High Yield Synthesis and Application of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
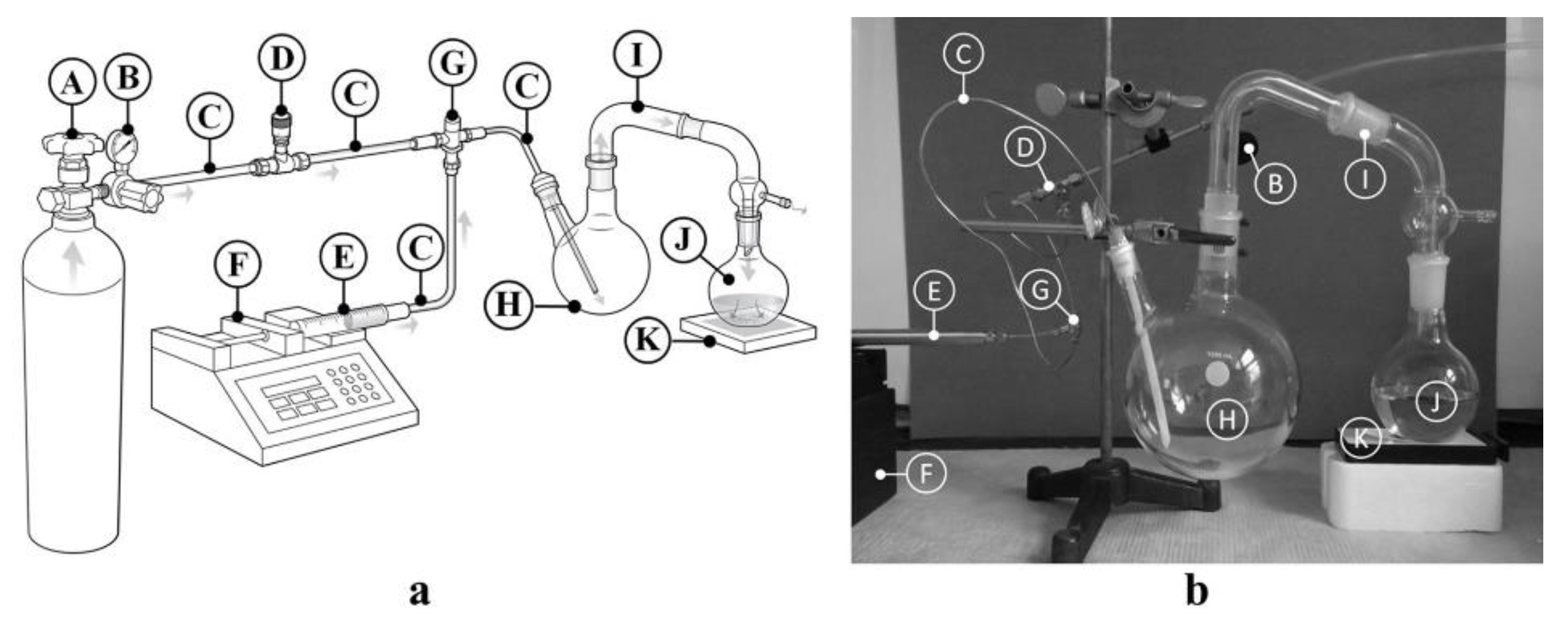
2.1. Apparatus
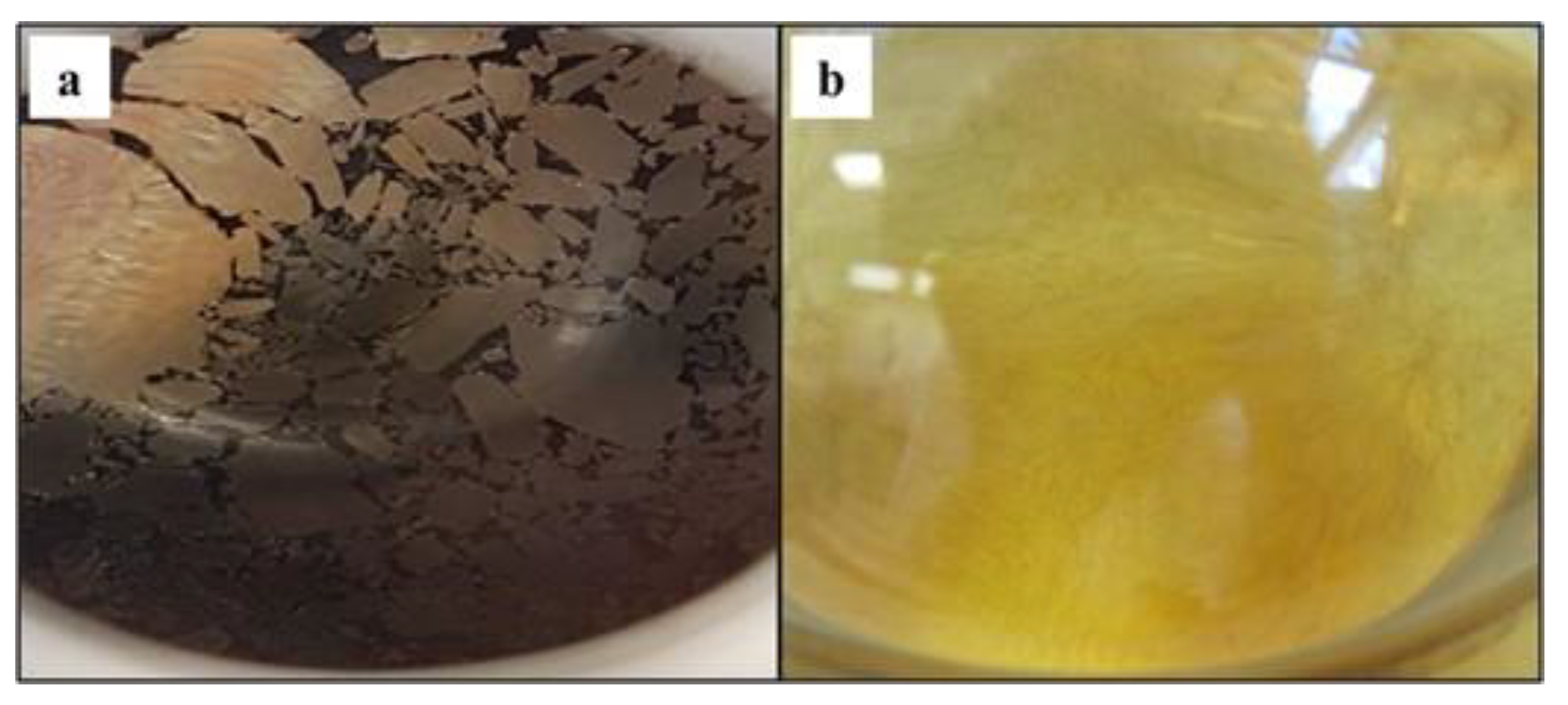
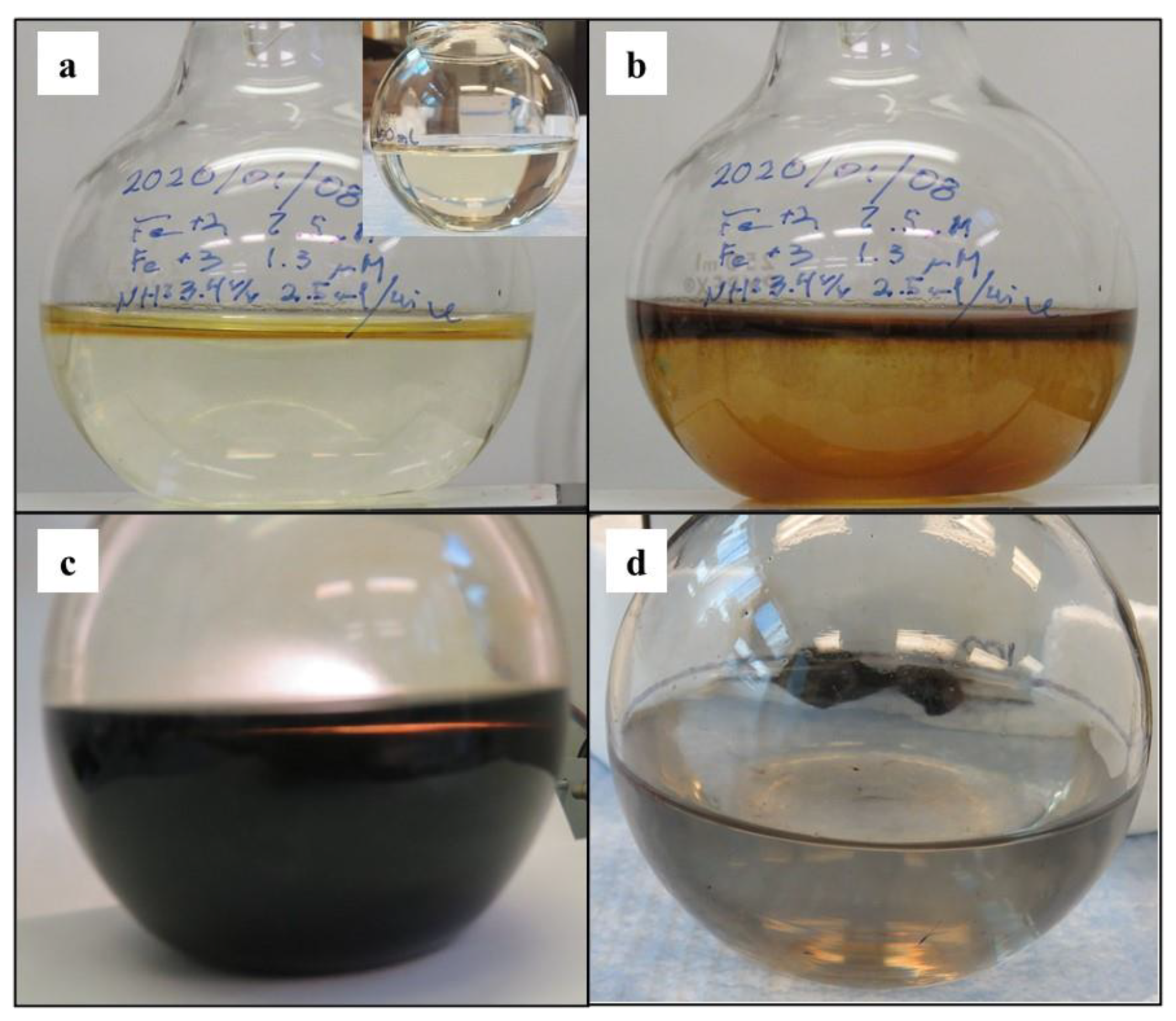
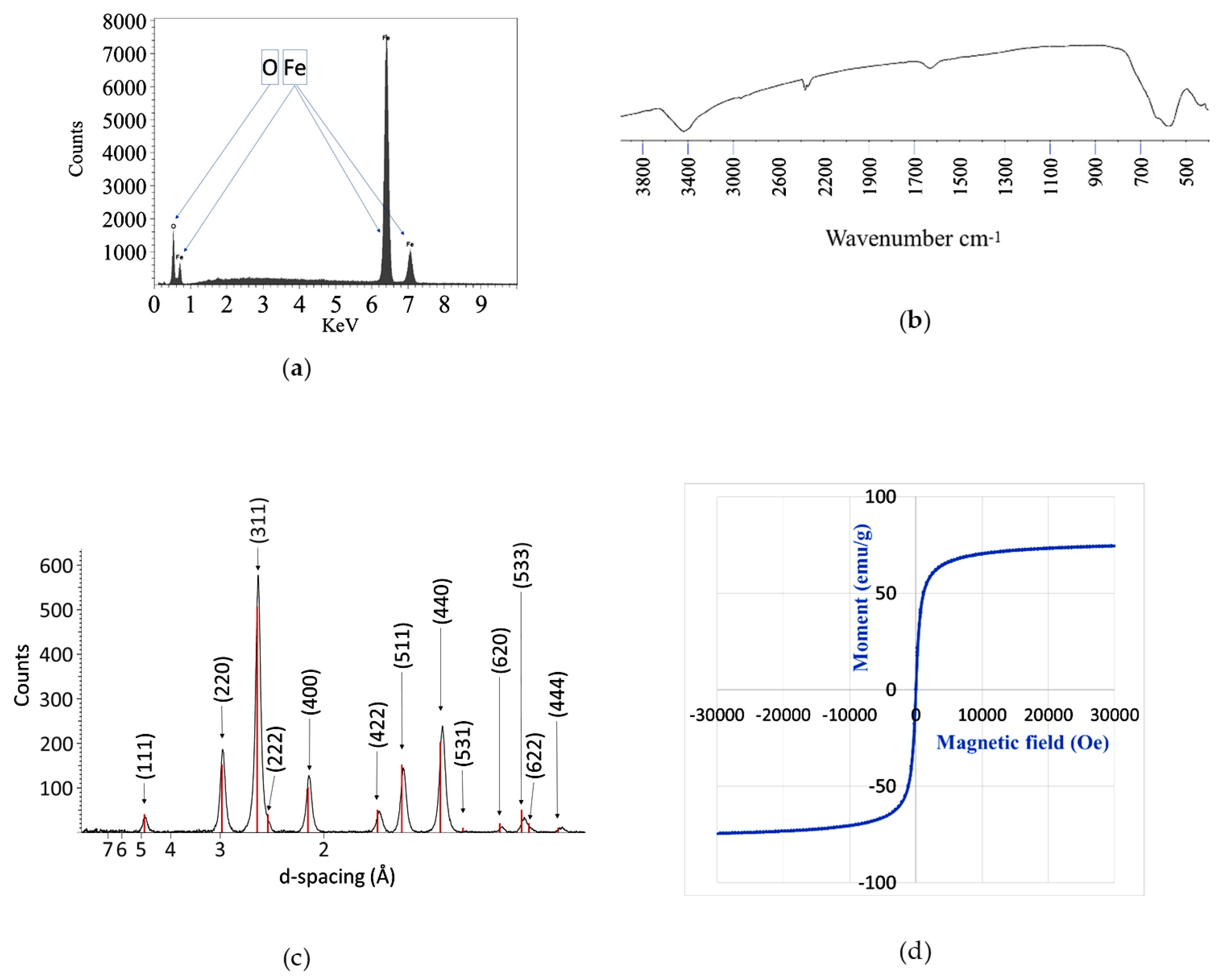
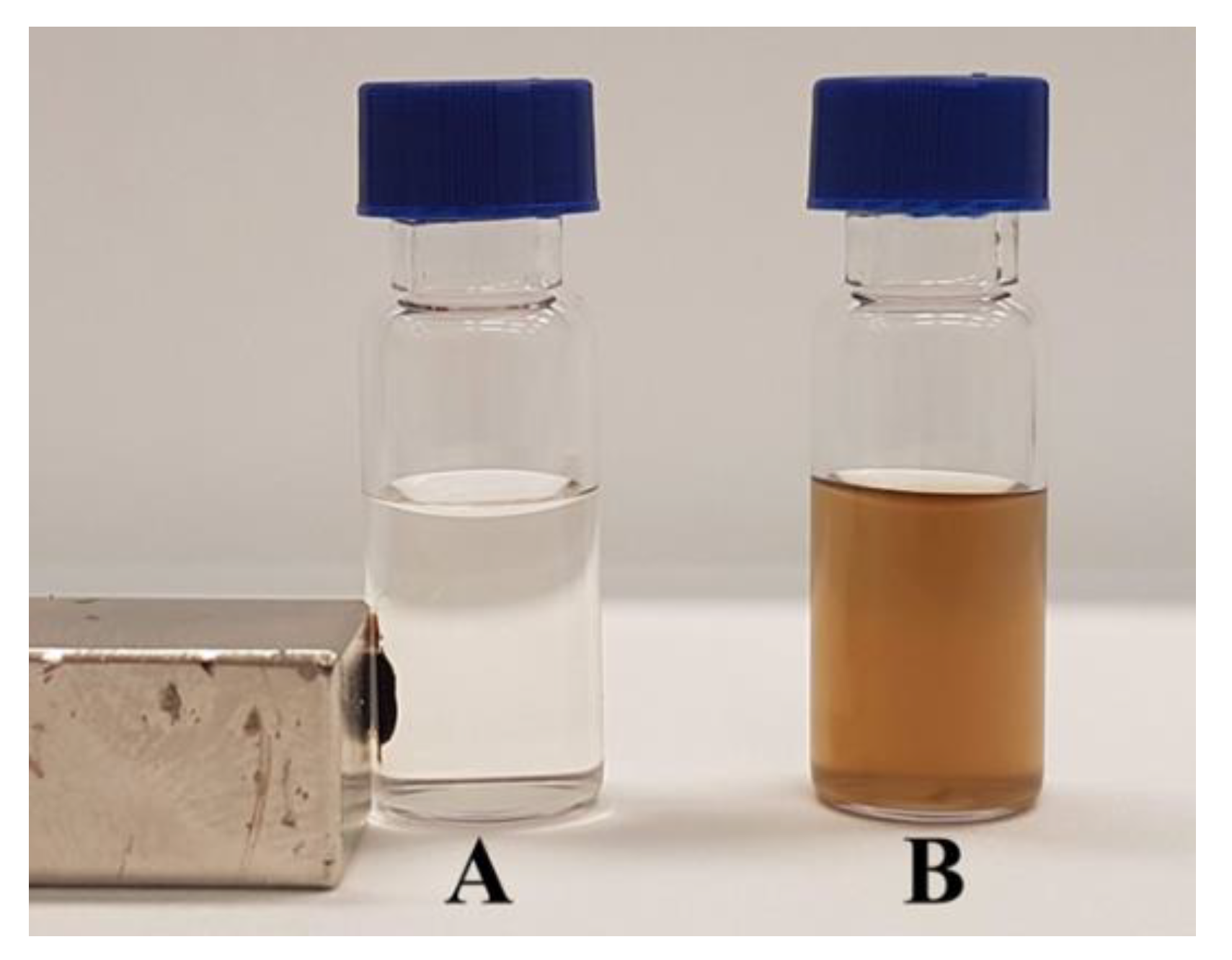
2.2. Material Analyses
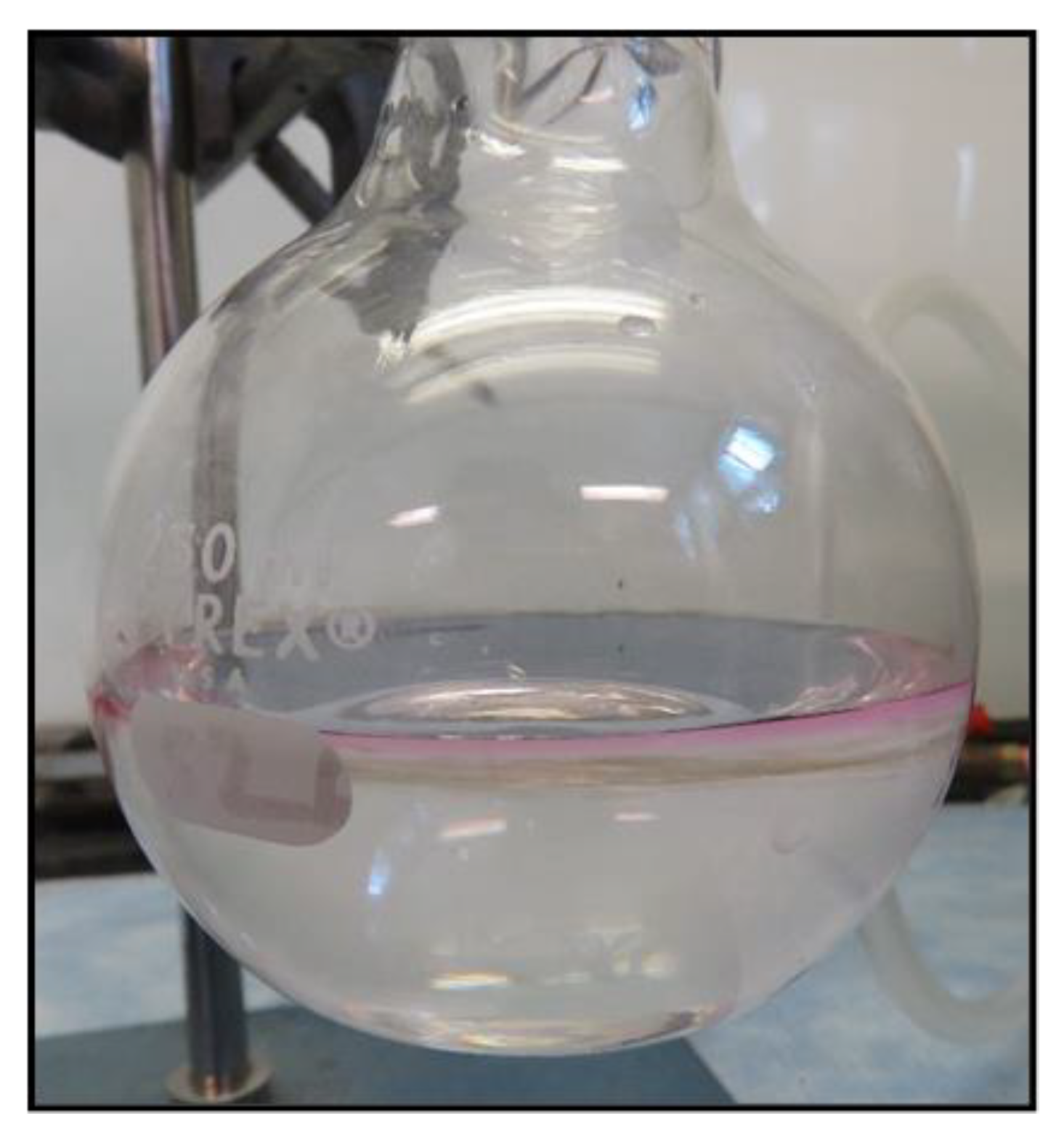
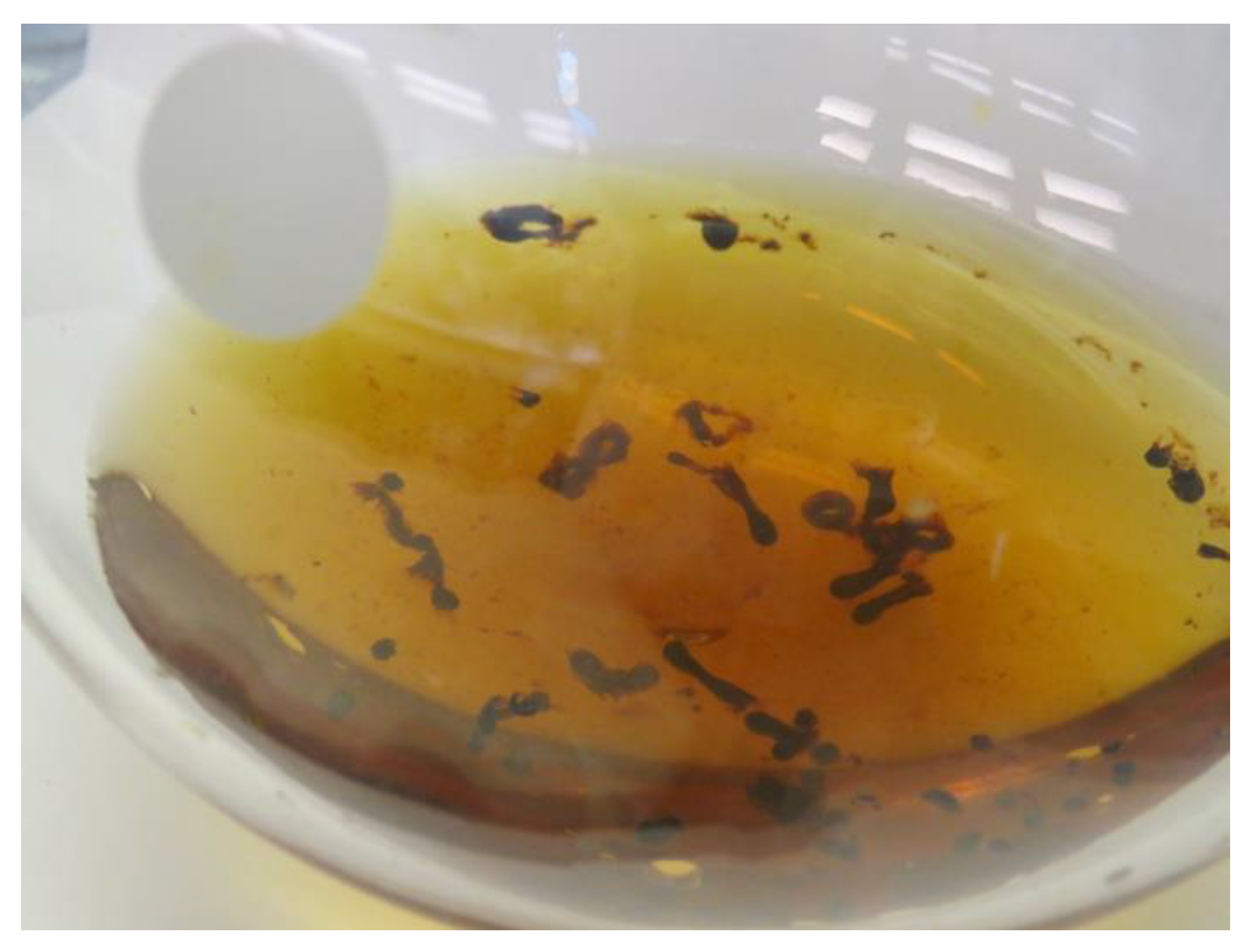
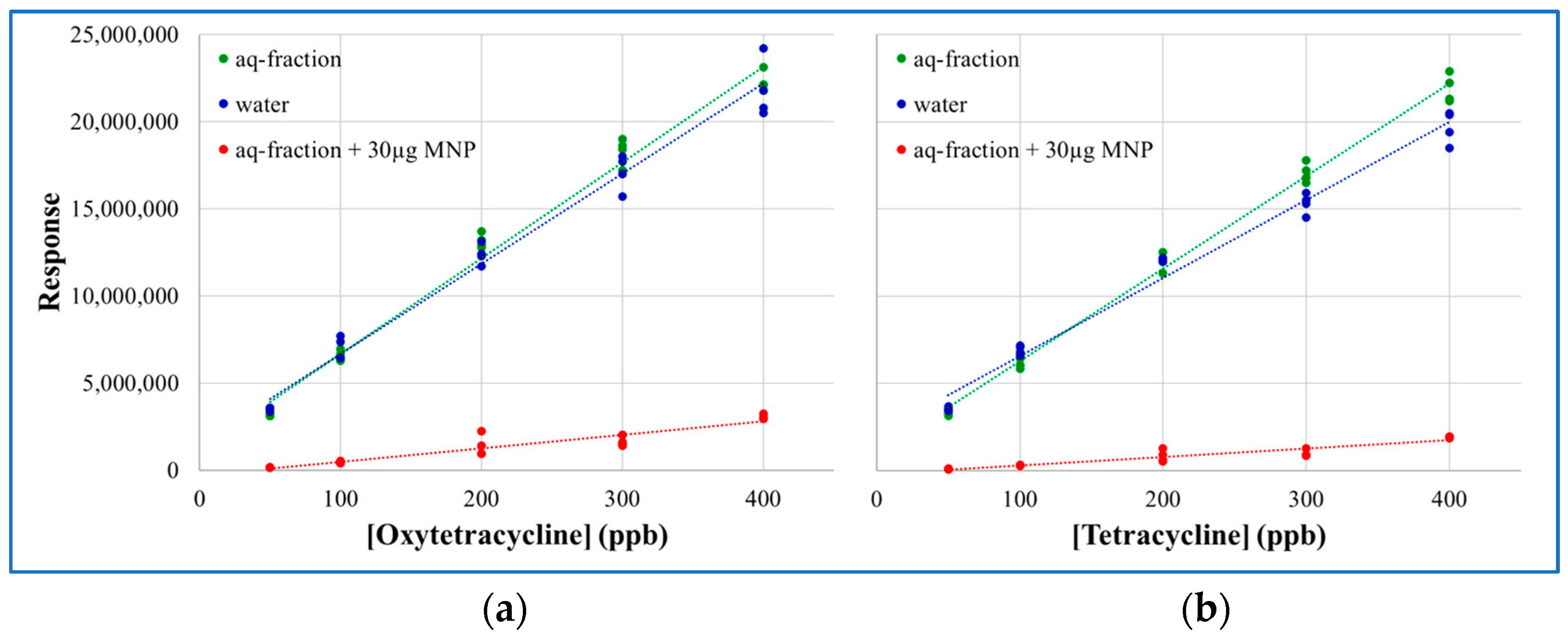
2.3. MNP Extraction of Tetracyclines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Magnetite Nanoparticle Synthesis
3.2.1. Chemical Co-Precipitation
3.2.2. Iron Salts Solutions (Fe2+ and Fe3+)
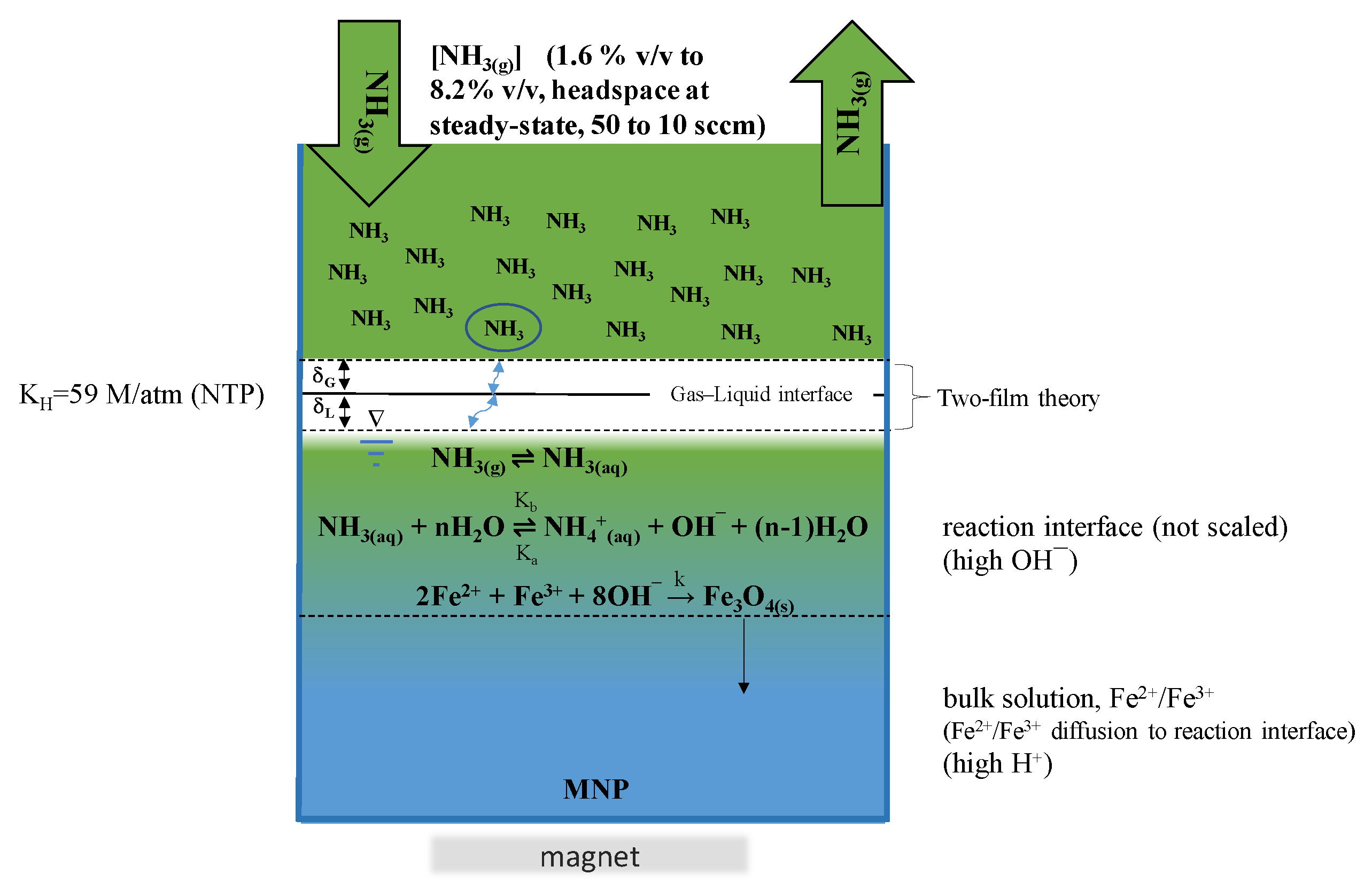
3.2.3. Steady State [NH3(g)]
3.2.4. Apparatus
3.3. Material Analyses
3.3.1. Preparation of Nanoparticles for Analyses
3.3.2. TEM
3.3.3. Particle Size Analyses
3.3.4. ICP-MS Analyses of Aqueous Fraction
3.3.5. EDXRF
3.3.6. FT-IR
3.3.7. XRD
3.3.8. Magnetization Saturation
3.3.9. Extraction of Tetracyclines with Magnetite Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, J.; Yuan, W.; Sui, X.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Shen, D. Synthesis, characterization, and controllable drug release of pH-sensitive hybrid magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2799–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Park, S.B.; Yoon, H.G.; Huh, Y.M.; Haam, S. Preparation