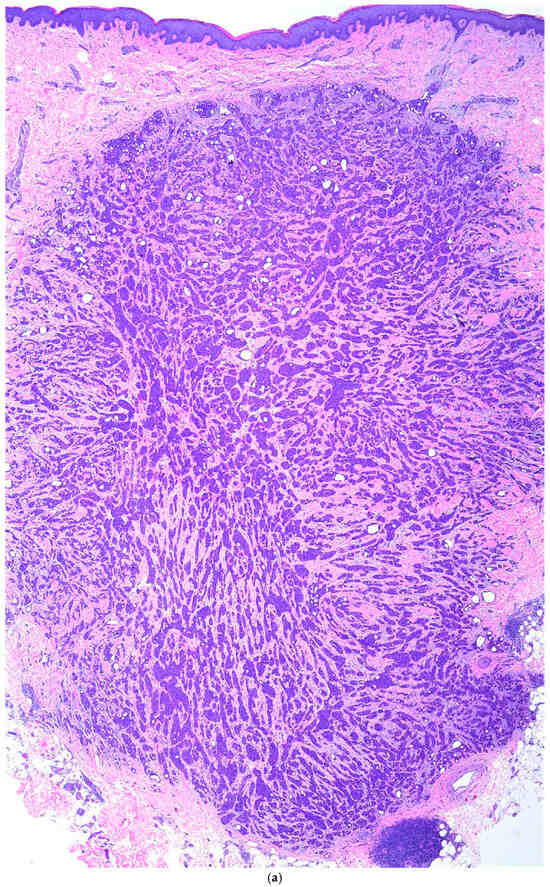
- Article
Methods to Diagnose Adiposity (Overweight/Obesity) in Children and Avoid Misdiagnosis: Relative Fat Mass vs. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
- Ana Rodriguez-Ventura,
- Nayeli Zuñiga-Puente and
- Luis F. Figueroa-Sanchez
- + 5 authors
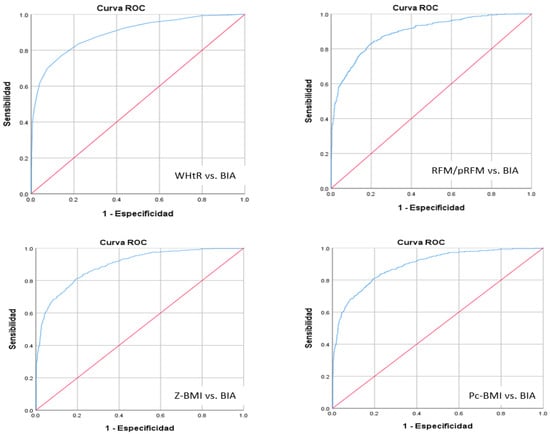
Background/Objectives: Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) are the gold standard to measure fat mass, but they are unavailable in regular consultations. Relative Fat Mass (RFM) and Pediatric Relative Fat Mass (pRFM) equations are calculated using DXA images in adults and children, but they have not been correlated with BIA. Methods: A longitudinal prospective study was conducted with 531 children from a public school followed over one year; sex, age, weight, height, waist circumference and fat mass percentage were recorded. We calculated body mass index Z-score (Z-BMI), body mass index percentile (Pc BMI), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), and RFM-pRFM to diagnose Overweight (Ow)/Obesity (Ob). We used descriptive statistics, Pearson’s correlation, sensitivity and specificity, 95% CI, and ROC curves; SPSS version 22 was used. Results: Adiposity was found in 34.5%, 33.2%, 21.5% and 43.5% of children using Z-BMI, Pc BMI, WHtR, and BIA, respectively; excluding children younger than 8 years old, the frequency of adiposity was 51.5% by RFM-pRFM. The highest correlation was between RFM-pRFM and BIA (0.84, p < 0.000). Of the total measurements of each visit considered as normal weight using Z-BMI, 21.5% had adiposity using BIA, and the proportion of girls underdiagnosed was twice that of boys. Conclusions: RFM-pRFM had the highest correlation with BIA but Z-BMI, Pc BMI, and WHtR are also helpful. It is important to consider that 21.5% of children with apparent normal weight present adiposity.
8 December 2025


![Tumor Node Metastasis 8th edition—Stage III NSCLC [4]. TNM, tumor, node and metastasis; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; SCF, supra-clavicular fossa. Created in BioRender. Horne, A. (2025) https://BioRender.com/xw2j7vi (accessed on 7 November 2025).](https://mdpi-res.com/biomed/biomed-05-00027/article_deploy/html/images/biomed-05-00027-g001-550.jpg)