Abstract
Developing precise tumor-targeting delivery systems while minimizing off-target toxicity continues to pose significant challenges in medicine application. The integration of two different functional materials has emerged as a promising strategy in current biomedical research. Herein, a hybrid nanocomposite consisting of Fe3O4 and ZnO was synthesized via a simple approach and employed as a nanoscale drug delivery system to explore the loading capacity and stimuli-responsive release characteristics of the anticancer agent doxorubicin (DOX). Results show that the synthesized nanoparticles (NPs) exhibit a multi-scale nanostructure consisting of the spindle-like ZnO nanorods with a mean length of 280 nm, on which the Fe3O4 NPs with a diameter of around 16 nm are uniformly dispersed. The ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs possess superparamagnetic behavior and a fast response to the external magnet and demonstrate exceptional near-infrared (NIR) photothermal conversion efficiency. In drug release studies, the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs achieve the controlled DOX release in the simulated acidic tumor microenvironment as well as NIR laser irradiation. Further, the ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX composites significantly suppress the viability of human cervical cancer cells (HeLa) upon laser activation. These findings suggest that ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs are promising candidates for combined photothermal therapy, magnetic-targeted drug delivery, and stimuli-responsive controlled release applications.
1. Introduction
Due to the high loss rate of conventional drugs during transport within the body, particularly the damage caused to normal tissue cells by chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment, achieving optimal drug transport efficiency remains a primary objective in carrier system research. Therefore, the development of drug carriers capable of highly precise drug delivery, efficient controlled and sustained release, low toxicity, and minimal side effects has become an important direction in drug carrier research [1]. Widely reported drug carriers include liposomes, micelles, inorganic nanoparticles, polymer copolymers, and exosomes, among others [2,3,4]. Recently, nanomaterials have gained considerable interest. Their distinct physicochemical and biological characteristics have led to widespread applications in biomedical fields such as biosensors, diagnostic imaging, pharmaceutical transport systems, and oncology therapies [5,6,7].
Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely studied for biomedical applications owing to their remarkable biocompatibility and unique magnetic properties. They are FDA-approved contrast agents and are now employed in iron replacement therapy, hyperthermia therapy, and tumor imaging and treatment [8,9,10]. When used as drug carriers, Fe3O4 NPs can achieve passive targeted drug delivery by applying an external magnetic field to the lesion site [11,12,13]. On the one hand, when subjected to an alternating magnetic field, these nanoparticles generate thermal energy, elevating the tumor’s temperature to a level that effectively eliminates cancerous cells [14,15,16]. On the other hand, when exposed to NIR light, Fe3O4 NPs quickly absorb the radiation and effectively transform it into concentrated thermal energy, destroying tumor cells [17,18]. Moreover, this approach delivers targeted therapy to the tumor site while minimizing harm to adjacent normal tissues and cells. The bio-behaviors, heating efficiency (usually reported as specific absorption rate), and targeting effect of Fe3O4 NPs are affected by various factors such as shape, phase composition, magnetic properties of particles, applied magnetic field strength and frequency, and especially the particle size [19,20,21]. Previous studies reported that the most suitable particle size range for IV injection of Fe3O4 NPs was 10 to 100 nm [22]. Consequently, Fe3O4 NPs with varied morphologies and dimensions are extensively investigated for applications in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy.
ZnO nanoparticle is another promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications, particularly in cancer therapy, photodynamic therapy, and cellular imaging, owing to its semiconducting characteristics, luminescent features, and biocompatibility [23,24,25]. In addition, ZnO NPs function as an effective nanoscale gatekeeper in drug delivery systems, enabling selective drug release through their pH-dependent solubility. Under physiological conditions (pH~7.4), ZnO remains stable in nanoparticle form, preventing premature drug leakage from carriers in healthy tissues. However, in the acidic tumor microenvironment, ZnO dissolves into Zn2+ ions, triggering controlled drug release, and even inducing tumor cell apoptosis when high concentrations of Zn2+ are accumulated [26,27]. Therefore, considerable attention has been directed toward the composite nanomaterials consisting of ZnO and Fe3O4 to extend their applications. Various strategic approaches have been employed to synthesize Fe3O4/ZnO NPs for drug delivery and other applications [28,29]. In particular, most research focuses on the core–shell Fe3O4@ZnO NPs, which consist of ZnO shell layer covering Fe3O4 core particle. These typical composites exhibit good heating efficacy, superparamagnetism, good cellular imaging capability, and significantly superior synergistic anticancer efficiency [30,31,32]. However, the composites reported in the literature typically exhibit a core–shell structure with uniform spherical morphology, and consist of ZnO-coated Fe3O4, where ZnO serves as the shell and Fe3O4 as the core.
Herein, a novel spindle-like ZnO@Fe3O4 composite nanoparticles were synthesized. The composite consists of the ZnO nanorods with a mean length of 280 nm wrapped by the Fe3O4 NPs with a diameter of around 14 nm. This characteristic structure may not only contribute to a more precise modulation of drug loading and release but could also result in distinct performance in drug delivery and controlled release applications when compared with conventional core–shell Fe3O4@ZnO composites. No similar studies have been previously published, based on the current literature. Further, the photothermal properties, magnetic characterizations, and drug release behaviors of the multi-scale nanostructured ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs were thoroughly analyzed. The findings of this study can provide a new approach to designing a multifunctional nanocarrier for targeted drug delivery and controlled release.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs
In the first step, 0.8 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and 0.2 g of zinc acetate ((CH3COO)2Zn·2H2O) (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) were mixed in 40 mL of deionized water under continuous stirring for 20 min. The mixture was transferred to a sealed stainless steel autoclave and maintained at 140 °C for two hours under hydrothermal conditions. The obtained ZnO product was subsequently purified through multiple washings with deionized water. ZnO@Fe3O4 nanocomposites were prepared by deposition of Fe3O4 NPs on the surface of ZnO nanorods through subsequent co-precipitation approach. Iron chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), iron sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O) (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), and the as-prepared ZnO nanorods were dissolved in deionized water, with the concentration of Fe3+ fixed at 0.1 mol L−1 and molar ratios of Fe3+ to Fe2+ of 1:1. Under continuous magnetic stirring at 50 °C, NaOH solution (0.15 mol L−1) was gradually added to the iron salt mixture. The mixture was then stirred overnight to ensure complete reaction. Subsequently, the resulting suspension was centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 10 min, followed by repeated washing with ethanol and deionized water to remove impurities. Finally, the purified product was dried in a vacuum oven at 60 °C to obtain the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs. Meanwhile, Fe3O4 NPs without ZnO were prepared by the same approach for comparison.
2.2. Material Characterizations
The microstructure of the synthesized ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs was examined using a transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL JEM-2100, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) and a field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, JEOL JSM-7100F, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The crystal structure and phase composition were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis conducted on a Bruker D8 diffractometer (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany) with a step rate of 3° min−1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was recorded on an ESCALAB 250Xi system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to gain the chemical structure. The photothermal experiments were conducted by exposing an aqueous solution of nanoparticles (0.5 mL) to an 808 nm laser at a power density of 2 W cm−2 for 8 min. The temperature of the nanoparticle suspensions was monitored and recorded at 30 s intervals using a Testo 875 infrared thermal imager (Testo SE & Co. KGaA, Titisee-Neustadt, Germany) during continuous irradiation. For comparative analysis, parallel tests were conducted with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) under the same experimental parameters. Additionally, the room-temperature magnetic characteristics of the synthesized NPs were evaluated employing a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM-7410 model, Lake Shore Cryotronics, Inc., Westerville, OH, USA).
