Abstract
(1) Background: To assess and compare speech intelligibility with conventional and universal musician-specific hearing protection devices (HPD); (2) Methods: The sample comprised 15 normal-hearing musicians of both sexes who had been professionals for more than 5 years. They underwent thorough audiological assessment and free-field audiometry to measure the attenuation levels of three HPD models (musician-specific, silicone, and foam devices). The sentence recognition thresholds in quiet (SRTQ) and noise (SRTN) were assessed with the Lists of Sentences in Portuguese. User satisfaction with musician HPD was assessed after 2 months; (3) Results: Conventional HPD had higher pure-tone mean attenuation levels than musician HPD. No statistically significant differences were found in SRTQ and SRTN between the three HPD types. However, the musician HPD had higher mean signal-to-noise ratios and percentages of correct words from sentences presented in noise than the other HPD. The answers also indicated a positive trend toward satisfaction with the musician-specific HPD; (4) Conclusions: Despite the lack of significant differences in speech intelligibility while wearing the three HPD models in either quiet or noise, the musician-specific HPD provided greater musical sound quality. This reinforces the possibility of an effective and adequate use of protection to preserve musicians’ hearing.
1. Introduction
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is one of the main occupational diseases and the second most prevalent cause of sensorineural hearing loss in adults, after age-related hearing loss [1,2].
Like other occupational categories, professional musicians are exposed daily to long hours of high sound pressure levels, which makes them prone to developing NIHL [3,4].
When source noise reduction is insufficient, hearing protection devices (HPD) work as a strategic acoustic barrier to eliminate or minimize the risk of hearing loss [5].
Effective HPD use can minimize the effects of noise on health. However, HPD also reduces the levels of speech and other important sounds, which leads users to often remove the device throughout the workday and/or use it inadequately, thus decreasing its protection [6,7,8].
One of the objectives of Hearing Loss Prevention Programs should be proper HPD use during shift hours. It should also seek means to enhance audibility and communication in the workplace while wearing HPDs—if they poorly match communication needs, workers may feel compelled to temporarily remove their devices, leading to unprotected exposure [9]. In the case of musicians, face-to-face communication involves information exchange with other musicians, sound technicians, and even the public during performances. Furthermore, musicians are susceptible to developing hearing loss, and individuals with hearing loss are known to be more affected by noise in communication situations that require HPD use.
Conventional HPD limits not only musicians’ communication but also their musical quality, as it may over-attenuate higher frequencies while permitting lower ones, distorting the perception of sound emitted by loudspeakers, instruments, and microphones [10].
To solve this problem, flat-frequency response HPD has been projected to equally reduce a wide range of frequencies, providing a more natural sound. Pre-molded musician-specific HPD can be used in various noisy environments, providing moderate high-fidelity and low-cost attenuation while still preserving sound quality [11].
Another practical problem is that the attenuation described by manufacturers does not correspond to what HPD provides in real situations. Due to these discrepancies, HPDs must be individually assessed to verify their effectiveness [12,13] and ensure that selected ones meet the specific needs of each occupational setting, including those related to speech intelligibility [14,15].
Moreover, musicians are often unaware of the importance of wearing HPD, which affects NIHL prevention in this population [11,15,16].
The effects of HPD (especially in noisy environments) on communication and sound quality are still controversial. However, few studies have compared musician-specific and non-specific HPD. Hence, it is essential to conduct such studies to promote HPD use among musicians as well—which justifies the present research.
The objectives of this study were to assess and compare professional musicians’ speech intelligibility in both noise and quiet while wearing conventional HPD and universal musician-specific HPD and verify user satisfaction with the latter.
2. Materials and Methods
This cross-sectional study was approved by the institution’s Research Ethics Committee (CAAE no. 30698114.8.0000.0065). All participants signed an informed consent form.
The study encompassed 15 professional musicians of both sexes, over 18 years old, who played various musical styles, had been exposed to music for more than 5 years, and had normal hearing thresholds. All participants were at acoustic rest for 14 h before examinations.
The participants’ ages ranged from 23 to 39 years, with a mean of 31.26 years (SD 4.33). Regarding sex, 7% were females and 93% were males. They had been musicians for 8 to 26 years, with a mean of 17 years (SD 4.70 years). Their weekly instrument practice time ranged from 10 to 42 h, with a mean of 27.13 h (SD 11.37 h).
