Abstract
Carbon dioxide (CO2) efflux from soil (or soil respiration, SR) is one of the most important yet variable characteristics of soil. When evaluating large areas, CO2 efflux modeling serves as a viable alternative to direct measurements. This research aims to identify site-specific differences and their effects on empirical CO2 efflux modeling. The experimental data from 25 years of field observations were utilized to identify the optimal site- and weather-specific models, parameterized for normal, wet, and dry years, for the forest and grassland ecosystems located on similar Entic Podzols (Arenic) in the same bioclimatic coniferous–deciduous forest zone. The following parameters were considered in the examined models: mean monthly soil or air temperatures (Tsoil and Tair), amount of precipitation during the current (P) and the previous (PP) months, and the storage of soil organic carbon (SOC) in the top 20 cm of soil. The weighted non-linear regression method was employed to estimate the model parameters for the normal, wet, and dry years. To increase the magnitude of the model resolutions, we controlled the slope and intercept of the linear model comparison between the measured and modeled data through the change in R0—CO2 efflux at Tsoil = 0 °C. The mean bias error (MBE), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and determination coefficient (R2) were employed to assess the quality of the model’s performance. The measured Tsoil, Tair, and P, as well as the litter (for forest) or sod (for grassland) horizon (modeled by the Soil SCLmate Statistical Simulator (SCLISS)), and soil temperatures (Tlit_m, Tsoil_m) and moistures (Mlit_m, Msoil_m), were used for SR simulation. For the CO2 efflux in the forest ecosystem with the lower SOC availability for mineralization, the direct Tsoil and Tair measurements in combination with SOC storage provided better parameterization for the empirical TPPC model. For the CO2 efflux in the grassland ecosystem with the high SOC availability for mineralization, the temperature became the governing factor, and the TPPrh model provided better performance over all the considered models. The model’s performance was the best for the wet years, and the worst for the dry years for both ecosystems. For forest ecosystems, the model performance for average precipitation years was equivalent to that in wet years. For grassland ecosystems, however, the model performance was equivalent to that in dry years due to differing exposure and hydrothermal regimes. The wet-year R0 obtained for both forest and grassland ecosystems differed from the normal- and dry-year values. The measured SR values relevant for the R0 estimations distribute along the precipitation range for the forest and along the temperature range for the grassland. The SCLISS-modeled Tlit_m and Mlit_m provide good alternatives to direct atmospheric measurements, and can be used as initial temperature and moisture data for CO2 efflux modeling when direct soil and moisture observations are not available on site.
1. Introduction
CO2 efflux (SR) and its modulation by climate change is a useful indicator of CO2 assimilation and utilization by plants [1], as well as CO2 release by the microbial decomposition of organic matter—reflecting the main pathways of carbon through terrestrial ecosystems [1,2,3,4] and soil organic carbon (SOC) decomposition [5]. CO2 efflux is the sum of two major parts—the respiration of autotrophs (Ra), i.e., plant roots with rhizosphere microorganisms, and the respiration of heterotrophs (Rh), decomposing soil organic matter (SOM). The contribution of both CO2 sources to the total CO2 efflux during the year varies from 10% to 90% [4,6,7].
The ecosystem types—forest vs. grassland—are important for the modulation of temperature and moisture regimes [8], whereas the quality of SOM and the composition of the soil microbial community modify their effects [9,10,11]. The ecosystem types are also characterized by specific litter or sod horizon decomposability values [12,13,14], governed by the differences in the C/N ratio and lignin content, which are higher for forests and lower for grasslands. All these directly affect CO2 efflux differences between forest and grassland ecosystems [15,16,17].
Due to the high spatial heterogeneity of CO2 effluxes and several practical limitations, it is impossible to allocate sufficient resources to cover large areas with field measurements [5]. One way to estimate CO2 effluxes is through modeling, which is an important alternative to direct chamber measurements [18,19]. At the same time, it is possible to consider simple empirical models using temperature (T) and precipitation (P) [16,20], as well as complex dynamic models based on the simulation of processes occurring in the soil [5,20,21,22].
Both CO2 efflux measurements and applications of empirical CO2 efflux models demonstrate a strong dependence of CO2 efflux on temperature [8,20,23,24,25,26,27], moisture [20,28,29,30], precipitation [19,20,31,32,33] and throughfall [34,35], soil water table changes [36], aboveground biomass partitioning [37,38], SOC quality and quantity [38,39,40,41,42,43], soil properties [11,43,44], and microbial community composition [45].
Raich and Potter (1995) [20] suggested that soil temperature and moisture are better data sources than meteorological data for empirical CO2 efflux modeling because the microbial activity should be directly related to these soil properties. If such measured data sources are not available at a site, they can be modeled using the meteorological conditions and budget modeling schemes such as SCLISS (Soil CLImate Statistical Simulator) [46]. The soil temperature and moisture modeling could be used to select the appropriate soil depth and the respective horizon that could be important to identify the sources of CO2 efflux and the appropriate CO2 efflux modeling approaches [25,47]. On the other hand, in dynamic models, such as RothC or Century, the soil moisture effect is obtained from the balance between the precipitation and potential evaporation. Due to the higher soil moisture–precipitation correlations at scales greater than daily [48], it is common to use precipitation as a proxy for moisture on the monthly scale [20,49,50].
Researchers emphasize that models need to be used only within their intended scope [51] and at the right spatial and temporal scales [52]. Empirical model research usually focuses either on a specific model or on the unrelated sets of models [25,33,36,37]. The novelty of the presented approach to empirical modeling is in using the ensembles of CO2 efflux models to investigate their applicability to weather-specific conditions depending on soil and ecosystem types. Our previous research has shown that the ensemble approach allows the direct comparison of models in order to investigate their conditional performance in an attempt to find the best models in ensembles [43,44,53]. It is shown that the combination of ensemble models as a function of temperature, precipitation and soil organic carbon allows us to reveal model dependencies and to generate soil- and weather-specific model combinations for two forest ecosystems with Entic Podzol and Haplic Luvisol [43,44]. In particular, it is important to use soil temperature (Tsoil) to estimate CO2 efflux during the cold period (Tsoil ≤ 2 °C), when soil temperatures mainly fluctuate around zero (−3 ≤ Tsoil ≤ +2 °C), while air temperatures are lower and fluctuate over a much larger range (−12 ≤ Tair ≤ +8 °C).
For this study, we apply the ensemble of empirical CO2 efflux models to the forest and grassland ecosystems on similar Entic Podzol, located in the same temperate continental climate zone, to investigate how the differences in ecosystem type, weather and soil conditions, and their effects on CO2 efflux, can be addressed by the model ensembles. We hypothesize that the accuracy of the modeling and quantification of the parameters of the applied models will be affected by the level of moisture during the year (wet, normal or dry). We also propose that interannual variability in tree and grass respiration due to differences in temperature, moisture and root allocation may highlight the role of soil horizons involved in CO2 efflux [42], and also affect simulation results. By modeling the litter (for forest) or sod (for grassland) horizon, and the soil temperature (Tlit_m, Tsoil_m) and moisture (Mlit_m, Msoil_m), with the SCLISS model, we evaluate which of the modeled values can adequately substitute measured soil temperatures and precipitation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The forest and grassland sites are located on similar sandy Entic Podzol (Arenic) [54] (54°54′ N, 37°33′ E) in the coniferous–deciduous (mixed) forest zone of Prioksko-Terrasny Nature Biosphere Reserve on the left (northern) bank of the Oka River. The distance between these two sites is about 160 m, with an elevation difference of 4 m. There is a gentle 2-degrees slope in the east–west direction from the forest site toward the grassland site and toward the nearby small river Sushka (see Figure S1 in the Supplementary Materials). This produces a difference in the site water regimes as the ground water is closer to the grassland surface, where the soil profile demonstrates gleyic colors beyond 70 cm depth due to the stagnic conditions (Figure 1b), providing the grassland site with additional moisture. The forest site is much drier, and there is no gleyic color in the soil profile until a 1 m depth (Figure 1a).

