- Review
Intervention Practices for Promoting Well-Being and Cognitive Development in Hospitalized Children: A Scoping Review
- Sofía Castro-Trigo,
- Alexa von Hagen and
- Augusto Ferreira-Umpiérrez
- + 5 authors
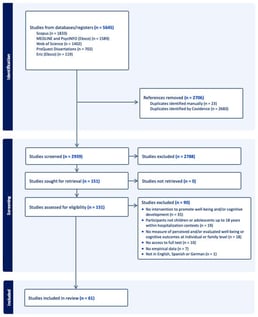
Psychosocial and cognitive interventions are increasingly implemented in pediatric hospital settings. However, evidence regarding their structure, delivery, and outcomes remains dispersed. This scoping review aimed to synthesize current evidence on these interventions, focusing on their design, professional delivery, reported outcomes, and existing research gaps. It was conducted using established scoping review methodology and is reported in accordance with PRISMA-ScR guidelines. Systematic searches were conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, PsycINFO, and ProQuest Dissertations to identify peer-reviewed and grey literature published between 2009 and 2024. Following study selection based on predefined inclusion criteria, data were charted using a standardized data extraction form and analyzed to synthesize and map key characteristics of interventions and outcomes in relation to the review questions. Sixty-one studies met the inclusion criteria. Interventions primarily targeted school-aged children and adolescents and were delivered by psychologists, educators, and nurses, frequently within interdisciplinary teams. A wide range of materials and resources were used, including digital technologies, playful and artistic materials, audiovisual and informational supports, and sensory or therapeutic objects. Techniques primarily involved guided conversation, cognitive and body-based exercises, and play-based approaches. Outcomes mainly focused on emotional well-being and recovery, while fewer interventions explicitly addressed cognitive processes such as attention and executive functioning. Overall, reported effects were generally positive. These findings suggest that psychosocial and cognitive interventions in pediatric hospital settings reflect a wide range of approaches, while also revealing methodological heterogeneity, variability in reporting, and the underrepresentation of low- and middle-income countries, pointing to the need for more robust and inclusive future research.
10 March 2026