Of the 15 participants, 66% played wind instruments (including brass and reed), 20% played string instruments, 7% played percussion instruments, and 7% played keyboard instruments. Half of the participants reported studying more than one musical instrument to improve their harmonic performance.
Participants with an abnormal tympanogram regarding acoustic immittance measures (suggestive of conductive changes); whose external acoustic meatus was obstructed by cerumen or foreign bodies; with a clinical history of hearing changes, such as otologic surgeries, severe complaints of hearing changes, and acoustic trauma; exposed to occupational noise other than music; with any type and degree of hearing loss; and/or with speech changes were excluded from the sample.
Participants underwent a thorough audiological assessment, with medical history survey, otoscopy, acoustic immittance measures (tympanometry and acoustic reflex measures), and pure-tone and speech audiometry (speech recognition threshold [SRT] and speech recognition percentage index [SRPI]).
After a thorough audiological assessment, the specific research procedures were applied. The whole equipment was calibrated according to international standards, and all procedures were conducted in an acoustically treated room and booth.
Specific Procedures
Real-ear attenuation at threshold (REAT) was used to determine the field threshold per frequency band with HPD (occluded ear) and without HPD (open ear) at 250 to 8000 Hz with warble stimuli. In the booth, participants were positioned 1 m away from the loudspeaker (0° azimuth) and were instructed to respond to the tones every time they heard them. These procedures were conducted without HPD and with conventional silicone HPD, ventilated foam HPD, and universal musician-specific HPD (Figure 1). Before the assessments with HPD, participants were instructed on how to properly fit each device.

Figure 1.
Hearing protection device models used in the study. Legend: (A)—3M Pomp Plus® hearing protection; (B)—Acoustic Foam hearing protection, manufactured by Mack’s®; (C)—Universal musician-specific high-fidelity hearing protection, manufactured by Mack’s®. Source A: https://www.3m.com.br/3M/pt_BR/p/d/v000491409/, accessed on 22 May 2022. Source B: https://www.macksearplugs.com/product/acoustic-foam-ear-plugs/, accessed on 22 May 2022. Source C: https://www.macksearplugs.com/product/hear-plugs-high-fidelity-ear-plugs/, accessed on 22 May 2022.
After REAT, free-field speech intelligibility was assessed with each HPD, using the Lists of Sentences in Portuguese [17] and a protocol developed to obtain sentence recognition thresholds in quiet (SRTQ) and noise (SRTN). These were separately measured in each situation—without HPD and with silicone, foam, and musician-specific HPD—to ensure that the tests with the different HPD types were balanced. A different list was used in each assessment situation; they had 10 sentences each, recorded in channel 1, while noise was recorded in channel 2 of the CD.
Participants were asked to repeat the sentences as they understood them to obtain the thresholds. The initial sentence intensity in quiet was 20 dBHL above the REAT, and the initial sentence intensity in noise was 68 dB. The noise remained at 65 dB throughout the test. When patients responded correctly, the researchers decreased sentence intensity by 4 dB; once they gave a wrong answer, researchers increased the intensity by 2 dB after each mistake and decreased it by 2 dB after each correct answer, until they finished the list. SRTQ and SRTN were obtained by calculating the mean intensity after the first mistake [17]. The same process was repeated in each step, with and without the three HPD types. Each subject began the occluded-ear assessment with a different type of HPD.
After the procedures, participants were asked to wear musician-specific HPD for 2 months during performances and rehearsals and were instructed on how to clean it. Then, they answered a user satisfaction questionnaire [18] in Google Forms. Its questions assessed HPD sound quality, comfort, and ease of use. Answers were given on a Likert scale (“totally agree”, “agree”, “indifferent”, “disagree”, and “totally disagree”) scoring from 5 to 1, with a total score ranging from 10 to 50 points—the higher the score, the more positive the respondent’s attitude. Negative sensations perceived while wearing the HPD were also surveyed.
SRTQ and SRTN values were compared between the four situations (without HPD and with silicone, foam, and universal musician-specific HPD). Hence, speech intelligibility values were compared in both quiet and noise and between HPD types.
