Abstract
Twenty-four healthy students walked at least four times for 1 hour under each of the four settings: by a busy road; by a busy road wearing ear plugs; in a park; and in a park but exposed to traffic noise (65 dB) through speakers. Particle mass (smaller than 2.5 and 1 µm, PM1 and PM2.5, (respectively)particle number and noise levels were measured throughout each walk. Lung function and exhaled nitric oxide (NO) were measured before, immediately after, 1 hour after, and approximately 24 h after each walk. Blood pressure and heart-rate variability were measured every 15 min during each walk. Air pollution levels reduced lung function levels; noise levels reduced systolic blood pressure and heart-rate variability.
1. Introduction
The acute effects of air pollutants have been demonstrated repeatedly in respiratory [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] and cardiovascular patients [16,17,18,19,20,21]. Such panel studies have been performed in the elderly [22,23,24,25] and in areas with high air pollution [1,14,26,27,28,29,30], but less so in young and healthy people in settings with moderate to low air pollution levels [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. We recruited healthy students from Vienna to study the physiological reactions of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems when exposed to everyday urban air pollution.
2. Materials and Methods
Twenty-four healthy students walked at least four times for 1 hour under each of the four settings: by a busy road; by a busy road wearing ear plugs; in a park; and in a park but exposed to traffic noise (65 dB) through speakers. Particle mass (smaller than 2.5 and 1 µm, PM2.5 and PM1, respectively, particle number and noise levels were measured throughout each walk. PM1 and PM2.5 were measured using a Grimm Portable Laser Aerosol Spectrometer Model 1.108. To measure particle numbers (PN), a miniature diffusion size classifier (miniDiSC, http://www.fierz.ch/minidisc/) was used. Concentrations were stored for each 6-second interval. Noise was measured with a Brühl and Kjaer sound level meter—type 2236. Every 15 min, the equivalent continuous sound level was noted and the instrument was reset.
Spirometric lung function and exhaled nitric oxide (NO) were measured before, immediately after, 1 hour after, and approximately 24 h after each walk. Spirometry was performed using an EasyOne spirometer (ndd Medizintechnik AG) in an upright standing position, applying a nose clip as follows standard procedures [40,41]. The level of NO in the exhaled air [42] was measured using the portable instrument NObreath (Bedfont Technical Instruments Ltd., Maidstone, UK).
Blood pressure and heart-rate variability were measured every 15 min during each walk. To measure heart-rate variability, the mobile ECG device eMotion Faros was used. ECG files were analyzed over windows of 15 min each with the Kubios software version 2.2.
Temperature readings were obtained from a nearby stationary meteorological station. Data on the fine particle (PM10) background concentration were also obtained from a nearby fixed monitor operated by the City of Vienna (station near the general hospital—AKH).
The data of respiratory and cardiovascular markers were entered in two separate files for further statistical analysis. In this study setting, each participant serves as his own control. Respiratory parameters (immediately after, 1 h after, and approximately 24 h after the exposure) were assessed per participant, with single air pollution markers serving as independent variables applying random-effects generalized least squares (GLS) regression. Fixed-effect models gave mostly very similar results and the Hausman test was mostly not significant. In the two adjusted models, either the same respiratory marker or NO in exhaled air before the exposure were included in the model to characterize unmeasured influences.
Cardiovascular markers were assessed every 15 min separately, again using random-effects GLS regression. Exposures in the preceding 15 min (noise and dust) served as independent variables. Temperature was included in the models as a confounder.
All calculations were conducted with STATA SE Vers. 13.1 [43].
3. Results
3.1. Participants and Exposure
In the first run from December 2016 until May 2017, 20 students (11 male, nine female) with an average age of 24 years (range 21–33 years) had, on average, 20 1-hour walks (range 13–38). They were all non-smokers and were reported to be healthy. In the second run, four more students were recruited. They underwent the same procedures in May and June 2018.