Figure 1.
Forest and grassland sites’ soil profiles: (a) For the forest site, (b) for the grassland site; the gleyic color below 70 cm depth is due to the stagnic water conditions for the grassland site.
The climate is temperate continental with an average annual air temperature of 4.8 °C, an average summer temperature of +17.6 °C (max 38–39 °C), and an average winter temperature of −8.3 °C (min −43 °C in 1978) over the period 1973−2023. The average precipitation is 671 mm (max 91 mm in July); the duration of the seasonal snow cover period is 133 days, with an average snow depth of 52 cm; the vegetation season lasts 186 days (https://pt-zapovednik.org/fiziko-geograficheskie-usloviya/, long-term meteorological observations from the Complex Background Monitoring Station near Danki settlement (hereafter Danki’ Monitoring Station) (red mark, Figure S1, accessed on 7 March 2024)).
2.2. Soils and Data Description
The Entic Podzols in forest and grassland ecosystems are characterized by a similar sandy texture (Table 1), which provides good drainage and low water-holding capacity of about 40.5% (for disturbed soil samples) [19]. The topsoils of both studied ecosystems are characterized by similar values of pHKCl and N stocks, while the C stock is higher in the forest soil compared to the grassland soil (Table 1). The strongest difference between the studied soils is in the C/N ratio, which is about 1.5 times higher for the forest soil, making the SOC of the upper horizons less available for microbial decomposition than that of the grassland due to the N limitation.

Table 1.
Basic soil properties (0–10 cm) of the forest and grassland sites (mean values ± standard error, SE are shown).
We used 25-year-long CO2 efflux time series that were collected at these sites [13,14] and measured once a week using the closed chamber method. The standard approach to gas measurements is to collect syringe samples at the sites and analyze CO2 concentrations by gas chromatography in the laboratory [18]. Simultaneously with the CO2 efflux, the soil temperature (Tsoil) at a 5 cm depth and the air temperature at a 1 m height were measured at the sites. Monthly averaged data for the air temperature (Tair) and precipitation (Prec) were collected from the Danki’ Monitoring Station located at the grassland site. All the data were quality-checked and averaged on a monthly basis to be fitted into the models.
The monthly averaged T and P data were also used to separate the years of the measurements into “wet”, “dry”, and “normal” by applying the following indices to the data:
Selyaninov hydrothermal coefficient—HTC = ∑ P/ ∑ T/ 10, when T > 10 °C (HTC6–8—summer period, June to August) [16,55];
Wetness Indexes—WI = lg (∑ P/∑ T) (WI5–8 and WI5–9 for May to August and May to September, respectively) [16].
Based on the ±STD (standard deviation) for these indices, the following 5 years were classified as “wet”—1999, 2003, 2006, 2008 and 2020; the following 9 years were classified as “dry”—2002, 2007, 2010, 2011, 2014, 2015, 2018, 2021 and 2022; and the remaining 11 years remained “normal”—1998, 2000, 2001, 2004, 2005, 2009, 2012, 2013, 2016, 2017 and 2019.
2.3. Empirical Model Descriptions
The following empirical CO2 efflux (SR) models are part of the ensemble:
Linking SR to [18],
Linking SR to and [18,20,33],
Linking SR to , , and [43,44],
where (g C m−2 day−1) is the CO2 efflux at Tsoil = 0 °C and normal moisture conditions. When is defined, the rest of the model parameters can be sequentially computed using nonlinear regression, as follows: and are the temperature coefficients; is the half-saturation constant between SR and ; is the precipitation redistribution coefficient between the current () and previous () months; is the half-saturation constant between SR and .
2.4. The Parameter Identification Procedure
For identification, we followed the procedure of [43,44,56] based on the intercept minimization technique (see Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials) with the weighted non-linear fitting of the ensemble equations (Equations (1)–(5)). In general, the CO2 efflux empirical model with slope < 1 and intercept > 0, used for the linear comparison between the measured and modeled data, underestimates the extremely large (summer) and small (winter) values. As the intercept moves to zero (intercept → 0+), the , representing the small soil-temperature-related CO2 efflux values, moves to the expected CO2 efflux value at Tsoil = 0 °C (see Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials). This procedure is particularly suitable for winter CO2 efflux modeling [43,44,56].
2.5. Soil CLImate Statistical Simulator Model (SCLISS)
The SCLISS model [46] was used to estimate the soil and the litter or sod horizon temperatures and moisture contents, which were fitted to the ensemble of the CO2 efflux models (Equations (1)–(5)). This simulator is actively used in the ROMUL and EFIMOD models [21,22,57] to provide estimates of soil temperature and moisture from meteorological observations, and to generate long-term climate data simulations (http://www.ecomodelling.ru/models/scliss, accessed on 23 February 2025).
3. Results
3.1. Robust SCLISS Litter or Sod Horizon and Soil Temperature Dependencies
The merits of the SCLISS model can be observed through a comparison of the SCLISS-simulated soil and litter (forest) or sod (grassland) horizon temperatures (Tlit_m and Tsoil_m, red and blue lines, Figure 2) with direct measurements of the soil (Tsoil) and air (Tair, black circles and lines) temperatures.
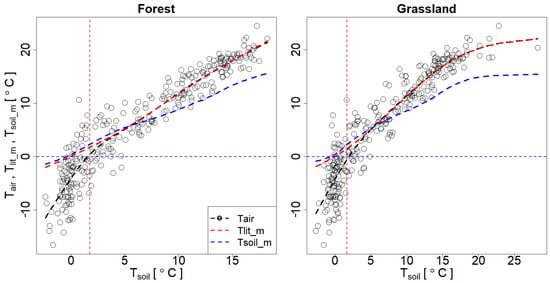
Figure 2.
Comparison among the measured air (Tair, black circles and lines) and SCLISS-modeled litter/sod and soil (Tlit_m, red lines; Tsoil_m, blue lines) temperatures with the measured soil temperature (Tsoil) for forest and grassland sites; the vertical dashed line is the Tsoil = 2 °C threshold when the average Tair = 0 °C.
During the cold period, the values of Tlit_m and Tsoil_m (red and blue lines, respectively, Figure 2) were found to be close to the measured soil temperature and higher than the air temperature. As the soil temperature increased towards the warm period, the Tlit_m (red line) followed the Tair (black circles and lines), indicating that the air was warming up at a similar rate to the topsoil (litter or sod horizon). Conversely, the Tsoil_m becomes lower than the Tair, indicating that deeper soil horizons maintain lower temperatures than the air.
The main difference between Tsoil and Tair is observed at the grassland site when Tsoil > 20 °C: Tsoil increases continuously due to direct solar heating. The corresponding Tair and air-heating are limited, possibly due to the shift in the heat balance and Bowen ratio during the growing season [58,59] towards active evapotranspiration from the grassland surface. This directly affects the CO2 efflux results when comparing forests with grassland.
During the cold period, the air temperature (−20 < Tair < 0 °C) is usually lower than the soil temperature (−4 < Tsoil < 1 °C). Both forest and grassland have the same Tsoil = 2 °C threshold (vertical dashed lines, Figure 2) when the Tair fluctuates around zero (see also [43]), which affects the respective estimates. At the same time, the modeled Tsoil_m and Tlit_m are close to Tsoil = 2 °C. These observations ensure that both Tsoil_m and Tlit_m are valid proxies for the Tsoil measurements.
Regarding the use of SCLISS-modeled litter or sod horizon and soil moisture (Mlit_m, Msoil_m (% by volume)) instead of precipitation (Figure 3a), both moisture values differ depending on soil depth. The litter or sod horizon is directly affected by evaporation, and its moisture level (red circles, Figure 3) is much lower than for the deeper soil horizons (blue circles, Figure 3), where Msoil_m is defined as the average moisture in the soil layer up to 1 m deep. The modeled litter or sod horizon moisture is closer to the soil moisture (W (% mass)) measured at the grassland site (Figure 3b) than the modeled soil moisture. We can try to use the model’s quality results to select the best moisture source. This is expected to have a direct impact on the CO2 efflux modeling results. The direct conversion between moisture values by volume and by mass is performed using soil bulk density, which is close to unity for sandy soils [60], justifying the direct comparison in Figure 3b for Entic Podzol.