2.3. In Vitro DOX Loading and Release
For doxorubicin (DOX) loading, 10 mg of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs was mixed with 10 mL of DOX solution at a concentration of 0.5 mg mL−1. The mixture was stirred at ambient conditions for 24 h, followed by centrifugation at 15,000 rpm (30 min duration). The remaining drug-loaded composites were washed repeatedly until supernatant clarification and were denoted as ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX. After dispersion in aqueous solution, UV-vis spectrophotometric analysis was subsequently conducted on the supernatant to confirm the loading of the DOX. As a contrast, Fe3O4-DOX samples were prepared in the same way.
2.3.1. PH-Dependent Drug Release
10 mL ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX solution with a concentration of 1 μg mL−1 was dispersed in PBS at pH 6.0 and 7.4, respectively. The supernatant was collected at 2 h intervals through centrifugation and analyzed using UV–vis spectrophotometry. The study was conducted for a duration of 24 h at 37 °C. The concentration of DOX was determined according to DOX UV-vis standard calibration curve at 488 nm.
2.3.2. NIR Triggered Drug Release
In total, 5.0 mg of the ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX composites and 5 mL of PBS solution (50 mM) were mixed at pH 7.4 and maintained at 37 °C under constant shaking. The DOX release of ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX composites with and without NIR laser irradiation was performed and the Laser group received 808 nm NIR irradiation (2.0 W cm−2, 5 min duration) at 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 h intervals. At designated time points, 1 mL supernatant was extracted for analysis while being replaced with an equal volume of fresh PBS buffer. DOX concentration in the supernatant was determined by measuring 480 nm absorbance using UV-Vis spectroscopy, with release kinetics quantified against a standard calibration curve.
2.4. Cell Viability
Hela cells were plated in 6-well plates and cultured for 24 h to allow cells to attach. Following attachment, the original medium was replaced with either fresh medium or medium containing varying concentrations of different nanoparticles. In designated laser-treated groups, cells incubated with ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX at different concentrations were subjected to irradiation using an 808 nm NIR laser at a power density of 2 W cm−2 for 5 min. All experimental groups were then further cultured for 24 h under standard conditions (37 °C, 5% CO2). Cell viability was assessed using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, while a live/dead cell staining kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) was employed to evaluate cytocompatibility.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Characterization
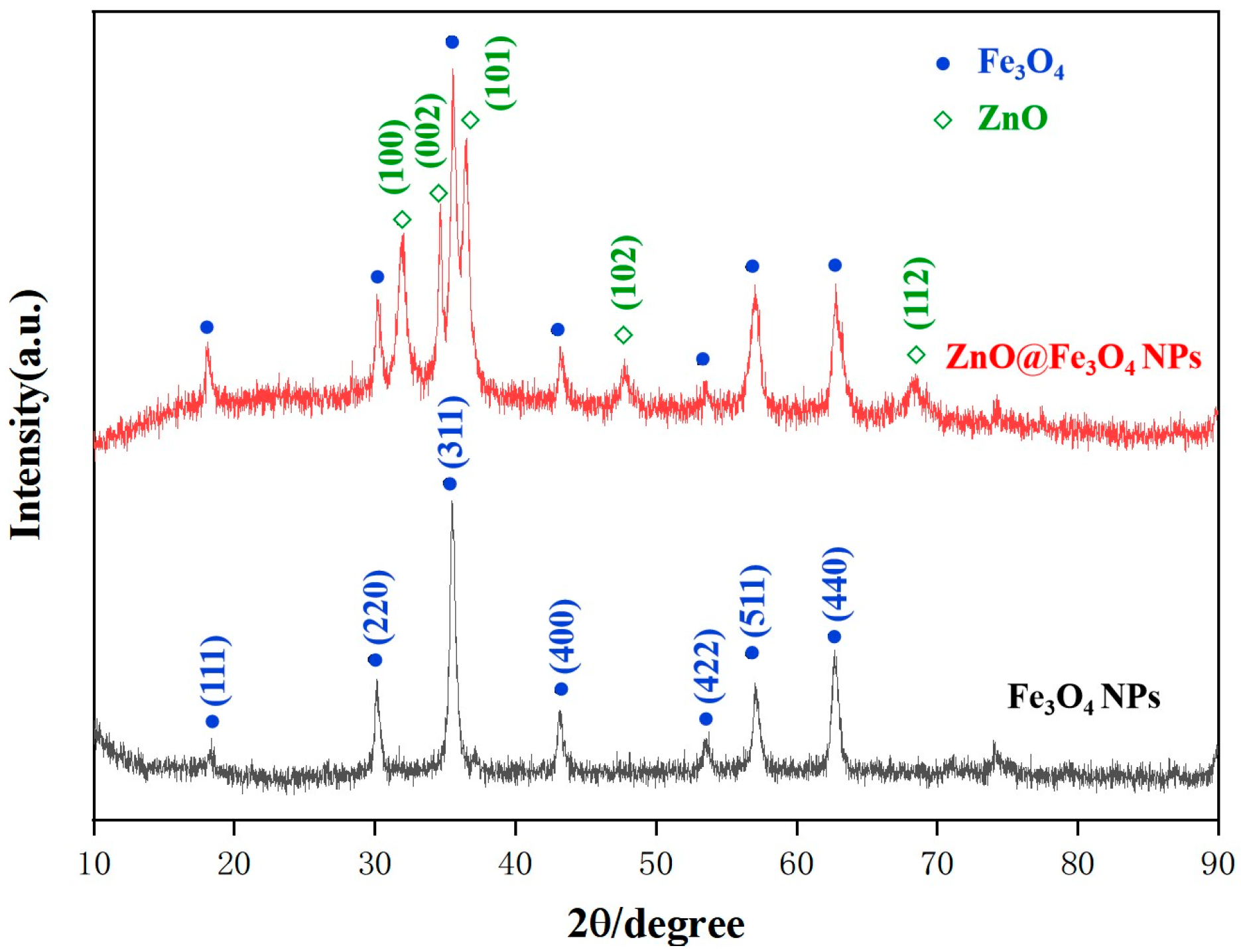
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of the synthesized ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs and Fe3O4 NPs to examine their crystallinity. The typical five diffraction peaks could be observed in both samples at 30.1°, 35.5°, 43.1°, 57.0°, and 62.6°, corresponding to (220), (311), (400), (511), and (440) crystal planes of Fe3O4, respectively (JCPDS No. 65-3107). Meanwhile, the sharp strong peaks observed in ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs patterns located at 31.8°, 34.4°, 36.1°, 47.5°, and 67.9° can be assigned to the (100), (002), (101), (102), and (112) planes of the hexagonal wurtzite phase of ZnO (JCPDS No.36-1451). All observed diffraction peaks could be exclusively indexed to the target phase, with no evidence of crystalline impurities. When the molar ratio of Fe3+ to Fe2+ is 1:1, a higher degree of Fe2+ excess can reduce the generation of incomplete Fe3O4 products and increase the purity of Fe3O4.
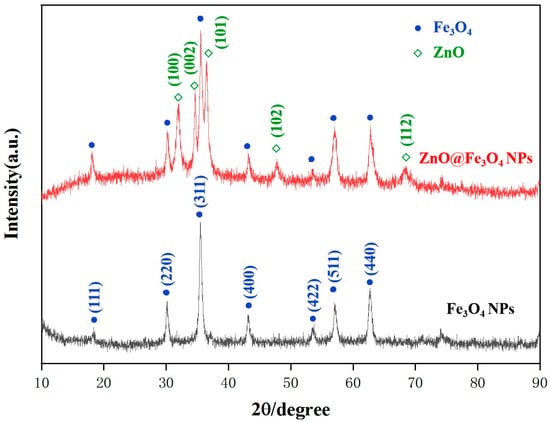
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs and Fe3O4 NPs.