Descriptive and inferential analyses were performed. Values obtained in each situation were compared with the ANOVA parametric test; the significance level was set at 5%.
3. Results
Despite the normal hearing thresholds (which was a research inclusion criterion), most participants had hearing complaints. The most reported ones were difficulties understanding speech in noise (67%), hypersensitivity to sounds (67%), and tinnitus (60%).
In general, all HPD types attenuated higher frequencies more than medium and lower frequencies (Figure 2 and Appendix A, Table A1). There were significant differences between the three HPD types only at 250 Hz (greater attenuation with silicone HPD) and 6 kHz (greater attenuation with foam HPD).
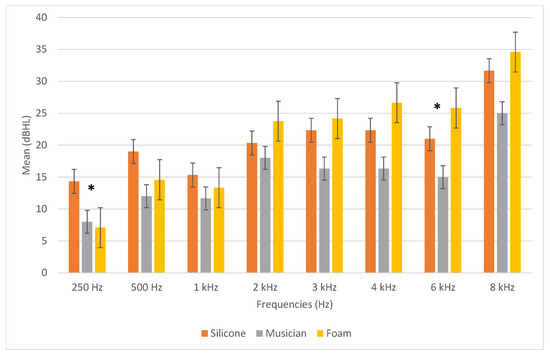
Figure 2.
Mean HPD attenuation values with REAT. Legend: HPD: hearing protection device; REAT: real-ear attenuation at threshold; dBHL: decibels hearing level. * significant (250 Hz—p = 0.012; 6 kHz—p = 0.048).
There was no statistically significant difference in SRTN between the situations with and without HPD (Figure 3 and Appendix A, Table A2).
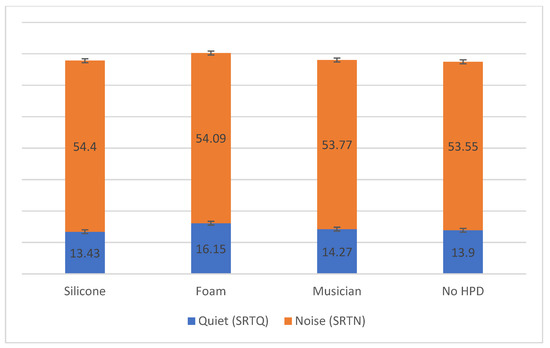
Figure 3.
Sentence recognition thresholds in quiet and noise with and without HPD. Legend—SRTQ: sentence recognition threshold in quiet (dBSL); SRTN: sentence recognition threshold in noise (dBSL).
There were no statistically significant differences in signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) between the different HPD types, although the musician-specific one had a higher SNR than the others (Figure 4 and Appendix A, Table A3). In this case, SNR was negative in all situations—i.e., the message was at a lower intensity than the noise.
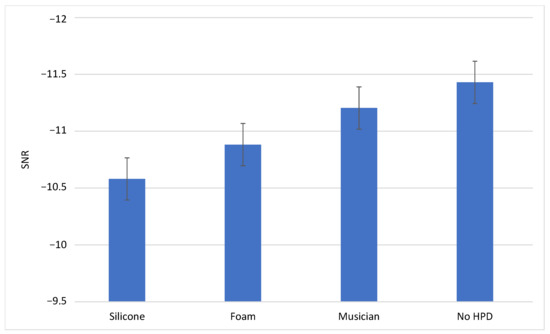
Figure 4.
Signal-to-noise ratio in sentence recognition with and without HPD. Legend—HPD: hearing protection device; SNR: signal-to-noise ratio.
There was no statistically significant difference in the percentage of correct words in sentence recognition between the different HPD types in either quiet or noise. Nonetheless, the foam HPD in quiet and musician HPD in noise enabled a higher percentage of correct answers (Figure 5 and Appendix A, Table A4).