Figure 3.
Comparison of the SCLISS-modeled litter or sod horizon (Mlit_m) and soil (Msoil_m) moisture with measured precipitation (Prec) at Danki (a) and measured soil moisture (W, % by mass) at the grassland site (b): red circles—Mlit_m (% by volume); blue circles—Msoil_m (% by volume).
Furthermore, the rationale underlying the comparability of the modeled CO2 efflux results to the measured precipitation (mm) and SCLISS-modeled litter and soil moistures (% by volume) is the dimensionlessness of the Michaelis–Menten (hyperbolical limitation) precipitation/moisture term utilized in the selected CO2 efflux model realizations (Equations (1)–(5)).
3.2. The Parameter Selection and Condition Comparisons
Following the standard procedure, we initiated the identification by selecting CO2 efflux in the 0 < Tsoil < 1 °C temperature range in the autumn–winter period, when freezing is absent. This range was selected for the estimation of , a crucial dimensional parameter in Equations (1) through (5). The was then estimated through the application of an intercept minimization technique, which sets the intercept → 0+ (see Figure S2). The values were estimated for the entire study period and divided into three distinct categories: normal, dry, and wet conditions (see Table 2). At this Tsoil range, the CO2 efflux remained consistent for both forest and grassland sites, ranging from 0.1 to 1.8 (g C m−2 day−1). This consistency enabled the direct inter-comparison of the obtained values.

Table 2.
The parameter (the CO2 efflux at Tsoil = 0 °C and normal conditions, g C m−2 day−1) selection for the single model over all years (all-years) and for the condition-specific models: normal, wet, and dry years; range—maximal difference among the condition-specific models.
Using the measured Tair−Prec and modeled Tlit_m−Mlit_m and Tsoil_m−Msoil_m combinations for the model initializations (Equations (1)–(5)), we obtained analogous distributions among the values for both forest and grassland sites. The parameter values were the largest for the wet years, and they were smaller and closer to each other for the normal and dry years. However, the directly measured combinations of Tsoil−Prec for the forest site exhibited an exception, whereby the wet-year value was the smallest. The all-years value generally remained within or close to the bounds of the respective condition-specific models, with the exception of the Tsoil_m−Msoil_m combination, where the all-years value was smaller than the respective condition-specific range values.
For both forest (left, Figure 4 and Figure 5) and grassland (right, Figure 4 and Figure 5) sites, lower temperatures (blue and green colors on CO2 efflux dots, Figure 5) and lower precipitation (red and brown colors on SR dots, Figure 4) reduced CO2 efflux (colored dots), affecting the estimates (colored lines).
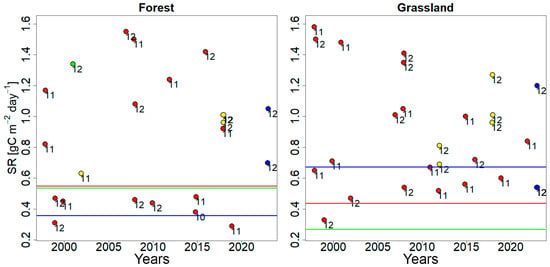
Figure 4.
Measured CO2 efflux (SR)–precipitation (Prec) dependency for the 0 < Tsoil < 1 °C for Entic Podzol under forest (left) and grassland (right) with the obtained R0 (g C m−2 day−1) for normal (green), dry (brown), and wet (blue) years—horizontal lines. Labels show months with their monthly precipitation: red (11 < Prec < 34 mm), brown (34 < Prec < 57 mm), yellow (57 < Prec < 80 mm), green (80 < Prec < 103 mm), and blue (103 < Prec <126 mm); numbers near colored cycles show individual values in October (10), November (11) and December (12).

Figure 5.
Measured CO2 efflux (SR)–soil temperature (Tsoil) dependency for the 0 < Tsoil < 1 °C for Entic Podzol under forest (left) and grassland (right) sites with the obtained R0 values (g C m−2 day−1) for normal (green), dry (brown), and wet (blue) years—horizontal lines. Labels show months with their measured soil temperatures: blue (0 < Tsoil < 0.2 °C), green (0.2 < Tsoil < 0.4 °C), yellow (0.4 < Tsoil < 0.6 °C), brown (0.6 < Tsoil < 0.8 °C), and red (0.8 < Tsoil < 1 °C); numbers near colored cycles are individual in October (10), November (11) and December (12).
For the forest site, the value maintains a narrow range for Tair−Prec (approximately 10%, Table 2) that is contingent on annual weather conditions (normal—green, wet—blue, dry—brown, Figure 4 and Figure 5), aligning with our prior findings [43]. Conversely, for the grassland site, the range in the estimate extends to 55% for Tair−Prec (Table 2), denoting pronounced impacts of weather conditions on the model performances at near-zero temperatures.
The findings can be corroborated by the correlations between CO2 efflux and Tsoil and CO2 efflux and Prec for the forest ecosystem, as well as between CO2 efflux and Tlit_m for the grassland ecosystem, within the respective 0 < Tsoil < 1°C temperature range (see Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials). In this case, CO2 efflux directly correlates with both Tsoil and Tlit and Prec. For the forest ecosystem, precipitation has been demonstrated to be a pivotal factor (Cor(SR,Prec) = 0.42, p-value = 0.04), as evidenced by the observation of the smallest Prec-related ranges in the forest ecosystem (see Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials). In the case of the grassland CO2 efflux, the litter or sod horizon temperature emerges as a pivotal factor (Cor(SR,Tlit_m) = 0.53, p-value = 0.003). This observation is accompanied by the observation of the smallest Tlit_m and Tair related ranges for the grassland, as illustrated in Table 2. The precipitation at the forest site and the sod horizon temperature at the grassland site both exhibited Pearson correlation coefficients with p < 0.05.
As previously mentioned, the groundwater level at the grassland site (downhill) is significantly closer to the surface compared to the forest site (uphill), suggesting that precipitation, particularly in the form of throughfall, may play a crucial role in influencing forest CO2 efflux. In summary, the observed differences in the obtained estimates and CO2 efflux correlations could be attributed to soil water content and SOC availability (lower in the forest and higher in the grassland), the location of root biomass (deeper in the forest and shallower in the grassland), and soil protection from direct exposure to solar radiation by the forest ecosystem.
3.3. Applying the Measured Temperatures and Precipitations and the SCLISS-Modeled Temperatures and Moistures for the Modeling of CO2 Efflux from Soil
Two models from the ensemble set (Equations (1)–(5))—TPPC and TPPrh—demonstrated the best performance, a finding that aligns with our prior observations [43]. The TPPC model (Equation (5)) exhibited sensitivity to SOC availability, while the TPPrh model (Equation (4)) demonstrated sensitivity to the variation in warm-season CO2 efflux driven by temperature. To assess the impact of weather conditions (norm, dry, wet) and measured and modeled temperatures (Tsoil, Tair, Tlit_m, Tsoil_m) and moistures (Prec, Mlit_m, Msoil_m) on the performance of the selected model, four metrics were employed—the R2 and the slope of the linear model, MBE, and RMSE.