of poly ε-caprolactone nanoparticles containing magnetite for magnetic drug carrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 324, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.K.; Morales, M.A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Labhasetwar, V. Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol. Pharm. 2005, 2, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, Y.; Akhtar, K.; Anwar, H.; Jamil, Y. MRI based on iron oxide nanoparticles contrast agents: Effect of oxidation state and architecture. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corot, C.; Robert, P.; Idée, J.M.; Port, M. Recent advances in iron oxide nanocrystal technology for medical imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1471–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck, A.M.; Cama, C.A.; Gannett, C.N.; Marschilok, A.C.; Takeuchi, E.S.; Takeuchi, K.J. Nanocrystalline iron oxide based electroactive materials in lithium ion batteries: The critical role of crystallite size, morphology, and electrode heterostructure on battery relevant electrochemistry. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E. Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Nanowires—A Brief Introduction. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, H.J.; Engates, K.E.; Guettner, A.M. Study of iron oxide nanoparticles in soil for remediation of arsenic. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiani, G.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Campàs, M. Magnetic Beads in Marine Toxin Detection: A Review. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchin, I.; Reddy, K.R.; Thomé, A.; Tessaro, E.F.; Schnaid, F. Nanobioremediation: Integration of nanoparticles and bioremediation for sustainable remediation of chlorinated organic contaminants in soils. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarcletti, M.; Vivod, D.; Luchs, T.; Rejek, T.; Portilla, L.; Müller, L.; Dietrich, H.; Hirsch, A.; Zahn, D.; Halik, M. Superoleophilic Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Hydrocarbon Removal from Water. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Yan, X.P. Amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for rapid capture and removal of bacterial pathogens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7908–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.; Kim, W.S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 23501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Özmen, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Paunov, V.N.; Li, G.; Huang, W.E. Functionalization of whole-cell bacterial reporters with magnetic nanoparticles. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, T.