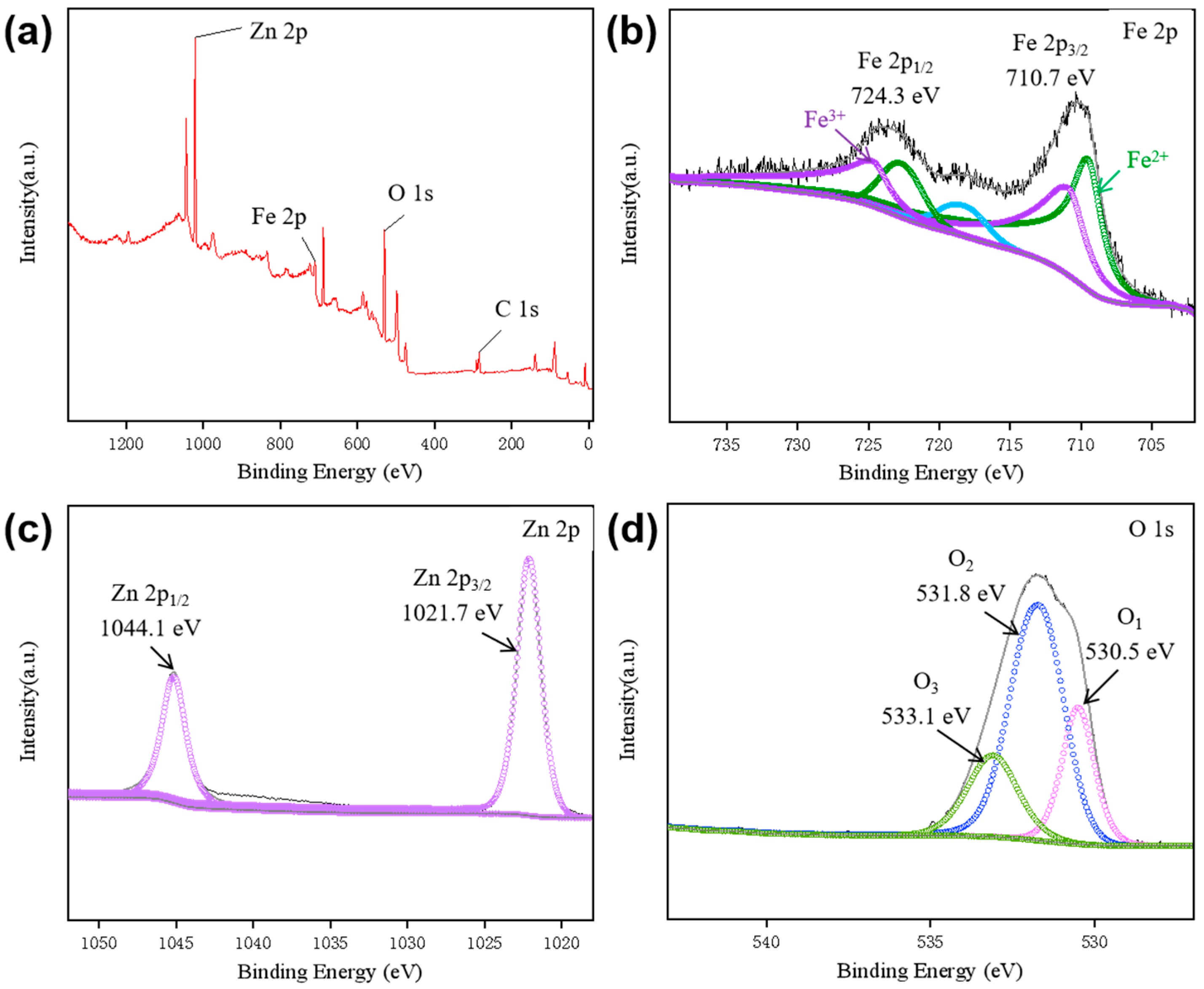
XPS measurements were performed to further confirm the presence of Fe and Zn in the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs as a support to the XRD results, as shown in Figure 2. The binding energies are calibrated using C 1s at 284.6 eV as a standard. The survey spectrum exhibits the significant peaks attributed to Fe 2p, Zn 2p, O 1s, and C 1s, indicating the existence of Zn, Fe, and O (Figure 2a). Based on the survey spectrum, the atomic ratio of Fe to Zn is approximately 8.07: 12.07. The Fe 2p XPS spectra in Figure 2b present the peaks located at 724.3 and 710.7 eV can be labeled as Fe 2p1/2 and Fe 2p3/2 orbitals in Fe3O4, respectively [33]. According to Figure 2c, the Zn 2p spectra display characteristic doublet peaks at 1044.1 eV (Zn 2p1/2) and 1021.7 eV (2p3/2), consistent with zinc in its oxidized state [34]. As shown in Figure 2d, the deconvolution of O 1s spectra was distinguished into three peaks. The peaks located at 530.5 (O1), 531.8 (O2), and 533.1 eV (O3) are corresponding to the lattice oxygen in ZnO, Fe3O4, and surface oxygen deficiency or hydroxyl species, respectively [31].
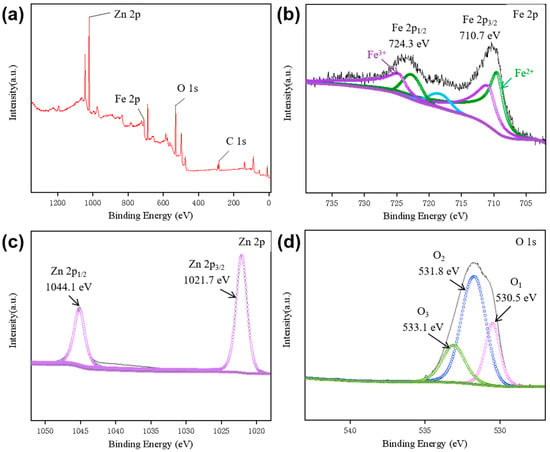
Figure 2.
(a) XPS survey scan and high-resolution XPS spectrum of (b) Fe 2p, (c) Zn 2p, and (d) O 1s of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs.