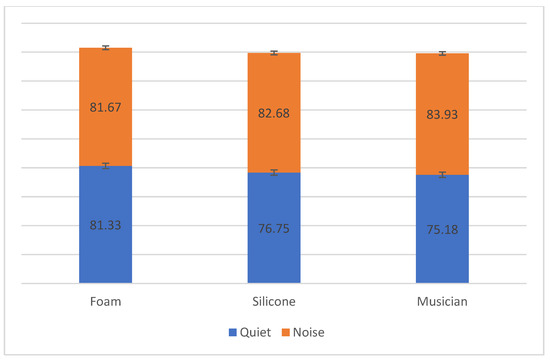
Figure 5.
Percentage of correct words from sentences in quiet and noise with and without HPD.
Altogether, 74% of participants answered the questionnaire about user satisfaction with universal musician-specific HPD. The distribution of answers per question indicating their degree of agreement is shown in Figure 6. Most statements tended to be answered with “agree” or “totally agree”, as the mean scores were around 4 (Appendix A, Table A5). The overall total also indicates positive answers, as the highest possible score was 50 and the mean one was 40. Answers were particularly positive to the following statements: “It allows to identify the timbre of other instruments”, “It allows to perceive high-pitched and low-pitched sounds”, “It is comfortable/convenient”, and “It fits easily”.
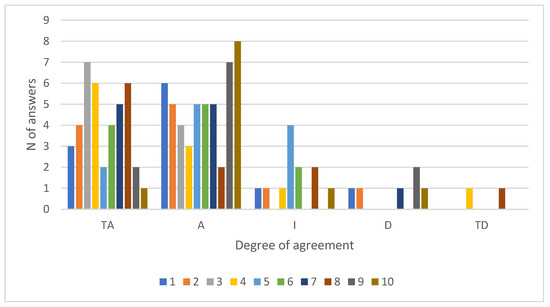
Figure 6.
Distribution of answers indicating degrees of agreement with each statement in the user satisfaction questionnaire with musician-specific hearing protection devices (n = 11).
4. Discussion
Questions still linger about HPD interference with both speech intelligibility and sound quality, which can negatively impact musicians’ occupational activities. Hence, this study aimed to investigate musician-specific and non-specific HPD regarding these aspects.
Despite the normal hearing thresholds (which were a study inclusion criterion), an important portion of this study sample complained of comprehension difficulties in noise, hypersensitivity to intense sounds, and tinnitus. This may indicate that the sound pressure levels to which musicians were exposed had already been enough to cause possible changes in the auditory system, despite the normal hearing thresholds—as some studies have suggested, referring to normal-hearing noise-exposed individuals [14,19,20].
Other studies have verified hearing complaints in an important number of pop/rock musicians (tinnitus in 39.1%; intolerance to intense sounds in 34.8%) [18] and symphony orchestra musicians (tinnitus in 53.34%; hearing difficulties in 43.34%; and intolerance to intense sounds in 33.34%) [21]. These symptoms may be associated with occupational exposure to high sound pressure levels, possibly accompanied by NIHL [16,22,23].
Conventional silicone and foam HPD and musician-specific HPD have different attenuation levels in the various frequencies assessed with REAT. However, no statistically significant differences were verified in most frequencies (except for 250 Hz and 6 kHz). All three HPD models attenuated higher frequencies more than medium and lower ones, which agrees with previous studies with insert HPD [13,24].
It also agrees with the manufacturer’s intention (https://www.macksearplugs.com/product/acoustic-foam-ear-plugs/, accessed on 26 December 2022), which is to use this foam HPD to appreciate musical concerts, in which high frequencies predominate. Unlike the silicone HPD, their model is ventilated, which explains why it does not attenuate lower frequencies as much as conventional foam and silicone models. Moreover, given its purpose, musician-specific HPD was expected to provide a lower and more uniform (flat) attenuation than the other ones [25], as observed in the comparison between the three models.
Findings on the hearing sensation levels in SRTQ with HPD suggest that the devices did not interfere with speech intelligibility in any of the assessed situations—which agrees with observations in another study [14].
As for SRTN, the more negative the SNR, the greater the skill needed to hear the sentence with a competing signal [6,14]. Our initial hypothesis was that the speech recognition threshold in noise would be better with the musician-specific HPD—which, however, was not confirmed. SNR was likewise similar in all assessed situations. It must be pointed out that speech intelligibility in noise is more intensely affected in people with hearing loss than in normal-hearing people because of possible deficits in both temporal and frequency resolution [6]. Therefore, more evident differences in speech intelligibility in noise with HPD might have been observed if the comparison involved musicians with hearing loss.
