Abstract
A flat circular transmission-line based 300 MHz resonator is implemented for the non- contact assessment of burn depths in biological tissue. Used as a transmit-and-receive sensor, it is placed here at a 2 mm distance from organic material test samples (pork fillet samples) which have been previously heated on one face in various heating conditions involving various temperatures, durations and procedures. Data extracted from the sensor by means of a distant monitoring coil were found to clearly correlate with the depth of burn observed on the tissue samples (up to 40% sensor output changes for a 7 mm burn depth) and with the heating conditions (around 5% sensor output changes for 5.5 mm burn depth obtained at 75 °C or 150 °C). These results open the way to the development of easy to implement burn assessment and monitoring techniques, which could be integrated in wearable medical dressing-like monitoring devices.
1. Introduction
The timely and accurate assessment of burn wound depth raises great interest in medicine since it has a significant impact on patient management outcome [1]. Burn wound depth assessment is usually carried out by clinical evaluation relying on subjective visual and tactile characterizations. Quantitative assessments require the use of dielectric contact probes [2] or advanced imaging techniques [1] which possibly suffer from practical limitations, e.g., when continuous monitoring of burn wounds is required. In this paper, we report on the relevance of a burn wound depth assessment method based on a non-contact electromagnetic technique. This method could lead to the development of low cost and easy to implement instrumented medical dressings dedicated to non-contact burn wound assessment and monitoring purposes.
Thermal burns in organic tissues result in the alteration of tissue cells and organic content, which induces noticeable changes in the local dielectric properties of the tissue [2,3]. Previous works have shown that radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic inductive methods are good candidates for the non- contact sensing of dielectric property changes in organic material [4]. In this paper, an inductive resonant RF probe is implemented and evaluated for the non-contact and wireless sensing of thermally induced burns on organic test samples made out from pork fillet pieces. First experimental sensing results are presented and discussed to evaluate the relevance of such a sensing method for the assessment and continuous monitoring of burn wounds.
2. Measurement Principle
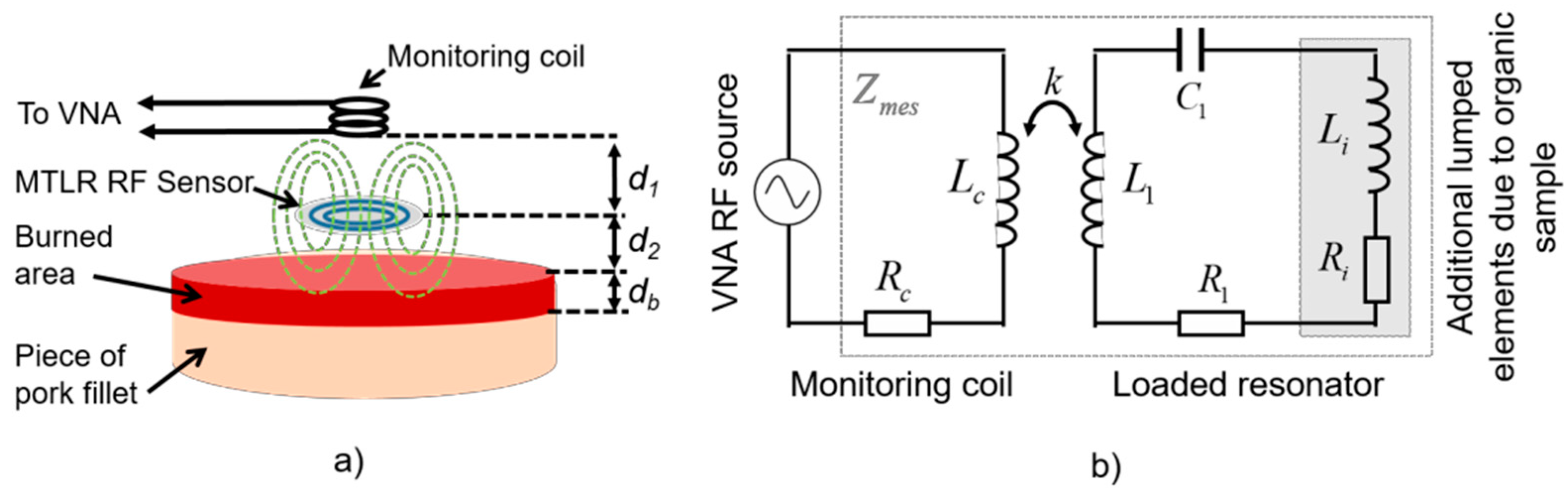
The probe used in this study is constituted of (i) a flat RF high-Q resonator acting as a non-contact transmit and receive sensor which radiates the electromagnetic field within the tissue, and (ii) a distant monitoring coil connected to a vector network analyzer (VNA), constituting a wireless sensor exciter and data “reader” able to sense the resonator impedance changes due to its interactions with the tissue (Figure 1a). The resonator is a flat 19 mm diameter multi-turn split conductor transmission line resonator (MTLR) similar to RF antennas used in the context of magnetic resonance measurement techniques [5]. It is made of a two rolled-up 1 mm width