Abstract
Paintings are complex multi-layered systems made of organic and inorganic materials. Several factors can affect the degradation of paintings, such as environmental conditions, past restoration works and, finally, the type of painting technique and the art materials used over the centuries. The chemical–physical characterization of paintings is a constant challenge that requires research into and the development of novel analytical methodologies and processes. In recent years, solvents and water-related issues in paintings are attracting more attention, and several studies have been focused on analyzing the interaction between water molecules and the constitutive materials. In this study, recent applications applying different NMR methodologies were shown, highlighting the weakness and the strength of the techniques in analyzing paintings. In particular, the study of water and its diffusive interactions within wall and oil paintings was performed to prove how the portable NMR can be used directly in museums for planning restoration work and to monitor the degradation processes. Furthermore, some preliminary results on the analysis of varnishes and binders, such us linseed oil, shellac, sandarac and colophony resins, were obtained by 1H HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy, highlighting the weakness and strengths of this technique in the field of conservation science.
1. Introduction
Cultural heritage paintings are complex and heterogeneous materials composed by a mixture of organic and inorganic compounds. From an analytical point of view, the characterization of the molecular composition of paintings involves several methodologies from multiple disciplines including materials science, chemistry, bioscience, and environmental sciences. Analytical methodologies are applied not only to characterize the historical materials used by the artists, but also to investigate their degradation states and processes, and finally to plan and monitor the best restoration practices. The study of degradation processes and the characterization of chemical compounds in wall and canvas paintings, represent fundamental steps for their conservation. Various organic compounds can be present in paintings, such as egg, oil, synthetic, and natural resins mixed in a multilayered structure. Wall painting is widely considered to involve a lime-based plaster usually painted by an aqueous solution of inorganic pigments. However, organic binders have habitually used also in wall paintings by the artists to provide protective layers or varnishes and as final touches. Furthermore, the presence of organic compounds used in past restoration works can equally be found [1,2,3].
One of the most important degradation issues is the presence of moisture and its complex interactions within the pores and the multi-layered structure of historical paintings. A significant amount of water can trigger several degradation processes, such as mechanical stress, the abundant precipitation of mineral salts, microbiological attack, color change in pigments, and formation of metal soaps [4,5,6,7]. Water uptake in paint can typically originate from the environment as well as from water-based cleaning treatments, the use of which is mostly encouraged because of their lower toxicity and safety with respect to the organic solvents. Because degradation processes may be typically activated or driven by diffusion, the possible interaction of water and solvents, and the diffusion of reacting species along the paint matrix must to be evaluated when studying the processes that underlie the formation of the painting degradation of undefined compounds.
In recent years, the exploitation of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) in conservation science has been increasingly widespread, and several successful new studies have been reported in the literature [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. This paper describes some recent applications using portable NMR and high-resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectroscopy to help in the planning of restoration procedures and to characterize the organic materials used in historical paintings.
The development of portable NMR probes was an outstanding innovation in the application of NMR methodologies for cultural heritage analysis. Combining an open magnet and a surface radio-frequency coil, a magnetic field was generated external to the sensor, enabling the analysis of large objects without any sampling. Although the magnetic field generated by these sensors is strongly inhomogeneous, it is possible to measure relevant parameters such as proton density, longitudinal (T1), and transverse (T2) relaxation times, and the self-diffusion coefficient, and to collect T1-T2 correlation maps. Furthermore, the signal can be detected on the surface as well as at different depths inside the sample. Portable NMR (called single-sided NMR or unilateral NMR) may be considered one of the most effective techniques to rigorously evaluate and monitor humidity and the effect of cleaning treatments applied on paintings [3,15,16,17]. Unilateral NMR has been previously used to measure the self-diffusion of water molecules in porous stone and in natural and synthetic polymers [18]. In the case of paintings, portable NMR could encode the profile of the multilayered structure [19,20] in a fully non-invasive way and map the work of art along its thickness by identifying possible locations where a sampling may be carried out [21]. With unilateral NMR, it is possible to measure the hydrogen depth profile, the relaxation times, and the self-diffusion coefficients of water and solvents within the paint layer in a nondestructive way.
