Abstract
Brassica crops, cultivated as vegetables, oilseeds, and forages, are vital economic resources in agricultural production. However, black rot caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) poses a significant threat to the production of these crops. This study aimed to enhance the resistance resource pool for Brassica crops by evaluating 29 inbred lines and 52 commercial cultivars of B. rapa through an inoculation test. Among these, 11 inbred lines, such as ‘E5’ and ‘LW’, and 8 commercial cultivars, such as ‘QX’ and ‘SY’, demonstrated high resistance. We constructed a genetic segregating population (P1, P2, F1, F2) using the highly resistant line ‘E5’ and the highly susceptible line ‘E4’ as parents. Utilizing a major gene plus polygenic mixed inheritance model for genetic analysis, our findings indicate that the resistance to black rot in ‘E5’ is governed by a pair of additive-dominant polygenes, and the main gene heritability is 93.43%. Furthermore, transmission electron microscopy examination revealed numerous autophagic structures in the xylem parenchyma cells of the highly resistant line ‘E5’, while the highly susceptible line exhibited cell necrosis, indicating that the resistant material might protect mesophyll cells and adjacent structures through programmed cell death. This research contributes novel genetic materials for breeding disease-resistant varieties, enhances our understanding of Xcc invasion mechanisms and host defense traits, and establishes a theoretical framework for the effective prevention and control of these diseases.
1. Introduction
Brassica crops, such as Chinese cabbage (B. rapa), cabbage (B. oleracea), oilseed rapa (B. napus), and mustard (B. juncea), are globally significant agricultural resources, being cultivated as vegetables, oilseeds, condiments, and forages [,]. Black rot is caused by the pathogenic strain Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc), characterized by primary symptoms including V-shaped chlorotic lesions at leaf margins, necrosis, and blackening of leaf veins []. This disease has become a significant threat to Brassica species, compromising both yield and quality []. In recent years, the severity of black rot has increased due to climate change and inadequate cultivation practices. Consequently, developing and disseminating resistant varieties has emerged as the most cost-effective and sustainable strategy for disease management [,].
The screening of resistant genotypes is essential for the development of black rot-resistant varieties. Bain identified the B. oleracea variety ‘Early Fuji’ as a valuable source of black rot resistance and employed it to develop multiple resistant cabbage varieties []. Silva demonstrated that the B. oleracea cultivars ‘TCA-549’ and ‘Melissa’ exhibited exceptional resistance to black rot, leading to minimal yield losses post-infection []. Liu and Kopta identified the B. rapa varieties ‘A24’, ‘A96’, and ‘Dwarf milk cabbage’ as exhibiting high resistance to black rot [,]. Guo screened two highly resistant B. napus accessions, ‘PI199947’ and ‘PI199949’ []. Griffiths evaluated resistance in 4084 accessions across 23 genera, identifying 5 accessions of B. carinate, 5 of B. rapa, 4 of B. nigra, and 2 of B. oleracea with excellent resistance to black rot. In conclusion, the A and B genomes of the Brassica genus possess more resistance resources compared to the C genome [].
Investigating the inheritance patterns of black rot resistance across diverse genetic materials is critical for breeding programs. Elston proposed the concept of a “one major gene plus polygenic” model, combining major and polygenic inheritance []. The mixed inheritance model of major plus polygenic genes is currently widely used in the genetic analysis of quantitative traits. This approach enables the detection of major and polygenic gene effects and the estimation of their genetic parameters []. This model has been extensively applied to numerous crops, such as wheat, rice, soybeans, and cucumbers [,,,].
Research on the inheritance patterns of black rot resistance in the Brassica genus has been conducted worldwide; however, the findings have been inconsistent, indicating a highly complex genetic basis for resistance. Bain proposed that black rot resistance in the ‘Huguenot’ cabbage is controlled by one or more pairs of dominant genes []. Williams suggested that black rot resistance in ‘Early Fuji’ cabbage is governed by a pair of recessive major genes, with additional contributions from both dominant and recessive modifier genes []. Singh and Sharma reported that black rot resistance in Ethiopian mustard HCA-6 is controlled by a single pair of dominant genes, whereas resistance in NPC-9 is a quantitative trait influenced by multiple genes [,].
Xcc primarily invades plants via hydathodes and colonizes their vascular bundles. Xcc secretes various cell-wall-degrading enzymes that degrade plant cell walls, leading to host cell separation and creating an environment conducive to saprophytic growth. Additionally, Xcc synthesizes xanthan gum and extracellular polysaccharides, which obstruct the host vascular system. This obstruction reduces water transport, resulting in leaf yellowing and wilting [,]. Over an extensive evolutionary period, host plants have evolved both passive and active resistance mechanisms to counteract pathogen invasion []. Histological studies, particularly those utilizing transmission electron microscopy to examine cellular responses, are invaluable for elucidating resistance mechanisms in plants during pathogen infection [,,,]. Currently, this research approach has been widely applied to crops such as rice; however, its application in studying black rot in Brassica species remains limited [,].