transmission lines constituted of 35 µm thick copper tracks deposited by photolithography on each side of a 250 µm thick low-loss dielectric substrate (CuFlon). Due to its geometrical and material features, the used MTLR exhibits a load free resonance frequency f0 = 302.6 MHz and a quality factor Q ≈ 300. It is modelled by means of an equivalent electric model featuring resistive, inductive and capacitive lumped elements denoted R1, L1, and C1, respectively, with R1 = 710 mΩ, L1 = 109 nH, and C1 = 2.55 pF [6].
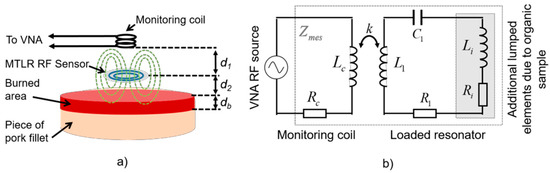
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic representation of the set up. (b) Modeling of the setup using an equivalent electrical circuit.
When placed at a distance d2 from the tissue sample, additional electrical lumped elements, namely resistance Ri and inductance Li, are added to the single mesh electrical model of the MTLR. These additional elements take account for the complex dielectric properties of the tissue sample. More precisely, Ri represents the electromagnetic energy transmitted by the MTLR which is dissipated by the organic material. It is related to the electrical conductivity of the material. Besides, Li represents the energy that is stored within the organic material. It is proportional to the dielectric constant of the tissue. These features were theoretically established in [4] for volume resonators. It was confirmed in [7] and verified experimentally for MTLR probes interacting with reference liquids used as test samples [8]. The monitoring coil is a 8 mm diameter, 11 mm height copper-wire bobbin- coil, modelled by resistance Rc (50 Ω) in series with inductance Lc (0.22 µH). The bobbin coil is placed at a distance d1 from the MTLR. It is electromagnetically coupled to the MTLR and connected to a HP4195A VNA through a 41951A impedance test kit (Figure 1a). The coupling between the monitoring coil, the MTLR and the tissue under evaluation is modelled by the equivalent circuit depicted in Figure 1b. Considering the electrical model of the probe presented in Figure 1b, the impedance Zmes measured at the end by the monitoring coil of the loaded RF probe reads:
In practice, a minimization algorithm such as the damped Gauss-Newton iterative minimization algorithm [9] can be used to fit the model of Equation (1) with the experimental data of Zmes acquired in a frequency bandwidth B centered on the resonance frequency of the sensor. In the case of the unloaded resonator (Ri and Li being equal to 0), the fitting allows R1, L1 and C1 to be estimated, knowing Zc and the resonance frequency f0 [6]. Using the same estimation technique, it is possible to read out the impedance of the resonator loaded with the organic material, and hence to estimate Ri and Li after prior estimation of R1, L1 and C1. Here, Ri and Li were estimated using data measured in a 2 MHz bandwidth around the observed resonance frequency of the loaded resonator.
3. Experiments and Results
In this study, a series of tissue samples were prepared so as to evaluate the feasibility of burn depth sensing using the MTLR probe. The tissue samples were cut out of a low-fat piece of pork fillet, to form a set of samples of similar shape (approx. 5 cm side length and 2 cm height) and mass (approx. 30 g).