Air pollution and ambient noise were higher near the street but were not correlated with each other due to different time trends. Individual noise exposure was further de-coupled from ambient conditions by design. Particle measures correlated well with each other and with the mass of particles smaller than 10 µm (PM10) at the nearby fixed monitoring station (R-values for all particle mass measured >0.9). Either personal exposure concentrations were actually higher than the concentrations at the fixed monitoring station, or the aerosol spectrometer overestimated particle mass concentrations systematically. As an example, hourly values of PM2.5 measured with the spectrometer and PM10 measured at the fixed station displayed a correlation coefficient of 0.96. A linear regression model with PM10 at the fixed station and the setting (road versus park) explained 92.5% of the variation in PM2.5. In this model, the difference between the road and the park was significant (p = 0.016) but not very large (4.2 µg/m³). The slope (ß of PM10) at the fixed station was 1.57 (p < 0.001). Table 1 describes the range of exposure for PM10 at the fixed station and the personal exposure measured as PM2.5 and PN. Due to the high correlation between the particle mass values, only PM1 from the personal monitoring and PM10 from the fixed site (controlling for setting—road versus park) were further analyzed for health effects. In addition, personal particle number concentrations (R with mass concentrations between 0.72 and 0.77) were investigated.

Table 1.
Exposure to particles during walks.
After controlling for seasonal and daily trends, the ambient noise levels at the road were approximately 10 dB louder than in the park. These ambient noise levels were partly overruled by ear plugs and/or speakers. The average sound pressure level, LAeq, was about 56 dB at the road. At the road wearing ear plugs, noise was assumed to be 30 dB lower. In the park it was measured to be about 46 dB, and the speakers were set to 65 dB.
3.2. Air Pollution and Respiratory Health
Air pollution levels reduced lung function levels. Measures of large airways resistance like FEV1 were reduced immediately after the walk, while measures indicative of the small airways like MEF25 remained low even 24 h later (Figure 1).
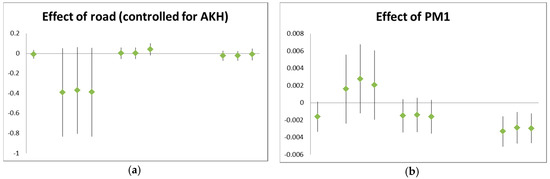
Figure 1.
Examples for air pollution effects on lung function: (a) effect of the setting “road” on FEV1 (in liters), controlled for background pollution; (b) effect of PM1 (µg/m³) on MEF25 (in L/s). Each triplet stands for: unadjusted; adjusted for lung function before exposure; and adjusted for exhaled NO before exposure. The time points are (left to right): before exposure (one value only); immediately after the walk; 1 h after the walk; and 24 h after the walk.
Exhaled NO was significantly reduced immediately after and 1 h after the walk with increasing dust levels. After controlling for background dust levels, walking beside the road increased NO 24 h later (Figure 2).
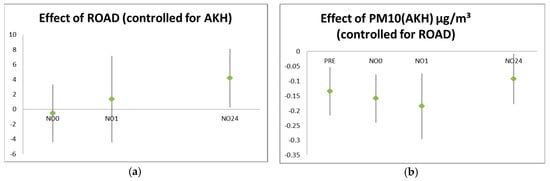
Figure 2.
Effect of exposure on exhaled nitric oxide (NO) values (in ppb) at different time points: (a) exposure near the road compared to the park, controlled for background concentration; (b) effect of background concentration (PM10 in µg/m³) controlled for setting. The background reflects the average exposure at that time for a longer period (and thus also affects NO before the setting) while the setting is added to the background exposure for a short and defined period of 1 h.
3.3. Air Pollution and Noise Effects on Cardiovascular System
Noise levels reduced systolic blood pressure and heart-rate variability (Figure 3). Temperature also had a clear effect on cardiovascular parameters but did not confound the noise effects. Air pollution effects were less pronounced and were not very consistent (data not shown).
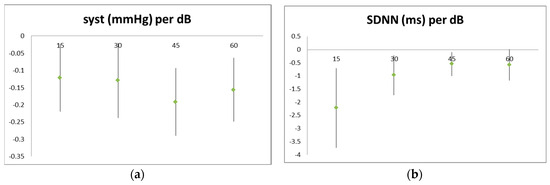
Figure 3.