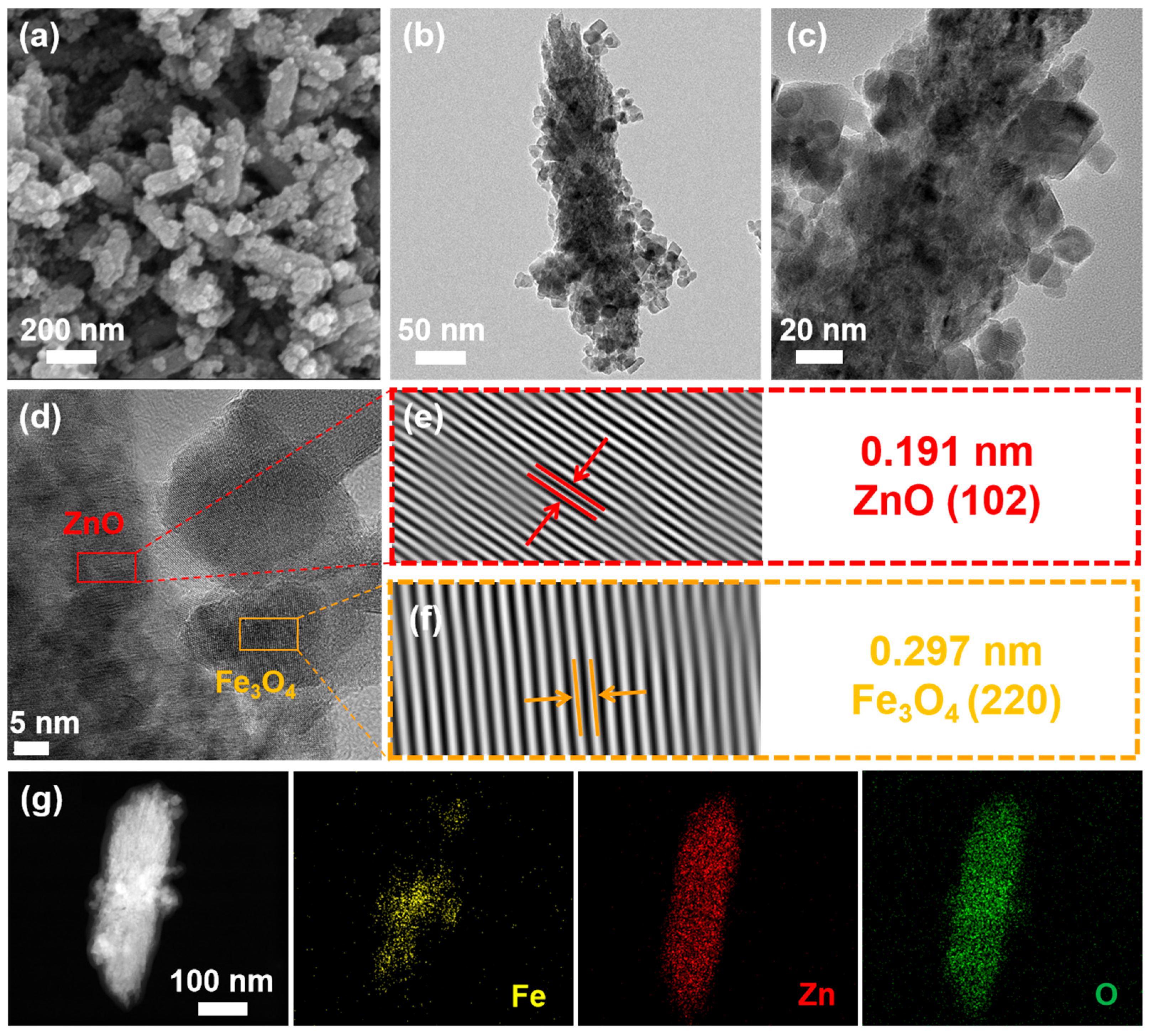
Figure 3a exhibits the SEM image of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs. It can be seen that the nanorods with a mean length of about 280 nm and a diameter of about 90 nm are uniformly wrapped by the nanoparticles. The obtained composites interlace and stack into a homogeneous nanoporous architecture and no obvious agglomeration was observed. TEM images (Figure 3b,c) indicate that the composites exhibit a typical spindle-like structure. The nanoparticles with a diameter of around 16 nm are dispersed on the nanorods. HRTEM image shows significant fringes with lattice spacing of 0.191 nm and 297 nm, which are in good agreement with the (102) plane of ZnO and the (220) plane of Fe3O4, respectively, confirming that the nanorods are ZnO and nanoparticles are Fe3O4, as shown in Figure 3d–f. Compared with single Fe3O4 NPs displayed in Figures S1 and S2, Fe3O4 NPs in the ZnO@Fe3O4 composites showed no significant morphological differences. The average diameters of the former and latter are 15 and 16 nm, respectively. However, the presence of clustered particles in these samples indicated a broad size distribution, which could potentially influence the properties of the Fe3O4-DOX nanocomposites. EDS mappings of Fe, Zn, and O elements are shown in Figure 3g. It can be seen that the Zn and O elements are uniformly distributed in the whole structure, indicating the formation of the uniform ZnO nanorods. However, it should be noted that the iron element exhibits slightly inhomogeneous distribution, which indicates a slight agglomeration of Fe3O4 NPs on the ZnO surface, consistent with the TEM analysis. This observed effect can be fundamentally explained by two key physicochemical principles. Firstly, consistent with established nanomaterial behavior, a direct correlation exists between particle dimensions and surface characteristics; as particle size decreases, there is a corresponding exponential increase in specific surface area. This geometric relationship results in a substantially higher ratio of surface atoms to bulk atoms, consequently generating elevated surface energy states. Consequently, this results in the agglomeration of nanoparticles. On the other hand, due to the inherent magnetic properties of Fe3O4 particles, magnetic attraction occurs between individual particles, leading to the aggregation of these NPs.
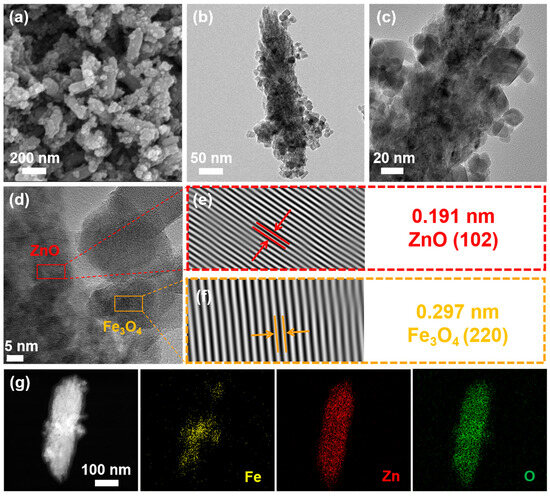
Figure 3.
(a) SEM image, (b,c) TEM images, and (d) HRTEM image of as-prepared ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs, (e,f) the inverse FFT crystalline lattice images of the selected area marked by the square, and (g) dark field and elemental mapping of Fe, Zn, and O elements.
