- Article
Design of a Dual-Chain Synchronization Monitoring System for Scraper Conveyors Based on Magnetic Sensing
- Jiacheng Li,
- Xishuo Zhu and
- Junyuan Li
- + 4 authors
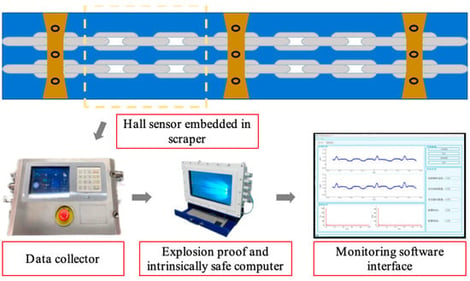
Chain breakage in dual-chain scraper conveyors poses significant risks to the safe and efficient operation of coal mines. To address the challenges of harsh underground environments and the lack of effective synchronization monitoring, this paper presents the design and implementation of an intelligent monitoring system for conveyor integrity. The system integrates non-contact Hall-effect sensors with a custom-designed intrinsically safe data acquisition unit. A systematic algorithmic framework is designed, comprising an adaptive threshold and plateau seeking (ATPS) module and an adaptive clustering-based identification (ACCI) module, to enable high-accuracy automatic identification of chain elements. Furthermore, a novel synchronization evaluation design based on event correlation and statistical features is introduced to quantify inter-chain timing deviations. This leads to the construction of a Chain Synchronization Index (CSI) for desynchronization anomaly detection. Field experiments conducted under representative operating conditions, including normal operation and controlled single-chain disconnection scenarios, demonstrate that the proposed design achieves a chain element recognition accuracy of 98.2%. Under normal conditions, the CSI remains consistently high, while breakage faults are sensitively detected. The proposed system provides a practical engineering solution for synchronization-aware condition monitoring and anomaly warning of scraper conveyor chains in underground coal mines.
9 February 2026