In this study, different NMR methodologies, such as portable NMR and HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy, were applied to study art paintings.
Portable NMR was used to evaluate the water content of a wall painting in the Turkish room, Villa Medici in Rome and to monitor the effects of water-based cleaning treatments applied on modern oil paints exhibited at the National Gallery of Modern Art (GNAM) in Rome. Unlike the more common NMR spectroscopy, unilateral NMR is a Time-Domain Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (TD-NMR) relaxometry and diffusometry method that does not provide any information about the chemical structure of molecules. The characterization of binders/varnishes in paintings by NMR spectroscopy has been conducted in previous studies using mostly liquid-state NMR, and solid-state NMR techniques [22,23,24,25,26,27]. Even if solid- and liquid-state NMR are powerful analytical techniques, they showed some limitations compared to the most-used traditional techniques for analyzing painting materials such as chromatography (GC/MS and HPLC) techniques and FT-IR spectroscopies. Actually, NMR is a low-sensitivity spectroscopy that demanded rather large amounts of the sample to be involved, from 20 to 100 mg, to perform a solid-state 13C NMR spectrum, and 1–2 mg to obtain a liquid-state 1H NMR spectrum. These amounts of material are very difficult to obtain from precious artworks, limiting the application of NMR spectroscopy to the painting’s characterization. Currently, new NMR microprobes and technologies have been developed to further reduce the amount of the sample analyzed. Among them, High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectroscopy allows the analysis of very small amount of soft-materials [28,29]. HR-MAS NMR has been used to study chemical reactions at the liquid–solid interface in heterogenous materials, and non-liquid biological samples [30]; to study the mechanism of chromatographic separations [31], and to evaluate the diffusion of hydrophobic drugs and water molecules in liposomes [32].
In the field of heritage science, HR-MAS spectroscopy was rarely applied, and to our knowledge few papers have been published in the literature to date. HR-MAS has been used to study the degradation of cellulose in the paper due to water [33,34]. More recently, we have used HR-MAS in combination with unilateral NMR to analyze the diffusion of water in lead oil paintings [35]. In this study, HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy was exploited to study linseed oil, shellac, colophony and sandarac to chemically distinguish these compounds in paintings using a reduced amount of the sample.
2. Results
2.1. Unilateral NMR to Analyze the Water Content in Wall Paintings
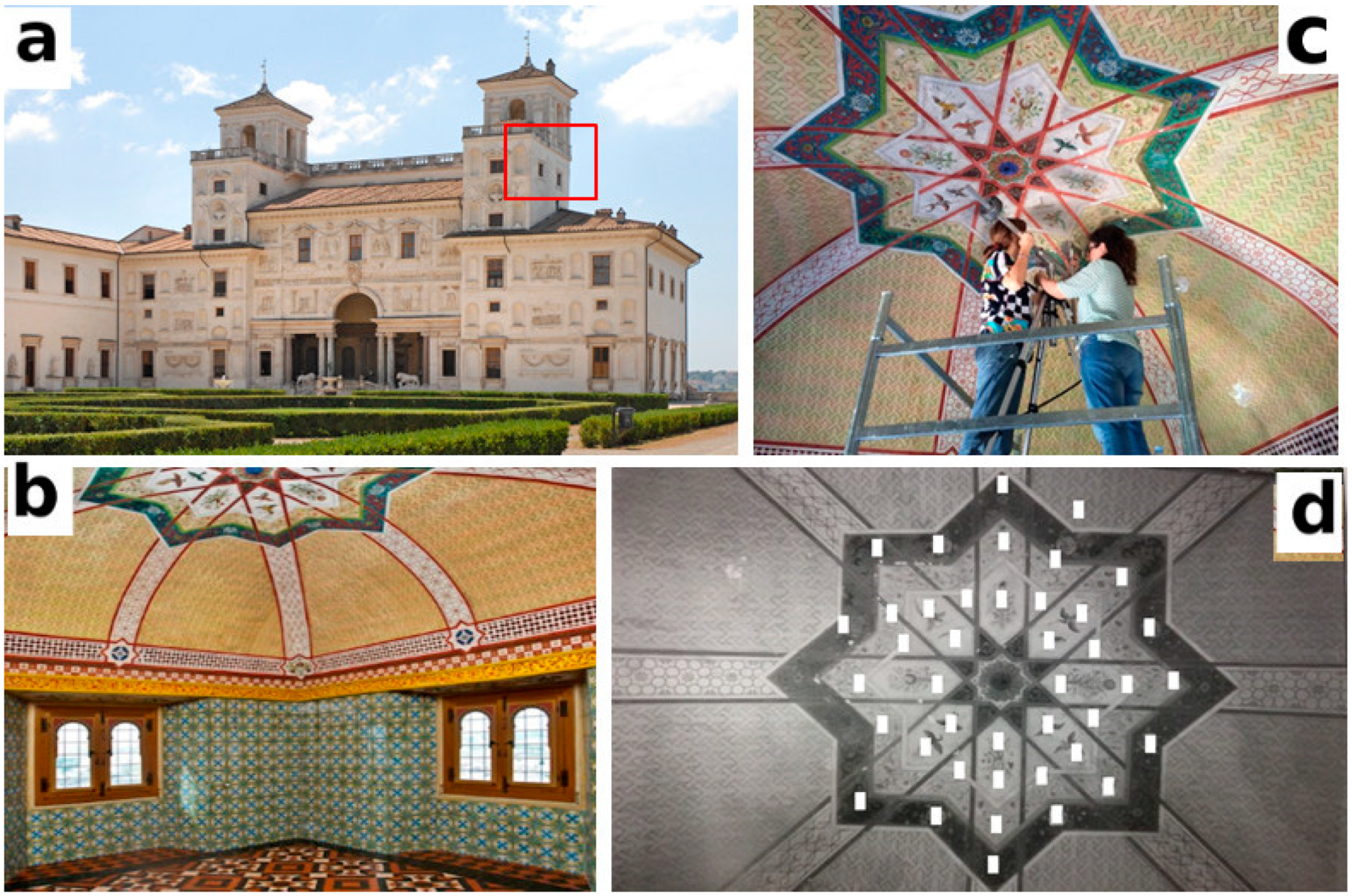
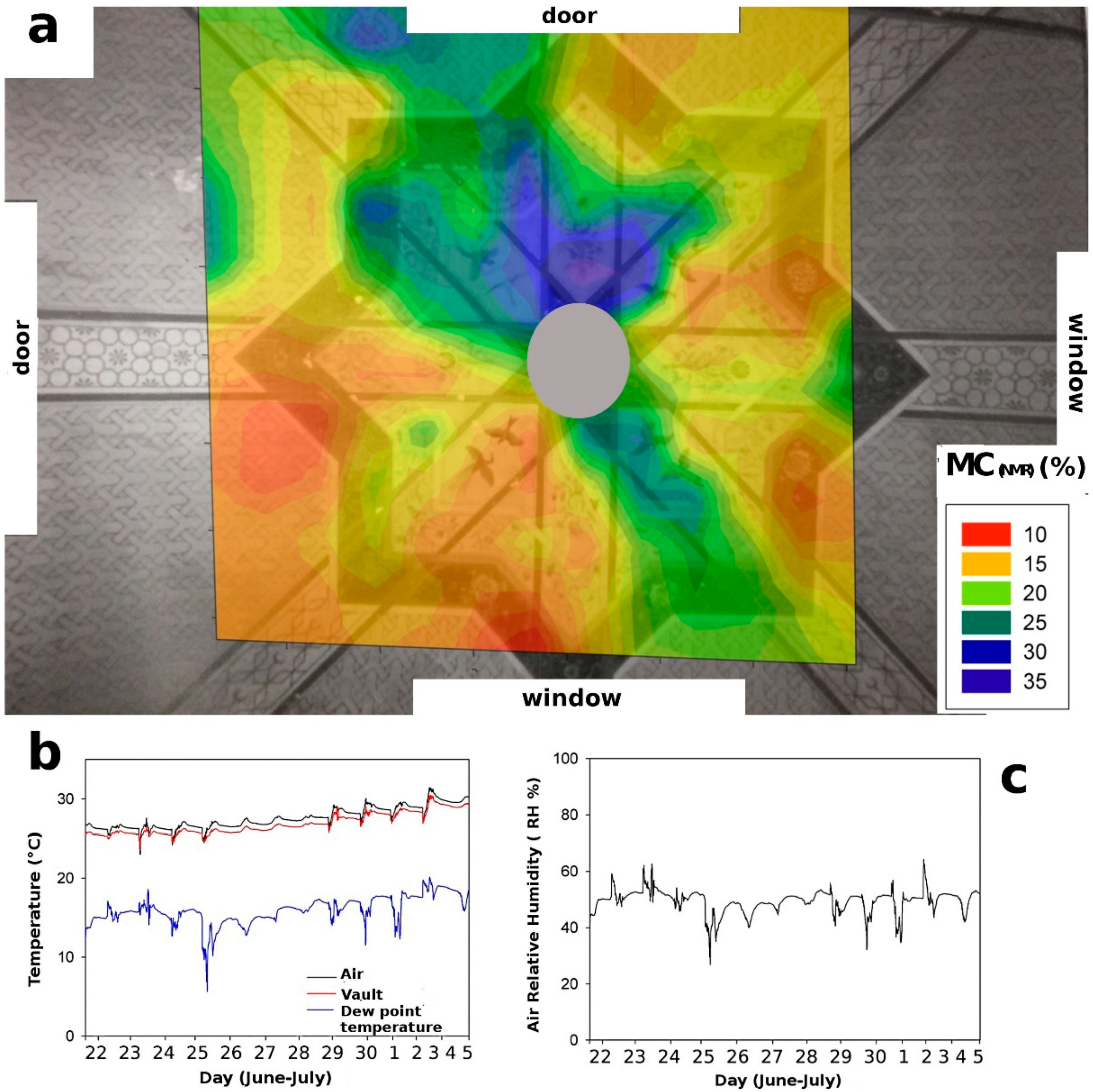
Portable NMR was applied to monitor the distribution of moisture in the Turkish room vault which was affected by rain percolation from the terrace located over the room. For this study, the NMR probe was mounted on a mobile metal arm to analyse the vault surface along a vertical direction. As is well known, the amplitude of the proton NMR signal is linearly proportional to the amount of water uptake [20]. The matrix of obtained data were interpolated to achieve a contour plot, representing a three-dimensional surface in which the x-y plane shows the dimension of matrix measured on the vault surface, and the z-axis contains the amplitude values of the NMR proton signal. In such a map, the distribution of water is pictured as a colormap in which the red areas reflect low water content, and blue areas reflect high water content, see Figure 1.
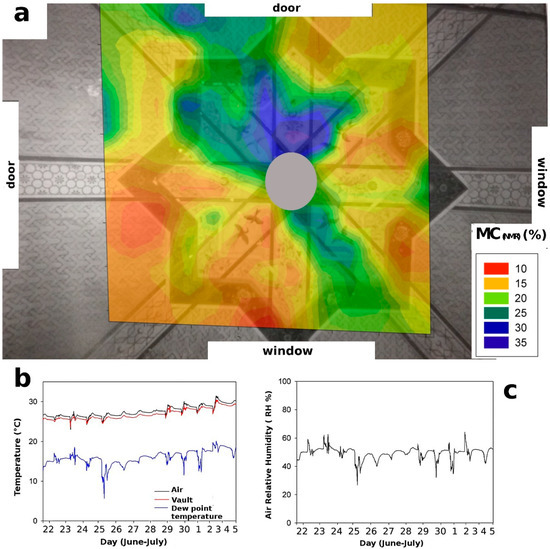
Figure 1.
(a) NMR moisture, (MCNMR) distribution map of painted vault measured in the Turkish room. The water content is shown as a gradient of color. Red indicates the lowest content of absorbed water, and blue indicates the highest content. The legend shows the percentage of MC(NMR). (b) Temperature of the air and vault (°C), dew point temperature (°C) on the vault surface; (c) Relative humidity of air (RH%). The maximum error on MC(NMR) values was evaluated using the error propagation theory and it was found to be less 10% of the nominal value.
To determine the water content (MC) in the vault, a calibration of the 1H NMR signal was performed using model plaster samples which were prepared according to the original recipe, dating from the 19th century. The calibration between the water content of the model samples, and the NMR signal was performed using the imbibition coefficient (ic) according to the following equations, as reported in [36]
where Api is the amplitude of the NMR signal measured on the vault, Apmin is the lowest value of the amplitude measured on the vault, and are the average values of the amplitude of the NMR signal measured in the dried and water-saturated model plaster samples, respectively. Psd and Psw are the weights of the model plaster samples in dried and water-saturated conditions.
As reported in Figure 1, the three regions with the highest water content (blue color) were observed in the colormap of the vault. Specifically, in the most humid region, a MC(NMR) values of about 35% were found. In fact, according to the calibration assessment, the maximum amplitude of the NMR proton signal, measured in model samples, corresponded to 35% of the water content absorbed by wall panting. Over the course of NMR measurements, a daily monitoring of the temperature and relative humidity of air in the Turkish room was carried out. Results showed that the air temperature was, on average, about 27.6 °C, with a maximum of 31.4 °C and a minimum of 23 °C; see Figure 2b,c. In the figure, the temperature of the surface of the vault is also reported.
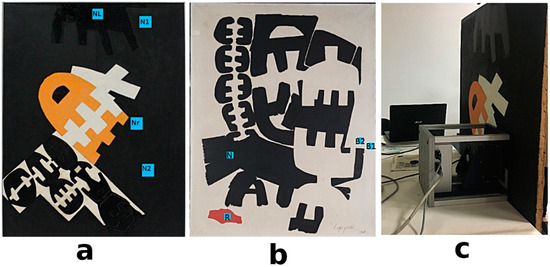
Figure 2.