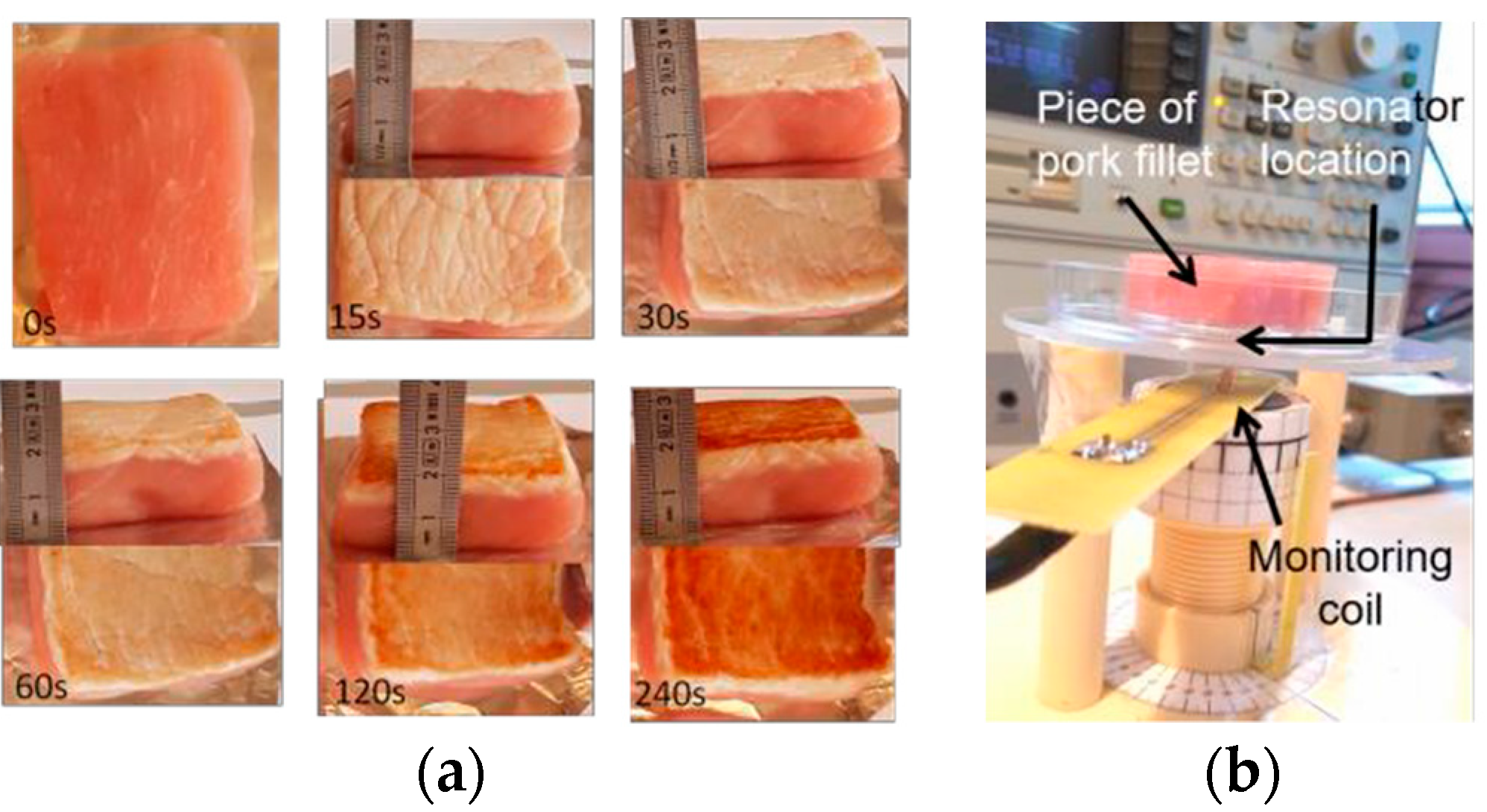
The samples were burned on one face by contact with a plate heated at 75 °C or 150 °C, with heating durations tH = 30, 60, 120 and 240 s. Also, two different heating procedures were used. In the continuous heating procedure (CHP), samples were heated from t = 0 s to t = tH without interruption. The CHP samples are then cooled down to ambient temperature (25 °C) and measured using the RF measurement probe. In the interrupted heating procedure (IHP), the samples are heated first from t = 0 s to t = 30 s, cooled down and measured, then heated again for 30 s, cooled down and measured, and so on. Figure 2a shows examples of prepared samples and Figure 2b shows the RF measurement set up.