Brassica rapa serves as a significant source of resistance to black rot []. Until recently, black rot resistance in B. rapa remains understudied in three critical areas: (1) comprehensive screening of resistant germplasm across diverse genetic resource is lacking; (2) the inheritance patterns governing Xcc resistance are unresolved; (3) subcellular defense mechanisms, particularly autophagy-mediated responses, in resistant genotypes are poorly understood. To address these gaps, this study employs a tripartite strategy: initially, we evaluate 81 accessions of B. rapa to identify new sources of resistance; subsequently, we employ a mixed major gene plus polygene inheritance model to elucidate the genetic architecture of resistance; finally, we conduct ultrastructural analyses to investigate autophagy-related cellular responses that differentiate resistant from susceptible lines. These findings will facilitate the development of resistant varieties and provide a theoretical basis for effective disease management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
This experiment selected 29 inbred lines and 52 commercial cultivars of B. rapa. Among these, 20 accessions were obtained from the mid-term gene bank of the National Vegetable Germplasm Center at the Institute of Vegetables and Flowers, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IVF-CAAS), 50 accessions were acquired from seed markets, and the remaining accessions were supplied by the Cabbage Research Group of the same institution. The seedlings were cultivated in a greenhouse to a 4–6 true leaves stage, approximately 21 days after germination, and they were watered every two days.
Brassica rapa materials ‘E5’ and ‘E4’ were systematically selected and subsequently maintained in our laboratory. In winter 2019, these accessions were sown in a greenhouse. Hybridization in spring 2020 produced the F1 generation. In spring 2021, self-pollination of F1 was performed to obtain the F2 generation. All plant materials were grown under the previously described conditions, and resistance evaluations were conducted in autumn 2021.
2.2. Inoculation Test
The Xcc race1 strain WH3811 was provided by Professor Vicente from the University of Warwick. The strain is maintained in PSB Medium, which consists of 10 g/L peptone, 10 g/L sucrose, 1.0 g/L L-glutamate, and has a pH of 7.0. The culture is incubated for approximately 12 h at 28 °C with shaking at 200 rpm, after which it is diluted to a concentration of 1 × 108 cfu/mL using sterile water.
When the seedlings developed 4 to 6 true leaves, a sterilized toothpick was used to dip into the bacterial suspension and make three uniform punctures along the main leaf vein, 0.5 to 2 cm from the leaf tip. The three treated leaves on each plant were selected to ensure they were of similar size and closely positioned. The inoculated seedlings were then incubated at 25 to 28 °C, and disease symptoms were assessed after 7 to 10 days.
2.3. Resistance Evaluation
Resistance assessments were conducted 7 to 10 days post-inoculation using a grading system based on the inoculated leaf units. The grading criteria were as follows: Grade 0, no symptoms on the inoculated leaf; Grade 1, lesion area covering < 5% of the leaf area; Grade 3, lesion area covering 5–15% of the leaf area; Grade 5, lesion area covering 15–30% of the leaf area; Grade 7, lesion area covering 30–50% of the leaf area; Grade 9, lesion area covering > 50% of the leaf area.
Disease index (DI) = Σ (disease rating scale × the number of leaves with a particular rating) × 100/(the total number of tested leaves × 9).
The resistance of each B. rapa accession was evaluated based on the following criteria: Immune (I), DI = 0; Highly Resistant (HR), 0 < DI ≤ 10; Resistant (R), 10 < DI ≤ 30; Moderately Resistant (MR), 30 < DI ≤ 50; Susceptible (S), 50 < DI ≤ 70; Highly Susceptible (HS), DI > 70.
2.4. Genetic Analysis
This study conducted genetic analysis of black rot resistance in B. rapa using the R package SEA v2.0 to evaluate the disease index across generations []. The relevant parameters for each model were calculated using the maximum likelihood function and the IECM algorithm. The optimal model was selected by minimizing the AIC value []. Goodness-of-fit tests, including the equal distribution test (U12, U22, and U32), the Smirnov test (nW2), and the Kolmogorov test (Dn), were conducted across all models to validate the selection. Genetic parameters, including gene effect values, were estimated via the least squares method, with calculations derived from the distribution parameters of each component in the optimal model.
