Abstract
Cost overrun has long been a significant concern in the construction sector, posing obstacles to project profitability and financial viability. It occurs when actual costs exceed the initial budget estimates, leading to financial hardship, delays, and stakeholder disagreements. This paper investigates the impact of project management techniques on construction project cost overruns. The study aims to identify various techniques used at different stages of construction projects and analyze their effects on cost performance. Additionally, it explores the reasons behind cost overruns and proposes solutions to prevent them in the future. This research highlights efficient methods with which to manage and prevent cost overruns, providing valuable insights for project managers to use when improving cost performance and enhancing project success. It contributes to the knowledge on project management in the construction sector and aids stakeholders in navigating cost overrun challenges. Future research should explore context-sensitive issues related to cost overruns and consider robust, adaptive, and agile cost management strategies based on project management skillsets.
1. Introduction
Project management practices are crucial for achieving successful construction projects, minimizing cost overruns, and ensuring positive outcomes. Key practices like efficient resource allocation, quality control, change management, and progress monitoring and control contribute to cost control and mitigate overruns [1]. Effective techniques such as scheduling, budget control, risk management, communication, collaboration, quality assurance, stakeholder engagement, and impact analysis enhance project efficiency and stakeholder satisfaction [2]. These practices are well documented in the literature, highlighting their positive impacts on project outcomes.
Cost overruns are a significant concern in the construction sector, hindering project profitability and financial viability. They happen when actual costs exceed the initial budget estimate, leading to financial hardship, delays, and stakeholder disagreements [3]. Studies have explored the relationship between project management practices and cost overruns, identifying accurate cost estimation, efficient scheduling, and resource allocation as crucial factors in prevention [4]. Moreover, project monitoring and control systems play vital roles in real-time tracking, the early identification of cost deviations, and the use of prompt corrective actions to prevent further escalation.
While existing studies have provided valuable insights, further research is essential to explore the specific effects of project management techniques on cost overruns in building projects. The connection between project management techniques and cost overrun in the construction sector contributes to the existing knowledge [5]. Effective project management techniques can significantly reduce the risk of cost overruns in building projects. Key practices include accurate cost estimation, well-defined budgets, scope management, thorough project plans, proactive risk identification and mitigation, transparent stakeholder communication, and ongoing cost monitoring and control [3]. Consistent expense tracking, variance analyses, budget comparisons, and preventative actions are also crucial aspects to consider.