Additionally, we compared the performances of all-weather models across the entire range of years and conditions (TPPC or TPPrh) with the performances of condition-specific combined models (TPPC_nwd or TPPrh_nwd), i.e., for normal (n), wet (w), and dry (d) years, separately. The findings reveal that the combined models (red lines, Figure 6 and Figure 7) consistently outperformed the all-weather models (green (n), orange (d), and blue (w) lines, Figure 6 and Figure 7) across all metrics (see Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials). The performances of the weather-specific models during normal, dry, and wet years are comparable to each other and to that of the combined model (red lines, Figure 6 and Figure 7). For both forest (left) and grassland (right) ecosystems, the all-weather models underestimate during normal years (green, TPPC_n and TPPrh_n) and overestimate during dry years (orange, TPPC_d and TPPrh_d). The estimates of the all-weather models for wet years (blue, TPPC_w and TPPrh_w) align with those of the condition-specific combined models (TPPC_nwd or TPPrh_nwd), indicating consistency with previously reported results [16,17,22]. This finding underscores the notion that the optimal model performance in wet conditions is concomitant with weather-specificity.
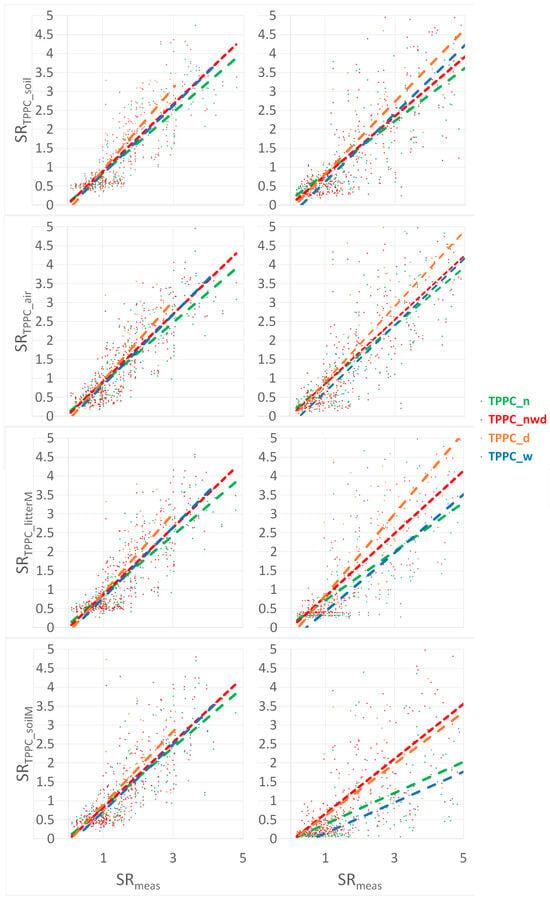
Figure 6.
The TPPC model CO2 efflux comparisons (SRTPPC) between the weather-specific model (red) and the all-weather model (green for normal, brown for dry, and blue for wet conditions) against the measured CO2 efflux data (SRmeas) with the respective regressions; for the measured soil and air and modeled litterM and soilM parameterizations; for the forest (left) and the grassland (right).
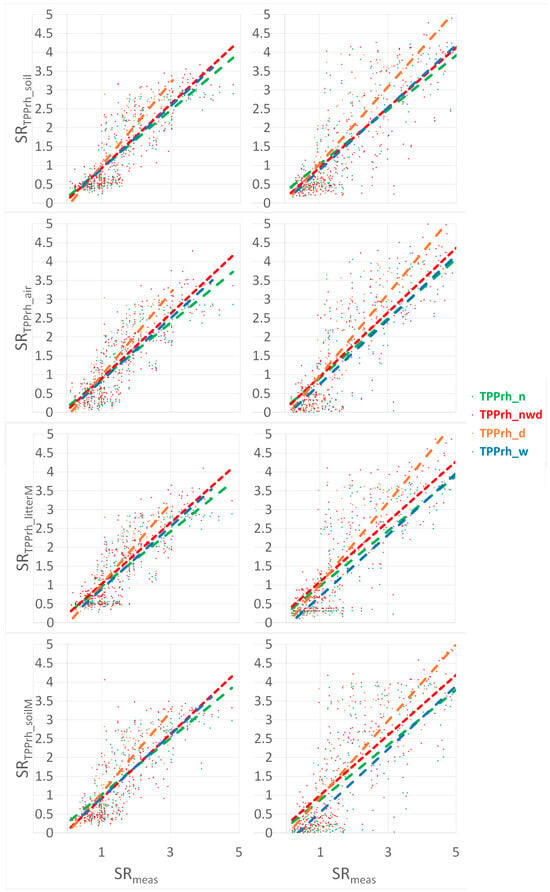
Figure 7.
The TPPrh model CO2 efflux comparisons (SRTPPrh) between the weather-specific model (red) and the all-weather model (green for normal, orange for dry, and blue for wet conditions) against the measured CO2 efflux data (SRmeas) with the respective regressions; for the measured soil and air and modeled litterM and soilM parameterizations; for the forest (left) and the grassland (right).
For the forest site, the combinations parameterized by measured Tsoil−Prec (soil), Tair−Prec (air), and modeled Tlit_m−Mlit_m (litterM) demonstrate favorable outcomes across all metrics. The TPPC_nwd condition-specific model exhibits a general superiority, contingent upon the availability of SOC in the slope, R2, and RMSE (refer to Table S2 in the Supplemental Materials). For the grassland site, the same parameterization combinations prevail; however, the best model is shown to be the TPPrh_nwd–Raich–Hashimoto-type condition-specific model with quadratic temperature dependency. This discrepancy can be attributed to variations in soil organic carbon (SOC) content and temperature. In high-C/N-ratio forest soil, SOC availability becomes the limiting factor, thereby favoring the TPPC-type models. Conversely, in grassland soil, high Tsoil and Tair values (see Figure 2) act as the limiting factor, thus supporting the findings of the TPPrh-type models.
A comparison of the performances in terms of temperatures (Tlit_m, Tsoil_m) and moistures (Mlit_m, Msoil_m) data (litterM and soilM, Figure 6 and Figure 7) modeled by SCLISS revealed that, for both forest and grassland, parameterization with the litter or sod horizon temperature and moisture (Tlit_m−Mlit_m) provides superior results in all metrics (R2, slope, MBE, and RMSE) in comparison to parameterization with the deeper-horizon soil temperature and moisture (Tsoil_m−Msoil_m) (see Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials). This finding suggests that the main source of soil CO2 efflux should be the topsoil litter or sod horizon, rather than the deeper soil.
For both forest (Figure 8) and grassland (Figure 9) ecosystems, the TPPC_nwd models demonstrate superior performance during cold winter periods, while exhibiting overestimation during warm periods. In contrast, the TPPrh_nwd models generally underestimate in winter and exhibit enhanced performance in summer. The Tlit_m−Mlit_m parameterized models (orange) demonstrate consistent superiority over the Tair−Prec parameterized models (blue) during winter periods, aligning with the Tsoil−Prec parameterized models (red). Furthermore, these Tlit_m−Mlit_m parameterized models exhibit reduced overestimation during summer (warm) periods when compared to the Tsoil−Prec parameterized models.
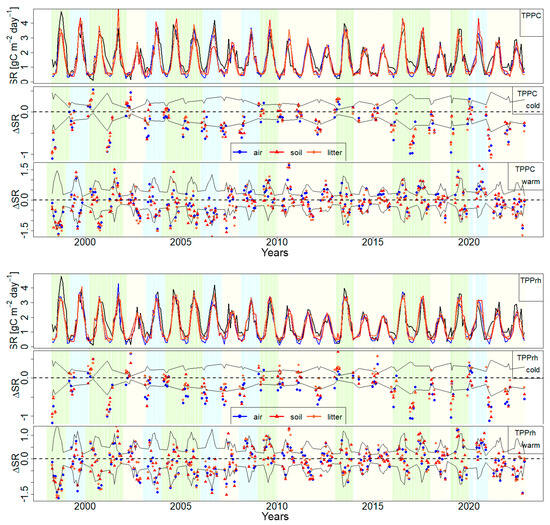
Figure 8.
