Abstract
A promising strategy to enhance the therapeutic effectiveness for the treatment of oncological diseases involves the development of combined therapeutic schemes. In our work, we showed the therapeutic potential of the combined action of the anticancer targeted toxin and PDT against HER2-positive breast cancer in vitro. Photodynamic treatment led to photoinduced cell death with IC50 0.64 µM, and after incubation with the toxin for 48 h, IC50 was 2.8 pM. When using two therapeutic agents at IC50 doses, significant increases in the effectiveness were observed; the viability of the combination-treated cell culture did not exceed 10%. The calculated combination index was 0.07, indicating a significant synergistic effect caused by the agents.
1. Introduction
The human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) is overexpressed in 30% of breast cancer patients and is associated with malignant cell transformation. Currently, targeted agents are used in clinical practice for the treatment of this cancer subtype [1]. Targeted agents block certain molecular pathways of the tumor cell that lead to the arrest of tumor proliferation and spread [2]. However, the mono therapeutic approach has limited effectiveness due to the development of acquired drug resistance by tumor cells. A promising strategy to enhance the therapeutic effectiveness for the treatment of oncological diseases is the development of combined schemes. This approach involves using several therapeutic agents with different mechanisms of action. It can lead to an additive or synergistic effect at a reduced therapeutic dose for each individual agent [3]. The high potential of this method was recently shown for a combination of targeted therapy and photodynamic treatment. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an attractive therapeutic approach for the treatment of oncological diseases. PDT is based on interactions between a photosensitizer, light and molecular oxygen (O2). A photosensitizer produces reactive oxygen species (ROS), which lead to oxidative stresses in cells and their subsequent death [4].
In this work, we studied the therapeutic potential of the combined action of the anticancer targeted toxin and PDT against HER2-positive breast cancer in vitro.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culturing of Cell Line
The experiments were performed on a cell line of human breast adenocarcinoma SK-BR-3, which was characterized by HER2 overexpression. Cells were cultured in DMEM medium with 10% (v/v) fetal calf serum and 2 mM L-glutamine in 5% CO2 at 37 °C. At each stage, the cells were treated with Trypsin-EDTA (1:1) solution.
2.2. Study of Combination Cytotoxicity
For the cytotoxicity study, SK-BR-3 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate, 2000 cells per well, and grown overnight. The medium was then exchanged with the fresh one containing different concentrations of DARPin-LoPE [5], and the cells were incubated for 48 h. Following this, the medium was exchanged with the medium containing different concentrations of Photodithazine (PD, OOO VETA-GRAND, Russia). The cells were incubated with PD for 4 h, and after changing the medium to the fresh one, irradiated at a dose of 20 J/cm2 (32 mW/cm2 for 10 min 25 s) in the spectral range of 655–675 nm using a light-emitting diode (LED) under thermostatically controlled conditions (37 °C). The MTT assay was used to estimate the viability of cell cultures 24 h after treatment. The combined action of targeted and photodynamic therapy was compared with mono therapeutic options.
3. Results and Discussion
The DARPin-LoPE is a recombinant protein agent, which consists of a targeting protein (DARPin9.29) and a cytotoxic moiety (LoPE). DARPin9.29 provides high-affinity specific binding to the extracellular domain of HER2. LoPE is a low-immunogenic fragment of the Pseudomonas exotoxin A, which irreversibly blocks protein synthesis in the cell at the translation level [6]. We have shown that after incubation with DARPin-LoPE for 48 h, the half-maximal inhibitory concentration IC50 was 2.8 pM. Photodynamic treatment with PD and irradiation at a dose of 20 J/cm2 led to photoinduced cell death with IC50 0.64 µM. Sequential application of two therapeutic agents at IC50 doses (Figure 1a) led to a significant increase in the effectiveness; the viability of the combination-treated cell culture did not exceed 10% (Figure 1b).

Figure 1.
(a) Scheme of the experiment to evaluate the combined action of DARPin-LoPE and PDT (20 J/cm2) in vitro. (b) Dependence of the relative viability of SK-BR-3 cells on the concentration of DARPin-LoPE and PDT under illumination at a dose of 20 J/cm2 individually and after their combination at doses corresponding to IC50. Adapted with permission from Ref. [7]. 2023 Springer Nature.
To analyze the mode of the drug interaction, we compared the dose-response curves for DARPin-LoPE and Photodithazine for monotherapeutic or combined treatments. The ratio between agents’ concentrations was maintained equal (1:250), which corresponds to the IC50 ratio (Figure 2).
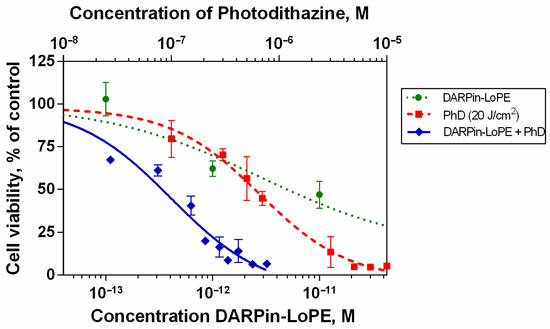
Figure 2.
Relative viability of SK-BR-3 cell after the treatment with DARPin-LoPE and PDT (20 J/cm2) and their combined effects. Adapted with permission from Ref. [7]. 2023 Springer Nature.
The calculated combination index was 0.07, indicating a significant synergistic effect of the agents [7]. The half-maximal decrease in the viability of the SK-BR-3 cell culture was observed at concentrations of the toxin and photosensitizer that are virtually non-toxic to cells when the agents are used separately. We hypothesize that the protein synthesis arrest via the DARPin-LoPE toxin is the main cause for sensitization of the cells to the subsequent PDT treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.V.B. and S.M.D.; methodology, I.V.B.; investigation, L.V.K., M.A.K., A.A.S., E.V.K. and E.L.G.; data curation, I.V.B. and A.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.V.K.; writing—review and editing, I.V.B. and S.M.D.; visualization, L.V.K.; funding acquisition, I.V.B. and S.M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation projects Nos. 19-14-00112 (obtaining the recombinant toxin) and 19-74-20168 (studying the efficiency of combination therapy).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Higgins, M.J.; Baselga, J. Targeted therapies for breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3797–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, D.E. Targeted therapies: A new generation of cancer treatments. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 77, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 6, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, L.V.; Peskova, N.N.; Otvagin, V.F.; Kuzmina, N.S.; Nyuchev, A.V.; Fedorov, A.Y.; Balalaeva, I.V. Novel Chlorine E6 Conjugate with Dual Targeting to Cancer Cells. Opera Medica Physiol. 2022, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Proshkina, G.M.; Kiseleva, D.V.; Shilova, O.N.; Ryabova, A.V.; Shramova, E.I.; Stremovskiy, O.A.; Deyev, S.M. Bifunctional Toxin DARP-LoPE Based on the Her2-Specific Innovative Module of a Non-Immunoglobulin Scaffold as a Promising Agent for Theranostics. Mol. Biol. 2017, 51, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, E.A.; Shilova, O.N.; Kiseleva, D.V.; Schulga, A.A.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Deyev, S.M. HER2-Specific Targeted Toxin DARPin-LoPE: Immunogenicity and Antitumor Effect on Intraperitoneal Ovarian Cancer Xenograft Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balalaeva, I.V.; Krylova, L.V.; Karpova, M.A.; Shulga, A.A.; Konovalova, E.V.; Guryev, E.L.; Deyev, S.M. Synergistic Effect of the Combined Action of Targeted and Photodynamic Therapy on HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 507, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).