- Article
Spider Test Modified for Pickleball: Reliable, but Do Not Use It
- Margaret J. Falknor,
- Eric A. Martin and
- Steven B. Kim
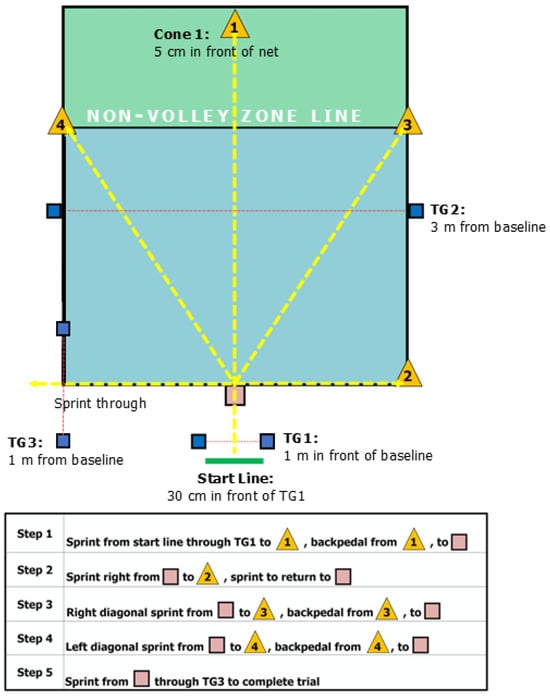
Change in direction ability (COD) is a fitness component that may be related to safe and effective participation in pickleball. The general aim of the research was to examine a COD test that may be specific to the movement demands of the sport. Therefore, we tested the inter-trial reliability of the modified spider test for pickleball, compared learning effects between younger and older adults, and examined the reliability and validity of hand timing compared to timing gates. In this cross-sectional study, 36 participants (ages 19–78) were grouped as adults (ages 18–49) or seniors (ages 50+) according to the USA Pickleball age groupings. Participants completed a standard warm-up, one practice trial, and five full-effort trials with 4–6 min of rest between trials. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to determine reliability across five trials. Inter-rater reliability and validity of hand timing were also examined with ICCs. Pairwise comparison t-tests of individual trials were performed using the Hochberg method to determine learning effect. Linear regression analyses were used to determine if any segment could predict total trial time. During participation, older players provided unsolicited feedback that they were concerned about the safety of the backpedaling in the spider test. We observed that one person fell while backpedaling, though suffered no injury. Results indicate that the spider test was reliable across all five trials (ICC = 0.977). A learning effect was detected between the first and second trial (p = 0.001), and the magnitude of the effect was significantly different between age groups (p = 0.009). Hand timing demonstrated excellent inter-rater reliability (ICC = 0.993) and validity (ICC = 0.990). Splits 2, 3, and 4 significantly predicted total test time (R2 = 0.973, 0.973, and 0.986, respectively). The test demonstrated reliability, but older players expressed concern about backpedaling. This raises questions about backpedaling safety in pickleball. Therefore, we do not recommend this test. Future research needs to determine appropriate tests to screen for fall risk in the dynamic movements relevant to pickleball.
24 December 2025