Despite the lack of statistically significant differences in the percentages of correct words in SRTQ and SRTN, participants reported a better sound quality with the musician-specific HPD, which was “sharper and clearer” than with the others. In general, musician HPD attenuates less than conventional ones, which must be considered when indicating this type of protection to professional musicians. Over-attenuation may hinder communication and environmental sound perception, which are greatly important to these professionals [25].
The answers in the user satisfaction questionnaire on musician-specific HPD (Hi-Fi Mack’s) after wearing it for 2 months indicated that this device was positively received by professionals. The questionnaire’s total mean score was around 40 points, which is higher than the one obtained in a previous study that used the same instrument with pop/rock musicians [18].
Aspects pointed out as the most positive ones include the perception of the instrument’s timbre, low-pitched/high-pitched sounds, ease of fitting, and comfort. These characteristics are important for effective HPD use [26].
A positive aspect mentioned by most musicians was the perception of higher frequencies. This disagrees with the findings by Santoni and Fiorini (2010) [18], who used the same instrument, though with a hi-fi HPD from another brand—this difference is probably related to manufacturer variations.
The participants’ most reported negative sensations in this study were that they did not clearly hear the singer’s voice and did not wear the HPD throughout concerts and rehearsals. These may be related to the occlusion effect of the insert HPD, whose use may be uncomfortable [16,18].
Professional musicians stated they could adapt to the difficulties of wearing HPD over time, considering the effective hearing protection [27]. The habit of wearing HPD is known to decrease the discomfort of the occlusion effect over time, as long as its size is appropriate to the user’s ear canal [18].
Other studies reported favorable experiences with musician-specific HPD use [28,29], and one paper verified that musicians with auditory symptoms used HPD more often than those who had no such symptoms and that professionals with hearing loss had already considered ending their musical careers [30].
Hence, it is essential to raise musicians’ awareness of the importance of wearing HPD, especially professionals whose hearing has not yet been impaired [31]. It must be highlighted that the best HPD to indicate is the one the individual believes to be the most comfortable and agrees to use correctly, wearing it full time [26,32] to prevent any impairments to the auditory system.
The limitations of the study include the sample size and the participation of only normal-hearing musicians. Future studies should compare musicians with and without hearing loss.
5. Conclusions
Despite the lack of significant differences in speech intelligibility while wearing the three HPD models in either quiet or noise, the musician-specific HPD provided greater musical sound quality, reinforcing the possibility of effective and adequate protection use to preserve musicians’ hearing.
Author Contributions
A.G.S. was responsible for the study design; data analysis; manuscript writing and final revision. G.C.P. was responsible for data collection, manuscript writing, and final review. C.H.R. and C.G.M. were responsible for data analysis; manuscript writing and final revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
GCP received a grant from Fapesp (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo)—Grant no. 2018/13788-9.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to the privacy of participants.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Analysis of variance in attenuation levels (obtained with REAT) between the three HPD models.
Table A1.
Analysis of variance in attenuation levels (obtained with REAT) between the three HPD models.