Effect of noise on cardiovascular parameters: (a) systolic blood pressure; (b) standard deviation of the NN intervals. Noise levels are averaged over 15 min (four periods per 1 h walk) each. Blood pressure was measured at the end of each period, while ECG readings were taken over the whole period.
As in the previous sub-chapter, only examples that are typical and representative for effects on other parameters can be presented.
4. Discussion
Exposure near a busy road causes statistically significant respiratory and cardiovascular reactions, even in healthy young adults. The effects were reversible and generally not very severe, but nevertheless clear and consistent.
Exhaled NO originates from different sources [44,45,46]. It is secreted by epithelial cells, inducing relaxation of the smooth muscle cells in the bronchial walls. This secretion is inducible and is a reaction after reflective muscular narrowing of the airways. An irritant stimulus will, at first, lead to increased muscle tone and thus, after a very short interval, lead to increased airway resistance. This resistance will be released by NO; therefore, increased NO will predict a lower airway resistance in the near future. NO also serves as a messenger molecule in inflammatory processes. Here, it is mostly involved in eosinophilic inflammation and signifies allergic asthma (thus increased bronchial reactivity and likely also increased airway resistance). Epithelial cells capable of producing NO can be compromised during (neutrophil) inflammation and by some toxic substances, e.g., cigarette smoke. Therefore, smokers generally have lower NO levels and, after the smoking of cigarettes, NO is further reduced.
NO might relax smooth muscles and thus reduce airway resistance. However, NO in the tissue acts as an oxidative stressor and thus contributes to an inflammatory response secondary to the reflective muscular response to an irritant. Therefore, after a certain delay, higher NO levels might predict an increase in airway resistance again.
These different and complex pathways make the interpretation of NO in a panel study a challenge. Timing is essential and even with our repeated measures (before, immediately after, 1 h after, and 24 h after a defined exposure of 1 h), we were not able to fully capture the complete time course. Considering both the background pollution levels that may better represent the longer-term average exposure and the effects per setting which, by design, lasted only for 1 hour, we could further disentangle the temporal variation. In that endeavor, we were hindered by the finding that the differences between settings were small compared to the differences in background exposure over time.
Nevertheless, we were able to demonstrate reduced NO levels due to higher background exposures, indicative of toxic damage to epithelial cells and increased levels of NO with 24 h latency after a 1-hour acute exposure indicative of inflammatory response. Reduced lung function led to an increase in NO levels, and higher NO levels were indicative of increased lung function levels at the next measurement point.
Effects on the larger airways signified by, for example, FEV1 were seen immediately after exposure, likely indicative of a muscular reflex response. Effects on the small airways signified, for example, by MEF25 persisted for 24 h, likely representing inflammatory responses that might be clinically more relevant.
Lung function values mostly remained in the physiologically normal range. This is not surprising considering the comparatively low exposures and the generally healthy state of the participants. We observed effects during everyday activities in everyday settings; therefore, massive detrimental health effects were not expected. However, it seems noteworthy that even under these conditions, even in young and healthy subjects, and even with a comparatively small number of subjects and a moderate number of repeated observations, most effects reached or at least approached significance. While acute effects shortly after exposure are likely physiological protective reactions under nervous control, the longer-term changes most clearly seen in the end-expiratory flows, and thus indicative of an increase in resistance in the small airways, are likely caused by inflammatory tissue responses and thus are a cause for concern. Even small effects, when accumulated over the years, will in the long run hasten the functional decline of the respiratory system.
Cardiovascular effects were mostly observed in relation to noise levels. These effects remained even after controlling for temperature, which was the most important predictor of heart rate, heart-rate variability, and blood pressure. Also, these effects remained in the physiological range which was to be expected. Again, even the subtle effects of everyday exposure during everyday activities can still be of concern in the long turn.
Other acute effects of air pollution have also been demonstrated in some panel studies, notably on glucose metabolism [47,48] and inflammation [49]. However, we are confident that we have covered the most important endpoints, including respiratory [50] and cardiovascular [51,52,53,54] effects.