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, H.M.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, J.D. Formation pathways of magnetite nanoparticles by coprecipitation method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6069–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, A.; Zhai, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Volinsky, A.A. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1882–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Hassan, A.; Dufrêchfer, J.F.; Sandre, O.; Mériguet, G.; Bernard, O.; Cabuil, V. Fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy for pH mapping in a coaxial flow microreactor: Application in the synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18097–18105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronc, E.; Belleville, P.; Jolivet, J.P.; Livage, J. Transformation of ferric hydroxide into spinel by Fe(II) adsorption. Langmuir 1992, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, J.; Chanéac, C.; Tronc, E. Iron oxide chemistry. From molecular clusters to extended solid networks. Chem. Commun. 2004, 98, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Jeong, J.R.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, J.D. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 282, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, R.; Meng, S.; Zhang, J. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using controlled ammonia vapor diffusion under ultrasonic irradiation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3534–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamani, J.B.; Gamarra, L.F.; De Souza Brito, G.E. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with perspectives in biomedical applications. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrushevska, M.; Pavlovska, K.; Laskova, J.; Zdravkovski, P.; Dodov, M.G. Transmission Electron Microscopy: Novel Application of Established Technique in Characterization of Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems. Prilozi 2019, 40, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habila, M.A.; Alothman, Z.A.; El-Toni, A.M.; Labis, J.P.; Soylak, M. Synthesis and application of Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 for photocatalytic decomposition of organic matrix simultaneously with magnetic solid phase extraction of heavy metals prior to ICP-MS analysis. Talanta 2016, 154, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, D.; Majetich, S.A.; Wilcoxon, J.P. Preparation and characterization of monodisperse Fe nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 11022–11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T.K. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Namvar, F.; Bin Ahmad, M.; Mohamad, R. Green biosynthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Sargassum muticum) aqueous extract. Molecules 2013, 18, 5954–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Suh, C.Y.; Cho, S.W.; Roh, K.M.; Kwon, H.; Song, K.; Shon, I.J. A new method for the identification and quantification of magnetite-maghemite mixture using conventional X-ray diffraction technique. Talanta 2012, 94, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.A.J.; Andrade, P.L.; Silva, M.P.C.; Bustamante, A.D.; De Los Santos Valladares, L.; Albino Aguiar, J. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with fucan polysaccharides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 343, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibeigi, S.; Vaezi, M.R. Phase transformation of iron oxide nanoparticles by varying the molar ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2008, 31, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Yadav, K.L. Structural, dielectric, vibrational and magnetic properties of Sm doped BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics prepared by a rapid liquid phase sintering method. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 9285–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Shivashankar, S.A. Single crystalline magnetite, maghemite, and hematite nanoparticles with rich coercivity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolen’Ko, Y.V.; Bañobre-López, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, C.; Carbó-Argibay, E.; Sailsman, A.; Piñeiro-Redondo, Y.; Cerqueira, M.F.; Petrovykh, D.Y.; Kovnir, K.; Lebedev, O.I.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of colloidal Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibiting high heating efficiency in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 8691–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhong, W.; Au, C.T.; Du, Y. Size dependence of the magnetic properties of Ni nanoparticles prepared by thermal decomposition method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Li, N.; Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.S. Recent application of magnetic solid phase extraction for food safety analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuvonen, P.J. Interactions with the Absorption of Tetracyclines. Drugs 1976, 11, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical, A.; National, S. 254th American Chemical Society National Meeting and Exposition; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 2022494016. [Google Scholar]


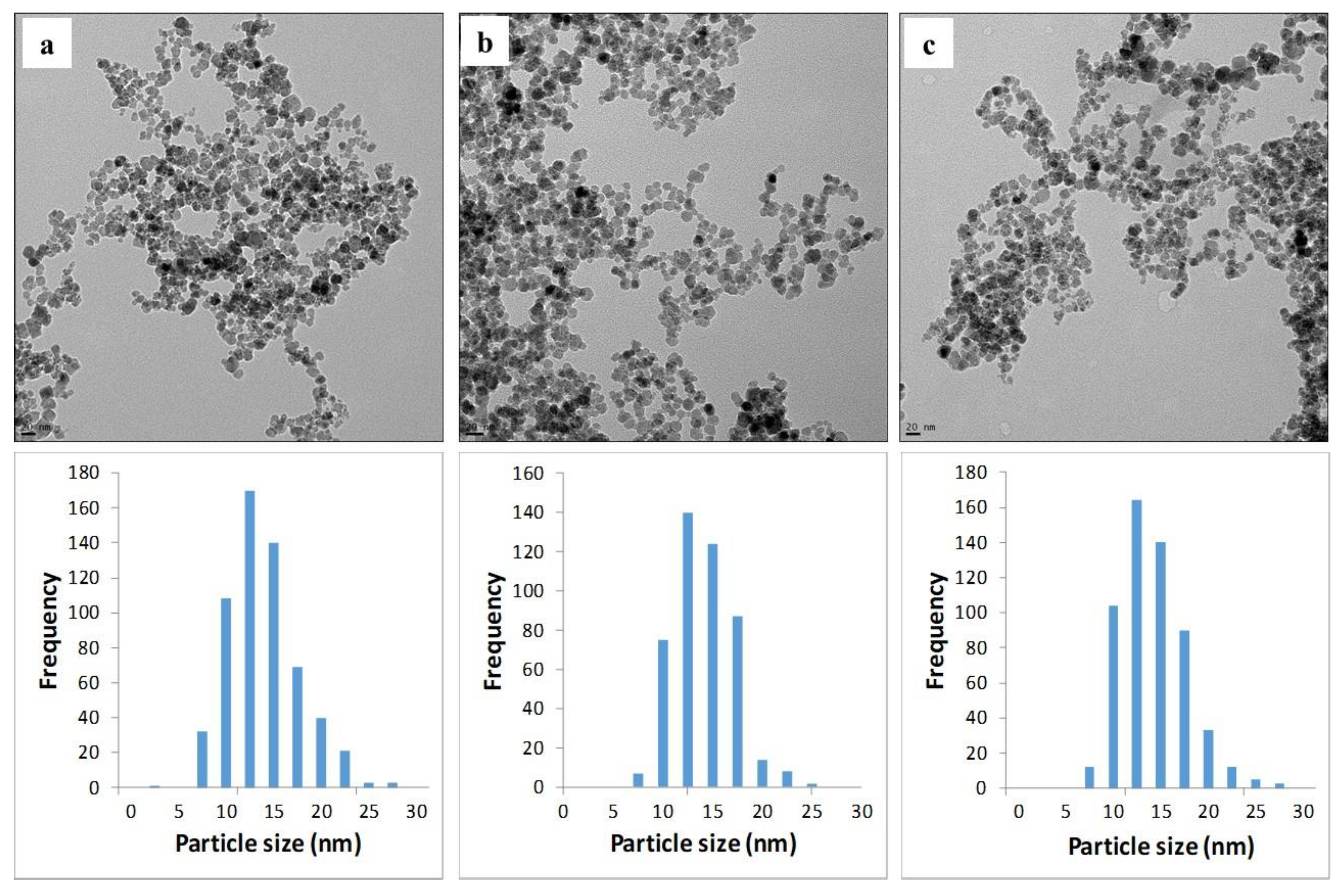
| [NH3(g)], %v/v | n | Mean (nm) | Median (nm) | S | ±1 S, % | Kurtosis | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.6 | 587 | 12.8 | 12.3 | ±3.7 | 70 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 3.3 | 457 | 12.9 | 12.6 | ±3.0 | 67 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| 8.4 | 563 | 12.9 | 12.5 | ±3.5 | 70 | 1.0 | 0.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wroblewski, C.; Volford, T.; Martos, B.; Samoluk, J.; Martos, P. High Yield Synthesis and Application of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4). Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry6020022
Wroblewski C, Volford T, Martos B, Samoluk J, Martos P. High Yield Synthesis and Application of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4). Magnetochemistry. 2020; 6(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry6020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWroblewski, Charles, Tunde Volford, Blake Martos, Jurek Samoluk, and Perry Martos. 2020. "High Yield Synthesis and Application of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4)" Magnetochemistry 6, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry6020022
APA StyleWroblewski, C., Volford, T., Martos, B., Samoluk, J., & Martos, P. (2020). High Yield Synthesis and Application of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4). Magnetochemistry, 6(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry6020022