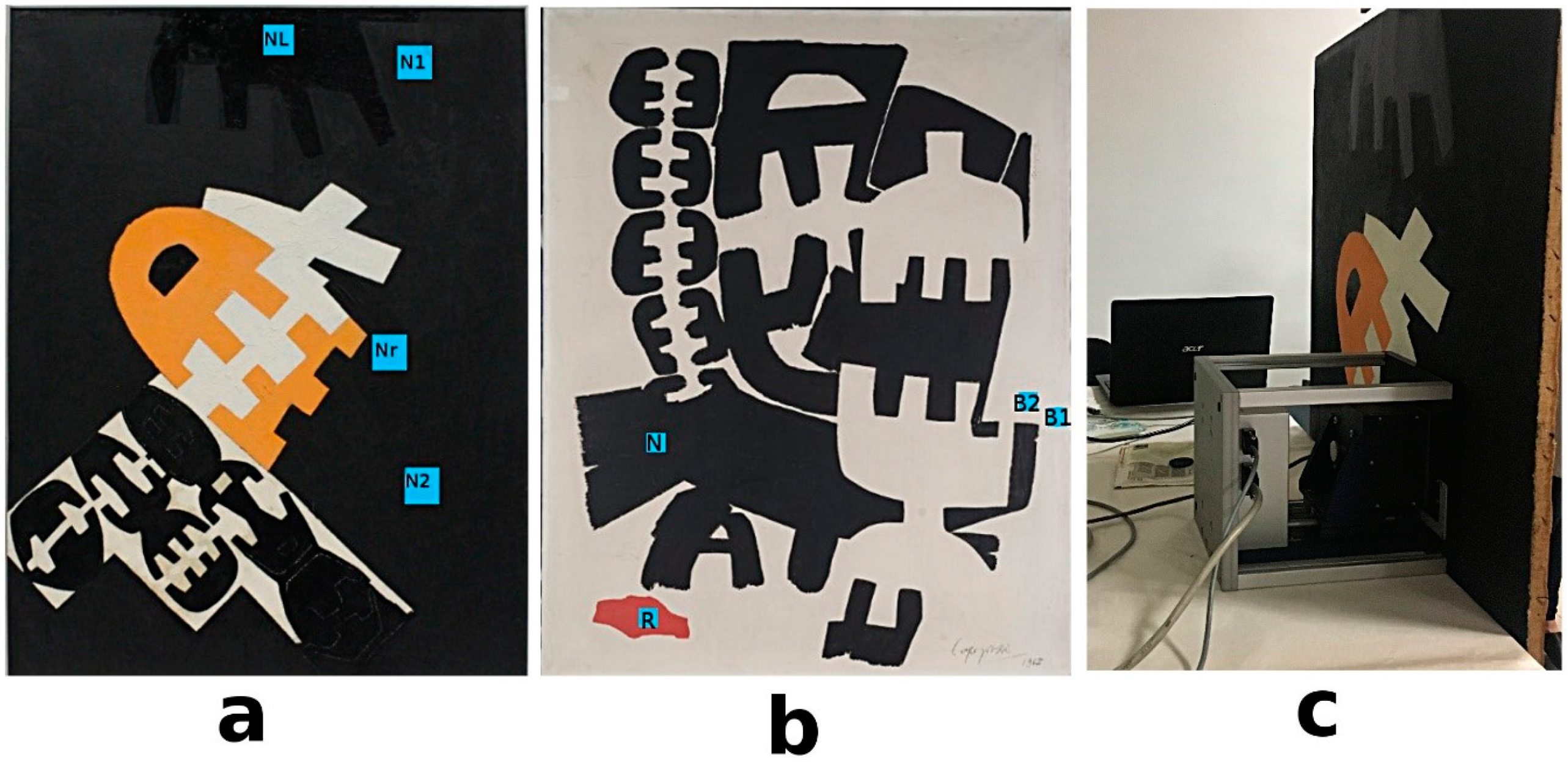
(a) “Surface 538” painting; (b) “Surface 553” painting; (c) portable NMR sensor while scanning the painting at the National Gallery of Modern Art (GNAM) in Rome. Nr indicates a repainted black area; NL indicates a shiny black area; N1 and N2 indicate two black areas with a similar appearance. N indicates a black area; R indicates a red area; B1 and B2 indicate two white areas with a similar appearance.
The surface temperature of the north-east wall, in the proximity of the exit door, showed an average value of 26.9 °C, with a maximum of 30.5 °C and a minimum of 23.5 °C. The average value of the dew point was 16 °C. Both the air temperature (minimum temperature 23 °C), and the surface temperature (minimum temperature 23.5 °C) were always found to be higher than the dew point, therefore, at least during the monitoring period, the occurrence of superficial condensation phenomena on the vault can be excluded. On the other hand, surface evaporation phenomena, in regions with a high-water content, are favored. The average relative air humidity was found to be 50% RH, with a maximum of 67% and a minimum of 27%; see Figure 3. To summarize, the results obtained indicate that the plaster of the wall is in a conservative environment with a low condensation risk and a rather good degree of water vapor exchange between the walls and the air.
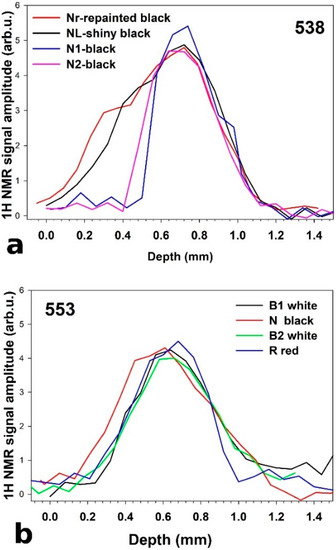
Figure 3.
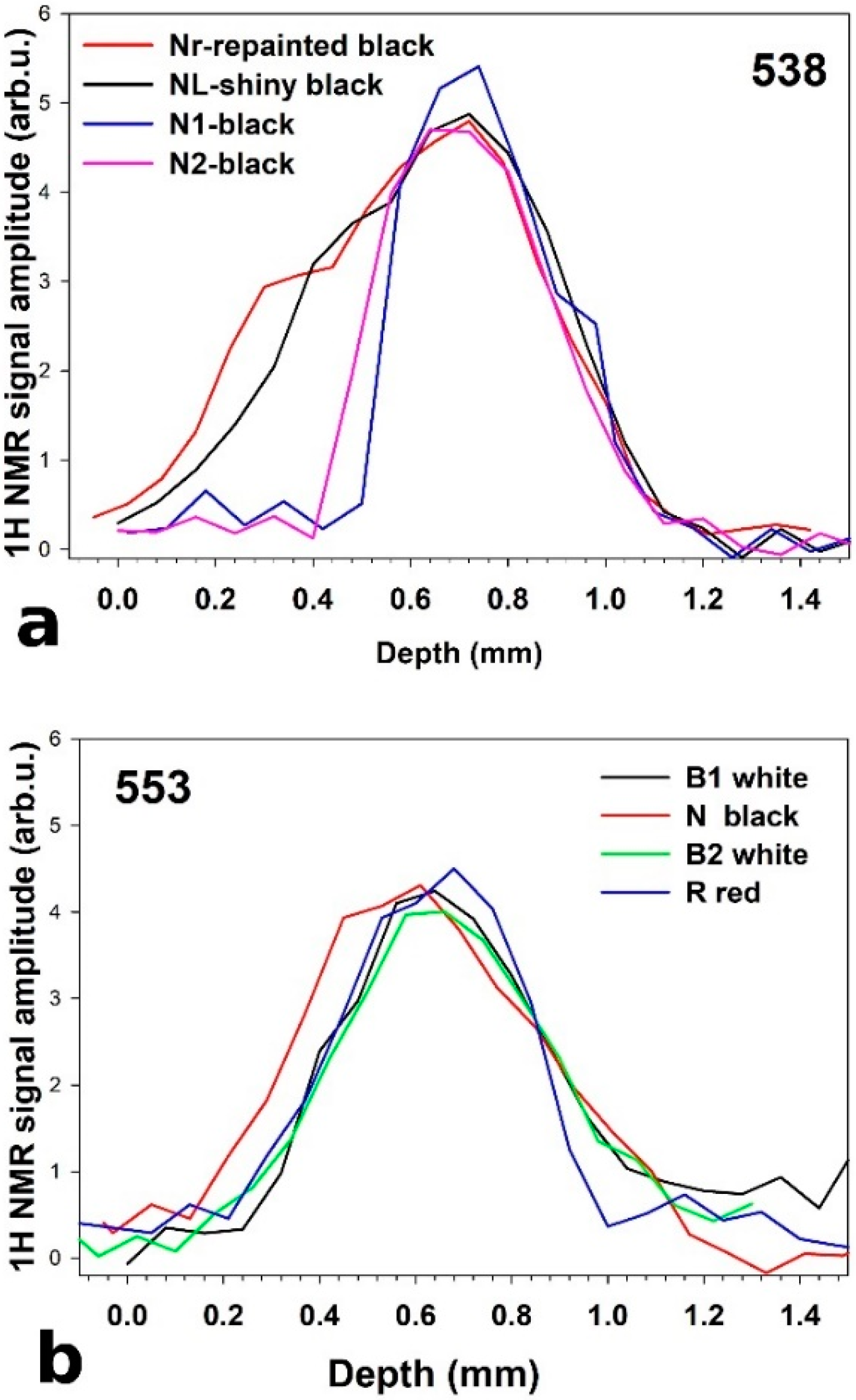
1H NMR depth profiles of painted areas in: (a) “Surface 538”; (b) “Surface 553”.
2.2. Unilateral NMR to Evaluate Water-Based Cleaning Systems Applied on Oil Paintings
Humidity in the environment is not the only cause of degradation that can affect the surface of paintings; water-based cleaning systems may also be important activating agents of degradation that should be evaluated.
The cleaning of artworks is performed to remove undesired coatings that may degrade artefacts such as efflorescences, oxidized metal layers, crusts, and naturally aged varnish layers. The cleaning of painted surfaces is an irreversible operation that may be potentially harmful to the conservation of the artefact [37]. To improve the selectivity and safety of this procedure, more efficient cleaning products are demanded [38,39,40]. The water released, as well as its distribution and penetration within a painting, strongly affect the performance of the cleaning treatment. Furthermore, both physical and chemical properties of the cleaning systems and the properties of the support to which the system is employed, should be carefully studied.