Author Contributions
H.M. designed the study and wrote the paper. The other authors carried out the field work and collected the data.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Pan, L.; Xu, J.; Shan, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, W.; Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Shima, M.; et al. Short-term effects of various ozone metrics on cardiopulmonary function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: Results from a panel study in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magzamen, S.; Oron, A.P.; Locke, E.R.; Fan, V.S. Association of ambient pollution with inhaler use among patients with COPD: A panel study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gu, Y.; Qiao, L.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Bai, C.; Sun, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Fine Particulate Constituents and Lung Dysfunction: A Time-Series Panel Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Parra, L.; Yohannessen, K.; Brea, C.; Vidal, D.; Ubilla, C.A.; Ruiz-Rudolph, P. Air pollution, PM2.5 composition, source factors, and respiratory symptoms in asthmatic and nonasthmatic children in Santiago, Chile. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemsma, L.D.; Hoek, G.; Smit, L.A. Panel studies of air pollution in patients with COPD: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikawa, C.L.; Weichenthal, S.; Wheeler, A.J.; Dobbin, N.A.; Smargiassi, A.; Evans, G.; Liu, L.; Goldberg, M.S.; Pollitt, K.J. Particulate Oxidative Burden as a Predictor of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wu, S.; Ji, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Shi, S.; Tu, X.; Li, H.; Pan, L.; Deng, F.; et al. The exposure metric choices have significant impact on the association between short-term exposure to outdoor particulate matter and changes in lung function: Findings from a panel study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, E.N.; Moshier, E.; Habre, R.; Rohr, A.; Godbold, J.; Nath, A.; Grunin, A.; Coull, B.; Koutrakis, P.; Kattan, M. Outdoor air pollution and health effects in urban children with moderate to severe asthma. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ni, Y.; Li, H.; Pan, L.; Yang, D.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Shima, M.; Guo, X. Short-term exposure to high ambient air pollution increases airway inflammation and respiratory symptoms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshammer, H.; Hutter, H.-P.; Hauck, H.; Neuberger, M. Low levels of air pollution induce changes of lung function in a panel of schoolchildren Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Lugo, M.; Ramírez-Aguilar, M.; Pérez-Padilla, R.; Sansores-Martínez, R.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Barraza-Villarreal, A. Effect of Personal Exposure to PM2.5 on Respiratory Health in a Mexican Panel of Patients with COPD. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10635–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, C.; Yost, M.; Sampson, P.; Arias, G.; Torres, E.; Vasquez, V.B.; Bhatti, P.; Karr, C. Regional PM2.5 and asthma morbidity in an agricultural community: A panel study. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, M.C.; Golan, R.; Greenwald, R.; Raysoni, A.U.; Holguin, F.; Kewada, P.; Winquist, A.; Flanders, W.D.; Sarnat, J.A. Modification of Traffic-related Respiratory Response by Asthma Control in a Population of Car Commuters. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Meneses, F.; Ruiz, S.; Huerta, J.; Sienra, J.J.; White, M.; Etzel, R.; Hernandez, M. Effects of intermittent ozone exposure on peak expiratory flow and respiratory symptoms among asthmatic children in Mexico City. Arch. Environ. Health 1997, 52, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiltermann, T.J.N.; de Bruijne, C.R.; Stolk, J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Spieksma, F.T.M.; Roemer, W.; Steerenberg, P.A.; Fischer, P.H.; van Bree, L.; Hiemstra, P.S. Effects of photochemical air pollution and allergen exposure on upper respiratory tract inflammation in asthmatics Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, M.S.; Luttmann-Gibson, H.; Schwartz, J.; Mittleman, M.A.; Wessler, B.; Gold, D.R.; Dockery, D.W.; Laden, F. Acute Exposure to Air Pollution Triggers Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Choi, B.G.; Kim, S.W.; Rha, S.W.; Shim, M.S.; Kim, D.J.; Seo, H.S.; Oh, D.J.; Jeong, M.H.; Other Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry (KAMIR) investigators. Air pollution and short-term clinical outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rückerl, R.; Schneider, A.; Hampel, R.; Breitner, S.; Cyrys, J.; Kraus, U.; Gu, J.; Soentgen, J.; Koenig, W.; Peters, A. Association of novel metrics of particulate matter with vascular markers of inflammation and coagulation in susceptible populations -results from a panel study. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Utell, M.J.; Schneider, A.; Zareba, W.; Frampton, M.W.; Oakes, D.; Hopke, P.K.; Wiltshire, J.; Kane, C.; Peters, A.; et al. Does total antioxidant capacity modify adverse cardiac responses associated with ambient ultrafine, accumulation mode, and fine particles in patients undergoing cardiac rehabilitation? Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.S.; Wheeler, A.J.; Burnett, R.T.; Mayo, N.E.; Valois, M.F.; Brophy, J.M.; Giannetti, N. Physiological and perceived health effects from daily changes in air pollution and weather among persons with heart failure: A panel study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Kario, K. Coexistence of PM2.5 and low temperature is associated with morning hypertension in hypertensives. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2015, 37, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieb, D.M.; Shutt, R.; Kauri, L.; Mason, S.; Chen, L.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Dobbin, N.A.; Rigden, M.; Jovic, B.; Mulholland, M.; et al. Cardio-Respiratory Effects of Air Pollution in a Panel Study of Outdoor Physical Activity and Health in Rural Older Adults. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 59, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanvand, M.; Naddafi, K.; Kashani, H.; Faridi, S.; Kunzli, N.; Nabizadeh, R.; Momeniha, F.; Gholampour, A.; Arhami, M.; Zare, A.; et al. Short-term effects of particle size fractions on circulating biomarkers of inflammation in a panel of elderly subjects and healthy young adults. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karottki, D.G.; Spilak, M.; Frederiksen, M.; Jovanovic Andersen, Z.; Madsen, A.M.; Ketzel, M.; Massling, A.; Gunnarsen, L.; Møller, P.; Loft, S. Indoor and outdoor exposure to ultrafine, fine and microbiologically derived particulate matter related to cardiovascular and respiratory effects in a panel of elderly urban citizens. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 1667–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Staimer, N.; Tjoa, T.; Gillen, D.L.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Hasheminassab, S.; Pakbin, P.; Longhurst, J.; Sioutas, C.; et al. Associations between microvascular function and short-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and particulate matter oxidative potential. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Morishita, M.; Bard, R.L.; et al. Short-Term Blood Pressure Responses to Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Exposures at the Extremes of Global Air Pollution Concentrations. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutt, R.H.; Kauri, L.M.; Weichenthal, S.; Kumarathasan, P.; Vincent, R.; Thomson, E.M.; Liu, L.; Mahmud, M.; Cakmak, S.; Dales, R. Exposure to air pollution near a steel plant is associated with reduced heart rate variability: A randomised crossover study. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.-W.; Qian, Z.; Bloom, M.S.; Nelson, E.J.; Liu, E.; Han, B.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Chen, D.-H.; et al. A panel study of airborne particulate matter concentration and impaired cardiopulmonary function in young adults by two different exposure measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 180, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, A.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; Xu, X.; Kan, H. Size-fractionated Particulate Air Pollution and Circulating Biomarkers of Inflammation, Coagulation, and Vasoconstriction in a Panel of Young Adults. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qiao, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, X.; et al. Fine Particulate Matter Constituents, Nitric Oxide Synthase DNA Methylation and Exhaled Nitric Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11859–11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Hunter, T.; de Nazelle, A.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Kubesch, N.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Matt, F.; Foraster, M.; Martínez, T.; Ambros, A.; Cirach, M.; et al. Estimated effects of air pollution and space-time-activity on cardiopulmonary outcomes in healthy adults: A repeated measures study. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, D.B.; Xiang, J.; Mo, J.; Li, F.; Chung, M.; Gong, J.; Weschler, C.J.; Ohman-Strickland, P.A.; Sundell, J.; Weng, W.; et al. Association of Ozone Exposure with Cardiorespiratory Pathophysiologic Mechanisms in Healthy Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Sun, Z.; Brook, J.R.; Zhao, X.; Ruan, Y.; Yan, J.; Mukherjee, B.; Rao, X.; Duan, F.; Sun, L.; et al. Extreme Air Pollution Conditions Adversely Affect Blood Pressure and Insulin Resistance: The Air Pollution and Cardiometabolic Disease Study. Hypertension 2016, 67, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole-Hunter, T.; Weichenthal, S.; Kubesch, N.; Foraster, M.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Bouso, L.; Martínez, D.; Westerdahl, D.; de Nazelle, A.