Overall, this research aims to provide valuable information to project managers, construction professionals, and other stakeholders. This was achieved through a thorough review of articles from reputable journals published in the last decade.
2. Project Management Practices in Different Stages of Construction Projects
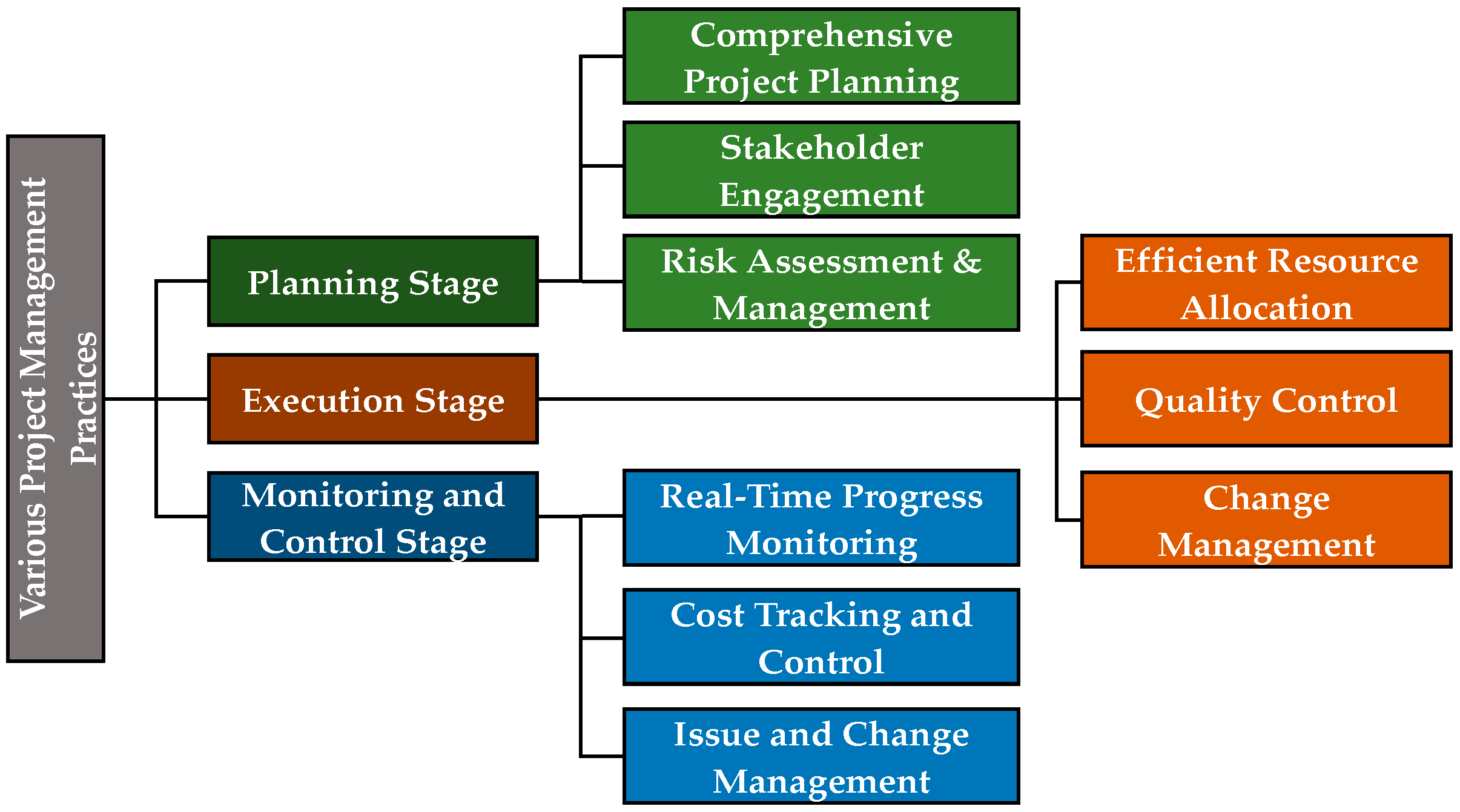
Key project management practices are crucial for successful construction projects, minimizing cost overruns and ensuring positive outcomes. Comprehensive project planning involves detailed planning of scope, resources, timelines, and risks [1]. The use of project management practices at different project stages significantly impacts the achievement of a project’s overall objectives by minimizing delays and improving efficiency, as shown in Figure 1. Adequate project management enables better budget control through accurate cost estimation, expense tracking, and cost management strategies [6]. Implementing quality control techniques like inspections, audits, and industry best practices leads to enhanced project deliverables and customer satisfaction [7]. The literature extensively documents the positive effects of these project management practices on construction projects, with benefits to outcomes, cost control, risk management, quality assurance, and stakeholder satisfaction.
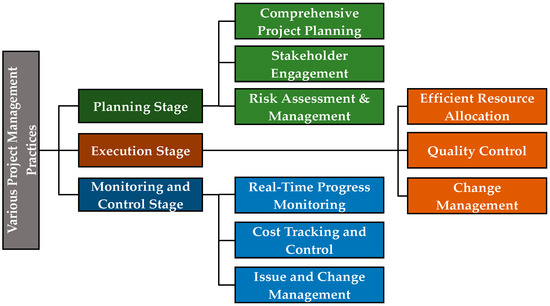
Figure 1.
Project management practices.
3. Cost Overrun in Construction Projects
Cost overrun in construction projects arises from factors beyond the budget, necessitating effective project management and cost control to identify common causes [1]. Effective project management involves addressing these causes through proper estimation, scope management, and robust contract management to enhance performance. Table 1 presents studies related to remedial measures for cost overrun, emphasizing the significance of accurate cost estimation and budgeting as the foundations of effective project cost management [8]. Timely corrective actions are facilitated by effective cost control and monitoring, practices that identify cost deviations early [9]. Collaboration and communication promote cost-conscious decision making and shared understanding during construction projects [6]. Proactive risk management via risk assessments, response plans, and regular monitoring reduces cost overruns [8]. Tracking expenses, conducting variance analysis, and performing periodic audits are vital methods of effectively controlling and monitoring cost. Implementing remedial measures in construction projects, minimizing cost overruns, and improving performance necessitate a proactive approach, stakeholder commitment, and effective management practices.

Table 1.
Remedial measures of cost overrun in construction projects.