Comparison of the weather-specific TPPC_nwd (top) or TPPrh_nwd (bottom) model performances parameterized by the Tair−Prec (blue), Tsoil−Prec (red), and Tlit_m−Mlit_m (brown) and their variations from the measurements taken for the cold and warm periods for the forest site; measured CO2 efflux—the thick black line; spatial variability of measurements—the thin black lines; normal (light green), dry (beige), and wet (light blue) years.

Figure 9.
Comparison of the weather-specific TPPC_nwd (top) or TPPrh_nwd (bottom) model performances parameterized by the Tair−Prec (blue), Tsoil−Prec (red), and Tlit_m−Mlit_m (brown) and their variation from the measurements taken for the cold and warm periods for the grassland site; measured CO2 efflux—the thick black line; spatial variability of measurements—the thin black lines; normal (light green), dry (beige), and wet (light blue) years.
During periods of elevated temperature, CO2 effluxes parameterized with the Tair−Prec (blue) and Tlit_m−Mlit_m (orange) are predominantly constrained by the values of the spatial variability measurements (representing approximately 30% of the CO2 efflux in absolute terms). The TPPC model demonstrates a broader range of modeled values than the TPPrh model. The Tsoil−Prec (red) parameterization is notable for being an outlier in grassland sites. During cold periods, the Tair−Prec (blue) parameterization frequently resides below the bounds of spatial variability, a phenomenon particularly evident in TPPrh models for both forest and grassland sites.
A further comparison of the TPPC and TPPrh models depending on moisture conditions (normal, wet, and dry years (see Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials)) has revealed that the best model performances, as indicated by the highest R2 and slope values, were achieved in wet conditions for both forest and grassland CO2 efflux, provided that temperatures did not reach extreme values. Conversely, the dry conditions exhibited the poorest model performance in both R2 and slope, a phenomenon potentially attributable to the highest temperatures and evaporation rates observed in these years.
For the forest ecosystem, the normal and wet conditions demonstrated comparable model performance. However, for the grassland ecosystem, the model results for normal conditions deteriorated as the conditions transitioned to dry, indicating variations in water demand and temperature when soil is directly exposed to sunlight.
In wet years, the utilization of modeled litter or sod horizon values (Tlit_m−Mlit_m) yields the best results for both TPPC and TPPrh models. Conversely, in years with normal or dry conditions, the performance of modeled litter or sod horizon values is marginally inferior to that of air parameterized values (Tair−Prec).
During the cold period identified by the Tsoil ≤ 2 °C threshold (see Figure 2, vertical dashed lines), the TPPC_nwd model demonstrated superior performance in both R2 and RMSE when utilizing the Tsoil−Prec, Tair−Prec, and Tlit_m−Mlit_m parameterizations (see Table S4). The TPPC_nwd parameterized with the modeled Tlit_m−Mlit_m is comparable to the TPPrh_nwd parameterized with the measured Tsoil−Prec and Tair−Prec. The Tsoil_m−Msoil_m parameterization demonstrates a substantial decrease in performance compared to the Tlit_m−Mlit_m one, indicating that the primary source of SR is the litter or sod horizon.
This result aligns with the earlier discussion on Tlit_m−Mlit_m (see Tables S3 and S4). Collectively, the findings from this analysis, in conjunction with the SCLISS model, suggest that parameterization using Tlit_m−Mlit_m, representing the modeled temperatures and moisture of litter or sod, is a viable alternative when direct soil temperature and moisture observations are not accessible on-site.
4. Discussion
4.1. Weather Conditions Affect the Modeling Quality
The dependencies of Q10 on hydrothermal conditions [16,17,19] demonstrate the significant impact of weather conditions on the variability of Q10 coefficients. The temperature–precipitation distributions for normal, wet, and dry conditions (green, blue, and brown dots, respectively, for monthly values; Figure 10) illustrate that wet years (blue) exhibit the highest precipitation levels within the T > 10 °C temperature range. Conversely, dry years (brown) are marked by the lowest precipitation levels, while normal years (green) exhibit a more balanced precipitation distribution. The precipitation patterns exhibit uneven distribution across years, with wet years (classified by Wetness Indexes during warm periods) typically experiencing the least precipitation (driest conditions) during cold periods (Tair < 0 °C).
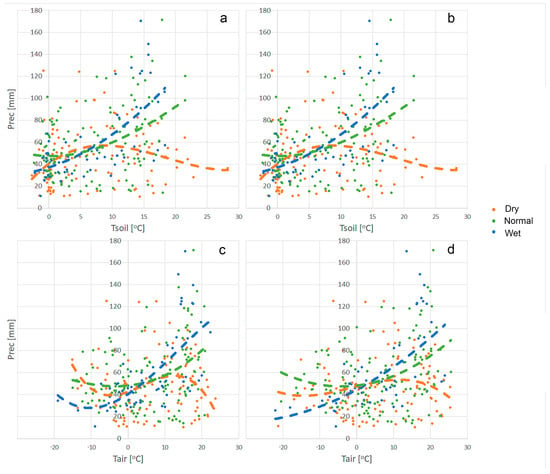
Figure 10.
Monthly precipitation distribution over the monthly temperature range of soil (a,b) and air (c,d) during the year for the normal (green), dry (brown), and wet (blue) years; colored dots—individual monthly measurements; colored lines—trends for the respective conditions; for forest (left) and grassland (right).
The wet years demonstrate the highest correlation between monthly values of Tsoil (Tair) and amount of precipitation, while for the dry years, this correlation is practically absent, and for the normal years, it is in between (Table 3). For both normal and especially wet years, the correlations are significant (p-value < 0.05), signaling that the monthly temperatures are directly modulated by precipitation. As anticipated, these correlations are more pronounced for soil temperatures, given that soil serves as a storage medium for precipitation-derived moisture, and is directly influenced by the latent cooling from evaporation.

Table 3.
Correlations between mean monthly temperature (Tsoil, Tair) and monthly precipitation (P) for the normal, wet and dry years.
The identified correlations between monthly values of Tsoil (Tair) and precipitation amount directly affect the quality of the model, depending on the weather conditions. To determine the significance (F > fcr; p-value < 0.05) of this weather-related distinction for the models’ performances in terms of both increases in determination (R2) and decreases in uncertainty (RMSE), one-way ANOVA testing was conducted. The analysis utilized data sets from models parameterized by air (a), soil (s), and litter (ml) from Table S3, exhibiting analogous responses. For the forest, the distinctions by both R2 (F = 12 > fcr = 3.5; p-value = 0.0003) and RMSE (F = 3.6 > fcr = 3.5; p-value = 0.045) are significant. A similar outcome can be observed in the grassland, where the distinctions by both R2 (F = 11 > fcr = 3.5; p-value = 0.0005) and RMSE (F = 11.6 > fcr = 3.5; p-value = 0.0004) were found to be significant.
The findings of this study corroborate the prevailing dependence of CO2 emission on temperature [8,20,37], and its secondary dependence on humidity/precipitation [20,28,29,30]. The influence of vegetation as a regulator of the hydrothermal conditions of soils for our sites is evident in the differences between forests and grasslands only in certain years (see Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials). For both ecosystems, the optimal modeling outcomes in terms of R2 and RMSE are evident in wet years, while the poorest outcomes are observed in dry years. However, in years with normal moisture conditions, the model performance varies by vegetation type. For the grassland site, the model results in normal conditions are analogous to those in dry years. Conversely, for the forest site, the model results are marginally worse than in wet years, and comparatively better than in dry years.
The enhanced predictive ability in wet conditions can be attributed to the prevailing temperature dependency [8,20] and the enhanced coupling between precipitation and soil moisture across all the examined models. Conversely, the deterioration in predictive ability during dryer periods, characterized by uncoupled precipitation and temperature, can be linked to the disconnection between precipitation and soil moisture, consistent with the observations of Raich and Potter regarding the effects of moisture and precipitation on empirical modeling [20].