3.2. Photothermal and Magnetic Properties Measurements
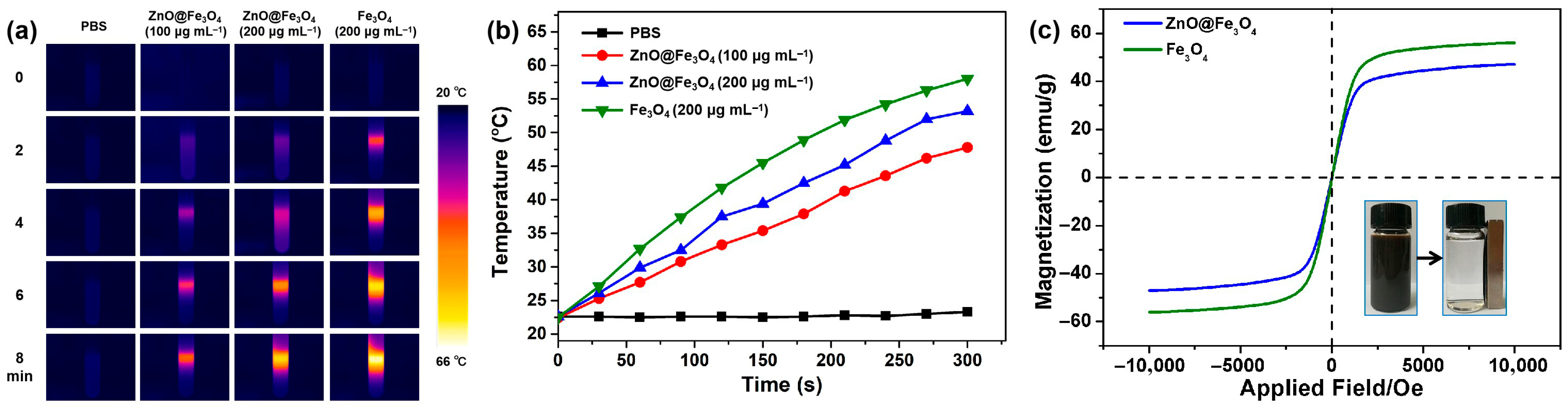
NIR-responsive photothermal therapy is often used in tumor treatment due to its enhanced tissue penetration depth and minimal harm to adjacent healthy tissues. Therefore, the photothermal effect of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs solutions with different concentrations was tested under NIR laser irradiation for 8 min at 2 W cm−2. As illustrated in Figure 4a, the experimental results demonstrate that both ZnO@Fe3O4 and Fe3O4 NPs solutions exhibit excellent NIR photothermal conversion capabilities, indicating their potential applicability in photothermal therapy. In addition, Figure 4b displays the temperature variation curves of different samples under laser irradiation. Notably, the rise in temperature showed a direct relationship with both nanoparticle concentration and irradiation duration. After 8 min, the temperature of the Fe3O4 solution increased by 37.9 °C and reached a high temperature of 60.4 °C, while that of the ZnO@Fe3O4 solution rose by 32.8 °C with the same concentration. When the concentration of the ZnO@Fe3O4 was reduced to 60 μg mL−1, the temperature just increased by 26.5 °C. In contrast, the temperature for PBS group varied insignificantly under the same conditions. The results indicate that the concentration had a significant impact on the NIR photothermal conversion capability. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that this capability was also highly dependent on the laser power density, which has been proven by previous studies [35].
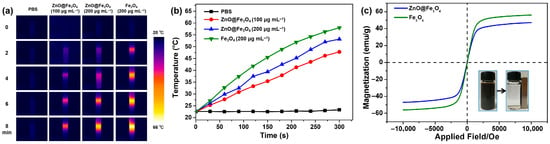
Figure 4.
(a) Thermographic images and (b) temperature elevation profile of PBS, ZnO@Fe3O4 (100 and 200 μg mL−1), and Fe3O4 (200 μg mL−1) solutions recorded at different NIR exposure durations. (c) Room temperature magnetization curves of the ZnO@Fe3O4 and Fe3O4 NPs.
The magnetic properties of the synthesized ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs were characterized at room temperature compared with single Fe3O4 NPs under an applied magnetic field sweeping between −10 to 10 kOe. The magnetization curves presented in Figure 4c demonstrate that the normalized saturation magnetizations (Ms) of the ZnO@Fe3O4 and Fe3O4 NPs are 47.06 and 56.18 emu/g, respectively. The reduction in MS value of ZnO@Fe3O4 was attributed to the decreased mass content of the magnetic component Fe3O4 as well as the non-magnetic property of the ZnO. Similar results have been reported by previous studies [31,32,36]. Meanwhile, the remanent magnetization of ZnO@Fe3O4 was found to be approximately 2 emu/g, indicating that the composites possess superparamagnetic behavior at ambient. Further, a fast response to the external magnet of the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs was observed by using a magnet in the aqueous solution (insert). The result confirms that the ZnO nanorods can modulate the saturation values of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs, while the nanocomposites retain strong magnetization and exhibit remarkable magnetic responsivity, suggesting the suitability for applications in magnetic-targeted drug delivery as the carriers. Firstly, superparamagnetic behavior prevents nanoparticle aggregation in the bloodstream while allowing strong attraction under an external magnetic field. An external gradient field can be applied to guide and accumulate nanoparticle carriers at a specific disease site, thereby enhancing localized drug concentration. Secondly, temperature-responsive nanocarriers have been designed based on the use of heating induced by alternating magnetic fields, which lead to excitation of the carrier that liberates the drug molecules. Last, superparamagnetic ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs can act as excellent contrast agents in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). This allows for real-time tracking of the carrier’s biodistribution, accumulation at the target site, and subsequent therapeutic response.
3.3. External Release Experiment of ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX Nanocomposites
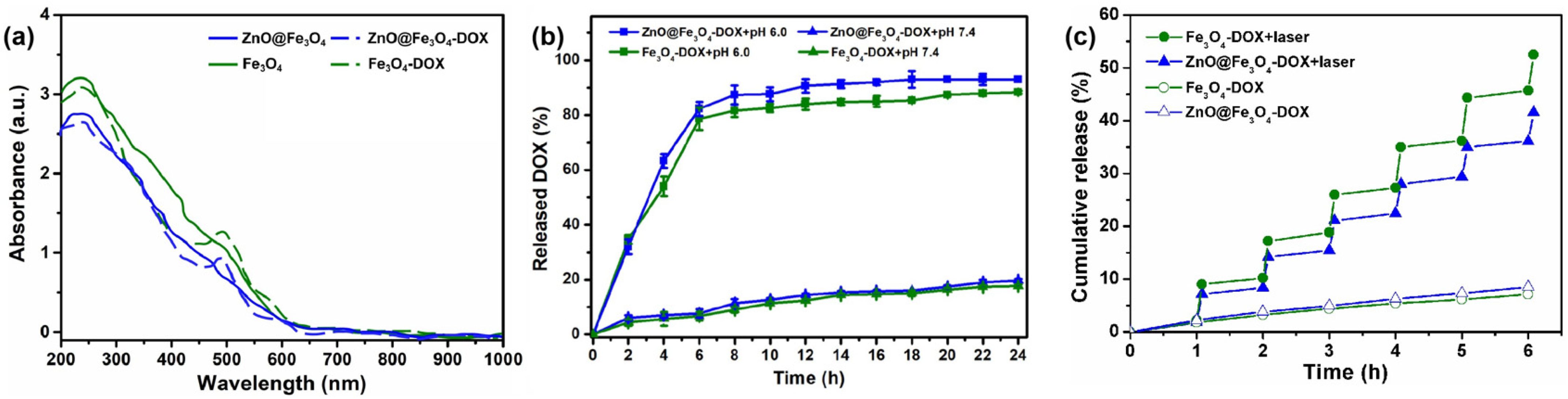
DOX served as a representative therapeutic agent that was conjugated to the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs carriers via physical adsorption. The loading content of DOX was calculated to be about 16.4% and 17.5% for Fe3O4-DOX and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX, respectively, based on the established calculation method [18,37]. The higher loading content of the latter is presumably attributed to the multi-scale nanostructure, the porous surface of the ZnO nanorods, and uniform dispersion compared with the former. The drug loading efficiency of DOX onto NPs was further verified through UV-Vis spectroscopy analysis. As illustrated in Figure 5a, distinct absorption peaks at 490 nm were observed across both drug-loaded samples, which is consistent with the results obtained for DOX shown in Figure S3, confirming the successful incorporation of DOX molecules onto the nanoparticle carriers.
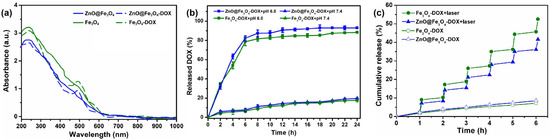
Figure 5.
(a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of Fe3O4-DOX and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX dispersed in aqueous solution. (b) External release of Fe3O4-DOX and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX nanocomposites in pH 6.0 and 7.4. (c) Drug release from Fe3O4-DOX and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX nanocomposites with or without NIR irradiation (808 nm, 2.0 W cm−2).