By 1H NMR depth profiles, the thickness of the painted layers and its variability on the whole area of the painting can be evaluated during the cleaning treatment [15]. It is equally possible to study the diffusivity of solvents and water-based cleaning system, and the thickness of residual layers which were poorly solubilized by the cleaning formulation [3]. an NMR depth profile can detect, non-invasively and in situ, the multi-layered structure of a painting. In recent years, Presciutti et al. [41] reported the first NMR stratigraphy collected in a wooden painting dating from the 15th century. The profile encodes the intensity of the 1H NMR signal as a function of the depth scanned, recognizing layers according to their hydrogen content.
In this study, 1H NMR depth profiles were measured on nine regions of two paintings, namely “Surface 538”, and “Surface 553”, made by Giuseppe Capogrossi in the 1960s. The NMR profiles revealed the thickness of the painted layers and identified possible heterogeneities in black, red, and white painted areas; see Figure 2.
As linseed oil is a material rich in hydrogen nuclei, it is possible to scan the proton density along the entire thickness of a paint layer and determine its changes. The x-axis, in Figure 3a,b, corresponds to the distance along the normal to the oil paint layer, where the zero value of the depth measured corresponds to the top of the paint and the greatest value of scanned depth corresponds to the bottom.
The thickness of the paint film was calculated as the full width at the maximum amplitude of the profile. In most of the analyzed area, the thickness of the paint was found to be about 300 µm; see Figure 3. Only in two areas, namely Nr and NL, was a greater value of thickness found, indicating the presence of additional coatings.
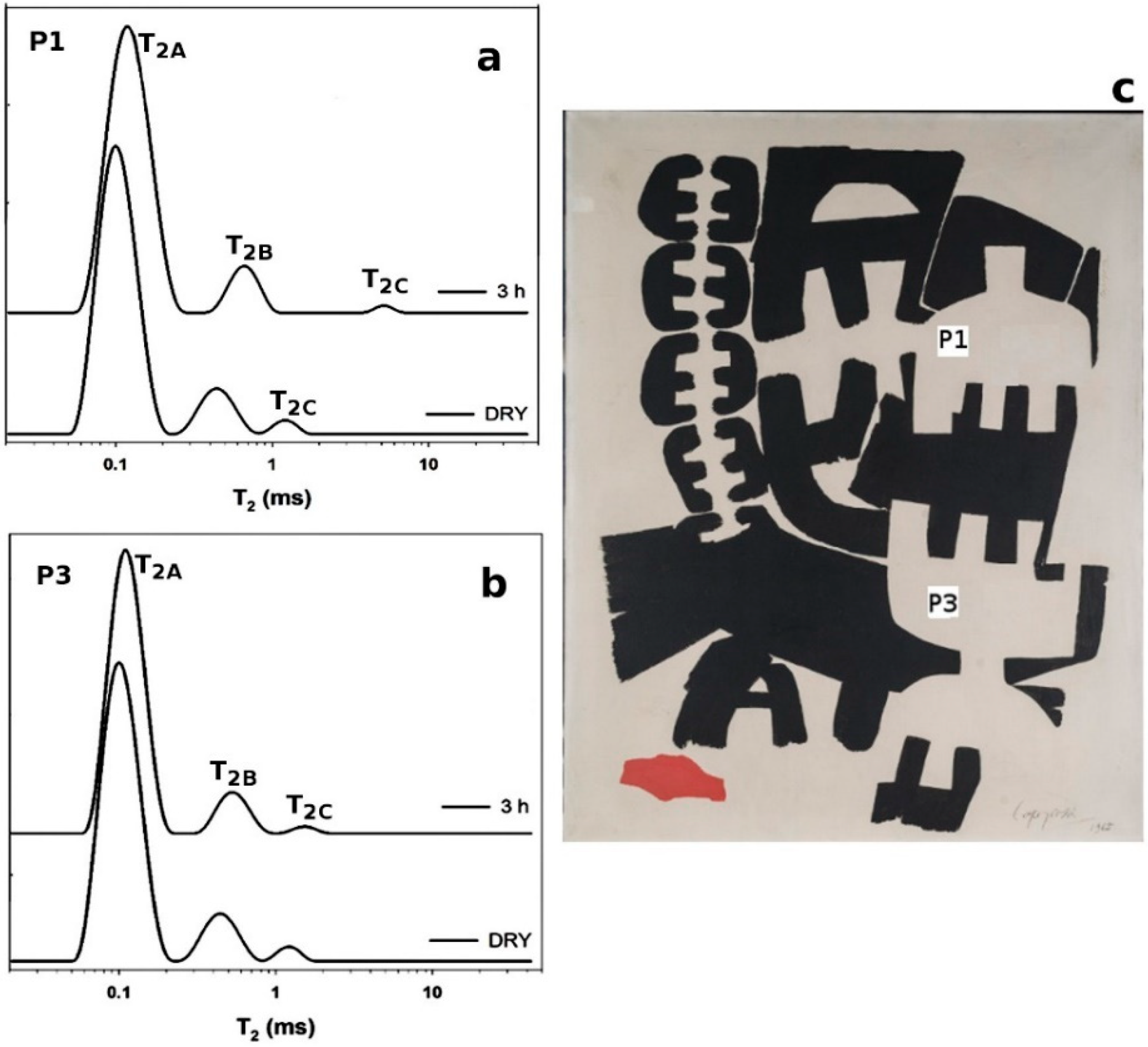
From a visual observation, these two areas were probably covered by a varnish coating and a repainted black area, respectively. As multilayered objects, paintings can show a high degree of heterogeneity due to the process of manufacturing, the degree of degradation and the presence of non-original materials used in past restoration works. The obtained profiles were used to select those regions with the highest NMR proton signal and similar values of thickness in which to perform relaxation time measurements, T2eff. Two similar and comparable white areas, namely P1 and P3, of the painting “Surface 553”, were selected and analyzed before and after the cleaning treatment. Effective transverse relaxation times, T2eff, were collected to a depth of 100 µm from the surface; see Figure 3b. The distribution of T2eff, collected before and after the application of the cleaning treatment, was reported in Figure 4a,b. For both areas, the distribution of transverse relaxation shows three components, indicating three different domains of proton mobility; see Table 1. It was found that the shortest component, T2A, of about 0.1 ms, involves a majority of the protons (85% of the population); an intermediate component, T2B, of about 0.5 ms, involves ~10% of the protons; and the longest component, T2C, of about 1 ms, involves 3% of the protons. Interestingly, these results are remarkably similar to those found in the model oil paintings studied and reported in [35]. In our samples, a slight shortening of the T2 values was observed with respect to the model oil paints. This shortening of T2eff values indicates that a more considerable degree of cross-link, due to the natural aging of the pictorial layer, has decreased the relative motional freedom of protons in each domain of mobility. The shortest component, T2A, corresponds to the protons contained in relatively rigid skeletons of the polymeric network. However, not all protons are bounded to the rigid network, e.g., terminal methyl groups in the aliphatic chains. In fact, aliphatic chains may have regions showing relative motional freedom [42]. As such, T2B may be assigned to the protons in a partially free domain of mobility. The longest component, T2C, may be assigned to protons in saturated free fatty acids or in residual fatty acids not completely cross-liked that have a higher degree of mobility than those connected to the polymeric framework. These mobile proton domains may be due to the presence of plasticizers, whose role in polymerized oil has been previously studied [43,44]. Furthermore, in paints subjected to a high degree of hydrolysis of the ester bonds, the mobile protons fraction can also be attributed to the presence of a higher amount of mono-, di-glycerides, glycerol, diacids and free fatty acids [22]. Furthermore, in modern oil paintings, the application of industrial common paint additives can be an additional source of chemical species with a significant degree of mobility within the polymeric matrix.
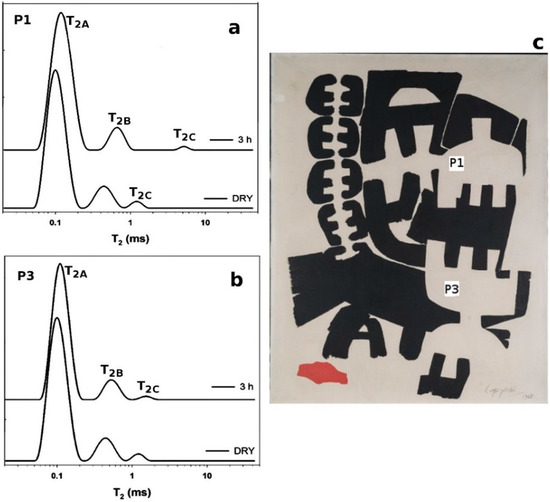
Figure 4.
Effective transverse relaxation times, T2eff: (a) white area P1; (b) white area P3 before and after the cleaning treatment; (c) P1 and P3 selected areas as indicated on the painting.

Table 1.
Values of T2eff (ms) measured in oil painting before and after the application of cleaning treatments. W indicates the normalized population of proton density (%). * (b) = before the cleaning treatment; (a) = after the cleaning treatment.
T2eff were measured, in P1 and P3, after the application of a buffer solution (pH 5.6) applied for 5 min, without and with a xantham gel (2%), respectively. The T2eff were measured in both areas 3 h after the treatment; see Figure 4a,b. T2c, in P1, was found to be longer after the application of the water buffer solution, achieving a value of 5 ms from an initial value of 1 ms. The observation that T2c in P1 was much longer than T2c in P3 indicates that the water transport on the surface of paintings was effectively controlled by the gel. Less diffusivity of water on the painting surface prevents an increase in the mobility of those mobile fractions that are more sensitive to the water action and can freely move within the painting.