| Frequency | HPD | Mean (SD) (dBHL) | Median (Min–Max) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 Hz | Silicone | 14.33 (9.42) | 15 (5–40) | 0.012 * |
| Foam | 7.08 (4.5) | 7,5 (0–15) | ||
| Musician | 8 (5.92) | 10 (0–20) | ||
| 500 Hz | Silicone | 19 (9.67) | 15 (5–45) | 0.060 |
| Foam | 14.58 (6.2) | 15 (5–25) | ||
| Musician | 12 (7.27) | 10 (5–30) | ||
| 1000 Hz | Silicone | 15.33 (8.34) | 15 (5–35) | 0.459 |
| Foam | 13.33 (8.07) | 10 (5–30) | ||
| Musician | 11.67 (7.48) | 15 (0–25) | ||
| 2000 Hz | Silicone | 20.33 (12.02) | 20 (0–40) | 0.479 |
| Foam | 23.75 (14.94) | 20 (10–60) | ||
| Musician | 18 (11.62) | 15 (5–35) | ||
| 3000 Hz | Silicone | 22.33 (12.66) | 20 (0–50) | 0.276 |
| Foam | 24.17 (16.21) | 27.5 (0–60) | ||
| Musician | 16.33 (12.17) | 15 (0–40) | ||
| 4000 Hz | Silicone | 22.33 (13.07) | 20 (10–55) | 0.083 |
| Foam | 26.67 (14.35) | 25 (10–55) | ||
| Musician | 16.33 (9.15) | 15 (5–35) | ||
| 6000 Hz | Silicone | 21 (12.13) | 15 (5–55) | 0.048 * |
| Foam | 25.83 (12.76) | 22.5 (10–45) | ||
| Musician | 15 (9.82) | 15 (0–35) | ||
| 8000 Hz | Silicone | 31.67 (12.49) | 35 (5–55) | 0.137 |
| Foam | 34.58 (14.22) | 32.5 (10–50) | ||
| Musician | 25 (12.82) | 25 (5–45) |
Legend–REAT: real-ear attenuation at threshold; HPD: hearing protection device; dBHL: decibels hearing level; SD: standard deviation; Hz: Hertz. *: significant.

Table A2.
Sentence recognition thresholds in quiet and in noise with and without HPD.
Table A2.
Sentence recognition thresholds in quiet and in noise with and without HPD.
| Situation | HPD | Mean (dBSL) (SD) | Median (Min–Max) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quiet (SRTQ) | Silicone | 13.43 (5.24) | 15.47 (5–20) | 0.483 |
| Foam | 16.15 (5.04) | 16.03 (7–27) | ||
| Musician | 14.27 (5.31) | 13.5 (5–21) | ||
| No HPD | 13.90 (4.66) | 15.36 (7–21) | ||
| Noise (SRTN) | Silicone | 54.40 (2.85) | 54 (49–60) | 0.903 |
| Foam | 54.09 (2.52) | 53.6 (50–59) | ||
| Musician | 53.77 (2.89) | 52.4 (49–59) | ||
| No HPD | 53.55 (4.33) | 52 (49–62) |
Legend—HPD: hearing protection device; dBSL: decibels sensation level; SD: standard deviation; SRTQ: sentence recognition threshold in quiet; SRTN: sentence recognition threshold in noise.

Table A3.
Signal-to-noise ratio in sentence recognition with and without HPD.
Table A3.
Signal-to-noise ratio in sentence recognition with and without HPD.
| Situation | Mean (SNR) (SD) | Median (Min–Max) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone | −10.58 (2.86) | −11 (−5–−15) | 0.904 |
| Foam | −10.88 (2.53) | −11.3 (−5–−14) | |
| Musician | −11.20 (2.90) | −12.6 (−5–−16) | |
| No HPD | −11.43 (4.35) | −13 (−3–−16) |
Legend—HPD: hearing protection device; SNR: signal-to-noise ratio; SD: standard deviation.

Table A4.
Percentage of correct words from sentences in quiet and noise with and without HPD.
Table A4.
Percentage of correct words from sentences in quiet and noise with and without HPD.
| Situation | HPD | Mean (%) (SD) | Median (Min–Max) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quiet | Foam | 81.33 (9.27) | 82 (66–94) | 0.340 |
| Silicone | 76.75 (6.83) | 76.42 (67–88) | ||
| Musician | 75.18 (5.08) | 74.49 (69–83) | ||
| Noise | Musician | 83.93 (3.89) | 83.64 (78–89) | 0.820 |
| Silicone | 82.68 (7.78) | 82.35 (70–94) | ||
| Foam | 81.67 (6.29) | 81.37 (72–88) |
Legend—HPD: hearing protection device; SD: standard deviation.

Table A5.
Distribution of answers regarding the degree of agreement with each statement in the user satisfaction questionnaire with musician-specific hearing protection devices (n = 11).
Table A5.