4. Relationship between Project Management Practices and Cost Overrun
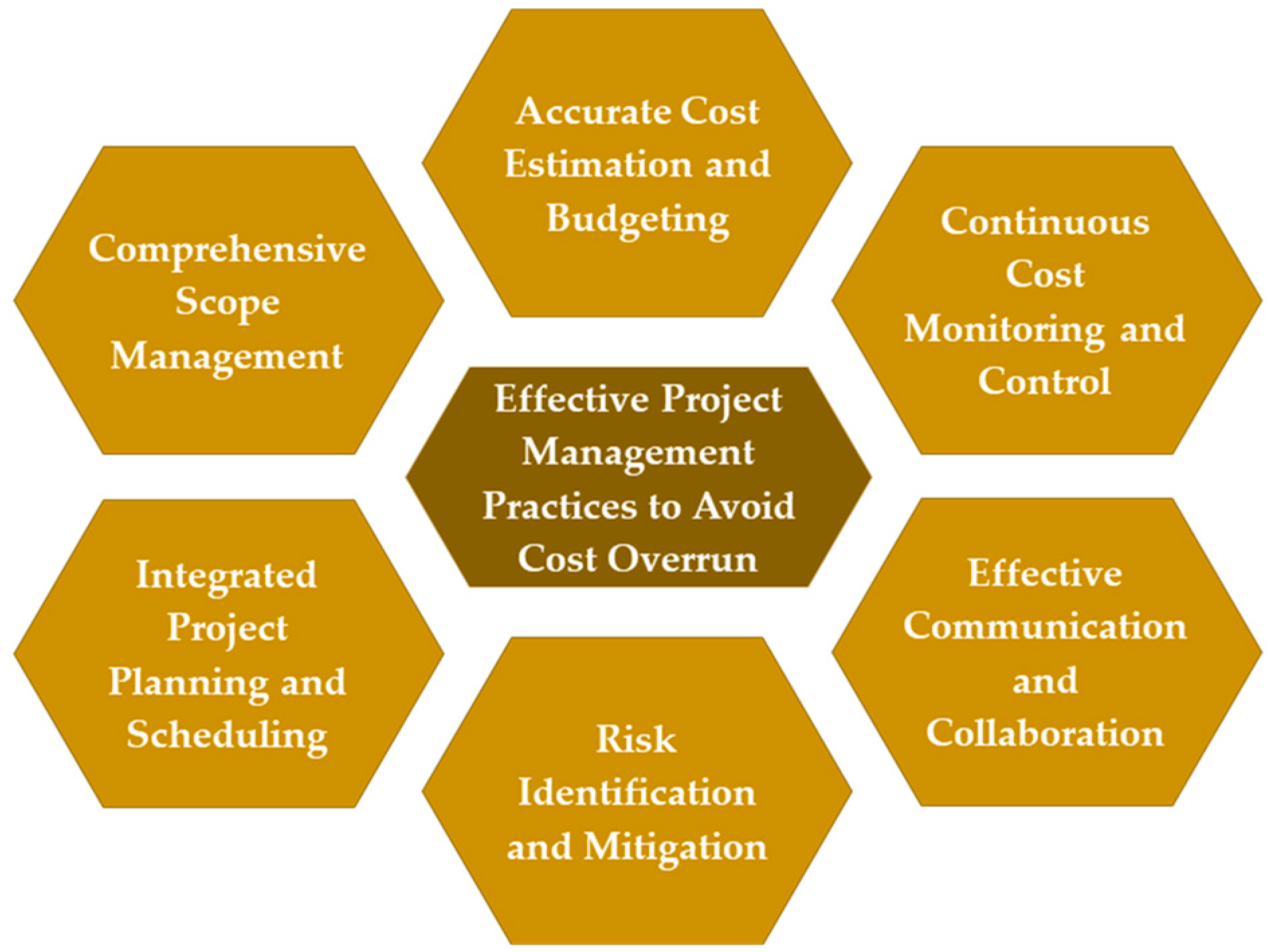
Effective project management practices significantly impact construction project cost overruns, minimizing risk and improving performance. A well-developed project plan with accurate cost estimation, realistic scheduling and sensible resource allocation helps prevent overruns. Table 2 shows the effects of project management practices on cost overrun in construction projects. Robust project planning and control enable timely corrective actions to avoid cost overruns [4]. Risk management minimizes the impact of risks on project costs and reduces the likelihood of overruns [11]. Stakeholder collaboration fosters cost-conscious decision making and reduces conflicts throughout the project lifecycle [7]. Procurement and contract management prevent cost overruns resulting from inflated prices, contractual disputes, or inadequate cost control by contractors [12]. Quality management minimizes cost-related issues arising from poor quality, leading to improved cost performance [6]. Implementing effective project management practices significantly re-duces the likelihood of cost overrun in construction projects [4]. The following section highlights key practices that can help prevent cost overruns. According to Figure 2, effective project management should inculcate integrated planning and scheduling with comprehensive scope management, effective cost estimation with monitoring and control, and effective communication with timely risk identification and mitigation.