These preliminary results are part of a wider joint project focused on the conservation problems related to modern art, funded by the IPERION CH.IT.
2.3. HR-MAS to Characterize Organic Materials in Paintings: Linseed Oil, Shellac, Colophony, and Sandarac
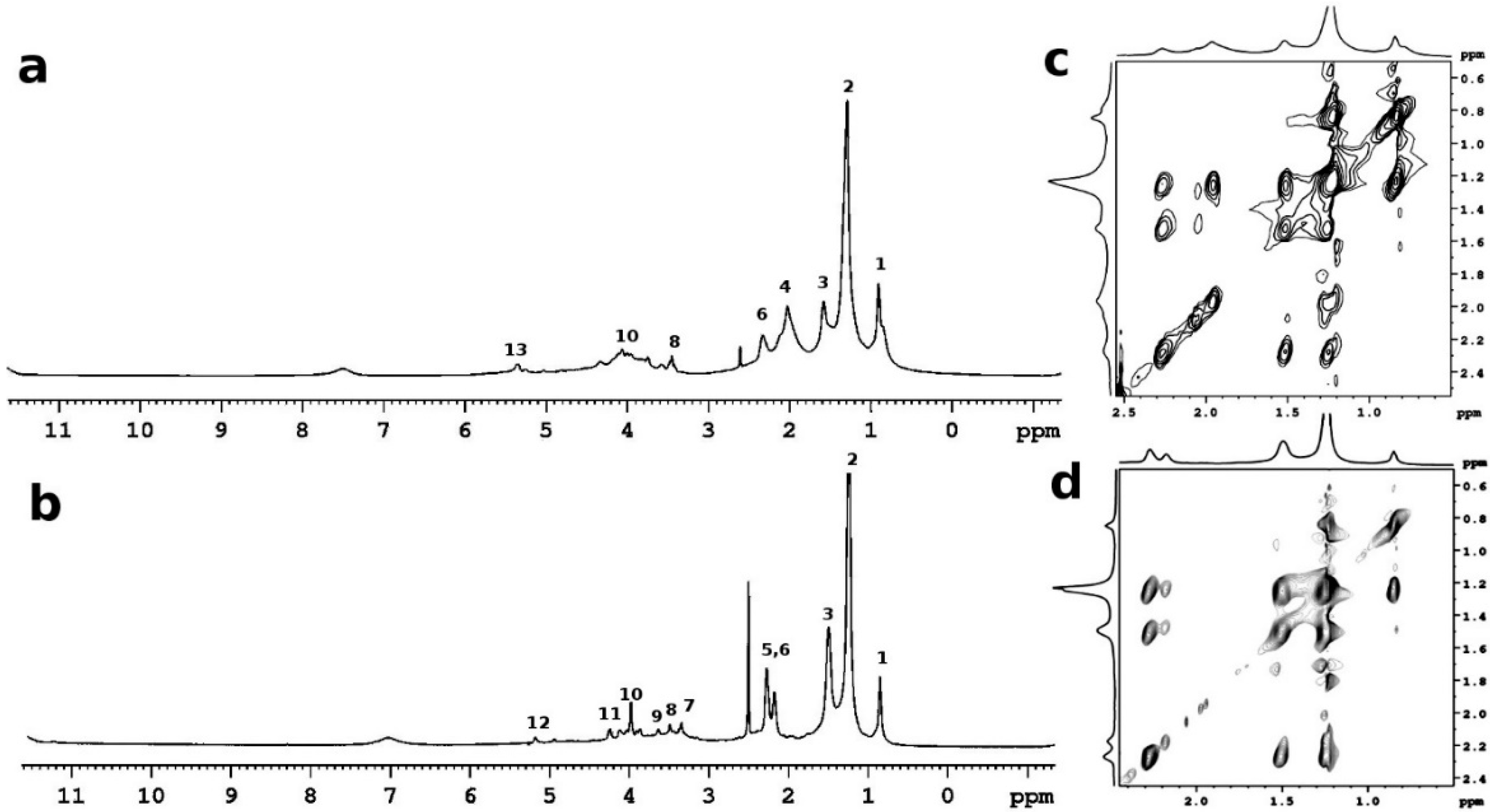
Since ancient times, organic compounds of natural origin, such as dried vegetable oils and resins, have been largely used as binders and varnishes of paints on canvas. Linseed oil is one of the most used drying oils in paintings. In drying oils, the unsaturated triglycerides crosslink in a polymeric matrix, stabilizing the pigments and solidifying the paint film. HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy is a remarkable analytical technique for studying the mobile phase of an oil in contact with a solvent. Two samples were analyzed by 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy; one sample was collected from an ancient oil wall painting dating from the 17th century; and another one was collected from a model paint made of linseed oil mixed to lead carbonate and naturally aged for 10 years. The 1H HR-MAS NMR spectra of the two samples show the most intense signals in the spectral region from 0.85 to 1.2 ppm due to protons of the aliphatic chains; see Figure 5. The resonances observed at 1.5 ppm was assigned to the methylene ester groups; the protons in the aliphatic methylene chains give the sharp peaks at 1.2–1.4 ppm. Finally, protons in the terminal CH3 of all fatty acids give resonances at 0.85 ppm.
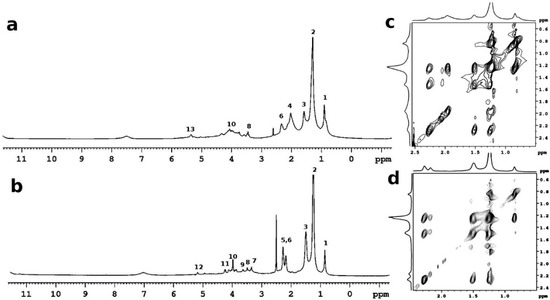
Figure 5.
1H HR-MAS NMR spectra (d6-DMSO δ = 2.55 ppm, H2O in DMSO δ = 3.33 ppm) of (a) model paint sample linseed oil with lead carbonate (1:1) naturally aged for 10 years; (b) oil wall painting (17th century); (c) 1H-1H TOCSY of the oil model paint sample; (d) 1H-1H TOCSY of the oil wall painting (17th century) sample. Peak numbers according to Table 2.
The broad peak at 2.3 ppm is related to the CH2 near the carbonyl groups of esterified free fatty acids and diacids, and the allylic CH2 gives the resonance at 2.02 ppm. The weak and broad peak in the spectral region at 3.3–3.9 ppm are likely related to the protons in -CHOH, and -CH2OH in 1-monoglycerides (δ = 3.3 ppm and δ = 3.7 ppm), and CHO oxo and hydroxy acids (δ = 3.9 ppm). The multiple broad peaks at 4 ppm were assigned to the CH2 of triglycerides and diglycerides, as reported in Table 1. The CH of the triglyceride moieties gives the resonance at 5.2 ppm, whereas the resonance at 5.2 ppm was assigned to the unsaturated vinyl protons. Even if 1H spectra are very similar in both samples, in the oil wall painting (17th) the peaks were sharper, indicating a higher degree of solubility of the paint in DMSO. By HR-MAS spectroscopy, samples are analyzed directly in contact with deuterated solvents in order to increment the local mobility and thereby to reduce the contribution of the strong dipolar interactions. Given this, in cases of polymerized oil a different degree of swelling can affect the resolution of the spectrum. We hypothesize that a considerable degree of hydrolysis can affect the oil wall painting (17th), causing the presence of a larger amount of extractable free fatty acids. The TOCSY 1H-1H 2D map showed both unsaturated and saturated fatty compounds in the model paint, indicating that a not-completed process of polymerization occurred; see Figure 5c,d. Even if lead is one of the most used driers for linseed oil, the polymerization is a very slow process that can take even centuries to be completed. Furthermore, lead (II) is a metal ion that can easily coordinate free fatty acids, forming insoluble metal soaps [45,46].
These results indicated that, the swelling degree is an important factor to be considered for obtaining well-resolved HR-MAS spectrum in oil paintings. Furthermore, further paraments should be considered, such us the type of pigment, solvent, cross-link degree, and degree of hydrolysis of linseed oil for studying the interactions at the solid–solvent interface in the paint film.
Chemically, varnish is a very complex system made of a mixture of drying oils and natural resins. In the conservation field, with special regards to easel paintings, the most employed resins are sesquiterpenoids (shellac), diterpenoids (colophony, sandarac, and copal) and triterpenoids (mastic and dammar) [47]. Varnishes have the tendency to change appearance, turning into a brittle film with age. Yellowing is one of the main problems recognized in the field of painting conservation, because it changes the solubility and the optical properties of the painting, e.g., obscuring the colors [48].
During cleaning treatment, the interaction of solvents and varnish layers remains a crucial aspect to be evaluated because the more soluble compounds and those that have more freedom of movement in the swollen painting can initiate further degradation processes. HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy can provide important molecular information at the liquid–solid interface, evidencing, in a single experiment, the interactions between polymerized varnishes and solvents.
