- Proceeding Paper
A Dynamic Approach for Operational Efficiency Improvement Using Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization
- Hari Sundar Mahadevan and
- Ashwarya Kumar
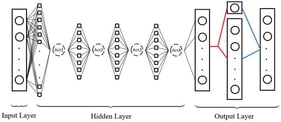
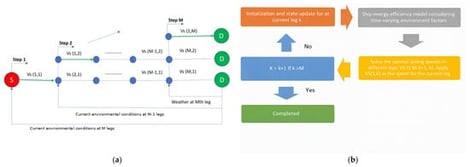
The maritime industry is experiencing significant growth due to globalized trade, but this expansion has led to increasing environmental concerns. Studies project that shipping emissions could reach 90–130% of 2008 levels by 2050 without intervention potentially contributing up to 17% of global CO2 emissions by 2050, thereby posing a major environmental challenge. Stringent environmental regulations from international organizations and government agencies necessitate the maritime industry to find effective solutions to reduce its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and improve energy efficiency. This research proposes a methodology for dynamically calculating optimal ship speed to enhance energy efficiency and reduce GHG emissions. By leveraging real-time environmental data (e.g., weather forecasts, sea state information) and operational parameters (e.g., ship characteristics, cargo load), the study utilizes an Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization based on Velocity Information (APSO-VI) to predict optimal speed over ground (SOG) in real time. The study utilizes the Energy Efficiency Operational Index (EEOI) as a performance metric. EEOI is a widely employed measure in the maritime industry that quantifies the grams of CO2 emitted per tonne-nautical mile (g CO2/t nm) of transport work. The effectiveness of the proposed dynamic optimization model (APSO-VI) is assessed by comparing its performance with constant velocity models through extensive simulations, showing a 5–12% reduction in EEOI with the optimized speed model. The results demonstrate significant reductions in fuel consumption and emissions, supporting the adoption of such technologies for a more sustainable maritime industry. Future research may explore integrating machine learning techniques and advanced weather forecasting models for even more robust optimization strategies.
6 February 2026



![Overview map of the narrow area of D28 Bjelovar bypass, Republic of Croatia, with the locations of traffic counters Reprinted with permission from Ref. [18]. Copyright 2020, Hrvatske ceste d.o.o.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/engproc/engproc-125-00017/article_deploy/html/images/engproc-125-00017-g001-550.jpg)
![Proposed integration of composite clock in Galileo, as per [12].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/engproc/engproc-126-00002/article_deploy/html/images/engproc-126-00002-g001-550.jpg)