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
To investigate the invasion mode of Xcc via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the procedure outlined the specific steps. (1) Fix leaves that have been sprayed with a bacterial suspension in 2% glutaraldehyde. (2) Rinse fixed samples 3× in PBS, 10 min per rinse. (3) Post-fix samples in 1% osmium tetroxide for 2 h. (4) Wash samples 3× in distilled water, 3 min per rinse. (5) Dehydration in an ethanol series: 30%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95%, 100% ethanol (15 min per step). (6) Dry using a CO2 critical point dryer (Leica CPD 030, Wetzlar, Germany). (7) Mount samples onto SEM stubs. (8) Coat samples using an ion sputter coater (HITACHI MC1000, Tokyo, Japan). (9) Observe using a scanning electron microscope (HITACH SU-8010, Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was employed to observe the changes in cellular ultrastructure following inoculation; the following outlines the specific steps. (1) Fix inoculated leaf samples in 2% glutaraldehyde. (2) Rinse fixed samples 3× in PBS, 10 min per rinse. (3) Post-fix samples in 1% osmium tetroxide for 2 h. (4) Wash samples 3× in PBS, 3 min per rinse. (5) Dehydration in an ethanol series: 30%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95%, 100% ethanol (15 min per step). (6) Replace ethanol with acetone 3× (15 min per step). (7) Infiltrate with a graded acetone: Spurr’s resin over 24 h at 35 °C. (8) Polymerize samples at 60 °C for a week. (9) Cut ultrathin sections (80 nm thickness) using an ultramicrotome (Leica EMUZ7, Wetzlar, Germany). (10) Stain sections with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. (11) Observe sections using a transmission electron microscope (HITACH H-7500, Tokyo, Japan).
2.7. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using Microsoft Excel 2013 and GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Screening of Resistant Sources to Black Rot in B. rapa
A total of 81 B. rapa accessions were assessed for black rot resistance. This group included 29 inbred lines and 52 commercial cultivars (Table S1). Significant differences in resistance were observed among the accessions, with disease index ranging from 0.82 to 73.85. Among the inbred lines, although no materials were completely immune, 11 exhibited high resistance, accounting for 37.93% (Figure 1a). The top-performing accessions were ‘LW’, ‘DY’, ‘JZ’, and ‘E5’, which had disease indices of 0.69, 1.11, 1.01, and 1.96, respectively (Figure 1c–e). Only three accessions exhibited high susceptibility, accounting for 10.34% of the total. These were ‘E4’, ‘A8’, and ‘LY’, which had disease indices of 70.48, 73.85, and 75.55, respectively (Figure 1f–h). Furthermore, only two accessions were susceptible, while six exhibited resistance and seven showed moderate resistance.
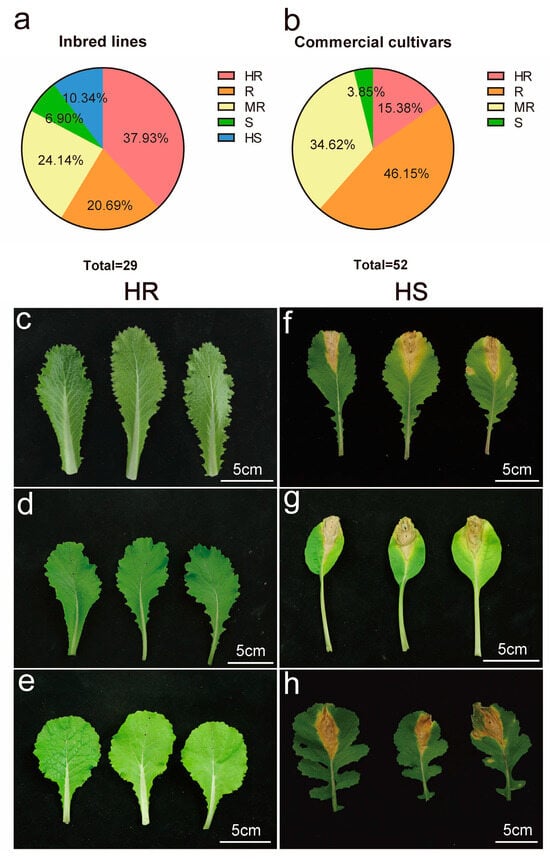
Figure 1.
Screening of resistant sources to black rot disease in B. rapa. (a) The proportion of different resistance levels of B. rapa in 29 inbred lines. HR is highly resistant, R is resistant, MR is moderately resistant, S is susceptible, HS is highly susceptible. (b) The proportion of different resistance levels of B. rapa in 52 commercial cultivars. (c) ‘E5’. (d) ‘LW’. (e) ‘JZ’. (f) ‘E4’. (g) ‘A8’. (h) ‘LY’. Scale bars: (c–h) 5 cm.
The primary commercial cultivars include 24 resistant accessions and 18 moderately resistant accessions, accounting for 46.15% and 34.62% of the total, respectively. Additionally, eight accessions were classified as highly resistant and two as susceptible, with no accessions exhibiting high susceptibility (Figure 1b). A comparison of the identification results between inbred lines and commercial cultivars reveals no significant difference in the average disease index; however, the distribution showed a clear distinction. This discrepancy stems from the fact that all commercial cultivars are F1 hybrids, whose quantitative traits may exhibit intermediate phenotypes resembling incomplete dominance.