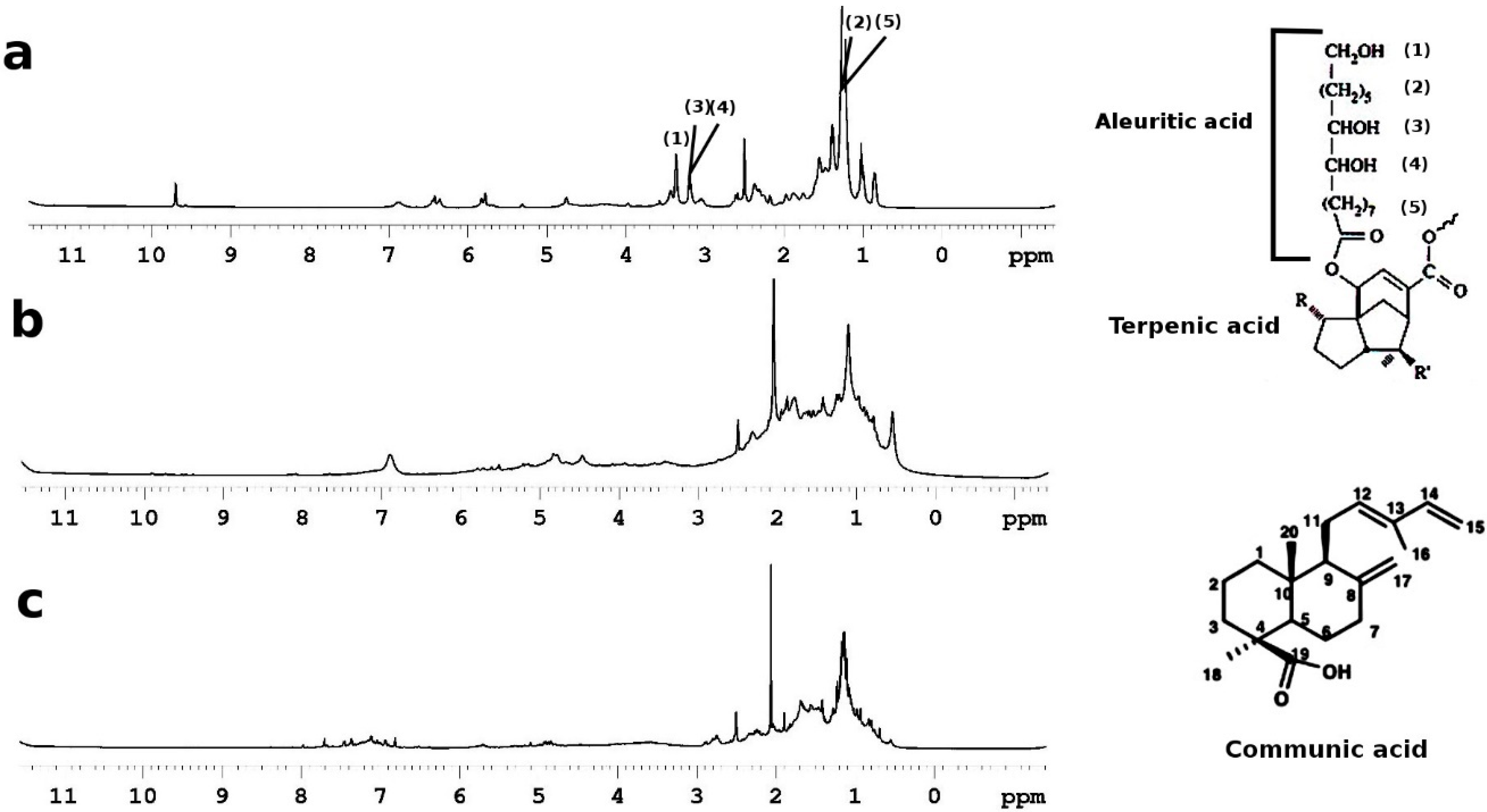
In this research, 1H HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy was used to analyze three types of natural resins, namely shellac (sequiterpenoid resin), sandarac, and colophony (diterpenoids resins) swelled in d6-DMSO; see Figure 6.
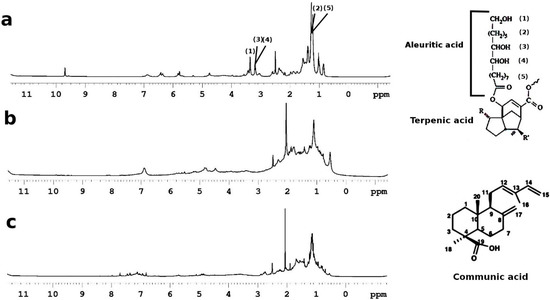
Figure 6.
1H HR-MAS spectroscopy spectra: (a) shellac; (b) sandarac and (c) colophony resin in d6-DMSO (δ = 2.55 ppm).
Shellac is a resinous secretion produced by Kerrie lacca bug, living in the branches of certain Indian and Thai trees. The resin is obtained from dried seed lac, following a process of purification and dissolution in ethyl alcohol. Shellac polymerizes in a long-lasting film that is primarily used as primer, wood finish, sealant, and odor blocker. The resin has a complex framework, primarily divided into a hard (70%) fraction and a soft (30%) fraction. Even if the chemical composition can vary depending on the type of insect, tress, and geographical region, the major compounds were recognized in mono and polyesters of hydroxy-aliphatic acids, such as aleuritic, and butolic, and sesquiterpenoid acids such as jalaric, and laccijalaric acids. In Figure 6a, the 1H HR-MAS spectrum, in DMSO, shows the most intense peaks assigned to the aleuritic acid. The peak at 1.2 ppm is due to protons CH2, the peak at 3.2 ppm is due to protons in CH2 near hydroxyl groups in the aliphatic chain, and the peak at 3.4 ppm is due to CH2OH terminal groups; see Figure 6a.
Sandarac and colophony are resins naturally synthesized by certain conifers, typically Cupressacea and Pinacea. Their chemical composition depends on the family of trees from which they were produced. Both sandarac and colophony are constituted of acids with two terpene units containing 20 carbon atoms.
Sandarac resin has been commonly used since the 16th century, as protective varnishes, additives, and fixatives for paintings on canvas [49,50]. The sandarac resin produces a rigid matrix following a process of polymerization and cross-linking of the diterpenoid acids. As constituted by hydrocarbons, the sandarac resin turns out to be insoluble in water and partially soluble in organic solvents. In Figure 6b, the 1H HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy of sandarac resin in DMSO was reported. The spectrum of the resin is dominated by the resonances, from 0.6 to 2.0 ppm, of saturated hydrocarbon alkanes. The presence of pimarane, labdane, and abietane alkanes shows an undifferentiated pattern from which various sharp peaks can be differentiated [51]. In the 1H HR-MAS spectrum, the most intense and sharp peaks were assigned based on the resonances of sandaracopimaric, and communic acid. Protons H1–H7—see Figure 6b—show characteristic splitting patterns and more intense peaks in the region of 1.0–2.1 ppm. The sharper peak at 2.09 ppm is probably due to H11. Olefinic protons emerged in the 1H NMR spectrum at 5.4, 4.9, 4.8, and 4.5 ppm.
Due to a very fast drying process, and very good solubility and compatibility with oils and other type of resins, colophony has been widely used as a primer and adhesive. Like sandarac, colophony is a diterpenic resin, mostly composed of a complex mixture of mono-carboxylic acids of alkyl hydro-phenanthrene, with higher concentrations of pimaric-, and abietic-type acids [52]. The 1H-NMR spectrum of colophony, in DMSO, was reported in Figure 6c. The spectrum showed a fingerprint similar to that found in sandarac. An extensive overlap can be observed in the saturated hydrocarbon alkane region, caused mainly by proton–proton coupling interactions. The weak signals between 4.7 and 5.0 ppm were assigned to endo- and exocyclic double bonds of abietic acid. Furthermore, the resonance bands of aromatic protons of abietic acid were also observed between 6.9 and 7.3 ppm [53].
The results showed that 1H HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy can be successfully applied for analyzing binders/varnishes and to obtain well-resolved spectra, using small amounts of the sample (300 µg) without performing any pretreatment of the sample. Even if GC/MS and FTIR spectroscopy remain the most powerful analytical techniques to chemically characterize and identify organic molecules in materials paintings, these preliminary results showed the potential of HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy in analyzing paintings and their degradation process at the solid–liquid interface. In varnishes, HR-MAS NMR showed a higher sensitivity in discriminating the soluble fraction of material from those less solubilized. For instance, the presence of sharp peaks assigned to the aleuritic acids and abietic acids indicates that these compounds are the most affected by the solvent action. Such information is essential for the conservation and restoration of varnish in paintings; the less soluble species may remain on the surface of the painting, triggering future degradation processes. On the contrary, the identification of the soluble fraction may help restorers in selecting the more efficient formulations for removing aged varnishes. Further studies will be performed to develop an analytical protocol for identifying the best deuterated solvents, and the most useful experiments of spectral editing and pattern recognition [54]. With these experiments, it became possible to investigate in detail the change in molecular dynamics due to the interactions at the surface of the polymerized materials.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cases Studies and Model Oil Paints
Villa Medici is located on Pincio Hill in Rome, where the gardens of Lucius Lucinius Lucullus, a Roman general, were built between 66 and 63 B.C. The major villa covered the entire area between Salaria Vetus and the current northern area of Pincio. In 1576, Ferdinando de’ Medici, devoted to Antiquity like many of his contemporaries, purchased the Villa to convert it in a museum. He conceived of a large gallery to present his collection of antique masterpieces, inserting in the facade a cycle of antique decorated bas-reliefs. After 1803, there was a radical change in the function of Villa Medici, from a secondary residence for the Medici’s family was to an Academy. The Villa was thus destined to lodge young French artists in a community of ideas and talent. The Turkish room is an unusual boudoir, located in one of the towers of the Villa. The wall’s decoration, in the room, was realized in neo-Moorish style, in 1833, by Director of the French Academy Horace Vernet, who had been influenced by a journey in Algiers at the time of the French governance.