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Impact of traffic-related air pollution on acute changes in cardiac autonomic modulation during rest and physical activity: A cross-over study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Eum, K.D.; Rodrigues, E.G.; Magari, S.R.; Fang, S.C.; Modest, G.A.; Christiani, D.C. Effects of Personal Exposure to Ambient Fine Particulate Matter on Acute Change in Nocturnal Heart Rate Variability in Subjects Without Overt Heart Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, E.B.; Louwies, T.; Cox, B.; op‘t Roodt, J.; Solmi, F.; Dons, E.; Int Panis, L.; De Boever, P.; Nawrot, T.S. Short-term fluctuations in personal black carbon exposure are associated with rapid changes in carotid arterial stiffening. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Shen, F.H.; Li, Y.R.; Tsao, T.M.; Tsai, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Hsu, S.H.; Chao, H.; Chuang, K.J.; et al. Association of short-term exposure to fine particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide with acute cardiovascular effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarjour, S.; Jerrett, M.; Westerdahl, D.; de Nazelle, A.; Hanning, C.; Daly, L.; Lipsitt, J.; Balmes, J. Cyclist route choice, traffic-related air pollution, and lung function: A scripted exposure study. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strak, M.; Boogaard, H.; Meliefste, K.; Oldenwening, M.; Zuurbier, M.; Brunekreef, B.; Hoek, G. Respiratory health effects of ultrafine and fine particle exposure in cyclists. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Crapo, R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. General considerations for lung function testing. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- STATA SE Vers. 13.1; StataCorp.: College Station, TX, USA, 2016.
- Gemicioglu, B.; Musellim, B.; Dogan, I.; Guven, K. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNo) in different asthma phenotypes. Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 5, e157–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.; Ryan, D.; Burden, A.; Von Ziegenweidt, J.; Gould, S.; Freeman, D.; Gruffydd-Jones, K.; Copland, A.; Godley, C.; Chisholm, A.; et al. Using fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) to diagnose steroid-responsive disease and guide asthma management in routine care. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2013, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweik, R.A.; Boggs, P.B. , Erzurum, S.C.; Irvin, C.G.; Leigh, M.W.; Lundberg, J.O.; Olin, A.C.; Plummer, A.L.; Taylor, D.R.; American Thoracic Society Committee on Interpretation of Exhaled Nitric Oxide Levels (FENO) for Clinical Applications. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: Interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FENO) for clinical applications. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, J.; Lu, J.; Ha, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Kan, H. Particulate air pollution and circulating biomarkers among type 2 diabetic mellitus patients: The roles of particle size and time windows of exposure. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Hampel, R.; Cyrys, J.; Breitner, S.; Geruschkat, U.; Kraus, U.; Zareba, W.; Schneider, A. Elevated particle number concentrations induce immediate changes in heart rate variability: A panel study in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism or diabetes. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.C.; Silva, C.A.; Braga, A.L.; Sallum, A.M.; Campos, L.M.; Farhat, S.C. Exposure to air pollutants increased disease activity in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Wichmann, H.E.; Tuch, T.; Heinrich, J.; Heyder, J. Respiratory effects are associated with the number of ultrafine particles Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Hatzopoulou, M.; Goldberg, M.S. Exposure to traffic-related air pollution during physical activity and acute changes in blood pressure, autonomic and micro-vascular function in women: A cross-over study. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buteau, S.; Goldberg, M.S. A structured review of panel studies used to investigate associations between ambient air pollution and heart rate variability. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 207–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.T.; Chuang, K.J.; Yang, W.T.; Wang, V.S.; Chuang, H.C.; Bao, B.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Chang, T.Y. Short-term exposure to noise, fine particulate matter and nitrogen oxides on ambulatory blood pressure: A repeated-measure study. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, M.; Bard, R.L.; Kaciroti, N.; Fitzner, C.A.; Dvonch, T.; Harkema, J.R.; Rajagopalan, S.; Brook, R.D. Exploration of the composition and sources of urban fine particulate matter associated with same-day cardiovascular health effects in Dearborn, Michigan. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).