3.2. Genetic Analysis of Resistance to Black Rot in B. rapa
In the winter of 2021, we assessed the resistance to black rot in a population generated from a cross between ‘E5’ and ‘E4’ (P1, P2, F1, F2). Notably, the F2 population displayed a significant skew in its distribution (Figures S1 and S2). This study conducted a mixed major gene plus polygene inheritance model, using disease indices from individual plants across generations, and employed a total of 25 models. The analysis revealed that the AIC value for the 1MG-AD model was the lowest among the evaluated models (Table 1). A goodness-of-fit test was performed for all models evaluated. Of the three models—1MG-AD, 1MG-EAD, and 1MG-NCD—only one statistical metric reached significance for each model, indicating limited significance overall (Table 2). Following the principle of minimizing AIC, we selected the 1MG-AD model as the most suitable, which suggests that resistance to black rot in B. rapa ‘E5’ is governed by a pair of additive-dominant major genes.

Table 1.
Max-likelihood-value and AIC value of each genetic model.

Table 2.
Statistical measures for the significance level achieved by each model.
The additive and dominance effects of the first-order genetic parameters in the 1MG-AD model were −14.1344 and −5.119, respectively. This indicates that both effects of the major genes contribute to a reduction in the disease index and enhancement of disease resistance. The potential ratio was 0.36, indicating that this gene exhibits partial dominance. For the second-order genetic parameters, the heritability of the major genes was 93.43%. This suggests that resistance to black rot in B. rapa is predominantly controlled by major genes, with minimal influence from environmental factors (Table 3).

Table 3.
The estimates of genetic parameters of the 1MG-AD model.
3.3. Observations on the Invasion Pathways of Xcc
Bacteria can invade plants through wounds and natural openings, including hydathodes, stomata, and lenticels. Current studies suggest that Xcc invades through the hydathodes at the leaf margins, resulting in the formation of “V”-shaped lesions. In this study, black rot pathogens were sprayed onto the leaf surfaces, and samples were collected for scanning electron microscopy after 24 and 48 h. The results indicated that 24 h after pathogen application, the pathogens aggregated around the stomata, with some already having entered them (Figure 2a,b). By 48 h, all pathogens had successfully infiltrated the stomata (Figure 2c). Five to six days post-inoculation, black dot-like lesions emerged on the leaf surfaces (Figure 2).
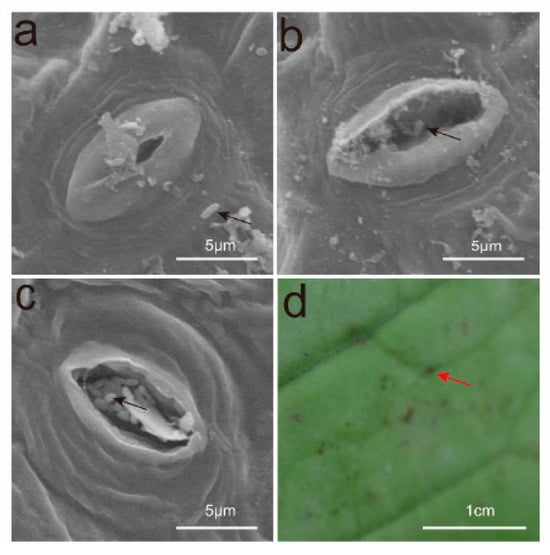
Figure 2.
Observations on the Invasion Pathways of Xcc. (a) After 24 h, Xcc accumulates around the stomata. (b) After 24 h, a small amount of Xcc has already entered the stomata. (c) After 48 h, nearly all of the Xcc has entered the stomata. (d) The black dot-like lesions are caused by Xcc entering through the stomata. The black arrow indicates Xcc, and the red arrow indicates black dot-like lesions. Scale Bars: (a–c) 5 μm; (d) 1 cm.
3.4. The Ultrastructure of Resistant and Susceptible B. rapa Leaves After Xcc Inoculation
Following Xcc invasion, the onset time, disease progression, and resistance levels vary among accessions with differing susceptibility. The interactions of affinity and incompatibility between Xcc and both resistant and susceptible accessions were investigated. This was accomplished by analyzing the ultrastructure of inoculation sites at various stages post-inoculation in ‘E5’ and ‘E4‘ using transmission electron microscopy.
Observations showed that 48 h post-inoculation, Xcc was present in all xylem vessels, with a significantly higher bacterial concentration in ‘E4’ compared to ‘E5’. The surrounding tissue fluid in the vessels was relatively viscous due to extracellular polysaccharides secreted by Xcc, which block the xylem vessels and impede the host’s transport of water and inorganic salts. The concentration of extracellular polysaccharides in the ‘E4’ vessels was greater than that in the ‘E5’ vessels, due to the higher bacterial content (Figure 3a).