Distribution of answers regarding the degree of agreement with each statement in the user satisfaction questionnaire with musician-specific hearing protection devices (n = 11).
| Identification | STATEMENT | Mean (SD) * | Degree of Agreement | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Musician Protection Device: | TA | A | I | D | TD | |||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |||
| 1 | It allows me to hear all other band instruments with quality. | 4.00 (1.03) | 3 | 27.3 | 6 | 54.5 | 1 | 9.1 | 1 | 9.1 | - | - |
| 2 | It allows me to identify the timbre of the other band instruments. | 4.09 (1.01) | 4 | 36.4 | 5 | 45.4 | 1 | 9.1 | 1 | 9.1 | - | - |
| 3 | It allows me to clearly perceive high-pitched sounds. | 4.64 (1.55) | 7 | 63.6 | 4 | 36.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | It allows me to clearly perceive low-pitched sounds. | 4.18 (1.26) | 6 | 54.5 | 3 | 27.3 | 1 | 9.1 | - | - | 1 | 9.1 |
| 5 | It allows me to clearly hear the singer’s voice. | 3.82 (0.85) | 2 | 18.2 | 5 | 45.4 | 4 | 36.4 | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | It is comfortable/convenient. | 4.18 (1.02) | 4 | 36.4 | 5 | 45.4 | 2 | 18.2 | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | It fits easily. | 4.27 (1.21) | 5 | 45.4 | 5 | 45.4 | - | - | 1 | 9.1 | - | - |
| 8 | It does not interfere with the musician’s looks. | 4.09 (1.22) | 6 | 54.5 | 2 | 18.2 | 2 | 18.2 | - | - | 1 | 9.1 |
| 9 | I could use such a device throughout all my rehearsals. | 3.82 (1.17) | 2 | 18.2 | 7 | 63.6 | - | - | 2 | 18.2 | - | - |
| 10 | I could use such a device throughout all my presentations. | 3.82 (1.33) | 1 | 9.1 | 8 | 72.7 | 1 | 9.1 | 1 | 9.1 | - | - |
| Total | Total | 40.91 (11.6) | ||||||||||
Legend—TA: totally agree; A: agree; I: indifferent; D: Disagree; TD: totally disagree. * Mean and SD: the highest score in each statement was 5 points and the highest total score was 50 points.
References
- Rabinowitz, P.M. Noise-induced hearing loss. Am. Fam. Physician 2000, 61, 2749–2756. Available online: https://www.aafp.org/afp/2000/0501/p2749.html (accessed on 26 December 2022). [PubMed]
- Masterson, E.A.; Deddens, J.A.; Themann, C.L.; Bertke, S.; Calvert, G.M. Trends in worker hearing loss by industry sector, 1981–2010. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2015, 58, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stadio, A. Which factors to induce hearing loss in professional musicians? Extensive literature review and histopathology findings can answer it. Hear. Balance Commun. 2017, 15, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stadio, A.; Dipietro, L.; Ricci, G.; Della Volpe, A.; Minni, A.; Greco, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Ralli, M. Hearing Loss, Tinnitus, Hyperacusis, and Diplacusis in Professional Musicians: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, W.E.; Swan, S.S.; McDaniel, M.M.; Camp, J.E.; Cohen, M.A.; Stebbins, J.G. Noise exposure and hearing loss prevention programmes after 20 years of regulations in the United States. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 63, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Clavier, O.H. Effects of noise on speech recognition: Challenges for communication by service members. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, C.; Laroche, C.; Vaillancourt, V. The interaction of hearing loss and level-dependent hearing protection on speech recognition in noise. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54, S9–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppler, H.; Ingeborg, D.; Sofie, D.; Bart, V. The effects of a hearing education program on recreational noise exposure, attitudes and beliefs toward noise, hearing loss, and hearing protector devices in young adults. Noise Health 2015, 17, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CSA Z1007:22. Hearing Loss Prevention Program (HLPP) Management. 2022. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/preview-pages/CSA/preview_2423263.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Hiselius, P.; Edvall, N.; Reimers, D. To measure the impact of hearing protectors on the perception of speech in noise. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J. Musicians’ Hearing Protection. A Review. Prepared by the Health and Safety Laboratory for the Health and Safety Executive. 2008. Available online: https://www.hse.gov.uk/research/rrpdf/rr664.