Abstract
In this work, κ-carrageenan (κ-C) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) were utilized to synthesize polymeric films (κ-C-PEO). A 2k experimental design was employed to optimize the synthesis of κ-C-PEO systems by considering the content of κ-carrageenan, PEO, and glycerin and their influence on the mechanical features of the resultant films. The κ-C-PEO systems were robustly characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analyses, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs) were utilized to load κ-C-PEO films as an efficient approach to enhance their biological performance. The activity of κ-C-PEO films was studied against Gram-negative bacteria through the Kirby–Bauer assay. Artemia salina nauplii were cultured to assess the possible toxicity of κ-C-PEO films. The results demonstrated that κ-C-PEO films were elongated with the heterogeneous distribution of MgO-NPs. The tensile strength, thickness, and swelling capacity of κ-C-PEO films were 129 kPa, 0.19 mm, and 52.01%, respectively. TGA and DTA analyses revealed that κ-C-PEO films are thermally stable structures presenting significant mass loss patterns at >200 °C. Treatment with κ-C-PEO films did not inhibit the growth of Escherichia coli nor Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Against A. salina nauplii, κ-C-PEO films did not decrease the survival rate nor compromise the morphology of the tested in vivo model. The retrieved data from this study expand the knowledge about integrating inorganic nanomaterials with polysaccharide-based structures and their possible application in treating chronic wounds. Even though this work provides innovative insights into the optimal design of bioactive structures, further approaches are required to improve the biological performance of the synthesized κ-C-PEO films.
1. Introduction
Wound healing, a critical physiological process that is documented across all ages, from children to the elderly [1], ensures the restoration of tissue integrity and functionality after injury. Mechanistically, the wound-healing process is divided into four stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling [2]. The hemostasis stage is the immediate response to injury and involves vasoconstriction, platelet adhesion, and fibrin clot formation phenomena. In the inflammatory and proliferation stages, the expansion of blood vessels leads to the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages, the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1 and IL-6), and the formation of fibrin matrix by fibroblasts [3]. In the remodeling stage, the collagen fibers are replaced and reorganized to improve the tensile strength of the wound [4]. In the same stage, there is an extracellular matrix adjustment, vascular regression, and increased fibroblast activity, resulting in improved wound tensile strength, scar formation, and tissue integrity.
Epidemiologically, the development of wounds by traumas, surgical procedures, burns, chronic conditions (e.g., obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases) [5,6,7], and infections were associated with 2.5% of the total population of the United States of America (USA) and correlated with the investment of more than 96.8 million USD in management strategies and treatment schemes [8]. Current treatment regimens to promote wound healing encompass the use of topical agents (e.g., antiseptics, growth factors, or insulin sensitizers) [9,10,11], negative pressure wound therapy, hyperbaric oxygen therapy [12], and electrical stimulation delivery [13]. In clinical practices, the consideration of wound-healing therapies has occurred with significant efficacy [14]; however, various factors can still hamper their performance, for example, inflammatory events, microbial contamination, or constant exposure to oxidative stress conditions [15,16].
Microorganisms in wounds can cause aberrations in the wound-healing mechanism by promoting biofilm formation, host immunity evasion, and reducing nutrient availability [17]. Common microorganisms involved in wound contamination include Escherichia coli [18], Pseudomonas aeruginosa [19], Proteus mirabilis [20], Staphylococcus aureus [21], and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [22]. They are characterized by their capability to cause tissue damage and loss of elasticity through the production of enzymes (e.g., ureases and collagenases), mild to severe skin infections through the production of toxins (e.g., lipopolysaccharides and hemolysins), abscess formation, and exacerbate inflammation by upregulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and TNF-α). The infection of wounds comprises the same stages mentioned in previous paragraphs; however, in the presence of pathogenic bacteria, it is initiated by contamination upon injury with foreign objects, and it is followed by colonization, which confers protection against antibiotics and immunological responses [23]. In contrast to healthy wound-healing events, infected wounds also include the exacerbated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can be acute or chronic and lead to tissue damage, impaired healing, and disrupted proliferation and remodeling stages [24]. The treatment of infected wounds is based on the administration of antibiotics such as amikacin [25], vancomycin [26], and ceftriaxone [27]; however, its efficacy is challenging, predominantly due to antibacterial resistance mechanisms [28].
Nanobiotechnology is devoted to designing, manipulating, and applying materials with nanometric architecture. For biomedical applications, nanomaterials (NMs) such as liposomes, nanotubes, and nanoparticles (NPs) are frequently utilized in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, magnetic resonance imaging, and biosensing [29]. According to their chemical composition, NMs are categorized into organic and inorganic. Polymers are biocompatible, biodegradable, and low-toxic materials with significant flexibility, tensile strength, and uniformity to synthesize nanostructures such as micelles, dendrimers, and capsules [30]. In contrast to other natural polysaccharides, κ-carrageenan is a sulfated polysaccharide derived from red algae that has gained considerable attention in research and clinical pipelines. Chemically, κ-carrageenan is constituted by alternating units of 1,3-linked β-D-galactose and 1,4-linked α-D-galactose units. For nanobiotechnological applications, κ-carrageenan has been utilized to fabricate biocompatible scaffolds for tissue engineering [31], spheres for cosmeceutical development [32], and films for antimicrobial and wound-healing applications [33,34].
For wound-healing applications, κ-carrageenan fibers are convenient materials since they are biocompatible structures exhibiting bioadhesive and occlusive properties while preventing inflammation [35]. The synthesis of fibers with biopolymers is often performed through cross-linking and electrospinning [36]. Cross-linking is a convenient route to obtain films with suitable barrier properties, surface area, and biodegradability for wound healing [37]. In this approach, cross-linking agents such as polyethylene oxide (PEO), formaldehyde [38], polyethylene glycol [39], and sodium tripolyphosphate can promote the formation of κ-carrageenan films [40]. In contrast to other cross-linking agents, PEO and its branch derivatives are advantageous polymers for manufacturing polymeric films for wound healing due to their non-toxicity, biocompatibility, and versatility when combined with other materials.
Biopolymeric films can be reinforced with NPs to enhance their properties and ensure their functionality together with mechanical strength, durability, and thermal stability [41]. Magnesium oxide (MgO) is a white inorganic compound that, due to its role in enzyme function, nutritional importance, and suitability to develop bioactive structures, is exploited to synthesize NMs with applications in cancer therapy [42], bone regeneration [43], and wound healing [44]. In wound healing, MgO-based NMs have been reported to be beneficial as their porosity and high surface area can promote cell attachment, infiltration, and proliferation. Together with this, they can dissolve in physiological media, release Mg2+ ions, modulate signaling pathways involved in cell migration and differentiation, and provide optimal alkaline environments for enzyme activity and growth factors release. Considering this, MgO-based NMs have attracted special attention for potential applications in developing wound-healing systems. The evidence regarding using MgO-NPs to reinforce κ-carrageenan films intended for wound healing is scarce since only a limited number of studies have focused on their modification with other NMs like Ag-NPs to disrupt the growth of pathogenic bacteria such as S. aureus [45], a Gram-positive pathogen involved in wound-healing infections.