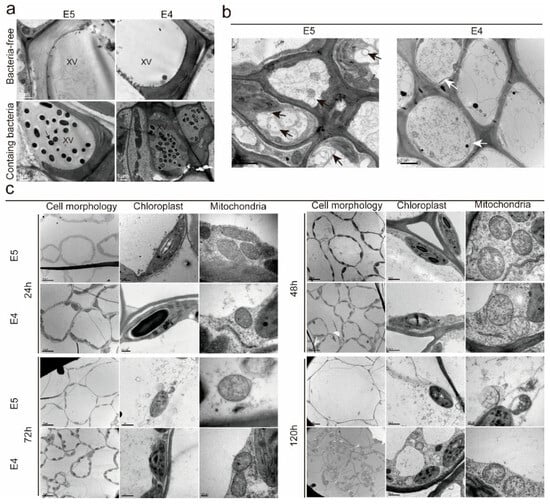
Figure 3.
Xcc colonizes the xylem vessels, and high-resistance material protects adjacent cells through autophagy of xylem parenchyma cells. (a) Xcc colonizes the xylem vessels and synthesizes xanthan gum, which obstructs their function. The black arrow indicates Xcc, and “XV” represents the xylem vessel. Bar = 1 μm. (b) Following inoculation, numerous membranous structures, both single and double-layered, resembling autophagosomes, are generated in the xylem parenchyma cells of ‘E5’. In contrast, significant plasmolysis is observed in the xylem parenchyma cells of ‘E4’. The black arrows indicate the structure of autophagosomes, while the white arrows indicate plasmolysis. (c) Comparison of the overall morphology, chloroplasts, and mitochondria of mesophyll cells in ‘E5’ and ‘E4’ at different time points post-inoculation. Scale Bars: (a) 1 μm; (b,c): refer to the annotation located in the lower-left corner of these images.
Transmission electron microscopy observations revealed that ‘E5’ demonstrates greater active resistance at both tissue and cellular levels compared to ‘E4’. At 72 h post-inoculation, numerous single- and double-membrane autophagic structures were observed in the xylem parenchyma cells of ‘E5’, while these structures were significantly less frequent in ‘E4’. In contrast, ‘E4’ displayed more characteristics of cellular necrosis, such as cell membrane rupture and plasmolysis. These findings suggest that ‘E5’ inhibits further colonization and expansion of pathogens via a more intense hypersensitive necrotic response (Figure 3b).
We further investigated the ultrastructure of mesophyll cells at various time points following inoculation with different substances to evaluate the extent of damage caused by these accessions. In the ‘E4’ group, significant cell deformation and plasmolysis were first observed 24 h post-inoculation. At 48 h, slight chloroplast deformation was observed, accompanied by a significant loss of mitochondrial matrix and disruption of the inner membrane cristae structure. At 72 h, chloroplast deformation and matrix loss became more pronounced, and by 120 h, complete cell rupture was observed. In the ‘E5’ group, 48 h post-inoculation, only a few cells exhibited mild deformation and plasmolysis; however, severe mitochondrial matrix loss occurred, resulting in cavity formation. At 72 h, the chloroplast matrix was first observed, and the inner membrane cristae structure of the mitochondria had become disorganized. At 120 h, vacuolar rupture was observed, accompanied by cavity formation in chloroplasts and complete matrix loss in some mitochondria. Overall, cells in the ‘E5’ group sustained less damage and exhibited delayed damage progression. A comparison of the mitochondria and chloroplasts—two organelles closely associated with energy metabolism—revealed that, regardless of the group (‘E5’ or ‘E4’), mitochondria sustained significantly more damage. Pathogenic microorganisms attacking plant cells are believed to induce the formation of mitochondrial membrane pores, resulting in the leakage of mitochondrial molecules and the collapse of the electrochemical gradient (Figure 3c) [].
4. Discussion
The broad host range of the Xcc enables it to infect nearly all Brassica crops, leading to devastating damage. Traditional physical and chemical control methods exhibit limited effectiveness and may lead to environmental pollution []. Consequently, breeding and cultivating disease-resistant varieties are considered the most effective and economical control strategies []. Previous studies indicate that the A genome of B. rapa contains substantial high-quality resistance sources []. However, research on the screening and genetic analysis of these resistance sources remains limited, and the cellular interaction mechanisms between the host and pathogen are still poorly understood []. This lack of knowledge hinders both the breeding of disease-resistant varieties and the development of new control methods.
Xcc exhibits notable physiological differentiation among its 11 classified races. Among these, race1 demonstrates the highest pathogenicity and is the predominant race worldwide [,]. Current resistance screening data within the Brassica genus indicates that A and B genomes confer stronger resistance to black rot relative to the C genome []. Consequently, this study selected race1 as the pathogen to ensure that the findings are applicable to most regions cultivating Brassica crops. A total of 81 B. rapa accessions were screened, comprising 29 inbred lines and 52 commercial cultivars. Among the inbred lines, 11 accessions exhibited high resistance, accounting for 37.93%, whereas the commercial cultivars included 8 resistant materials, representing 15.38%. These findings enrich the repository of resistance resources and establish a foundational basis for breeding resistant varieties against black rot. The commercial cultivars primarily consist of resistant and moderately resistant materials, exhibiting a notable distribution difference compared to inbred lines. This disparity may be due to the fact that all commercial varieties are hybrids []. Therefore, we recommend selecting high-resistance materials from both parents during the development of commercial cultivars.