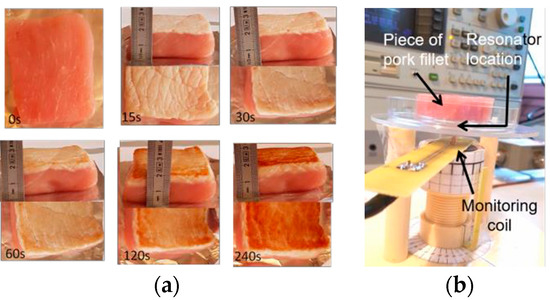
Figure 2.
(a) Examples of low fat pork filet samples, raw and burned during up to 240 s; (b) RF measurement set up.
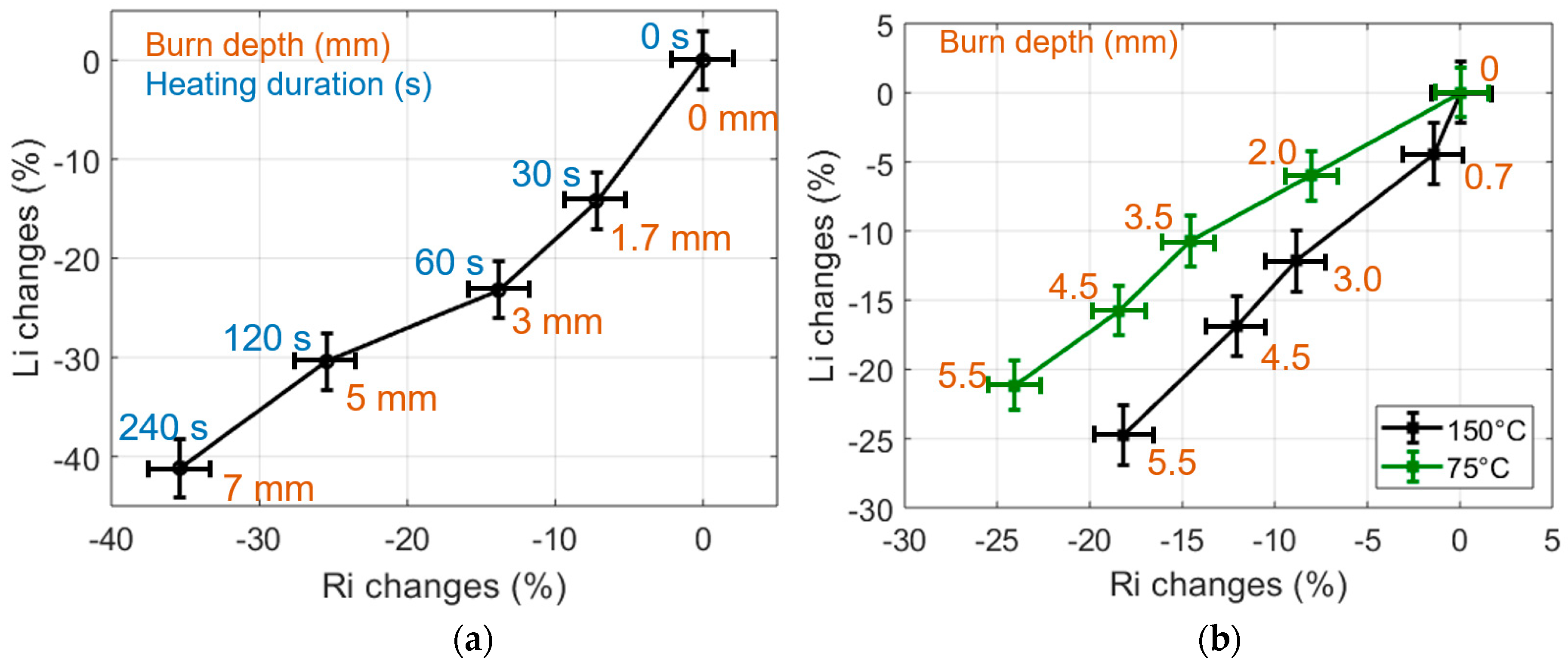
The relative variations of Ri and Li, estimated from data measured on CHP and IHP samples heated at temperatures of 75 °C or 150 °C, are shown in Figure 3. Each point on these graphs results from the averaging of 9 estimations carried out on three samples featuring the same burn state; the error bars are the standard deviation of the estimations. Furthermore, each type of sample has been cut after RF measurements in order to estimate the actual burn depth by means of microscope observations. One can see that the changes of Ri and Li with the burn depth are significant, with e.g., almost 40% Ri and Li changes observed for a sample heated at 75 °C during 240 s and featuring a 7 mm burn depth. Also, these changes clearly correlate with the depth of the burns made on the tissue samples. Finally, temperature and heating procedures provide different dielectric property changes that are clearly sensed by the proposed non-contact sensing technique (Figure 3b).