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Hager, L.D. Fit-testing hearing protectors: An idea whose time has come. Noise Health 2011, 13, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.H.; Longo, I.A.; Moreira, R.R.; Samelli, A.G. Evaluation of the hearing protector in a real work situation using the field-microphone-in-real-ear method. CoDAS 2016, 28, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.H.; Lisboa, G.; Padilha, F.Y.O.M.M.; Rabelo, C.M.; Samelli, A.G. Effects of hearing protector devices on speech intelligibility: The importance of individualized assessment. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2022, 28, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSHA’s Alliance ProgramBest Practice Bulletin: Hearing Protection-Emerging Trends: Individual Fit Testing. 13 May 2008. Available online: http://www.hearingconservation.org/assets/docs/AllianceRecommendationForFitTesting_Final.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Mendes, M.H.; Morata, T.C. Exposição profissional à música: Uma revisão. Rev. Soc. Bras. Fonoaudiol. 2007, 12, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Santos, S.N.; Lessa, A.H.; Mezzomo, C.L. Proposal for implementing the Sentence Recognition Index in individuals with hearing disorders. CoDAS 2015, 27, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, C.B.; Fiorini, A.C. Músicos de pop-rock: Avaliação da satisfação com protetores auditivos. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaette, R.; McAlpine, D. Tinnitus with a normal audiogram: Physiological evidence for hidden hearing loss and computational model. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13452–13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plack, C.J.; Barker, D.; Prendergast, G. Perceptual consequences of ‘hidden’ hearing loss. Trends Hear. 2014, 18, e2331216514550621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüders, D.; Gonçalves, C.G.D.O.; Lacerda, A.B.M.D.; Schettini, S.R.L.; Silva, L.S.G.; Albizu, E.J.; Marques, J.M. Audição e qualidade de vida de músicos de uma orquestra sinfônica brasileira. Audiol. Commun. Res. 2016, 21, e1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.G.D.O.; Lacerda, A.B.M.D.; Zeigelboim, B.S.; Marques, J.M.; Lüders, D. Limiares auditivos em músicos militares: Convencionais e altas frequências. CoDAS 2013, 25, 181–187. Available online: https://www.scielo.br/j/codas/a/mSqzQ49jFRvf3cNTLqb664h/abstract/?lang=pt (accessed on 26 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.M.D.C.; Amorim, C.M.T.; Felipe, I.M.A.F.; Dias, R.D.S. Perfil audiométrico de músicos profissionais: Revisão sistemática. Rev. Bras. Promoç. Saúde 2018, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, J.; Park, M. Laboratory versus field attenuation of selected hearing protectors. Sound Vib. 1991, 25, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bockstael, A.; De Coensel, B.; Botteldooren, D.; D’Haenens, W.; Keppler, H.; Maes, L.; Philips, B.; Swinnen, F.; Bart, V. Speech recognition in noise with active and passive hearing protectors: A comparative study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 3702–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samelli, A.G.; Gomes, R.F.; Chammas, T.V.; Silva, B.G.; Moreira, R.R.; Fiorini, A.C. The study of attenuation levels and the comfort of earplugs. Noise Health 2018, 20, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, I.; Driscoll, T.; Williams, W.; Ackermann, B. A clinical trial of active hearing protection for orchestral musicians. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2014, 11, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.L.; Killion, M.C.; Lentz, J.J.; Kidd, G.R. Hearing protection success: Musicians have a favorable response to hearing protection and listeners are unable to identify music produced by musicians wearing hearing protection. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2020, 31, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.S.; Smith, R.; Teglas, S.; Hodges, D.A. Musicians’ earplugs: Do they affect performance or listeners’ perceptions? Med. Probl. Perform. Art. 2020, 35, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Størmer, C.C.L.; Laukli, E.; Høydal, E.H.; Stenklev, N.C. Hearing loss and tinnitus in rock musicians: A Norwegian survey. Noise Health 2015, 17, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, G.; Koravand, A.; Swirp, M. Prevalence of hearing loss among university music students. Can. Acoust. 2018, 46, 37–51. Available online: https://jcaa.caa-aca.ca/index.php/jcaa/article/view/3042 (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Sviech, P.S.; Gonçalves, C.G.D.O.; Morata, T.C.; Marques, J.M. Avaliação do conforto do protetor auditivo individual numa intervenção para prevenção de perdas auditivas. Rev. CEFAC 2013, 15, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).