The genetic mechanisms underlying resistance to black rot in Brassica crops are complex, and research findings regarding different materials are often inconsistent []. Even when the same material is inoculated with different physiological races, the results can vary significantly []. This variability is primarily associated with both the genotype of the plant and the genotype of Xcc, highlighting the interaction between the host and the pathogen [,]. Currently, research on the genetic mechanisms of resistance to black rot in B. rapa remains limited. Soegnas demonstrated that the resistance of Chinese cabbage B162 to black rot is governed by additive polygenes []. In contrast, our research indicates that the resistance genetic pattern of ‘E5’ is governed by a pair of additive dominant major genes (1MG-AD model), with the heritability of these major genes reaching 93.43%. This finding suggests that the resistance of ‘E5’ to black rot is predominantly inherited through major genes, making it a promising candidate for breeding programs focused on resistance.
Over time, plants have evolved sophisticated immune systems to counteract potential infections by various pathogens. The result of the interaction between plants and pathogens determines whether a plant exhibits resistance or susceptibility to disease []. The hypersensitive response (HR), a rapid form of programmed cell death (PCD), restricts pathogen spread by triggering localized apoptosis and autophagy [,]. During autophagy, double-membrane autophagosomes sequester cytoplasmic cargo, which subsequently fuse with lysosomes to form single-membrane autolysosomes for degradation []. In Arabidopsis thaliana, autophagy enhances resistance to Pseudomonas syringae by promoting pathogen containment in mesophyll cells []. Cell necrosis, a form of non-programmed cell death, is characterized by early plasma membrane rupture, protoplast contraction, and non-vacuolated cell death []. Xylem parenchyma cells—lignified cells in direct contact with Xcc—exhibit distinct responses in resistant and susceptible cabbage lines. In this study, xylem parenchyma cells from the resistant line ‘E5’ displayed numerous single- and double-membrane autophagic structures during early infection, indicative of active autophagy. In contrast, the susceptible line ‘E4’ showed negligible autophagic activity, resulting in pronounced necrosis, including plasmolysis and membrane rupture. Necrotic cells in ‘E4’ likely release nutrients that promote Xcc proliferation. Notably, mesophyll cell damage in ‘E5’ was significantly reduced compared to ‘E4’ post-inoculation. This disparity raises the possibility that autophagy in ‘E5’ xylem parenchyma cells might play a role in inducing systemic acquired resistance (SAR), potentially amplifying defense responses across tissues [].
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated 81 B. rapa accessions for their resistance to black rot, identifying 11 highly resistant materials from inbred lines and 8 from commercial cultivars. The highly resistant material ‘E5’ and the highly susceptible material ‘E4’ were used as parental lines to create a genetic segregation population for analysis. The results revealed that resistance to B. rapa black rot is governed by a pair of additive dominant major genes, with a heritability rate of 93.43%. Transmission electron microscopy observations of materials ‘E5’ and ‘E4’ at various time points post-inoculation revealed significant cytological differences. The highly resistant material ‘E5’ exhibited a greater abundance of autophagosome structures, whereas the highly susceptible material ‘E4’ showed signs of plasmolysis and cell necrosis. The findings of this study not only establish a foundation for breeding black rot-resistant varieties, but also partially clarify the interaction between Xcc and the host, along with the host’s disease resistance mechanisms. This research offers new insights into understanding resistance to black rot of B. rapa.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11060626/s1, Figure S1: Frequency distribution of different resistant levels in F2; Figure S2: Population sizes for genetic analysis; Table S1: Detailed information and resistance evaluation of 81 tested B. rapa materials; Table S2: The specific values for the goodness-of-fit tests of all models.
Author Contributions
S.D.: Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Visualization. C.K.: Writing—review and editing, Formal analysis. H.M.: Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation. J.J.: Supervision, Project administration. Y.W.: Supervision, Project administration. Y.Z.: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. M.Z.: Resources, Project administration. L.Y.: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Z.F.: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision. V.T.: Writing—review. A.M.A.: Project administration, Writing—review. H.L.: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFE0111400), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-IVFCAAS), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-23). This work was also partly supported by the Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education (No. 075-15-2023-582).
