | RF Wireless | GUI/Pattern Matching | Low (RF Interference) | Breathing Pattern |
| This Work | CS-TENG + PIN | Optical Wireless | CNN-LSTM Network | High (Optical Isolation) | Human Action Triggers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Wang, H.; Pu, M.; Luo, P.; Yu, M.; Zhu, Z. Integration of Silicon PIN Detectors and TENGs for Self-Powered Wireless AI Intelligent Recognition. Electron. Mater. 2025, 6, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat6040022
Tang J, Wang H, Pu M, Luo P, Yu M, Zhu Z. Integration of Silicon PIN Detectors and TENGs for Self-Powered Wireless AI Intelligent Recognition. Electronic Materials. 2025; 6(4):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat6040022
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Junjie, Huafei Wang, Maoqiu Pu, Penghui Luo, Min Yu, and Zhiyuan Zhu. 2025. "Integration of Silicon PIN Detectors and TENGs for Self-Powered Wireless AI Intelligent Recognition" Electronic Materials 6, no. 4: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat6040022
APA StyleTang, J., Wang, H., Pu, M., Luo, P., Yu, M., & Zhu, Z. (2025). Integration of Silicon PIN Detectors and TENGs for Self-Powered Wireless AI Intelligent Recognition. Electronic Materials, 6(4), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat6040022