The oil paintings analyzed in this study were made by Giuseppe Capogrossi and are exhibited at the National Gallery of Modern Art in Rome. Giuseppe Capogrossi was born on March 7, 1900, in Rome. In 1933, he collaborated on the “Manifesto del primordialismo plastico” (Manifesto of plastic primordialism). From the mid-1930s, Capogrossi adopted a darker palette, and between 1945 and 1948 his figurative tonal painting gave way to an increasingly abstract geometric style. A significant shift in Capogrossi’s career took place in 1949, when he developed irregular fork-shaped signs. Capogrossi’s singularity was recognized both in Italy and abroad, and he took part in group exhibitions at Galerie Nina Dausset, Paris (1951); Guggenheim Museum (1953); Venice Biennale (1954, 1962); Documenta, Kassel, West Germany (1955, 1959); Carnegie International, Pittsburgh (1958, 1961); and Tate Gallery, London (1964). “Surface 553” and “Surface 538” paintings were made on canvas in the 1960s; the white areas of the paintings were constituted by linseed oil, zinc white, and titanium white. The black areas were constituted of carbon black pigment and linseed oil [55].
“L’Annunciazione” is an oil wall painting painted by Francesco Albani, said the Passignano. The cycle of paintings is located in the Rivaldi Chapel, “Santa Maria della Pace” basilica in Rome. This chapel was built in 1611 and all the ornaments were completed in 1614. The wall painting is an example of late Mannerist decoration. Above the prepared wall support, an oil layer has been applied, the thickness of which exceeds 200 µm, made of a pink-brown color and a very heterogeneous composition: iron oxides, aluminosilicates (probably due to clay material), carbon black, calcium-based pigments and white lead [56].
The model oil paint was made using drying linseed oil (Kramer) and lead carbonate (Sigma-Aldrich) with a concentration of 1:1 (weight/weight). The pictorial layer was applied by brush on glass in 2006; the sample was then stored in the laboratory under natural aging for 10 years. Sandarac, shellac and colophony (Kramer) model paint were prepared, solubilizing the resins in ethyl acetate, and then applying a thin layer on glass by brush. Samples were dried and cured in laboratory for 1 year.
3.2. Unilateral NMR
Measurements were performed on wall painting with an NMR probe from Bruker Biospin, operating at 17 MHz. Measurements were carried out at a depth of 0.3 cm from the surface, with a π/2 pulse width of 3 µs. Because of the inhomogeneity of the magnetic field, the Free Induction Decay, (FID) cannot be directly collected and must be recovered stroboscopically. Due to this limitation, by unilateral NMR it is possible to measure the 1H NMR signal by applying a Hahn echo pulse sequence [57]. On the vault, measurements were performed following a matrix of 40 points to cover the central area; see Figure 7d. Each point corresponds to an area of 20 × 50 mm2. The unilateral NMR probe consists of a U-shaped magnet constituted of an rf coil positioned in the gap of two anti-parallel permanent magnets mounted on an iron yoke. Such a probe generates a magnetic field external to the device, enabling large objects to be analyzed without any sampling. Since the inhomogeneous magnetic field is a further source of relaxation, the transverse relaxation time is an effective relaxation time, T2eff, shorter than that measured in a homogeneous field. To analyze the distribution of water, experimental data were interpolated, applying an algorithm for smoothing sharp variations in the proton NMR signal within the 3D dataset. Details of the calibration procedure are given in [36].

Figure 7.
(a) Villa Medici; (b)the Turkish room; (c) NMR probe mounted on its metal arm while measuring the vault surface; (d) Matrix of area analyzed on the vault by NMR.
To analyze the 1H NMR depth profiles and relaxation times (T2eff), in painting on canvas, a portable NMR operating at 13.6 MHz was used. The probe was constituted of an electronic unit from Bruker Biospin interfaced with a single-sided sensor ACT, developed by RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany [57]. This probe generates a magnetic field with an extremely uniform gradient which could analyze the proton density at different depths of measurement (1, 3, 5, and 10 mm) For each selected maximum depth of measurement, it is possible to obtain an 1H NMR profile with a micrometric resolution. The intensity of the 1H NMR signal reported in the depth profile was obtained averaging the amplitude of the first echoes of the decay, and applying a CPMG pulse sequence. A time domain of 32 echoes, an echo time of 40 µs, and a nominal resolution of 50 µm were used. The NMR probe was repositioned in steps of 100 µm for scanning the whole thickness of the paintings up to a depth of 2 mm. T2eff [57] were measured at 100 µm from the surface of the painting, a CPMG pulse sequence using 512 echoes and an echo time (2τ) of 40 µs.
3.3. High Resolution NMR Spectroscopy
1H High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) spectra were collected using a Bruker AVIII NMR spectrometer, operating at 600.13 MHz of proton frequency. The spectrometer was equipped with a MAS probe (and triple-resonance 4-mm with built-in z-gradient probe head from Bruker Biospin, which included a 2H lock channel. All measurements were carried out at 27 °C, 300 µg of the sample was held with d6-DMSO in a rotor with a volume of 12 µL, using a spin rate of 6 kHz to increase the spectral resolution.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, recent case studies were reported using different NMR techniques, such us portable NMR and 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy for characterizing and monitoring paintings. The use of new NMR techniques for analyzing paintings is still undervalued for the conservation of cultural heritage, and our findings indicated the possibility of increasing knowledge, developing innovative methods, and improving the uptake of research in the conservation of paintings. Since NMR probes and methods are continuously undergoing new developments and improvements to increase the sensitivity of the technique, a more widespread use in the field of cultural heritage and of NMR spectroscopy is probably expected. In fact, portable NMR and HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy are important tools to study the physical–chemical properties of both soluble and insoluble fractions of materials constituting artefacts and to directly analyze the interactions that may occur in swollen-state paintings. Furthermore, restorers can easily use these methodologies throughout the cleaning tests for shedding light on the performance of cleaning formulations and their effects on the surface of paintings. NMR is also an important analytical technique to study structural modifications that may occur by degradation processes, e.g., oxidation, hydrolysis and depolymerization. Finally, the development of portable NMR sensors has made the evaluation of the water content and its diffusivity possible in extended aeras of wall-paintings in historical buildings.
Author Contributions
V.D.T.: conceptualization, data curation, writing, review and editing; N.P.: collaboration on data curation, review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was founded by Regione Lazio (Italy), ITER project “Infrastrutture, metodologie chimiche, nuove tecnologie applicate allo sviluppo delle imprese”, L313/2008 2015-2017 And IPERION-CH project (Integrated Platform for the European Research Infrastructure ON Cultural Heritage), H2020-INFRAIA-2014-2015, grant agreement ID 654028.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Paola Carnazza, Daphne De Luca, and Eleonora Maniccia of the National Gallery of Modern Art (GNAM) in Rome. Capogrossi’s painting study is part of a research project supported by IPERION CH.IT (laboratory MOLAB and FIXLAB), infrastructure of E-HIRS (European Research Infrastructure for Heritage Science). The authors thanks to Lucia Calzona (MIBACT) and Eleonora Gioventù for providing oil wall painting samples in the framework of the research project “La Bio-restauration des oeuvres d’art”, Villa Medici. The authors would like to thank Emiliano Ricchi (DeCesaris srl) for his logistics support during the measurements at the Turkish room, Villa Medici, Rome.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Casadio, F.; Giangualano, I.; Piqué, F. Organic materials in wall paintings: The historical and analytical literature. Stud. Conserv. 2004, 49, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casoli, A.; Santoro, S. Organic materials in the wall paintings in Pompei: A case study of Insula del Centenario. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tullio, V.; Sciutto, G.; Proietti, N.; Prati, S.; Mazzeo, R.; Colombo, C.; Cantisani, E.; Romè, V.; Rigaglia, D.; Capitani, D. 1H NMR depth profiles combined with portable and micro-analytical techniques for evaluating cleaning methods and identifying original, non-original, and degraded materials of a 16th century Italian wall painting. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, E.; Murray, A. Effects of Water Exposure on the Mechanical Properties of Early Artists’ Acrylic Paints. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 2004, 852, OO2.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, A. Color Changes and Chemical Reactivity in Seventeenth-Century Oil Paintings. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Keune, K.; Boon, J.J. Analytical Imaging Studies of CrossSections of Paintings Affected by Lead Soap Aggregate Formation. Stud. Conserv. 2007, 52, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Brett, R.A. Chemical reactions in paint films. J. Oil Colour Chem. Assoc. 1969, 52, 1054–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Rehorn, C.; Blümich, B. Cultural Heritage Studies with Mobile NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baias, M.; Blümich, B. Nondestructive Testing of Objects from Cultural Heritage with NMR. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Webb, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Blümich, B.; Casanova, F.; Perlo, J.; Presciutti, F.; Anselmi, C.; Doherty, B. Noninvasive Testing of Art and Cultural Heritage by Mobile NMR. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 6, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Perras, F.A.; Murphy, A.; Yao, Y.; Catalano, J.; Centeno, S.A.; Dybowski, C.; Zumbulyadis, N.; Pruski, M. DNP-enhanced ultrawideline 207Pb solid-state NMR spectroscopy: An application to cultural heritage science. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, N.; Capitani, D.; Di Tullio, V. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, a Powerful Tool in Cultural Heritage. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, C.; Fiocco, G.; Iwanicka, M.; Kowalska, M.; Targowski, P.; Blümich, B.; Rehorn, C.; Gabrielli, V.; Bersani, D.; Licchelli, M.; et al. Non-invasive mobile technology to study the stratigraphy of ancient Cremonese violins: OCT, NMR-MOUSE, XRF and reflection FT-IR spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, D.; Di Tullio, V.; Proietti, N. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance to characterize and monitor Cultural Heritage. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spetrosc. 2012, 64, 29–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, P.; Cartechini, L.; Miliani, C. Single-sided NMR: A non-invasive diagnostic tool for monitoring swelling effects in paint films subjected to solvent cleaning. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oligschläger, D.; Waldow, S.; Haber, A.; Zia, W.; Blümich, B. Moisture dynamics in wall paintings monitoredby single-sided NMR. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, S.; Sciutto, G.; Volpi, F.; Rehorn, C.; Vurro, R.; Blumich, B.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Giorgini, L.; Samori, C.; Galletti, P. Cleaning oil paintings: NMR relaxometry and SPME to evaluate the effects of green solvents and innovative green gels. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8229–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.; Blümich, B. Single-Sided NMR of Semicrystalline Polymers. Macromol. Symp. 2013, 327, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tullio, V.; Capitani, D.; Presciutti, F.; Gentile, G.; Gentile, G.; Brunetti, B.G.; Proietti, N. Non-invasive NMR stratigraphy of a multi-layered artefact: An ancient detached mural painting. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 8669–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tullio, V.; Proietti, N.; Gobbino, M.; Capitani, D.; Olmi, R.; Riminesi, C.; Giani, E. Non-destructive mapping of dampness and salts in degraded wall paintings in hypogeous buildings: The case of St. Clement at mass fresco in St. Clement Basilica, Rome. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tullio, V.; Capitani, D.; Atrei, A.; Benetti, F.; Perra, G.; Presciutti, F.; Proietti, N.; Marchettini, N. Advanced NMR methodologies and micro-analytical techniques to investigate the stratigraphy and materials of 14th century Sienese wooden paintings. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyros, A.; Anglos, D. Study of Aging in Oil Paintings by 1D and 2D NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4929–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinella, A.; Malagodi, M.; Saladino, M.L.; Weththimuni, M.L.; Caponetti, E.; Licchelli, M. A step forward in disclosing the secret of stradivari’s varnish by NMR spectroscopy. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 3949–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlet, C.; Kuvvetli, F.; Catalano, A.; Dittmer, J. Solid-state NMR for the study of Asger Jorn’s paintings. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakianaki, S.; Kouloumpi, E.; Anglos, D.; Spyros, A. Egg yolk identification and aging in mixed paint binding media by NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Res. Chem. 2015, 53, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, J.; Yao, Y.; Murphy, A.; Zumbulyadis, N.; Centeno, S.A.; Dybowski, C. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectra and 207Pb Chemical-Shift Tensors of Lead Carboxylates Relevant to Soap Formation in Oil Paintings. Appl. Spectrosc. 2014, 68, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolozzi, G.; Marchiafava, V.; Mirabello, V.; Peruzzini, M.; Picollo, M. Chemical curing in alkyd paints: An evaluation via FT-IR and NMR spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, T.M.; Jenkins, J.E. HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy in Material Science. In Advanced Aspect of Spectroscopy; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 279–306. [Google Scholar]
- Viel, S.; Ziarelli, F.; Pagès, G.; Carrara, C.; Caldarelli, S. Pulsed field gradient magic angle spinning NMR self-diffusion measurements in liquids. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 190, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.L. Tissue and Cell Samples by HR-MAS NMR. In eMagRes; Wiley Online Library, John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, S.; Hellriegel, C.; Wegmann, J.; Händel, H.; Albert, K. Characterization of polyalkylvinyl ether phases by solid-state and suspended-state nuclear magnetic resonance investigations. Solid State Nucl. Mag. 2000, 17, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaede, H.C.; Gawrisch, K. Lateral Diffusion Rates of Lipid, Water and a Hydrophobic Drug in a Multilamellar Liposome. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, C.; Mallamace, D.; Vasi, S.; Pietronero, L.; Mallamace, F.; Missori, M. The role of water in the degradation process of paper using 1H HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 33335–33343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsaro, C.; Mallamace, D.; Łojewska, J.; Mallamace, F.; Pietronero, L.; Missori, M. Molecular degradation of ancient documents revealed by 1H HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tullio, V.; Zumbulyadis, N.; Centeno, S.A.; Catalano, J.; Wagner, M.; Dybowski, C. Water Diffusion and Transport in Oil Paints as Studied by Unilateral NMR and 1H High-Resolution MAS-NMR Spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2020, 21, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, D.; Proietti, N.; Gobbino, M.; Soroldoni, L.; Casellato, U.; Valentini, M.; Rosina, E. An integrated study for mapping the moisture distribution in an ancient damaged wall painting. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauri, K.L.; Bandyopadhyay, J.K. Carbonate Stone: Chemical Behaviour, Durability and Conservation; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Canevali, C.; Fasoli, M.; Bertasa, M.; Botteon, A.; Colombo, A.; Di Tullio, V.; Capitani, D.; Proietti, N.; Scalarone, D.; Sansonetti, A. A multi-analytical approach for the study of copper stain removal by agar gels. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Giorgi, R.; Berti, D.; Baglioni, P. Smart cleaning of cultural heritage: A new challenge for soft nanoscience. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Sathasivam, S.; Song, J.; Crick, C.R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Robust self-cleaning surfaces that function when exposed to either air or oil. Science 2015, 347, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presciutti, F.; Perlo, J.; Casanova, F.; Glöggler, S.; Miliani, C.; Blümich, B.; Brunetti, B.G.; Sgamellotti, A. Noninvasive nuclear magnetic resonance profiling of painting layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 033505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Lopes, L.V.S.; Tambelli, C.E.; Donoso, J.P.; Lozano, H.; Gonzalez, G. NMR Study of Slow Motions of HDA Hydrocarbons Chains Inside Lamellar Structures. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2006, 483, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, D.; Tumosa, C.S.; Mecklenburg, M.F. Long-Term Chemical and Physical Processes in Oil Paint Films. Stud. Conserv. 2005, 50, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von den Berg, J.D.J.; van den Berg, K.J.; Boon, J.J. Identification of non-cross-linked compounds in methanolic extracts of cured and aged linseed oil-based paint films using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 950, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, J.; Murphy, A.; Yao, Y.; Yap, G.P.A.; Zumbulyadis, N.; Centeno, S.A.; Dybowski, C. Coordination geometry of lead carboxylates—Spectroscopic and crystallographic evidence. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadio, F.; Keune, K.; Noble, P.; Van Loon, A.; Hendriks, E.; Centeno, S.A.; Osmond, G. Metal Soaps in Art; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J.S.; White, R. The Organic Chemistry of Museum Objects, 2nd ed.; Oxford Butterworths-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999; p. 206. ISBN 0-7506-1693-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dietemann, P.; Higgitt, C.; Kalin, M.; Edelmann, M.J.; Knochenmuss, R.; Zenobi, R. Aging and yellowing of triterpenoid resin varnishes e Influence of aging conditions and resin composition. J. Cult. Herit. 2009, 10, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Noguera, J.; Martín-Sánchez, I.; Doménech-Carbó, M.T.; Osete-Cortina, L.; López-Miras, M.M.; Bolívar-Galiano, F. Analytical characterisation of the biodeterioration of diterpenoid labdanic varnishes used in pictorial techniques: Sandarac and Manila copal. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalarone, D.; Duursma, M.C.; Boon, J.J.; Chiantore, O. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry on cellulosic surfaces of fresh and photo-aged di- and triterpenoid varnish resins. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 40, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononenko, I. Molecular Characterization and Ageing of the Sandarac Resin and Its Principal Component Communic Acid. Analytical Chemistry. Université Pierre et Marie Curie—Paris VI: Paris, France, Unpublished Thesis. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Echard, J.P.; Bertrand, L.; von Bohlen, A.; Le Hô, A.S.; Paris, C.; Bellot-Gurlet, L.; Soulier, B.; Lattuati-Derieux, A.; Thao, S.; Robinet, L.; et al. Cover Picture: The Nature of the Extraordinary Finish of Stradivari’s Instruments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, K.; Melliou, E.; Prokopios, M. High-Throughput 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Screening for the Identification and Quantification of Heartwood Diterpenic Acids in Four Black Pine (Pinus nigra Arn.) Marginal Provenances in Greece. Molecules 2019, 24, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bollard, M.E.; Keun, H.; Antti, H.; Beckonert, O.; Ebbels, T.M.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Tang, H.; Nicholson, G.K. Spectral editing and pattern recognition methods applied to high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of liver tissues. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 323, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, L.M.; Morelli, F.R.; Rivosecchi, V.; Bertolino, G.; Pola, F.; Mastinu, G.; Salvagnini, S.; Bolpagni, P.; D’Angelo, L. Capogrossi: A Retrospective; Marsilio: Venice, Italy, 2013; p. 394. [Google Scholar]
- Barnaba, C.; Bertorello, C. I Dipinti ad olio su muro del Passignano nella Cappella Rivaldi in Santa Maria della Pace a Roma. Rivisitazione di un Restauro della metà degli anni ’80 del ‘900. In Proceedings of the IV National Congress of the Italian Group of International Institute for Conservation (IGIIC), Lo Stato dell’Arte, L’Aquila, Italy, 20–22 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Blümich, B.; Perlo, J.; Casanova, F. Mobile single-sided NMR. Progr. Nucl. Magn. Res. Sp. 2008, 52, 197–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).