Data Availability Statement
The study’s data are included in the article. The corresponding author can be contacted for further inquiries.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Joana G. Vicente from the University of Warwick, UK, for providing the Xcc strain WHI3811 (race1).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lv, H.; Fang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. An Update on the Arsenal: Mining Resistance Genes for Disease Management of Brassica Crops in the Genomic Era. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Han, F.; Fang, Z.; Lv, H. Map-Based Cloning and CRISPR/Cas9-Based Editing Uncover BoNA1 as the Causal Gene for the No-Anthocyanin-Accumulation Phenotype in Curly Kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica). Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.H. Black Rot : A Continuing Threat to World Crucifers. Plant Dis. 1980, 64, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.G.; Holub, E.B. Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Cause of Black Rot of Crucifers) in the Genomic Era Is Still a Worldwide Threat to Brassica Crops. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Izzah, N.K.; Jayakodi, M.; Perumal, S.; Joh, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.-C.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, K.-W.; Nou, I.-S.; et al. Genome-Wide SNP Identification and QTL Mapping for Black Rot Resistance in Cabbage. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Li, B.; et al. Research Progress on Clubroot Disease in Brassicaceae Crops—Advances and Perspectives. Veg. Res. 2024, 4, e022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, D.C. Reaction of Brassica Seedlings to Blackrot. Phytopathology 1952, 42, 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, D.; Andre, L.; Joara, S.; Eizanilda, R.; Timothy, B. Screening Cabbage Cultivars for Resistance to Black Rot Under Field Conditions. HortTechnology 2020, 30, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, N.; Zhu, X.; Han, K.; Gu, R.; Bai, J.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of CC-NBS-LRR Family in Response to Downy Mildew and Black Rot in Chinese Cabbage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopta, T.; Penazova, E.; Jurica, M.; Pokluda, R. Evaluation of the Potential Yield and Primary Symptoms of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris Infection in Asian Vegetables Grown in the Czech Republic. Acta Agrobot. 2018, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Dickson, M.H.; Hunter, J.E. Brassica napus Sources of Resistance to Black Rot in Crucifers and Inheritance of Resistance. HortScience 1991, 26, 1545–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.D.; Marek, L.F.; Robertson, L.D. Identification of Crucifer Accessions from the NC-7 and NE-9 Plant Introduction Collections That Are Resistant to Black Rot (Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris) Races 1 and 4. Hortence Publ. Am. Soc. Hortic. Ence 2009, 44, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, R.C. The Genetic Analysis of Quantitative Trait Differences Between Two Homozygous Lines. Genetics 1984, 108, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiaolei, W.U.; Chen, S. A Comparative Study on Segregation Analysis and QTL Mapping of Quantitative Traits in Plants—With a Case in Soybean. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khattak, G.S.S.; Khan, A.J.; Subhan, F.; Ali, A. Genetic Control of Flag Leaf Area in Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Crosses. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 3978–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; He, X.; Zhi, H.; Zhang, Y. Mixed Major-Gene Plus Polygenes Inheritance Analysis for Resistance in Soybean to Bean Pyralid (Lamprosema indicata Fabricius). Soybean Sci. 2008, 27, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Gu, X.-F.; Zhang, S.-P.; Zou, Z.-R. Inheritance of Downy Mildew Resistance in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2010, 26, 2416–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.-J.; Liu, Z.-H.; Zhao, J.-M.; Chen, W.-F. Genetic Analysis of Stripe Disease Resistance in Rice Restorer Line C224 Using Major Gene Plus Polygene Mixed Effect Model. Rice Sci. 2012, 19, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, D. Resistance of Cabbage to Black Rot. Phytopathology 1955, 45, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.H. Inheritance of Resistance in Cabbage to Black Rot. Phytopathology 1971, 62, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Parkash, C.; Dey, R.; Bhatia, K.; Raj, G. Inter Specific Hybridization (Brassica carinata × Brassica oleracea) for Introgression of Black Rot Resistance Genes into Indian Cauliflower (B. oleracea var. botrytis L.). Euphytica Int. J. Plant Breed. 2015, 204, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.B.; Kalia, P.; Yadava, D.K.; Singh, D.; Sharma, T.R. Genetics and Molecular Mapping of Black Rot Resistance Locus Xca1bc on Chromosome B-7 in Ethiopian Mustard (Brassica carinata A. Braun). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saile, E.; Mcgarvey, J.A.; Schell, M.A.; Denny, T.P. Role of Extracellular Polysaccharide and Endoglucanase in Root Invasion and Colonization of Tomato Plants by Ralstonia Solanacearum. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcgarvey, J.A.; Denny, T.P.; Schell, M.A. Spatial-Temporal and Quantitative Analysis of Growth and EPS I Production by Ralstonia Solanacearum in Resistant and Susceptible Tomato Cultivars. Phytopathology 1999, 89, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayliffe, M.; Jin, Y.; Kang, Z.; Persson, M.; Steffenson, B.; Wang, S.; Leung, H. Determining the Basis of Nonhost Resistance in Rice to Cereal Rusts. Euphytica 2011, 179, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.C. Nonhost Resistance and Nonspecific Plant Defenses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Bi, Z.; Yu, N.; Cheng, S.; Cao, L. Fine Mapping of the Lesion Mimic and Early Senescence 1 (Lmes1) in Rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Physiol. Biochem. Ppb 2014, 80, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, S.; Brown, I.; Mansfield, J.W. Cellular Reactions in Arabidopsis Following Challenge by Strains of Pseudomonas syringae: From Basal Resistance to Compatibility. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 66, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Yan, C.Q.; Wang, X.M.; Yu, C.L.; Cheng, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.P. Xylem Secondary Cell-Wall Thickening Involved in Defense Responses of Oryza Meyerianato Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2012, 42, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Tang, L.; Li, Q.; Cai, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Guo, N.; Wei, X.; Tang, S. YGL3 Encoding an IPP and DMAPP Synthase Interacts with OsPIL11 to Regulate Chloroplast Development in Rice. Rice 2024, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Tian, Y.; Dang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L. Vascular Network-Mediated Systemic Spread of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae Causes the Bacterial Canker of Kiwifruit. Hortic. Plant J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Conway, J.; Roberts, S.J.; Astley, D.; Vicente, J.G. Sources and Origin of Resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica Genomes. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Ren, W.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Ge, C.; Zhang, Y. SEA v2.0: An R Software Package for Mixed Major Genes plus Polygenes Inheritance Analysis of Quantitative Traits. ACTA Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedow, J.N.; Rhoads, D.M.; Ward, G.C.; Levings, C.S. The Relationship Between the Mitochondrial Gene T-Urf13 and Fungal Pathotoxin Sensitivity in Maize. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1271, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Xie, B.; Luo, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z.; Yue, Z.; et al. Physical, Chemical, and Biological Control of Black Rot of Brassicaceae Vegetables: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1023826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Bischoff-Schaefer, M.; Bluemel, S.; Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S.; Dreux, L.; Jansen, J.-P.; Kiss, J.; Köhl, J.; Kudsk, P.; Malausa, T.; et al. Identifying Obstacles and Ranking Common Biological Control Research Priorities for Europe to Manage Most Economically Important Pests in Arable, Vegetable and Perennial Crops. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, M.; Cartea, M.E.; Francisco, M.; Velasco, P.; Soengas, P. Screening for Resistance to Black Rot in a Spanish Collection of Brassica rapa. Plant Breed. 2015, 134, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Chen, G.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Fang, Z.; Lv, H. Germplasm Screening and Inheritance Analysis of Resistance to Cabbage Black Rot in a Worldwide Collection of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) Resources. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Tenreiro, R.; Cruz, L. Assessment of Diversity of Xanthomonas campestris Pathovars Affecting Cruciferous Plants in Portugal and Disclosure of Two Novel X. campestris pv. campestris Races. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Sahu, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, H.-T.; Watanabe, M.; Park, J.-I. Molecular Marker Development for Specific Amplification of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris Race 8 Causing Black Rot Disease in Brassica Crops. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2025, 91, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ji, R.; Havlickova, L.; Wang, L.; Bancroft, I. Genome Structural Evolution in Brassica Crops. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.B. Genetic Architecture of Complex Traits in Plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Yan, L.; Ge, C.; Li, J.; Dai, J.; Ding, H. Genetic Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci Conferring Resistance to Race 4 of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 138, 102660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, J.A.; Robson, P.J.; Taylor, M.J.; Lydiate, D.; Parkin, I.; Vicente, G. Inheritance of Race-Specific Resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica Genomes. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The Plant Immune System. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Kalia, P.; Sharma, M.; Singh, D. New Source of Black Rot Disease Resistance in Brassica oleracea and Genetic Analysis of Resistance. Euphytica 2016, 207, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soengas, P.; Hand, P.; Vicente, J.G.; Pole, J.M.; Pink, D.A.C. Identification of Quantitative Trait Loci for Resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica Rapa. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint-Kurti, P. The Plant Hypersensitive Response: Concepts, Control and Consequences. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Vandenabeele, P.; Abrams, J.; Alnemri, E.S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Golstein, P.; Green, D.R.; et al. Classification of Cell Death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zeng, L. Immunity-Associated Programmed Cell Death as a Tool for the Identification of Genes Essential for Plant Innate Immunity. Plant Program. Cell Death Methods Protoc. 2018, 1743, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbage, M.; Kessens, R.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Williams, B. The Life and Death of a Plant Cell. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 375–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.S.; Jang, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.-H.; Nam, M.H.; Tobimatsu, Y.; Park, O.K. Pathogen-Induced Autophagy Regulates Monolignol Transport and Lignin Formation in Plant Immunity. Autophagy 2023, 19, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doorn, W.G.; Beers, E.P.; Dangl, J.L.; Franklin-Tong, V.E.; Gallois, P.; Hara-Nishimura, I.; Jones, A.M.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Lam, E.; Mundy, J.; et al. Morphological Classification of Plant Cell Deaths. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, H.; Curtis, C.; Fu, Z.Q. Go in for the Kill: How Plants Deploy Effector-Triggered Immunity to Combat Pathogens. Virulence 2014, 5, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).