Previous studies indicated that the drug release kinetics of DOX from metal oxide NPs demonstrated significant pH-responsive characteristics, which demonstrated enhanced solubility and accelerated release kinetics under acidic conditions [32,37,38]. Thus, we evaluated the release behaviors of DOX from Fe3O4-DOX and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX nanocomposites in PBS buffer with pH values of 6.0 and 7.4. The release kinetics, presented in Figure 5b, demonstrated a persistent and gradual release of DOX with released percentages of about 20% for both samples in pH 7 medium at 24 h. However, the curve exhibits an obvious two-stage process in pH 6.0: an immediate burst release was observed initially, which subsequently transitioned to a slow, sustained release phase. And nearly 91% and 86% of the DOX was released for ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX and Fe3O4-DOX, respectively. The faster release can be ascribed to the higher solubility of the DOX under acidic conditions. Thus, the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs were expected to achieve controlled drug delivery by enhancing release in the acidic tumor microenvironment and preventing untimely release in the normal organs.
The release behavior of ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX and Fe3O4-DOX composites controlled by NIR irradiation was evaluated in PBS buffer at pH 7.4. As demonstrated in Figure 5c, the release kinetics during NIR laser irradiation showed significantly enhanced efficiency compared to non-irradiated conditions, highlighting the photothermal-triggered release capability. Upon extended laser irradiation over 6 h, the release profiles revealed significant differences, with Fe3O4-DOX and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX exhibiting 44.59% and 32.41% higher cumulative release compared to their non-irradiated counterparts, respectively. Meanwhile, the control groups exhibited distinct drug release profiles without laser irradiation, and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX demonstrated the higher cumulative drug release compared to the other. Thus, although Fe3O4-DOX demonstrated accelerated drug release kinetics under laser irradiation compared to ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX, the stability of the latter was obviously higher than the former.
3.4. Cell Viability
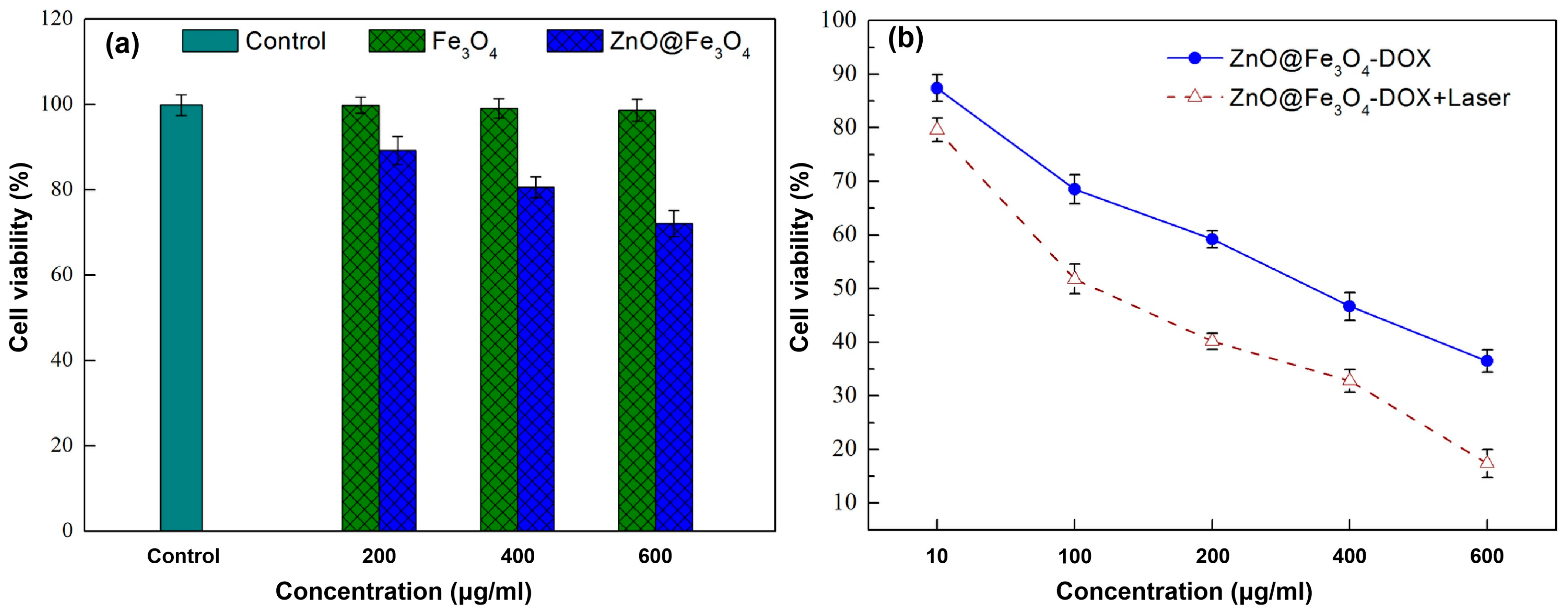
The in vitro cytotoxic effects of synthesized Fe3O4 and ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs on HeLa cells were evaluated using CCK-8 assays. As shown in Figure 6a, Fe3O4 NPs maintained cell viability without significant reduction at concentrations up to 600 μg/mL. In contrast, ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs induced toxicity at higher concentrations (200–600 μg/mL), likely due to the ZnO shell-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). To further assess the anticancer potential, the cytotoxicities of ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX with and without laser irradiation were compared. As illustrated in Figure 6b, both treatments induced concentration-dependent cytotoxicity in HeLa cells, with a markedly enhanced effect under laser exposure. At 600 μg/mL, the cell survival rate decreased to 19% following irradiation, compared to 41% in the non-irradiated group. This pronounced improvement of cell killing efficiency is attributed to a synergistic mechanism combining photothermal effects and NIR-triggered DOX release, enabling effective chemo-photothermal therapy.
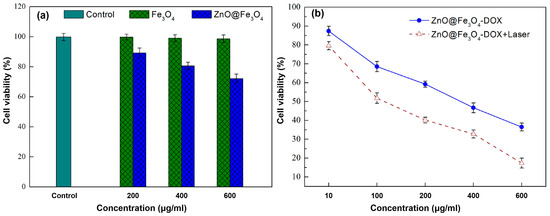
Figure 6.
(a) Cell viability curves of HeLa cells incubated with different concentrations of Fe3O4 and ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs for 24 h. (b) Relative viabilities of HeLa cells after incubation with ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX with and without laser irradiation (2 W cm−2, 5 min) at different concentrations.