Given the need to develop novel alternatives to treat wound healing through nanobiotechnological approaches, this work sought to optimize the synthesis of κ-carrageenan films reinforced with MgO-NPs by a 2k factor experimental design. The morphology of the fabricated materials was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). In contrast, their thermal stability and chemical composition were investigated through thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential thermal analysis (DTA), and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The tensile strength, swelling capacity, and thickness of DS and DS-MgO-NPs were also studied. The antibacterial activity of the developed materials was evaluated against Gram-negative (E. coli and P. aeruginosa) bacteria. The in vivo toxicity of the obtained materials was determined against Artemia salina nauplii.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
κ-carrageenan (1.007 × 106 Da molecular weight, >99.0% purity, 10 Pa-s viscosity) was purchased from Chemico (Jalisco, Mexico). Polyethylene oxide with an approximate molecular weight of 200,000 (PolyOX™ WSR N80) and 7,000,000 (PolyOX™ WSR 303) was obtained from DuPont™ (Midland, MI, USA). Glycerin USP was from AzuMex® (Mexico City, Mexico). All systems were prepared using water from a Milli-Q® (MQ) filtration system Millipore (Billerica, MA, USA). MgO-NPs were obtained as published [46].
2.2. 2k Experimental Design and Development of κ-C-PEO Films
A 2k experimental design was conducted using Minitab® V-21.1.0 software. Table 1 outlines the factors and levels proposed for the study.

Table 1.
Outcome variables considered for the development of κ-C-PEO films.
To develop κ-C-PEO films, two systems were prepared in separate containers containing 50% of the total water. PEO was added to the first container, and κ-C with glycerin at 70% of the polymer weight was incorporated into the second. Both solutions were maintained for 30 min under agitation at 300 rpm and 70 ± 5 °C. Subsequently, the two systems were mixed for 30 min at the same stirring speed and temperature. Then, 6.5 mL of the resulting mixture was poured into a glass Petri dish with dimensions of and dried in an oven at 45 ± 5 °C for 5 h. After this period, the obtained κ-C-PEO was refrigerated at 8 °C for 1 day. The same procedure was repeated to reinforce κ-C-PEO films with 1.0% w/w of MgO-NPs previously dispersed into the PEO system. The percentage of raw materials was considered based on the design matrix. Scheme 1 represents the synthesis process of κ-C-PEO films.
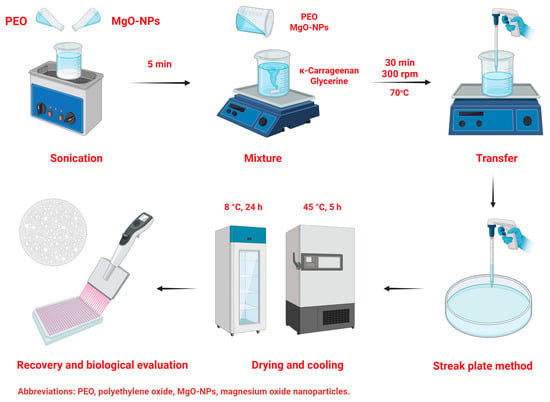
Scheme 1.
Development process of κ-C-PEO-MgO-NPs films.
2.3. Analysis of the Tensile Strength, Thickness, Swelling Capacity, and Water Solubility of κ-C-PEO Films
The tensile strength of κ-C-PEO films was measured using a ZP-500N tensiometer (Shenzhen Ailigu Instrument Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). Briefly, empty or reinforced κ-C-PEO films were cut into a dumbbell shape (6.57 ± 0.55 cm in length and 6.57 ± 0.55 cm in width) and uniaxially stretched until they broke at a controlled speed. Then, Equation (1) was considered to determine their tensile strength (TS); in this equation, Fo is the loading force, whereas w and t are the original width and thickness of the sample, respectively. Moreover, the TC of κ-C-PEO films was carried out with a digital micrometer. For the SC evaluation, a plastic tube filled with 2 mL of aqueous solution at pH 7.5 was placed in a dry bath (Benchmark, BSH300, Sayreville, NJ, USA) until it reached 33 ± 0.5 °C. After this, 0.2 g of κ-C-PEO films was placed into the tube and swelled for 2 min. The swelling capacity (SC) of κ-C-PEO films was determined using Equation (2). The SC of sample 4 was evaluated for 0, 5, 15, and 30 min, and 4 and 24 h; this was according to optimization results. The water solubility of the same sample was analyzed as reported [47]. Briefly, sample 4 (2 × 2 cm) was placed into Erlenmeyer flasks containing 30 mL of deionized water. The mixture was maintained in contact with water at 25 °C for 24 h. After this, the resultant solution was filtered, and the filter paper was allowed to air dry for another day.
2.4. Characterization of κ-C-PEO Films
Considering these results and the data listed in Table 2, sample 4 was utilized to incorporate MgO-NPs and further utilized for characterization and biological activity analysis. Samples were designated as DS (dressing system; unloaded κ-C-PEO film) and DS-MgO-NPs (dressing system/MgO-NPs). The developed κ-C-PEO films were characterized through FTIR spectroscopy, TGA and DTA analyses, and SEM. The chemical composition of κ-C-PEO films was investigated using a Cary 630 FTIR spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) within the 4000–500 cm−1 range. The measurements were performed utilizing the attenuated total reflectance mode and 4 cm−1 resolution with a one-minute collection time. For TGA and DTA evaluation, 10 mg of raw materials and κ-C-PEO films were placed in alumina crucibles and analyzed with an STA 2500 Regulus TGA/DTA thermal analyzer (Netzsch Japan, Ltd., Yokohama, Japan). Measurements were conducted under nitrogen flow within the temperature range of 20 °C to 600 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min. The structural features of empty or reinforced κ-C-PEO films, previously coated with gold in a vacuum ion sputter coater (SEC, MCM-100), were investigated using a Tescan MAIA3 (Brno-Kohoutovice, Czech Republic) at an accelerating voltage of 6.5 kV.

Table 2.
Tensile strength, swelling capacity, and thickness of κ-carrageenan and PEO films.