4.2. Distributions of the Measured CO2 Efflux Relevant for the Weather-Specific R0 Estimations
For all models that were examined, is a pivotal parameter that exerts a considerable influence on the slope of the linear regression between the measured and simulation values, as well as on the overall modeling accuracy [18,61]. The obtained values ranged from 0.25 to 0.75 (g C m−2 day−1), contingent on the yearly conditions, and were approximately two times smaller than the prior estimates. For instance, the early version of the T&P model suggested an value of 1.334 [17]. However, subsequent modifications to the model’s parameters, aimed at enhancing the simulation outcomes, employed an value of 1.250 [61]. Our estimates are also within the same range as the direct CO2 efflux measurements for these sites when Tsoil ≈ 0 °C and under fair weather conditions, which increases the reliability of our method (Section 2.4).
As demonstrated in Figure 11, the most pertinent CO2 efflux measurements for the derived values are predominantly situated within the range of 0 < Tsoil < 0.4 °C and Prec < 80 mm per month (colored ellipses for normal, wet, and dry conditions) for both forest and grassland ecosystems. For example, the values obtained for the normal and dry conditions are practically indistinguishable, while the values obtained for the wet conditions are clearly distinguishable. For the forest ecosystem, the wet value is located in the region of higher precipitation, highlighting the expected dependence of Entic Podzol CO2 efflux on precipitation that was described previously [43,44,56]. For the grassland ecosystem, the wet value is actually located in the region of higher soil temperature, highlighting the general CO2 efflux–temperature dependence. At the same time, for both normal and dry conditions, the relevant CO2 efflux for forest is less temperature-restricted, and for grassland is less precipitation-restricted (extended along the respective axes of the shaped ellipses), than the relevant CO2 efflux for wet conditions.
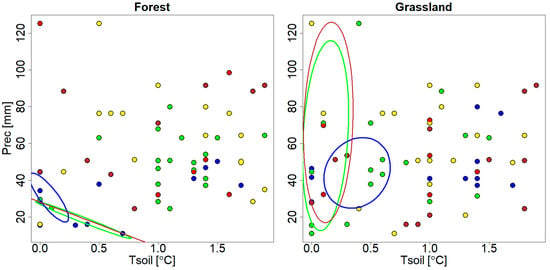
Figure 11.
Soil temperature (Tsoil)–precipitation (Prec) diagram of the measured CO2 efflux (SR) (colored dots) (g C m−2 day−1): blue (0.1 < SR < 0.51 °C), green (0.51 < SR < 0.92 °C), yellow (0.92 < SR < 1.34 °C), brown (1.34 < SR < 1.75 °C), and red (1.75 < SR < 2.16 °C). Ellipses—confidence (40%) locations of the -related measured CO2 efflux clouds for the normal (green), wet (blue), and dry (brown) conditions.
The results obtained in this and the previous sections fully support our hypothesis that the humidity during the year (wet, normal or dry) affects both the accuracy of the empirical models and the quantification of the parameters of the models applied.
The presented relevant CO2 efflux distribution results (ellipses, Figure 11) provide quantifications of the temperatures and precipitation (also depending on the water availability in the soil) applicable for the selection of the sets of CO2 efflux measurements for the correct estimations (Table 4). They show that the standard approach, where the selection of measurements is made when 0 < Tsoil < 1 °C and without consideration of precipitation, is generally too broad, and potentially overestimates the weather-specific (see [17,62]).

Table 4.
Monthly averaged temperature and precipitation ranges used to select applicable CO2 efflux measurements for the respective R0 estimations depending on weather conditions.
These relevant CO2 efflux distribution results (ellipses, Figure 11) are also consistent with our previous observation of the differences in values due to the different levels of water availability in the forest (drier) and grassland (wetter) sites caused by the sloping terrain orography at the sites, as well as the results from Section 3.3. This highlights the importance of considering the indirect effects of orography on changes in CO2 efflux, which are modified by weather conditions.
4.3. The Weather-Specific Effects and the Model Performances for Different Models and Forest Soils in the Same Climate Zone
According to our hypothesis, we showed that the weather-specific CO2 efflux models (both TPPC_nwd and TPPrh_nwd), parameterized separately for normal (n), wet (w) and dry (d) years, give better results in all (R2, slope, MBE and RMSE) metrics compared to the single all-weather models parameterized over the whole range of years. All models perform better in wet years and worse in dry years, consistent with previous research [16,17,37]. In contrast, the normal year performances differ between the ecosystems. For the forest, the normal-year statistics coincide with the wet-year statistics, while for the grassland, the normal-year statistics coincide with the dry-year statistics. This fact could be explained by the possible difference in radiation exposure and soil water regime between these sites. Similar results were observed when using the simple linear dependencies between lnSR and Tsoil (or Tair) [16,17,19]. The Q10 values for the same CO2 efflux data (20–25 year rows) were lowest for dry years and much higher for normal and wet years. Water availability, determined by aridity/humidity conditions during the growing season, was a key driver of the interannual and seasonal variability of Q10 values in temperate forest ecosystems [16]. Moisture limitation suppresses microbial activity regardless of temperature, resulting in a reduction in the temperature effect on CO2 efflux rate [63]. Thus, soil moisture limitation makes CO2 efflux insensitive to temperature increase [64,65], thus reducing the accuracy of the models tested.
We performed a comparison between the investigated TPPC empirical model, the Romul_Hum process-based model modeling heterotrophic respiration for the Haplic Luvisol (Siltic) [54] (54°50′ N, 37°34′ E) under the forest site [22], and two empirical T-models (Equation (1)) applied to the same Entic Podzol and Haplic Luvisol for the forest and grassland ecosystems [16,17]. All sites are located in the same climatic zone, but the ecosystems formed on Haplic Luvisol are located about 10 km south on the right (south) bank of the Oka River, and belong to the deciduous forest zone. We should note that the presented comparison is rather indirect, and should not be taken as quantitative (by absolute values), but only as qualitative (by relationships to each other), as the forests and soils are different.
In terms of the R2 (the predictive ability), there is a similarity between all the models for both forest and grassland sites. Namely, the best model results are shown for the wet years and the worst model results are shown for the dry years, while the normal- and all-weather models stayed in the middle (see Tables S5 and S6 in the Supplementary Materials). This highlights the common model trends whereby, under wet conditions, the microbial community should be in more comfortable conditions not affected by strong drying, with all models being better off and showing better predictive ability, with the total CO2 efflux modeling performance appearing independent of the soil type.
However, for both dry years and all years, the predictive abilities of the models are better on the Entic Podzol than on the Haplic Luvisol. The total CO2 efflux is the same in terms of slope—the Entic Podzol results are much closer to each other than the Haplic Luvisol results. As discussed earlier, these results may be more indicative of the general modeling challenge in dry conditions that actually occurred for all models, and especially for the Haplic Luvisol. We have already seen this situation occur in our previous research [43] when comparing these two soil types.
Note that the TPPC and T models were parameterized for weather conditions, whereas the Romul_Hum model was not modified for different weather conditions. The overall lower R2 (predictive ability) values for the temperature-only T model (see Tables S5 and S6 in the Supplementary Materials) compared to the more complex TPPC model may be due to the lower sensitivity of the model to changes in moisture regimes.
The comparisons of the CO2 efflux model performances for the modeled temperatures and moistures for the litter (in forest) or sod (in grassland) horizon (Tlit_m–Mlit_m) and the soil horizon (Tsoil–Prec) (see Tables S3 and S4 in theSupplementary Materials) highlight the remarkable influence of the litter/sod horizon on the CO2 efflux for both forest and grassland ecosystems. Together with the statistically valid correlation between CO2 efflux and Tlit_m for grassland in the temperature range 0 < Tsoil < 1 °C, these obtained results fully support our suggestion that the interannual variability in the activities of trees and grasses due to the different temperature and moisture regimes, and their respective root allocations, play a crucial role in the soil horizons most involved in the CO2 efflux process.