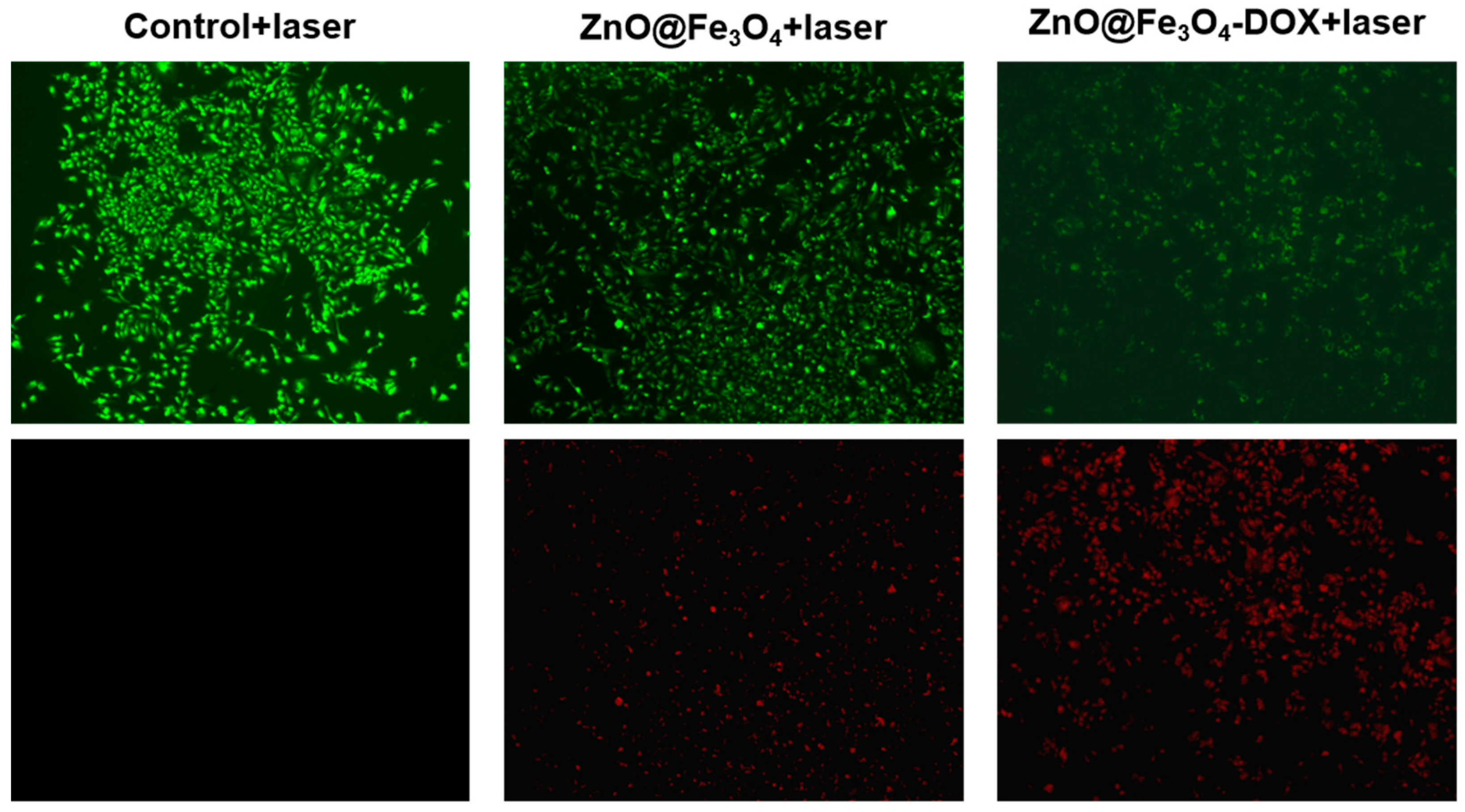
Further, the synergistic phototoxic and chemotoxic effects of ZnO@Fe3O4 and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX on HeLa cells were evaluated via live/dead fluorescence staining following laser irradiation. As shown in Figure 7, HeLa cells of control group exposed solely to laser irradiation exhibited robust growth and no red fluorescence, confirming that only laser irradiation could not damage cells. In the presence of ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs under irradiation, weak red fluorescence was detected, suggesting limited photothermal toxicity. In contrast, a substantial reduction in cell viability was observed with ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX, as evidenced by intense red fluorescence, which reflects the combined action of photothermal ablation and DOX-mediated chemotherapy. These findings collectively demonstrate that the ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX nanoplatform serves as an effective targeted drug delivery system with synergistic chemo-photothermal therapeutic performance.
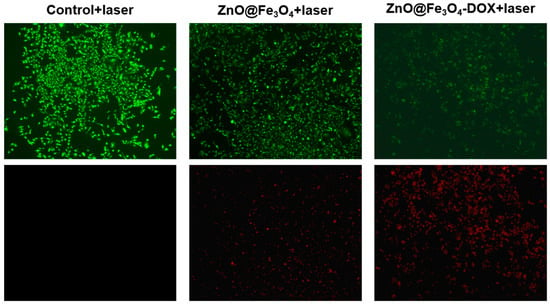
Figure 7.
Live/dead staining to determine the viability of HeLa cells incubated with control (without samples), ZnO@Fe3O4, and ZnO@Fe3O4-DOX with 808 nm laser irradiation for 5 min.
All above results demonstrated that the synthesized ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs with multi-scale nanostructure exhibited higher drug loading content, faster release in the acidic tumor microenvironment, and higher stability under NIR-triggered release than Fe3O4 NPs, while they still possessed superparamagnetic behavior and a fast response to the external magnet. Meanwhile, comparison of some characteristics of the ZnO-Fe3O4 composites prepared in this experiment with those reported in the literature is shown in Table S1. These characteristics are crucial for ensuring optimal drug delivery to tumor sites while minimizing systemic toxicity to healthy tissues and present a more promising candidate for triggered drug release applications.
4. Conclusions
This study successfully synthesized ZnO@Fe3O4 composite nanoparticles using a straightforward co-precipitation approach. The composites consist of the spindle-like ZnO nanorods with a mean length of about 280 nm and a diameter of about 90 nm wrapped by the Fe3O4 NPs with a diameter of around 14 nm. Additionally, the composite NPs retain the parent Fe3O4′s superparamagnetism and exhibit excellent NIR photothermal conversion capabilities, highlighting their potential for magnetic-targeted drug delivery and photothermal therapy. In drug release experiments in vitro, the ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs also demonstrated a significant pH-responsive as well as NIR light-triggered release characteristics, therefore promising to be multifunctional nanocarriers with stimuli-responsive controlled release performance. In future investigations, we aim to comprehensively assess the cytotoxicity, in vivo drug delivery efficiency, and release kinetics of the synthesized ZnO@Fe3O4 NPs to further elucidate their biomedical applicability and therapeutic potential.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/magnetochemistry12010002/s1, Figure S1: TEM images of single Fe3O4 NPs with (a) low and (b) high magnification, and the inverse FFT lattice image in the inset; Figure S2: Size distribution of Fe3O4 NPs; Figure S3: UV-Vis absorption spectrum of DOX in aqueous solution; Table S1: Comparison of some characteristics of the ZnO-Fe3O4 composites prepared in this experiment with those reported in the literature [28,32,39,40,41,42,43,44].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.G. and T.S.; methodology, Y.G.; software, Y.G. and Y.W.; formal analysis, Z.T.; investigation, Y.G. and M.Y.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.G.; writing—review and editing, T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hu, S.; Zhao, R.; Shen, Y.; Lyu, B. Revolutionizing drug delivery: The power of stimulus-responsive nanoscale systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.F.; Ferreira, A.H.; Thipe, V.C. The state of the art of theranostic nanomaterials for lung, breast, and prostate cancers. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Devi, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Yashavarddhan, M.; Bohra, D.; Ganguly, N. Exosomes as nature’s nano carriers: Promising drug delivery tools and targeted therapy for glioma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 182, 117754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.M.H.; Salazar, C.J.J.; Nurunnabi, M. Recent advances in bionanomaterials for liver cancer diagnosis and treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4821–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoneef, M.; Awad, M.; Aldosari, H.; Hendi, A.; Alshammari, S.; Aldehish, H.; Merghani, N.; Alsahli, A.; Almutairi, B.; Alharbi, R.; et al. Eco-friendly synthesis of magnetic ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposites: Structural, morphological, antimicrobial, and anticancer evaluation. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 2025, 10, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thani, A.; Jan, A.; Abbas, M.; Geetha, M.; Sadasivuni, K. Nanoparticles in cancer theragnostic and drug delivery: A comprehensive review. Life Sci. 2024, 352, 122899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.I.P.; Borges, J.P. Recent advances in magnetic electrospun nanofibers for cancer theranostics application. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2021, 31, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, D.; Ugolini, S.; Busti, F.; Marchi, G.; Castagna, A. Modern iron replacement therapy: Clinical and pathophysiological insights. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 107, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Z.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Chiu-Lam, A.; Hensley, D.; Dhavalikar, R.; Zhou, X.; Yu, E.; Goodwill, P.; Zheng, B.; Rinaldi, C.; et al. Magnetic particle imaging-guided heating in vivo using gradient fields for arbitrary localization of magnetic hyperthermia therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3699–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, P.; Chauhan, P. Facile synthesis of water-soluble Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@PVA nanoparticles for dual-contrast T1- and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 95, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Hung, C.; Lo, Y.; Li, C.; Ravula, V.; Wang, L. A biotin-selective molecular imprinted polymer containing Fe3O4 nanoparticles and CD44-selective aptamer for targeting cancer hyperthermia therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2025, 109, 106972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei-Asl, R.; Motaali, S.; Ebrahimie, E.; Mohammadi-Dehcheshmeh, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Pashaiasl, M. Delivery of doxorubicin by Fe3O4 nanoparticles, reduces multidrug resistance gene expression in ovarian cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 263, 155667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Khairudin, N.B.B.A.