2.5. Strains Culture and Antibacterial Activity Analysis of κ-C-PEO Films
The antibacterial activity of DS and DS-MgO-NPs was studied against E. coli (ATCC 25922) and P. aeruginosa (ATCC 14210) through the Kirby–Bauer method. Briefly, strains were cultured in Muller–Hinton (MH) broth (Becton & Dickinson), maintained under orbital shaking for 24 h, and adjusted to 0.05 at 600 nm in a Cary 60 spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), with 100 mL of the final suspension were dispensed into Petri dishes containing MH agar. Then, DS or DS-MgO-NPs were carefully cut and placed into Petri dishes, which were further incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Discs impregnated with amikacin were considered the positive control for E. coli and P. aeruginosa. Discs without treatment were considered the negative control. The antibacterial activity of samples was determined by measuring the zone of inhibition (ZI) around the films. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.6. Treatment of A. salina with κ-C-PEO Films
A. salina dried cysts were mixed into 1 L of distilled water that contained 35 g of sea salt and kept at 32 °C for 48 h. The toxicity assay on A. salina nauplii was carried out by carefully placing 250 µL of specimens into a 96-well plate, along with empty or reinforced κ-C-PEO films at concentrations of 60, 120, 180, 240, and 300 μg/mL, respectively. The survival rate of nauplii was observed after 24 h of treatment using a Leica DMi1 inverted microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) with a FLEXACAM C1 camera. Images were captured using Leica software version 3.3.0 (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany). Treatment with K2Cr2O7 at the same concentrations as the synthesized materials was appraised as the positive control.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s mean separation test utilizing OriginPro 2023 data processing software (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA) was utilized to determine significant statistical differences between the retrieved data from the antibacterial and antioxidant activity of empty or reinforced κ-C-PEO films.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Tensile Strength, Swelling Capacity, and Thickness
The tensile strength, swelling capacity, and thickness of the developed formulations are listed in Table 2. According to the optimization results and the determined tensile strength, thickness, and swelling capacity, only sample 4 was utilized for further characterization and biological activity analyses. In an independent experiment, its content was maintained, but 1% of MgO-NPs was added. In this context, sample 4 was designated as DS, and when reinforced with MgO-NPs, it was referred to as DS-MgO-NPs.
3.2. Effect of Outcome Variables on κ-C-PEO Films
Figure 1 illustrates the effect of κ-carrageenan, PEO, and PEO MW content on the thickness, tensile strength, and swelling capacity of κ-C-PEO films. The swelling capacity of sample 4 (2.5% κ-carrageenan and 0.50% PEO N303) after 0, 5, 15, and 30 min and 4 and 24 h is represented in Figure S1 and listed in Table S1. The calculated water solubility of sample 4 was 14.67 ± 7.74% after 24 h.
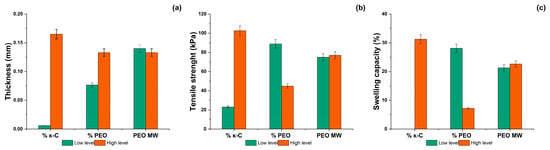
Figure 1.
Effect of the outcome variables κ-carrageenan (κ-C) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) on the (a) thickness, (b) tensile strength, and (c) swelling capacity of κ-C-PEO films.
3.3. Characterization of DS and DS-MgO-NPs
3.3.1. SEM Analysis
DS exhibited a continuous polymeric matrix constituted by elongated films (see Figure 2A–C). The surface of such structures presented a rough texture and visible heterogeneous distribution of MgO-NPs (see Figure 2D–F).
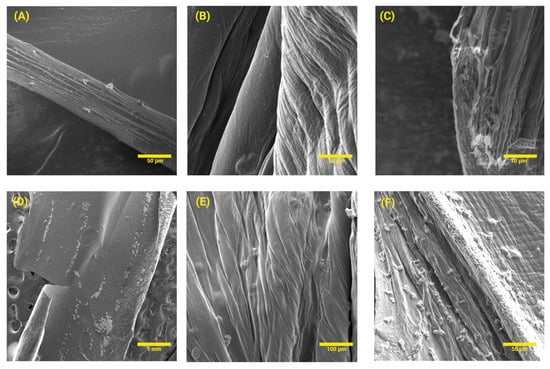
Figure 2.
SEM analysis of (A–C) DS and (D–F) DS-MgO-NPs. For this evaluation, only sample 4 was studied considering optimization analyses.
3.3.2. TGA and DTA Analysis
As observed in Figure 3A, κ-carrageenan presented thermal stability between 26.07–218.57 °C, presenting mass loss patterns from 99.28 to 79.81%. The primary decomposition of κ-carrageenan was recorded from 221.07 to 578.57 °C, causing 79.37–30.28% mass loss. The TGA of PEO-303 revealed that from 18.56–258.56, it exhibited 99.87–67.18% mass loss, whereas at 266.06–348.56, it lost 59.39–0.69% mass (see Figure 3B). Meanwhile, it was noted that glycerin did not exhibit significant mass loss patterns (100–80.21%) as the temperature increased (25.35–185.38 °C) until it reached 240.35 °C, causing 4.49% mass loss (see Figure 3C). In Figure 3D, it can be noted that MgO-NPs remained stable within the range of 26.97–69.38°C; however, it presented mass loss patterns (78.31–50.06%) from 71.97–334.49 °C. According to Figure 3E, the significant mass loss of the developed DS was recorded until 247.53–577.53 °C, which caused 47.69–21.14% mass loss. Similarly, DS-MgO-NPs did not exhibit significant mass loss changes until 220.91–588.41°C (60.92–23.43%). DTA analyses are also illustrated in Figure 3 and indicate the phase transitions and decomposition of DS and DS-MgO-NPs between 0 and 600 °C. The same phenomena can be associated with the raw materials utilized for their development.
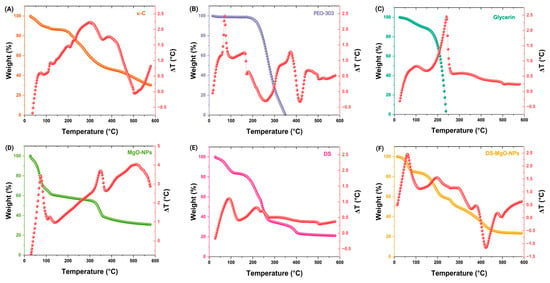
Figure 3.
(A–F) TGA and DTA analyses of DS and DS-MgO-NPs utilized for their preparation. The analysis of raw materials utilized for their development is also depicted in this figure: κ-C; κ-carrageenan; PEO-303; polyethylene oxide 303; MgO-NPs, magnesium oxide nanoparticles. The analyzed samples (DS and DS-MgO-NPs) correspond to sample 4, which was selected according to optimization evaluation.
3.3.3. FTIR Analysis
The chemical composition of DS and DS-MgO-NPs together with the raw materials utilized for their development is represented in Figure 4. For DS, the 3400 cm−1 band can be related to the stretching vibration of hydroxyl groups, whereas the bands at 2800 and 1200 cm−1 can be associated with the stretching of methyl groups. The peaks presented at 1250 cm−1 can correspond to sulfate esters, which are representative of κ-carrageenan. Similarly, the FTIR spectrum of DS-MgO-NPs demonstrates the stretching of hydroxyl and methyl groups at 3400 and 2800 cm−1, respectively. However, it also contained broad peaks related to the stretching (800–600 cm−1) and bending (500–400 cm−1) vibrations of Mg–oxygen bonds. Comparably, the FTIR spectra of PEO 303 and glycerin demonstrated the stretching of hydroxyl, methyl, and carbonyl groups. Regarding the analysis of DS, it was noted that the signal intensity of the peaks decreased to 648.55–775.28 cm−1, which may be associated with the carbonyl stretching and glycoside bond interaction between κ-carrageenan and PEO 303. Similar findings have been reported in other studies involving the use of these polymers for hydrogel membrane development [48].