Table 2.
Effects of project management practices on cost overrun in construction projects.
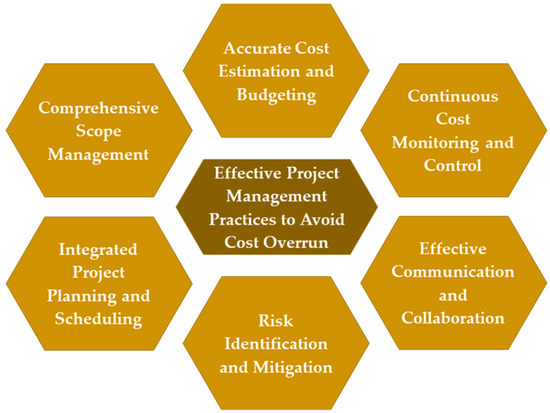
Figure 2.
Effective project management practices to avoid cost overrun in construction projects.
5. Conclusions
Cost overrun is a significant challenge in the construction industry, impacting project success and financial viability. Based on this review, it was evident that project management deployment and optimization acts as key factors in enabling cost management and the delivery of positive outcomes. The following conclusions can be drawn from the conducted study:
- Effective cost control in construction requires crucial project management practices like accurate cost estimation, risk management, and resource allocation.
- Real-time project monitoring and control systems play vital roles in enhancing cost control mechanisms, ensuring timely identification, and resolving cost overruns.
- Integrating cost control mechanisms throughout the project lifecycle is essential for project success and financial viability in the face of cost overrun challenges.
Overall, this research provides valuable insights for project managers and stakeholders into the challenges of cost overrun and can be used to promote efficient project management practices.
6. Novelty and Future Research Direction
The research identified critical factors contributing to cost overrun in construction projects, with an influence of project management practices in managing costing issues. Further research is needed to collect context-sensitive data from construction sites in order to explore these variables in the local context and correlate them with their respective implications. The research added new dimensions to applicable project management aspects, although these may vary based on the site, nature, typology, scale, and size of construction projects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.; methodology, S.A. and O.S.B.; investigation, F.H.S.; data curation, F.H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, F.H.S.; writing—review and editing, S.A. and O.S.B.; supervision, S.A. and O.S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank every person who supported in conducting this research. The careful review and constructive suggestions by the anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ibrahim, A.H.; Elshwadfy, L.M. Factors affecting the accuracy of construction project cost estimation in Egypt. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 15, 329–344. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.S.U.; Shafiq, M.T.; Ullah, F. Automated Computer Vision-Based Construction Progress Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Buildings 2022, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Garrido, A.J.; Navarro, I.J.; García, J.; Yepes, V. A systematic literature review on modern methods of construction in building: An integrated approach using machine learning. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemakhem, M.A.; Chtourou, H. Efficient robustness measures for the resource-constrained project scheduling problem. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2013, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.B.H.; Abdul-Rahman, H.; Chen, W. Collaborative model: Managing design changes with reusable project experiences through project learning and effective communication. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.A.; Adamu, H.; Abdu, A.A.; Singhry, I.M. Influence of building contractors’ performance on construction process in Nigeria: A review of emerging literature. J. Energy Technol. Policy 2015, 5, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona, S.; Ezzamel, M. Management Accounting and Strategy—A Review and Reflections on Future Research. Eur. Account. Rev. 2023, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkanani, S.; Franzoi, R. Gaps in megaproject management system literature: A systematic overview. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2022, 30, 1300–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, J.; Kirytopoulos, K.; Ma, T. Optimism bias within the project management context: A systematic quantitative literature review. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2017, 10, 370–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, T.; Nehdi, M.L. Data acquisition technologies for construction progress tracking. Autom. Constr. 2016, 70, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, F.; Yunfei, S.; Nazir, M.; Bhatti, S.M. A review of artificial intelligence based risk assessment methods for capturing complexity-risk interdependencies: Cost overrun in construction projects. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2021, 14, 300–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Kermanshachi, S. Phase-based analysis of key cost and schedule performance causes and preventive strategies: Research trends and implications. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2018, 25, 1009–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).