5. Conclusions
The accuracy of soil CO2 efflux modeling for forest and grassland ecosystems strongly depends on weather conditions. For both ecosystems studied, dry conditions lead to the worst model performances due to the highest temperatures reached at those years, with the highest evaporation rates leading to an absence of water and inhibited microbial activity. The normal and wet conditions showed similar model performances for the forest ecosystem. For the grassland ecosystem, however, the model results for normal conditions worsened toward dry conditions, signaling water demand and temperature differences when the soil is less protected by overlaying vegetation cover.
We found that for the forest CO2 efflux, the direct Tsoil measurements in combination with SOC provide better parameterization for the empirical TPPC model than if only Tsoil or Tair parameterization had been used. This can be associated with the low SOC availability for microbial decomposition due to the high C/N ratio.
Temperature becomes the dominant factor for grassland CO2 efflux due to the reduced vegetation protection, and the TPPrh model with quadratic temperature dependence provides better performance among all models considered. The absence of SOC limitation in this case may be related to the higher SOC availability for mineralization in the soil due to the low C/N ratio.
We have also shown that modeling the litter (for forest) or sod (for grassland) horizon, Tlit_m–Mlit_m, with the SCLISS model can be a good alternative, and can provide the temperature and moisture data for CO2 efflux modeling when direct Tsoil and moisture observations are not available on site.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/soilsystems9010025/s1, Figure S1: Grassland and forest site locations; Figure S2: The identification procedure; Table S1: Correlation coefficients between the CO2 efflux (SR) and temperature and moisture sources for the 0 < Tsoil < 1 °C soil temperatures; Table S2: Comparison among the all-at-once (TPPC, TPPrh) and condition-specific (TPPC_nwd, TPPrh_nwd) models; Table S3: Comparison between the TPPC- and TPPrh-type models parameterized by the measured and modeled data; Table S4: The cold period (Tsoil ≤ 2 °C) statistics for the combined condition-specific models depended on the types of parameterizations; Table S5: Parameters of the linear regressions between the measured and modeled values for the TPPC, and T models on the Entic Podzol (mixed forest ecosystem) and the Romul_Hum and T models on the Haplic Luvisol (deciduous forest ecosystem) depending on the weather-specific conditions; Table S6: Parameters of the linear regression between the measured and modeled values for the TPPC, and T models on the Entic Podzol (grassland ecosystem) and the T model on the Haplic Luvisol (grassland ecosystem) depending on the weather-specific conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K. and I.K.; methodology, S.K. and S.B.; software, S.B. and I.P.; validation, S.K. and S.B.; formal analysis, S.K.; investigation, S.K.; resources, V.L.d.G., D.K. and T.M.; data curation, V.L.d.G. and D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K.; writing—review and editing, S.K., I.K., Y.K., I.P., Y.W. and S.B.; visualization, S.K., Y.K. and D.K.; supervision, I.K.; project administration, I.K. and I.P.; funding acquisition, I.K. and I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The data collection and preparation, data analysis, and CO2 efflux modeling, as well as the SCLISS modeling works, were supported by State Assignment No. 122040500037-6 and the RUDN University Strategic Academic Leadership Program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank Vladimir Shanin for his valuable comments and attention to this work. We give thanks to Vera Ableeva (Station of Background Monitoring, Roshydromet), who provided us with the meteorological data set (1973 to 2022) for the study area. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their thorough attention to the manuscript and their constructive comments and suggestions that improved its quality.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ryan, M.; Law, B. Interpreting, measuring, and modeling soil respiration. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, R.; Matteucci, G.; Dolman, A.J.; Schulze, E.D.; Rebmann, C.; Moors, E.J.; Granier, A.; Gross, P.; Jensen, N.O.; Pilegaard, K.; et al. Respiration as the main determinant of carbon balance in European forests. Nature 2000, 404, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Quéré, C.; Moriarty, R.; Andrew, R.M.; Peters, G.P.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Jones, S.D.; Sitch, S.; Tans, P.; Arneth, A.; et al. Global carbon budget 2014. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2015, 7, 47–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Ballantyne, A.; Berryman, E.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Jian, J.; Morris, K.A.; Rey, A.; Vargas, R. Twenty years of progress, challenges, and opportunities in measuring and understanding soil respiration. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2024, 129, e2023JG007637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M.; Thürig, E.; Ogle, S.; Palosuo, T.; Schrumpf, M.; Wutzler, T.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Chertov, O.; Komarov, A.; Mikhailov, A.; et al. Models in country scale carbon accounting of forest soils. Silva Fenn. 2007, 41, 575–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Edwards, N.T.; Garten, C.T.; Andrews, J.A. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoroshaev, D.; Kurganova, I.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.; Sapronov, D.; Kivalov, S.; Aloufi, A.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Vegetation and Precipitation Patterns Define Annual Dynamics of CO2 Efflux from Soil and Its Components. Land 2024, 13, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhoveeva, O.E.; Karelin, D.V.; Zolotukhin, A.N.; Pochikalov, A.V. Soil Respiration in Agricultural and Natural Ecosystems of European Russia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.J.; Heal, O.W.; Anderson, J.M. Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Inubushi, K.; Sakamoto, K. Effect of vegetations and temperature on microbial biomass carbon and metabolic quotients of temperate volcanic forest soils. Geoderma 2006, 136, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, D.; Rey, A.; Ruan, H.; Craine, J.M.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y. Soil properties control decomposition of soil organic carbon: Results from data-assimilation analysis. Geoderma 2016, 262, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, C.H.; Pugh, G.J.F. Biology of Plant Litter Decomposition; Academic Press: London, UK, 1974; Volumes 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Khoroshaev, D.A.; Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O. Heterotrophic Soil Respiration Response to the Summer Precipitation Regime and Different Depths of Snow Cover in a Temperate Continental Climate. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 1667–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jílková, V. Soil respiration in temperate forests is increased by a shift from coniferous to deciduous trees but not by an increase in temperature. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 154, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Tufekciogul, A. Vegetation and soil respiration: Correlations and controls. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurganova, I.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.; Khoroshaev, D.; Myakshina, T.; Sapronov, D.; Zhmurin, V. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Respiration in Two Temperate Forest Ecosystems: The Synthesis of a 24-Year Continuous Observation. Forests 2022, 13, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Myakshina, T.N.; Sapronov, D.V.; Khoroshaev, D.A. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Respiration in Grasslands in Temperate Continental Climate Zone: Analysis of 25-Year-Long Monitoring Data. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 1232–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Myakshina, T.N.; Sapronov, D.V.; Romashkin, I.V.; Zhmurin, V.A.; Kudeyarov, V.N. Native and model assessment of Respiration of forest sod-podzolic soil in Prioksko-Terrasny Biospheric Reserve. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2020, 13, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Khoroshaev, D.A.; Myakshina, T.N.; Sapronov, D.V.; Zhmurin, V.A.; Kudeyarov, V.N. Analysis of the Long-Term Soil Respiration Dynamics in the Forest and Meadow Cenoses of the Prioksko-Terrasny Biosphere Reserve in the Perspective of Current Climate Trends. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S. Global patterns of carbon dioxide emission from soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertov, O.G.; Komarov, A.S.; Nadporozhskaya, M.; Bykhovets, S.S.; Zudin, S.L. ROMUL—A model of forest soil organic matter dynamics as a substantial tool for forest ecosystem modeling. Ecol. Model. 2001, 138, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priputina, I.V.; Bykhovets, S.S.; Frolov, P.V.; Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Sapronov, D.V.; Mjakshina, T.N. Application of Mathematical Models ROMUL and Romul_Hum for Estimating CO2 Emission and Dynamics of Organic Matter in Albic Luvisol under Deciduous Forest in the South of Moscow Oblast. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes De Gerenyu, V.O.; Kurganova, I.N.; Rozanova, L.N.; Kudeyarov, V.N. Effect of temperature and moisture on CO2 evolution rate of cultivated Phaeozem: Analyses of long-term field experiment. Plant Soil Environ. 