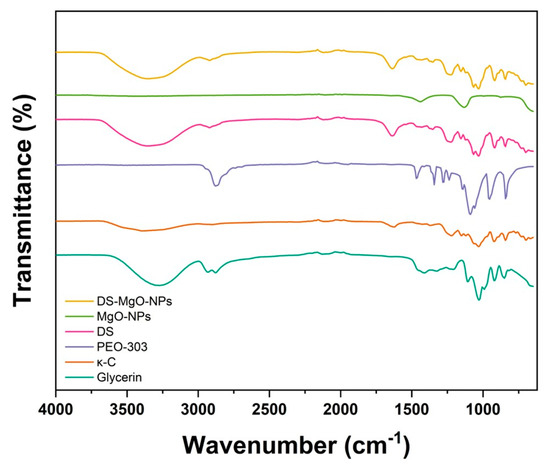
Figure 4.
FTIR analysis of the raw materials utilized to develop DS and DS-MgO-NPs. The composition of DS and DS-MgO-NPs is associated with sample 4, which was selected based on optimization analyses.
4. Biological Activities
4.1. Antibacterial Activity
As illustrated in Figure 5, treatment with DS did not inhibit the growth of E. coli and P. aeruginosa. Similar results were obtained after bacteria cultures were exposed to DS-MgO-NPs. The center of the plates represents the zone of inhibition of amikacin, the positive control utilized in this study toward E. coli and P. aeruginosa. For the former, treatment with amikacin inhibited 23 mm of its growth, whereas for the latter, it resulted in a 21 mm inhibition zone.
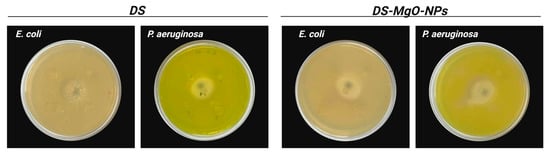
Figure 5.
Antibacterial activity DS and DS-MgO-NPs against E. coli and P. aeruginosa. The evaluated samples (DS and DS-MgO-NPs) correspond to sample 4, which was selected based on optimization analyses.
4.2. Treatment of A. salina with DS and DS-MgO-NPs
As represented in Figure 6, A. salina nauplii exposed to DS and DS-MgO-NPs did not present significant anatomical aberrations. In addition, treatment with the developed films did not decrease their viability.

Figure 6.
Microscopy images of A. salina treated with DS and DS-MgO-NPs. The formulation of the tested samples corresponds to sample 4, which was selected based on optimization results.
5. Discussion
Biopolymers such as polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids constitute attractive sources for designing structures for biomedical applications. Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of long chains of monosaccharide units linked together by glycosidic bonds [49]. Biologically, polysaccharides and their derivatives are recognized because of their capacity to participate in energy storage, structural support, cell recognition, the modulation of cell signaling pathways, cell adhesion, development, and the upregulation of the growth of beneficial gut microbiota events [50,51,52]. Biomedically, the intrinsic therapeutic features of polysaccharides are leveraged to rationally design structures for drug delivery [53], wound healing, vaccine development [54], skin, bone, and cartilage engineering [55], and next-generation medical devices [56].
Optimization is a systematic process by which the properties and performance of NMs are assessed for specific applications. Current approaches to optimize the development of NMs, such as bimetallic NPs [57], carbon nanotubes [58], and smart hybrid composites [59], encompass factorial experimental design, response surface methodology, molecular dynamics simulation, and machine learning. In contrast to other statistical methods, the 2k factorial experimental design evaluates the effect factors on outcome variables categorizing it into low and high.
Here, the evaluated factors consisted of κ-carrageenan, PEO, and PEO MW content, and the outcome variables included tensile strength, swelling capacity, and thickness. According to the factorial design analysis performed in Minitab® (V-21.1.0) software, it was evidenced that the κ-carrageenan and PEO content highly influence the thickness of films (see Figure 1). In the same context, it was observed that the content of κ-carrageenan and PEO MW affects the tensile strength and swelling capacity of the developed films (see Figure 1). The cross-linking of κ-carrageenan and PEO is based on the hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl groups of both polymers, which leads to the formation of a network-type structure. The results illustrated in Figure 1 can be associated with the fact that higher concentrations of κ-carrageenan and PEO MW can occur in thicker films due to an extensive network formation. The κ-carrageenan and PEO MW content can also increase the developed films’ tensile strength since it can enhance the entanglement of the polymer chains, number of intermolecular forces, and resilience under tensile stress [60].
According to the optimization process, one formulation of κ-carrageenan films was selected, designated as sample 4 in Table 2, and utilized to incorporate MgO-NPs. Notably, the amount of MgO-NPs was not considered during the 2k factorial experimental design since this study envisioned optimizing the development of films based on their κ-carrageenan and PEO MW content. Together with this, the amount of MgO-NPs was selected based on other reports where it has been demonstrated that adding 1% of metal-based NPs (e.g., ZnO- and FexOy-NPs) can occur in films with improved physicochemical and mechanical features and antimicrobial and antioxidant performance [60,61].
The developed films were analyzed for their tensile strength, swelling capacity, and thickness. Tensile strength is appraised as the maximum tensile stress a material can withstand before breaking, deforming, or fracturing. For polymer-based films designed for biomedical applications such as wound healing, evaluating their tensile strength is required to ensure their integrity over time, functional barrier capability, and biological performance (e.g., antimicrobial, antioxidant, or anti-inflammatory) during their application. For instance, it was noted that samples containing 2.5% κ-carrageenan and 0.5% PEO N303 resulted in 129 kPa, whereas films synthesized with 0.75% PEO N303 occurred in 87 kPa. On the other hand, it was determined that the tensile strength of films containing 0.5% of κ-carrageenan and 0.5% of PEO N80 occurred at 92 kPa. In contrast, samples of 1.5% of κ-carrageenan and 0.75% of PEO N80 exhibited 46 kPa. When films were developed with 2.5% κ-carrageenan and 0.5% PEO N80, the calculated tensile strength of the obtained material was 214 kPa.
Swelling capacity is the ability of diverse materials to absorb moisture and expand without dissolving. For developing wound-healing dressing systems from polymeric films, evaluating their swelling capacity is necessary to correlate their possible capacity to facilitate cell migration and tissue regeneration, absorb excess exudate, enhance the release of bioactive compounds, and confer protection against external irritants. Regarding their swelling capacity, it can be observed in Table 2 that films with 0.5 and 1.5% κ-carrageenan tended to disintegrate completely, while those with 2.5% of the same polymer exhibited 3.76–52.01% swelling capacity. It was noted that the swelling capacity of sample 4 increased in a time-dependent manner (0–30 min and 4–24 h). Even though no statistical differences were determined between the retrieved values (61.8 ± 1.86–64.10 ± 3.87%), it was observed that the κ-carrageen film softened and became fragile in the medium due to manipulation. Still, when dried, the sample maintained its original appearance. This is presented in Figure S1 and Table S1 and can be associated with the fact that the content of MgO-NPs influenced the capability of the film to absorb water. The differences between the swelling capacity and content of κ-carrageenan can be associated with the presence of PEO and its derivatives since it was recorded that samples with 0.5% of PEO N303 or PEO N80 presented 52.01% and 0% swelling capacity. In contrast, films containing 0.75% of the same PEO MW occurred in 34.52 and 15.89% swelling capacity, respectively. Interestingly, it was assessed that 1.0% of PEO N303 affected its swelling capacity, resulting in 3.76%, whereas it benefited the swelling capacity of films containing 1.0% of PEO N80, occurring in 24.88%. The water solubility was only determined for sample 4 based on the optimization results. In this regard, it was recorded that sample 4 presented 14.64 ± 74% mass loss in solution after 24 h, indicating its suitability to be applied for wound-healing applications by being slowly solubilized and controllably releasing the entrapped MgO-NPs under the physiological conditions of the wound site.
