- Proceeding Paper
Enhancing Steering Responsiveness in Four-Wheel Steering Steer-by-Wire Systems Using Machine Learning
- Amarnathvarma Angani,
- Teressa Talluri and
- Hyun Rok Cha
- + 2 authors
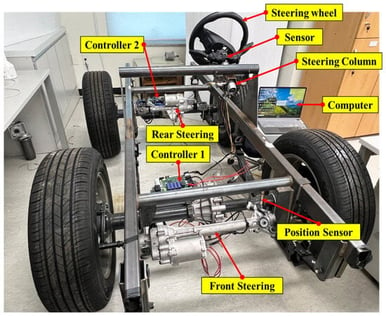
Steer-by-wire (SBW) systems in wheel-steering vehicles enhance maneuverability by eliminating mechanical linkages. However, they are susceptible to delays between steering input and pinion response, which can compromise control precision and safety. To mitigate these delays, we developed a machine learning-based compensation method employing a hybrid architecture of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and gated recurrent units (GRUs) to predict and adjust pinion behavior in real time. The model was trained using experimental data collected from a four-wheel steering test platform, including steering angle inputs, motor signals, and pinion position feedback. By learning the relationship between steering commands and rack force, the model enables dynamic delay correction under both nominal and fault conditions. The system is implemented on an NXP microcontroller and validated through experimental testing, and compared with other hybrid model configurations for performance evaluation. The results demonstrate that the CNN–GRU approach reduces the average steering delay to 3 ms, outperforming conventional PID tuning methods while maintaining high accuracy and system stability.
5 February 2026



![Overview map of the narrow area of D28 Bjelovar bypass, Republic of Croatia, with the locations of traffic counters Reprinted with permission from Ref. [18]. Copyright 2020, Hrvatske ceste d.o.o.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/engproc/engproc-125-00017/article_deploy/html/images/engproc-125-00017-g001-550.jpg)
![Proposed integration of composite clock in Galileo, as per [12].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/engproc/engproc-126-00002/article_deploy/html/images/engproc-126-00002-g001-550.jpg)