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Naiki, T.; Lee, K.X. Green biosynthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and biomedical applications in targeted anticancer drug delivery system: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2287–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Nema, A.; Shetake, N.; Gupta, J.; Barick, K.; Lawande, M.; Pandey, B.; Priyadarsini, I.; Hassan, P. Glutamic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for tumor-targeted imaging and therapeutics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Prakash, A.; Jaiswal, M.; Agarrwal, A.; Bahadur, D. Superparamagnetic iron oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid-a vehicle for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia treatment of cancer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 448, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Luong, H.; Pham, D.; Cao, L.; Nguyen, T.; Le, T. Drug-loaded Fe3O4/lignin nanoparticles to treat bacterial infections. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Huang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, R.; Cui, S.; Li, Y.; Kadasala, N.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. A multifunctional nanoplatform based on Fe3O4@Au NCs with magnetic targeting ability for single NIR light-triggered PTT/PDT synergistic therapy of cancer. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 944, 169206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Qi, X.; Ge, Y.; Shen, S. Azo-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: A Near-infrared light triggered drug delivery system for combined therapy of cancer with low toxicity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3660–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Pham, Q.; Riviere, E.; Thanh, P.; Nam, P.; Hai, P.; Anh, N.; Phuc, L.; Hong, N. Optimizing fabrication parameters of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enhancing magnetic hyperthermia efficiency. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 343, 130983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.M.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Kong, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Du, Y.P.; Jin, Y.; et al. Appropriate size of magnetic nanoparticles for various bioapplications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3092–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Wang, K.; Ge, Y.; Ma, W.; Qi, X.; Shen, S. Effect of magnetic nanoparticles size on rheumatoid arthritis targeting and photothermal therapy. Colloid Surf. B 2018, 170, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Ahmad, M.; Shadab, G.; Siddique, H. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles based cancer theranostics: A double edge sword to fight against cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 117–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasthuri, K.; Kumar, J.; Rajkumar, P.; Ranchani, A.; Kaliyamurthy, J. Bio-inspired synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Taraxacum officinale for antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 170, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, L.; Qian, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Recent advances on nanomaterials for antibacterial treatment of oral diseases. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, E.; Stoian, G.; Cojocaru, B.; Parvulescu, V.; Coman, S. ZnO/CQDs nanocomposites for visible light photodegradation of organic pollutants. Catalysts 2022, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Gurunathan, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6521–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Li, C.; Wu, K.; Hu, C.; Yang, N. Detection of tumor marker using ZnO@reduced graphene oxide decorated with alkaline phosphatase-labeled magnetic beads. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7747–7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Tang, D.; Meng, L.; Cui, B. ZnO capped flower-like porous carbon-Fe3O4 composite as carrier for bi-triggered drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astuti; Arief, S.; Muldarisnur, M.; Zulhadjri; Usna, S. Enhancement in photoluminescence performance of carbon-based Fe3O4@ZnO-C nanocomposites. Vacuum 2023, 211, 111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, D.; Zheltova, V.; Meshina, K.; Vorontsov-Velyaminov, P.; Emelianova, M.; Bobrysheva, N.; Osmolowsky, M.; Voznesenskiy, M.; Osmolovskaya, O. Fe3O4@ZnO Core-shell nanoparticles–a novel facile fabricated magnetically separable photocatalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 672, 160873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Huang, W.; Ding, X.; He, J.; Huang, Q.; Tan, J.; Cheng, H.; Feng, J.; Li, L. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO:La. J. Rare Earth 2020, 38, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, M. A dual-targeting Fe3O4@C/ZnO-DOX-FA nanoplatform with pH-responsive drug release and synergetic chemo-photothermal antitumor in vitro and in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.; Jung, Y.; Lee, T.; Park, I.; Ahn, J. Fabrication of Fe3O4-ZnO core-shell nanoparticles by rotational atomic layer deposition and their multi-functional properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Liang, C. Tunable zinc corrosion rate by laser surface modification for implants with controllable degradation direction. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 18263–18277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.G.; Guo, Y.; Deng, M.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J. Facile Approach to Prepare rGO@Fe3O4 Microspheres for the Magnetically Targeted and NIR-responsive Chemo-photothermal Combination Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchakeaw, A.; Nonthing, S.; Dulyasucharit, R.; Nanan, S. Improved photocatalytic activity of magnetically separable Fe3O4/ZnO photocatalyst for complete sunlight-active removal of tetracycline antibiotic. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2025, 862, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Qi, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Ge, Y.; Shen, S. Ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles for nuclei targeting drug delivery and photothermal therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2020, 58, 101782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, A.; Abdouss, M.; Kalaee, M.; Homami, S.; Pourmadadi, M. Targeted delivery of quercetin using gelatin/starch/Fe3O4 nanocarrier to suppress the growth of liver cancer HepG2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Hassan, P.A.; Barick, K.C. Core-shell Fe3O4@ZnO nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia and bio-imaging applications. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 025207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, S.; Abdulnabi, W.; Abdul kader, H. Synthesis, characterization and environmental remediation applications of polyoxometalates-based magnetic zinc oxide nanocomposites (Fe3O4@ZnO/PMOs). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 13, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, V.M.; Huong, N.T.; Nam, D.T.; Dung, N.D.T.; Thu, L.V.; Nguyen-Le, M. Synthesis of Ternary Fe3O4/ZnO/Chitosan Magnetic Nanoparticles via an Ultrasound-Assisted Coprecipitation Process for Antibacterial Applications. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 8875471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atla, S.B.; Lin, W.; Chien, T.; Tseng, M.; Shu, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, C. Fabrication of Fe3O4/ZnO magnetite core shell and its application in photocatalysis using sunlight. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, N.; Ding, S.; Xiong, J.; Wu, P. Theranostics for hepatocellular carcinoma with Fe3O4@ZnO nanocomposites. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Cui, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Chang, Z.; Wang, Y. A multifunctional β-CD-modified Fe3O4@ZnO:Er3+,Yb3+ nanocarrier for antitumor drug delivery and microwave-triggered drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.