Thickness is related to measuring how wide a film or material is, and it can be expressed in micrometers or millimeters. For wound-healing systems, the thickness of films is of great significance since it influences their ability to act as competent barriers against potential pathogenic microorganisms or contaminants, moisture retention or evaporation management, durability under physiological stress, comfort and wearability, and adhesion efficiency. When evaluated for their thickness, it was recorded that the content of κ-carrageenan and PEO derivatives also alters the thickness of the obtained materials. For example, it was seen that samples containing 2.5, 1.5, or 0.5% of κ-carrageenan and varying proportions of PEO N303 or PN80 occurred in films with thicknesses ranging from 0.05 to 0.29, meaning that films with the highest thickness contained 2.5% of κ-carrageenan and 1.0% of PEO N80. In the same context, it was noted that films with lower thickness contained 2.5% of κ-carrageenan and 0.5–0.75% of PEO N80.
The variabilities between the swelling capacity of the developed κ-carrageenan films can be correlated to the molecular weight of the PEO used since it has been documented that higher-molecular-weight PEO derivatives lead to greater water retention due to their larger chain structure. Comparably, the differences among samples can be associated with thickness and its influence on restricting or enhancing water diffusion patterns. The variabilities of tensile strength between films can be associated with the fact that PEO 303 has a higher molecular weight. Still, parameters such as type, molecular weight, degree of crystallinity, and processing conditions can also influence the tensile strength of the developed materials.
Infectious diseases can be caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites. In contrast to other disorders, infections caused by bacteria are challenging to treat due to their multiple drug-resistance mechanisms. E. coli is a Gram-negative bacterium that, in the clinical pipeline, can cause diarrhea, vomiting, sepsis, or neonatal meningitis [62]. During wound healing, E. coli is considered an opportunistic pathogen that can lead to localized pain, redness, or severe disorders such as peritonitis. P. aeruginosa is another opportunistic Gram-negative pathogen related to respiratory, urinary, and wound infections [63]. The persistence of P. aeruginosa in contaminated surfaces such as medical equipment is associated with delayed epithelialization, inflammation, and increased pain [64]. Here, it was recorded that treatment did not inhibit the growth of E. coli nor P. aeruginosa when slices of DS or DS-MgO-NPs were placed into Petri dishes.
In contrast to these results, recent scientific evidence suggests that κ-carrageenan-based films can inhibit the growth of bacteria strains (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, and Salmonella enterica) when incorporated into melanin pigment [65], polyoxometalates [66], or orange essential oil [67]. Even though there are no studies where κ-carrageenan-based films have been incorporated into MgO-NPs for potential wound treatment, it has been reported that, when incorporated with nanostructures such as copper NPs, κ-carrageenan-based films can decrease the viability of E. coli and S. aureus together with near-infrared irradiation [68]. Similarly, it has been reported that κ-carrageenan-based films reinforced with zinc oxide (ZnO-NPs) can decrease the growth of Listeria monocytogenes [69]. Comparable results have been documented in another study utilizing iron oxide NPs [70]. The variabilities between the retrieved results in this work and other studies can be associated with experimental differences during the development of films, the NPs synthesis route, and the implemented antibacterial assay. For instance, it has been reported that NPs with small sizes (<50 nm) exhibit greater antibacterial activity due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio, enhancing their interaction with bacterial components. The larger size (102.60 ± 23.34 nm) of the synthesized MgO-NPs in work by a previous research group might have limited their activity toward the cultured strains under the proposed conditions [46]. In the same context, it has been documented that green synthesis routes are preferred to synthesize antibacterial NPs since they can act in synergy with extracts from natural sources such as Falcaria vulgaris to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria involved in wound infections [71]. Similar effects have been unveiled when additional elements such as cobalt, copper, and zinc have been used as dopants during the synthesis of MgO-NPs [72]. Regarding film features, it has been reported that films with high porosity tend to exhibit enhanced bacterial interaction [73]. In contrast, films with high tensile strength can exert prolonged contact with bacteria, leading to their death.
A. salina, or brine shrimp, belongs to the family Artemiidae. They are an elongated and translucent species frequently found in hypersaline environments (e.g., salt lakes, salt flats, and coastal lagoons). Compared to other species, A. salina poses significant ecological importance as a food source for invertebrates and as a research model to investigate genetic diversity, microbial interactions, and toxicity of organic and inorganic compounds. The use of A. salina nauplii to evaluate the biocompatibility of polymeric films is limited; however, it can provide important data about their capacity to cause growth and development aberrations, modify behavior, and have a potential environmental impact. Here, it was determined that DS and DS-MgO-NPs did not decrease the viability of A. salina nauplii nor cause anatomical aberrations. In both cases, the retrieved results suggest the compatibility of the developed κ-carrageenan based films. The evidence about the evaluation of the in vivo toxicity of κ-carrageenan-based films is limited; however, it has been reported that, when incorporated with ZnO-NPs, they can decrease the survival rate and deposit in the gut regions of A. salina at 25–500 mg/mL [74]. Table 3 presents a comparative overview of the characterization features of κ-carrageenan-based films developed in other studies.

Table 3.
Comparative overview of characterization features and antibacterial outcome of κ-carrageenan-based films.