2005, 51, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, C.; Huzsvai, L.; Kovács, E.; Kovács, G.; Tuba, G.; Sinka, L.; Zsembeli, J. Carbon Dioxide Efflux of Bare Soil as a Function of Soil Temperature and Moisture Content under Weather Conditions of Warm, Temperate, Dry Climate Zone. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyukarev, E.A.; Kurakov, S.A. Response of Bare Soil Respiration to Air and Soil Temperature Variations According to Different Models: A Case Study of an Urban Grassland. Land 2023, 12, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, M.; Pavelka, M.; Montagnani, L.; Kutsch, W.; Lindroth, A.; Juszczak, R.; Janouš, D. Soil surface CO2 efflux measurements in Norway spruce forests: Comparison between four different sites across Europe—From boreal to alpine forest. Geoderma 2013, 192, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, B.; Chodak, M.; Niklińska, M. Soil respiration in seven types of temperate forests exhibits similar temperature sensitivity. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, V.A.; Cook, F.J. Relationship between soil respiration and soil moisture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1983, 15, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Schack-Kirchner, H.; Hildebrand, E.E.; Holst, J. Pore-space CO2 dynamics in a deep, well-aerated soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellei-Kovács, E.; Kovács-Láng, E.; Botta-Dukát, Z.; Kalapos, T.; Emmett, B.; Beier, C. Thresholds and interactive effects of soil moisture on the temperature response of soil respiration. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karelin, D.V.; Zamolodchikov, D.G.; Isaev, A.S. Unconsidered sporadic sources of carbon dioxide emission from soils in taiga forests. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2017, 475, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes De Gerenyu, V.O.; Myakshina, T.N.; Sapronov, D.V.; Savin, I.Y.; Shorohova, E.V. Carbon balance in forest ecosystems of southern part of Moscow region under a rising aridity of climate. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 10, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhoveeva, O.E.; Karelin, D.V. Assessment of Soil Respiration with the Raich−Hashimoto Model: Parameterisation and Prediction. Izvestia RAN. Ser. Geogr. 2022, 86, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Duan, C.; Wu., H.; Luo, X.; Han, L. Effects of changes in throughfall on soil GHG fluxes under a mature temperate forest, northeastern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X. Effect of Changes in Throughfall on Soil Respiration in Global Forest Ecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. Forests 2023, 14, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, M.; Darenova, E.; Dusek, J. Modeling of soil CO2 efflux during water table fluctuation based on in situ measured data from a sedge-grass marsh. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 14, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Rey, A.; Freibauer, A.; Tenhunen, J.; Valnetini, R.; Banza, J.; Caslas, P.; Cheng, Y.; Grunzweig, J.M.; Irvine, J.; et al. Modeling temporal and large-scale spatial variability of soil respiration from soil water availability, temperature and vegetation productivity indices. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, C.A.; Anderson, I.C.; Khachane, A.; Singh, B.P.; Barton, C.V.M.; Duursma, R.A.; Ellsworth, D.S.; Singh, B.K. Plant productivity is a key driver of soil respiration response to climate change in a nutrient-limited soil. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 50, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Forest soils and carbon sequestration. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 220, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A.; Luo, Y.Q. On the variability of respiration in terrestrial ecosystems: Moving beyond Q10. Glob. Change Biol. 2006, 12, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J.; Shen, Q.; Hu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, G. Modeling interannual variability of global soil respiration from climate and soil properties. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Gavrishkiva, O. Time lag between photosynthesis and carbon dioxide efflux from soil: A review of mechanisms and controls. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 3386–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivalov, S.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Khoroshaev, D.A.; Myakshina, T.; Sapronov, D.; Ivashchenko, K.V.; Kurganova, I.N. Soil Temperature, Organic-Carbon Storage, and Water-Holding Ability Should Be Accounted for the Empirical Soil Respiration Model Selection in Two Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2023, 14, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivalov, S.N.; Kurganova, I.N.; Lopez de Guerenu, V.O.; Myakshina, T.N.; Sapronov, D.V.; Khoroshaev, D.A. Application of T&P Models for Estimating Respiration of Forest Soils in the Temperate Continental Climate Zone. J. Soils Environ. 2024, 7, e252, (In Russian with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, R.K.; Lipson, D.L.; Burns, S.P.; Turnipseed, A.A.; Delany, A.C.; Williams, M.W.; Schmidt, S.K. Winter forest soil respiration controlled by climate and microbial community composition. Nature 2006, 439, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykhovets, S.S.; Komarov, A.S. A simple statistical model of soil climate with a monthly step. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2002, 35, 392–400. [Google Scholar]
- Reichstein, M.; Beer, C. Soil respiration across scales: The importance of a model-data integration framework for data interpretation. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Di, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Characterization of the coherence between soil moisture and precipitation at regional scales. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, K.; Jenkinson, D.S. RothC—A model for the turnover of carbon in soil. In Rothamsted Research; Herts: Harpenden, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lugato, E.; Bampa, F.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L.; Jones, A. Potential carbon sequestration of European arable soils estimated by modelling a comprehensive set of management practices. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 3557–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.; Carbone, M.S.; Reichstein, M.; Baldocchi, D.D. Frontiers and challenges in soil respiration research: From measurements to model-data integration. Biogeochemistry 2011, 102, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karelin, D.V.; Azovskii, A.I.; Kumanyaev, A.S.; Zamolodchikov, D.G. Role of Spatial and Temporal Scales in Factor Studies of Soil CO2 Fluxes in Forests of Valdai Hills. For. Sci. 2019, 1, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, M.; Darenova, E.; Krupková, L.; Pavelka, M. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of soil CO2 efflux in a Norway spruce forest over an eight-year study. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256–257, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB 2014. 2015. Available online: https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-classification/world-reference-base/en/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Selyaninov, G.L. About the agricultural evaluation of the climate. Tr. GGO 1928, 20, 177–185. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kivalov, S.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Khoroshaev, D.A.; Myakshina, T.; Sapronov, D.; Ivashchenko, K.V.; Kurganova, I.N. Optimization of empirical models for the control and assessment of winter soil respiration. In Proceedings of the Eighth National Scientific Conference with International Participation “Mathematical Modeling in Ecology” (EcoMatMod-2023), Pushchino, Russia, 9–11 November 2023; pp. 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Nadporozhskaya, M.A.; Maksimova, E.Y.; Abakumov, E.V.; Chertov, O.G.; Bykhovets, S.S.; Show, S.H. Recurring surface fires cause soil degradation of forest land: A simulation experiment with the EFIMOD model. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Fitzjarrald, D.; Sakai, R.; Goulden, M.; Munger, J.; Wofsy, S. Seasonal Variation in Radiative and Turbulent Exchange at a Deciduous Forest in Central Massachusetts. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalić, B.; Fitzjarrald, D. Bowen ratio and daily temperature range thresholds: Are they signals of transient seasons? In Proceedings of the EMS Annual Meeting 2021, Online, 6–10 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, R.G.; Cameron, K.C. Soil Science—An Introduction to the Properties and Management of New Zealand Soils; Oxford University Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 1990; pp. 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S.; Bhagawatti, D. Interannual variability in global soil respiration, 1980–1994. Glob. Change Biol. 2002, 8, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priputina, I.V.; Frolov, P.V.; Shanin, V.N.; Bykhovets, S.S.; Kurganova, I.N.; Lopes de Gerenyu, V.O.; Sapronov, D.V.; Zubkova, E.V.; Mjakshina, T.N.; Khoroshaev, D.A. Simulation Modeling of Forest Soil Respiration: Case Study of Entic Carbic Podzol under Coniferous–Broadleaved Forest in the South of Moscow Oblast. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Carbon Decomposition and Feedbacks to Climate Change. Nature 2006, 440, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Ge, J.; Chu, J. Annual and Seasonal Variations of Q10 Soil Respiration in the Sub-Alpine Forests of the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, Y. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Q 10 Determined by Soil Respiration Measurements at a Sierra Nevadan Forest. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).