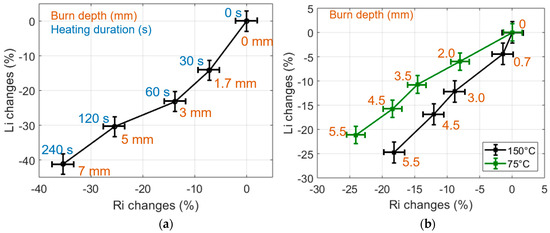
Figure 3.
(a) Changes of the dielectric properties of 75 °C CHP-samples expressed in % in the (Ri, Li) impedance plane. (b) Changes of the dielectric properties of 75 °C and 150 °C IHP-samples expressed in % in the (Ri, Li) impedance plane. Heating durations are 0, 30, 60, 120, 240 s.
4. Conclusions
The implementation of a non-contact RF probe was carried out for the sensing of burns made on pork fillet samples, used as organic tissue test samples. The proposed method appeared relevant to sense the complex dielectric changes of burned tissues, through the changes of the Ri and Li parameters provided by the proposed measurement method. Also, tissue heating conditions involving different temperatures and/or procedures provide different sensing results. These preliminary results open the way to promising non-contact diagnostic and monitoring of burn wounds using MTLR sensors, which, owing to its planar geometry and wireless implementation, could be integrated in smart medical dressings in the future.
Author Contributions
S.S. more specifically worked on the measurement principle and its experimental implementation, T.H.N.D. specifically worked on the sample preparation and measurements. T.H.N.D. and P.-Y.J. more specifically worked on study methodology and data analysis, and wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by LabeX LaSIPS (ANR-10-LABX-0040-LaSIPS) managed by the French National Research Agency (n°ANR-11-IDEX-0003-02).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Burke-Smith, A.; Collier, J.; Jones, I. A comparison of non-invasive imaging modalities: Infrared thermography, spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis and laser Doppler imaging for the assessment of adult burns. Burns 2015, 41, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusson, M.; Rossignol, J.; Binczak, S.; Laurent, G.; de Fonseca, B. Assessment of Burn Depths on Organs by Microwave. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Wake, K.; Watanabe, S. Measurement of the dielectric properties of the epidermis and dermis at frequencies from 0.5 GHz to 110 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 4739–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, T.-H.-N.; Wang, M.; Serfaty, S.; Joubert, P.-Y. Contactless Radio Frequency Monitoring of Dielectric Properties of Egg White during Gelation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfaty, S.; Haziza, N.; Darrasse, L.; Kan, S. Multi-turn split-conductor transmission-line resonators. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masilamany, G.; Joubert, P.-Y.; Serfaty, S.; Roucaries, B.; le Diraison, Y. Radiofrequency inductive probe for non- contact dielectric characterization of organic medium. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Wang, M.; Serfaty, S.; Placko, D.; Joubert, P.-Y. Evaluation of a dielectric inclusion using inductive RF antennas and artificial neural networks for tissue diagnosis. Stud. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. Electromagn. Nondestruct. Eval 2018, 43, 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Masilamany, G.; Joubert, P.-Y.; Serfaty, S.; Roucaries, B.; Griesmar, P. Wireless implementation of high sensitivity radiofrequency probes for the dielectric characterization of biological tissues. In Proceedings of the IEEE MeMeA 2014—IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–12 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, J.E., Jr.; Moré, J.J. Quasi-Newton Methods, Motivation and Theory. SIAM Rev. 1977, 19, 46–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).