6. Conclusions
This study reported the synthesis of κ-carrageenan films through a 2k factorial experimental design, which evidenced that the content of κ-carrageenan and PEO highly influences the tensile strength, swelling capacity, and thickness of the developed films. Considering optimization results, samples utilized in this work were termed DS and DS-MgO-NPs. Through SEM analyses, it was evidenced that DS-MgO-NPs exhibited an elongated structure and heterogeneous distribution of MgO-NPs. TGA and DTA studies revealed the thermal stability of DS and DS-MgO-NPs as they exhibited mass loss patterns at >200 °C. FTIR spectroscopy evaluation confirmed the chemical composition of films, indicating the presence of characteristic functional groups such as hydroxyl, methyl, and sulfate esters. The antibacterial activity of DS and DS-MgO-NPs was poor since they did not inhibit the growth of E. coli and P. aeruginosa. In the same context, the developed films did not affect the survival rate or morphology of A. salina nauplii, suggesting their biocompatibility. This study reports, for the first time, the development and optimization of κ-carrageenan films incorporated with MgO-NPs for the potential treatment of chronic wounds and validates their biological performance through in vitro and in vivo models. Further approaches are required to improve the activity of the optimized formulation by modifying the synthesis route and the amount of added MgO-NPs, altering the surface chemistry of the developed films by inserting positively charged groups that can disrupt bacterial membranes, and revising the cross-link of the synthesized matrix to ensure the sustained release and activity of the added substance. Considering the retrieved data, integrating additional spectroscopy approaches, such as energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, is required to confirm the uniform distribution of the incorporated NPs and correlate it with the recorded biological activities. In addition to film characterization, other variables that must be considered are its wettability, contact angle measurement, roughness, and porosity, correlating them with their biological performance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/polysaccharides6020045/s1, Figure S1: Representative images of the swelling capacity of sample 4 after 0, 5, 15, and 30 min and 4 and 24 h; Table S1: Swelling capacity (%) of sample 4 after 0, 5, 15, and 30 min and 4 and 24 h.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.M.-M. and S.A.B.-C.; validation, J.L.M.-M., E.R.L.-M., and S.A.B.-C.; investigation, L.R.-V., J.L.M.-M., E.R.L.-M. and S.A.B.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.R.-V., J.L.M.-M. and S.A.B.-C.; writing—review and editing, E.R.L.-M. and S.A.B.-C.; visualization, L.R.-V. and E.R.L.-M.; supervision, S.A.B.-C.; funding acquisition; J.L.M.-M., E.R.L.-M. and S.A.B.-C.; project administration, J.L.M.-M. and S.A.B.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
COECYTJAL partially funded this work through the FODECIJAL 2023 Program and Tecnologico de Monterrey through the Nanotechnology and Devices Design Research Group.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhai, W.; Gao, Y.; Pu, L. Epidemiological Characteristics and Factors Affecting Healing in Unintentional Pediatric Wounds. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1352176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Moghaddam, A.; Amiri, A.M.; Charoghdoozi, K.; Mohammadi, M.; Dehnavi, S.; Orazizadeh, M. Improving the Wound Healing Process: Pivotal Role of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells and Immune Cells. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2025, 21, 680–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, C.-H.; Chang, L.; Ho, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-Y.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wang, W.-H.; Wang, T.-W. Immunomodulatory Hydrogel Orchestrates Pro-Regenerative Response of Macrophages and Angiogenesis for Chronic Wound Healing. Biomaterials 2025, 314, 122848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yang, X.; Qin, X.; Shen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L.; Ke, X.; Yang, R. Co-Assembled Supramolecular Hydrogel of Asiaticoside and Panax notoginseng Saponins for Enhanced Wound Healing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2025, 207, 114617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, T.; Li, S.; Bao, J.; Guo, H.; Tan, L.; Xie, X.; Zhuang, Y.; et al. Downregulation of Nutrition Sensor GCN2 in Macrophages Contributes to Poor Wound Healing in Diabetes. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, E.F.; Honig, S.E.; Wang, K.E.; Amro, C.; Davis, H.D.; Habarth-Morales, T.E.; Broach, R.B.; Fischer, J.P. Obesity as a Risk Factor in Cosmetic Abdominal Body Contouring: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024, 48, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; You, H.; Ding, J.; Shi, D.; Long, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, Z.; He, X. Platelets Could Be Key Regulators of Epithelial/Endothelial-to- Mesenchymal Transition in Atherosclerosis and Wound Healing. Med. Hypotheses 2024, 189, 111397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.; Matos, A.C. Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF) Technology as Adjuvant to Ab Externo Trabeculectomy. Int. Ophthalmol. 2024, 44, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombulturk, F.K.; Soydas, T.; Kanigur-Sultuybek, G. Topical Metformin Accelerates Wound Healing by Promoting Collagen Synthesis and Inhibiting Apoptosis in a Diabetic Wound Model. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalhin, A.; Ryu, H.S.; Yoo, S.H.; Abueva, C.; Seo, H.H.; Park, S.Y.; Chung, P.-S.; Woo, S.H. Antiseptic, Hemostatic, and Wound Activity of Poly(Vinylpyrrolidone)-Iodine Gel with Trimethyl Chitosan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalatbary, A.R.; Sarabandi, S.; Ahmadi, F.; Kasmaie, F.M.; Sadeghi, N.; Soleimani, S.; Disfani, R.A.; Raoofi, A.; Nasiry, D. Transplantation of Bioengineered Dermal Derived Matrix-Scaffold in Combination with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improves Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Tissue Cell 2024, 89, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, T.; Han, F.; Cao, L.; Li, M.; Ge, Z.; Sun, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, W.; Zhou, N.; et al. A Wearable Self-Powered Microneedle System Based on Conductive Drugs for Infected Wound Healing: A New Electrical Stimulation Delivery Strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, C.; Kashyap, B.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Chandra Kalita, M.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Deka, S. Antibiofilm and Wound Healing Efficacy of Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant against Pathogenic Bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 195, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Nie, L.; Liu, P.; Xiong, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Bu, P.; Zhou, B.; Tan, M.; Zhan, F.; et al. From Hemostasis to Proliferation: Accelerating the Infected Wound Healing through a Comprehensive Repair Strategy Based on GA/OKGM Hydrogel Loaded with MXene@TiO2 Nanosheets. Biomaterials 2024, 308, 122548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.-F.; Zheng, B.-D.; Xu, Y.-L.; Li, B.-X.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.-T. Multifunctional Fish-Skin Collagen-Based Hydrogel Sealant with Dual-Dynamic-Bond Cross-Linked for Rapid Hemostasis and Accelerated Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberoi, A.; McCready-Vangi, A.; Grice, E.A. The Wound Microbiota: Microbial Mechanisms of Impaired Wound Healing and Infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R. Morphological Variability of Escherichia coli Colonizing Human Wounds: A Case Report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshimy, R.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Okba, M.M.; Ashour, R.M.S.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Hassanen, E.I.; Aboul-Ella, H.; Ali, M.E. Unveiling the Antimicrobial, Antivirulence, and Wound-Healing Accelerating Potentials of Resveratrol against Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA)-Septic Wound in a Murine Model. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhosseini, M.A.; El-Banna, T.E.; Sonbol, F.I.; El-Bouseary, M.M. Potential Antivirulence Activity of Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations of Ciprofloxacin against Proteus Mirabilis Isolates: An in-Vitro and in-Vivo Study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2024, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandaswamy, K.; Prasad Panda, S.; Subramanian, R.; Khan, H.; Rafi Shaik, M.; Althaf Hussain, S.; Guru, A.; Arockiaraj, J. Synergistic Berberine Chloride and Curcumin-Loaded Nanofiber Therapies against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Augmented Immune and Inflammatory Responses in Zebrafish Wound Healing. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimi, L.Y.; Noubom, M.; Bisso, B.N.; Singor Njateng, G.S.; Dzoyem, J.P. Biofilm Formation, Pyocyanin Production, and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Wounds. Int. J. Microbiol. 2024, 2024, 1207536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, N.; Ouyang, X.-K.; Hu, J. Light-Triggered Release of Nitric Oxide from Chitosan-Based Cationic Hydrogels for Promoting Infected Wounds Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-da-Silva, J.V.; Pereira, J.O.; do Carmo, F.A.; Patricio, B.F. Skin and Wound Healing: Conventional Dosage versus Nanobased Emulsions Forms. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 12837–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Wu, Q.; Chu, S.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Y.; You, J.; Yang, C.; Tan, H. Multifunctional Gelatin Nanoparticle Stabilized-Pickering Emulsion Hydrogel Based on Dextran and Amikacin with Controlled Drug Release and Enhanced Antibacterial Capability for Promoting Infected Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 130172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Shu, X.; He, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yu, J.; Guo, J.; Chen, Q. Vancomycin-Loaded Hydrogels with Thermal-Responsive, Self-Peeling, and Sustainable Antibacterial Properties for Wound Dressing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.U.; Chengfeng, X.; Jiang, M.-Q.; Khan, Z.U.; Razzaq, A.; Ullah, A.; Ni, J.; Abdullah; Iqbal, H.; Jin, Z.M. Obstructed Vein Delivery of Ceftriaxone via Poly(Vinyl-Pyrrolidone)-Iodine-Chitosan Nanofibers for the Management of Diabetic Foot Infections and Burn Wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.V.; Kien, H.T.; Hoang, L.H.; Cuong, N.H.; Quang, H.X.; Le, T.D.; Thang, T.B.; Viet, T.T.; Thuc, L.C.; Hung, D.V.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Pathogens Isolated from Patients with Wound Infection at a Teaching Hospital in Vietnam. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, V.; Poursadegh, H.; Amini-Fazl, M.S.; Salari, D.; Javanbakht, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Bio-Nanocomposite Hydrogel Beads Based on Magnetic Hydroxyapatite and Chitosan: A pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery System for Potential Implantable Anticancer Platform. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 7499–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, R.V.; Antanitta, S.V.; Khonde, R.; Kandasubramanian, B. Cellulose and Derivatives Serving as Natural, Versatile and Biocompatible Polymers in Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2024, 74, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavarache, C.; Ghebaur, A.; Serafim, A.; Vlăsceanu, G.M.; Vasile, E.; Gârea, S.A.; Iovu, H. Fabrication of K-Carrageenan/Alginate/Carboxymethyl Cellulose basedScaffolds via 3D Printing for Potential Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicka, K.; Smola-Dmochowska, A.; Dobrzyński, P.; Śmigiel-Gac, N.; Jelonek, K.; Musiał-Kulik, M.; Rychter, P. Microspheres Based on Blends of Chitosan Derivatives with Carrageenan as Vitamin Carriers in Cosmeceuticals. Polymers 2024, 16, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santinon, C.; Borges, A.; Simões, M.; Gonçalves, A.S.C.; Beppu, M.M.; Vieira, M.G.A. Visible-Light Photoactivated Proanthocyanidin and Kappa-Carrageenan Coating with Anti-Adhesive Properties against Clinically Relevant Bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, G.; Bazzo, G.C.; Argenta, D.F.; Conte, J.; Saatkamp, R.H.; Caon, T.; Stulzer, H.K.; Parize, A.L. Development of Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose Acetate Succinate and Kappa Carrageenan Films Loaded with Curcumin for Wound Healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.H.M.; Saccol, C.P.; Custódio, V.N.; da Rosa, L.S.; da Costa, J.S.; Fajardo, A.R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Cruz, L. Carrageenan-Xanthan Nanocomposite Film with Improved Bioadhesion and Permeation Profile in Human Skin: A Cutaneous-Friendly Platform for Ketoprofen Local Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Y.; Shahbazi, Y.; Shavisi, N. Intelligent Locust Bean Gum-k-Carrageenan Nanofibrous Mats with Rosa Canina Petal Anthocyanins and Chitosan Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Application for Monitoring of Beef Meat Freshness. LWT 2024, 208, 116707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, W.; Ramezan, Y.; Riahi, Z.; Khan, A.; Huang, Z. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Plant-Derived Aldehydes: A New Role as Cross-Linking Agents in Biopolymer-Based Food Packaging Films. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, D.V.; Sankar, M.R.; Reddy, T.N. Effect of Glyoxal Concentration and Nanoparticles Reinforcement on the Functional Properties of Composite Hydrogel for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Res. 2025, 33, 569–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.; Özuğur Uysal, B. Effect of MoS2 on Simple and Novel PEG/κ-Carrageenan Hydrogels for TNBC Cancer Drug Delivery. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2025, 64, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wu, C.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Q. An Intelligent Fruit Freshness Monitoring System Using Hydrophobic Indicator Labels Based on Methylcellulose, k-Carrageenan, and Sodium Tripolyphosphate, Combined with Deep Learning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 140001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatabe, M.J.A.; Ghorbanpour, M. Development of Biodegradable Chitosan Films Reinforced with Zinc-Exchanged Bentonite for Enhanced Mechanical, Water Barrier, and Antibacterial Properties. Indian Chem. Eng. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, C.; Khan, M.I.; Hussein-Al-Ali, S.H.; Abualassal, Q.; helmi Abudayeh, Z.; Arulselvan, P.; Bharathi, M.; Surya, P. Bio-Fabrication of Chitosan-Stabilized Magnesium Oxide Nanomaterials: Investigation of Photocatalytic, in Vitro Cytotoxicity Activities and Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 300, 139926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yao, H.; Chang, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Dai, B.; Chen, X.; Lei, L.; et al. Magnesium Nanocomposite Hydrogel Reverses the Pathologies to Enhance Mandible Regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2312920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.F.; Haider, A.J.; Al-Musawi, S.; Abbas, E.M.; Alnayli, R.S.; Taha, B.A.; Choubani, M.; Arsad, N.; Ibrahim, H.I. Optimizing Wound Healing with Antibacterial Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: A Comparative Analysis of Efficacy and Biological Mechanisms. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 105, 106563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, L.; de Souza, M.C.; Bonafe, E.G.; Martins, A.F.; Monteiro, J.P. Optimized Incorporation of Silver Nanoparticles onto Cotton Fabric Using K-Carrageenan Coatings for Enhanced Antimicrobial Properties. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 6908–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio Zurita-Mápula, J.; Alcalá-Alcalá, S.; Alberto Bernal-Chávez, S. Lipid Functionalization of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization. Mater. Lett. 2024, 368, 136660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, E.; Hoffmann, T.G.; Schmitz, F.R.W.; Helm, C.V.; Roy, S.; Bertoli, S.L.; de Souza, C.K. Development of Ternary Polymeric Films Based on Cassava Starch, Pea Flour and Green Banana Flour for Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Verma, C.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, B. Preparation of Thyme Oil Loaded κ-Carrageenan-Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogel Membranes as Wound Care System. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X. Purification and Structural Characterization of a Neutral Polysaccharide from Boletus Auripes Using Self-Made Quaternary Chitosan Cryogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 139091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, N.; Elahimanesh, M.; Bakhshandeh, M.; Najafi, M. Heparin Suppresses FoxO1/pFoxO1 Signaling Axis in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2025, 41, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronsivalle, V.; Santonocito, S.; Giudice, R.; Bocchieri, S.; Didomenico, S.; Cicciù, M. The Role of Hyaluronic Acid in Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review of Its Biological and Regenerative Potential According to PRISMA Guidelines and the Cochrane Handbook. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashhour, D.M.; Al-Hossainy, A.F.; Abd El-Aal, M.; Ibrahim, S.M. Combining Computational and Experimental Studies for Synthesis of Oxidative Derivatives of Glycogen Using Kinetics and Mechanism of Oxidation of Glycogen by Alkaline Permanganate: Homogenous Catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 4353–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Nie, F.; Lin, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y. Natural Polysaccharide-Small Molecule Smart Responsive Nanogels: Design, Synthesis, and Synergistic Chemoimmunotherapy for Tumors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 140930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Shi, C.; An, R.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.-C.; Xiao, M.; Xu, L. In Silico-Guided Discovery of Polysaccharide Derivatives as Adjuvants in Nanoparticle Vaccines for Cancer Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 2099–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Nooshin Banitaba, S.; Khademolqorani, S.; Han, X.; Chen, G. Multipurpose Triadic MXene/Garlic/Gellan Gum-Based Architecture in the Horizon of Bone Tissue Regeneration. Nanoscale 2025, 17, 2528–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J. Naturally Sourced Hydrogels: Emerging Fundamental Materials for next-Generation Healthcare Sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2992–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.A.; Alruwaili, H.A.; Alhumaimess, M.S.; Alanazi, A.H.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Alshammari, M.S.; Hussein, M.F.; Alsohaimi, I.H. Sustainable Nitrophenol Reduction Using Ce-Mof-808-Supported Bimetallic Nanoparticles Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choyal, V.; Mishra, S.; Luhadiya, N.; Kundalwal, S.I. Development and Evaluation of Machine-Learned Interatomic Potentials for Carbon Nanotubes for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Carbon. Lett. 2025, 36, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.R.; Gugulothu, S.K.; Krishnaiah, T.; Grandhi, S.K. Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Machinability of Al-Cu-SiC-GNP Smart Hybrid Composite Using Machine Learning Optimization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, J.A.A.; Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Benítez, J.J.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Biopolymer-Based Films Reinforced with FexOy-Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadi, H.; Shahdadi, F.; Salehi Sardoei, A.; Hatami, M.; Ghorbanpour, M. Investigation of Physio-Mechanical, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Starch–Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Active Films Reinforced with Ferula Gummosa Boiss Essential Oil. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villavicencio-Carrisoza, O.; Grobeisen-Duque, O.; Garcia-Correa, A.L.; Monroy-Muñoz, I.E.; Villeda-Gabriel, G.; Sosa-González, I.E.; Flores-Herrera, H.; Figueroa-Damian, R.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Rivera-Gutierrez, S.; et al. Advancing Understanding of Escherichia coli Pathogenicity in Preterm Neonatal Sepsis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Gu, H.; Pan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, A.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa T6SS Secretes an Oxygen-Binding Hemerythrin to Facilitate Competitive Growth under Microaerobic Conditions. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 293, 128052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, S.; Nilly, F.; Berry, L.; Bonhoure, A.; Alford, M.A.; Louis, M.; Nogaret, P.; Bains, M.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Hancock, R.E.W.; et al. Intracellular Pseudomonas aeruginosa Persist and Evade Antibiotic Treatment in a Wound Infection Model. PLoS Pathog. 2025, 21, e1012922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil Kumar, B.T.; Reddy, J.P.; Vanajakshi, V.; Dasalkar, A.H.; Yannam, S.K.; Hebbar, U.H.; Singh, S.A. Development and Characterization of Carrageenan-Based Antibacterial Films Incorporated with Natural Melanin Pigment from Niger Seed Hulls (Guizotia abyssinica) and Their Efficacy to Enhance the Shelf-Life of Strawberries. Food Control 2025, 174, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Lai, D.; Lin, S.; Hu, J. Preparation and Characterization of Biodegradable κ-Carrageenan Based Anti-Bacterial Film Functionalized with Wells-Dawson Polyoxometalate. Foods 2022, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simona, J.; Dani, D.; Petr, S.; Marcela, N.; Jakub, T.; Bohuslava, T. Edible Films from Carrageenan/Orange Essential Oil/Trehalose—Structure, Optical Properties, and Antimicrobial Activity. Polymers 2021, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhe, T.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L. Copper Sulfide Nanoparticle-Carrageenan Films for Packaging Application. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Carrageenan-Based Antimicrobial Bionanocomposite Films Incorporated with ZnO Nanoparticles Stabilized by Melanin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, S.; Shokri, M.; Priyadarshi, R.; Rhim, J.-W. Carrageenan-Based Antimicrobial Films Integrated with Sulfur-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SNP). ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4913–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, M.; Meskaraf-Asadabadi, M.; Khazaei, F.; Kadivarian, S.; Ghanbari, E. Green Synthesis of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles Using the Extract of Falcaria Vulgaris to Enhance the Healing of Burn Wounds. J. Drug Target. 2025, 33, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.; Kumar, R.; Thakur, N.; Singh, M.; Kumar, K. Ocimum Sanctum-Mediated Co/Cu/Zn-Doped Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles: Photocatalytic, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Properties for Environmental Remediation. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, A.; Lappa, I.K.; Manikas, A.C.; Pastore Carbone, M.G.; Natsia, A.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Kopsahelis, N. Grafting Bacterial Cellulose Nanowhiskers into Whey Protein/Essential Oil Film Composites: Effect on Structure, Essential Oil Release and Antibacterial Properties of Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Saravanakumar, K.; Malaikozhundan, B.; Divya, M.; Vaseeharan, B.; Durán-Lara, E.F.; Wang, M.-H. Biopolymer K-Carrageenan Wrapped ZnO Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles for Anti MRSA Therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Song, Z.; Ni, W.; Ma, Y.; Xin, K.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, L. Composite Nanoparticle-Filled Oxidized Hydroxypropyl Starch/Carrageenan Films: Robust, Water-Resistant, Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Biodegradable Properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-X.; Ge, Z.-T.; Hao, H.-S.; Bi, J.-R.; Hou, H.-M.; Zhang, G.-L. An Antibacterial Film Using κ-Carrageenan Loaded with Benzyl Isothiocyanate Nanoemulsion: Characterization and Application in Beef Preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Kumari, A.; Ahmed, J.; Jasrotia, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Lakshmaiya, N.; Kondal, N.; Kandwal, A.; Sharma, R. Enhancing UV Protection and Antimicrobial Properties in Food Packaging Through the Use of Copper Nanoparticles and κ-Carrageenan Based Nanocomposite Film. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2024, 34, 5538–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amokrane-Aidat, R.; Brahmi, F.; Chennit, B.; Smaoui, S.; Elhadef, K.; Chaari, M.; Madani, K.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L. Sustainable Gelatin-Kappa Carrageenan Active Packaging with Mekwiya Date Seeds to Enhance Goat Meat Quality and Shelf Life. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).