Abstract
The genus Quercus is an ecological keystone and economically vital component of Northern Hemisphere forests. While genomic studies have advanced our understanding of its nuclear and chloroplast genomes, the mitochondrial genomes of oaks remain less explored due to their complex evolutionary dynamics, which include extreme size variation, frequent rearrangements, and recurrent horizontal gene transfer. This study presents the assembly, annotation, and comparative analysis of mitogenomes from three closely related Asian oaks—Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis—using PacBio HiFi sequencing. The assemblies revealed distinct structural organizations: the Q. engleriana and Q. kongshanensis mitogenomes each comprised one circular contig and one linear contig, whereas the Q. tungmaiensis mitogenome comprised one circular contig and two linear contigs. Comparative analyses revealed variations in codon usage bias, simple sequence repeats, and predicted RNA editing sites. Notably, RNA editing in rps12 was uniquely observed in Q. kongshanensis. Mitochondrial targeting of plastid transcripts constituted 1.39%, 1.79%, and 2.24% of the mitogenomes, respectively. Phylogenetic reconstruction based on mitochondrial PCGs robustly resolved Q. kongshanensis and Q. tungmaiensis as sister species, with all three forming a distinct clade separate from other Quercus species. This study provides comprehensive mitogenomic resources essential for elucidating Quercus evolutionary biology and supporting germplasm development.
1. Introduction
Mitochondria are indispensable organelles that serve as the primary energy-generating centers (“powerhouses”) of plant cells. In addition to their role in energy production, they play critical roles in diverse biological processes, including metabolic regulation, interorganellar communication, and signal transduction. A well-characterized instance of this mechanism is reductive stress, which induces mitochondrial retrograde signaling via the transcription factor ANAC017. This pathway subsequently reprograms nuclear gene expression to restore endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis through the enhancement of mitochondrial respiratory function [1]. These complex functions are orchestrated through intricate interactions between the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes [2]. Angiosperm mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) exhibit remarkable complexity and are characterized by substantial size variation (ranging from ~208 kb in Brassica hirta [3] to ~11.3 Mb in Silene conica [4]), frequent gene rearrangements, and sequence mutations [5]. This inherent variation provides valuable insights into plant adaptation mechanisms to environmental pressures. Moreover, mitogenome diversity serves as a crucial tool for deciphering population genetic structure and elucidating evolutionary relationships among species. Consequently, the study of plant mitogenomes is fundamental to understanding plant adaptation, genetics, and evolutionary history.
Compared with those of chloroplast or nuclear genomes, the assembly of angiosperm mitogenomes presents significant challenges, primarily because of their high content of repetitive sequences and propensity for complex structural variations [6]. However, the advent of third-generation sequencing (TGS) technologies, particularly long-read platforms such as PacBio HiFi and Oxford Nanopore, has revolutionized mitogenome research [7]. These technologies excel at resolving complex genomic regions and structural variants. To assemble the mitochondrial genome accurately, Flye will be used—a long-read assembler optimized for resolving complex repetitive structures and generating high-contiguity assemblies. The resulting assembly will be rigorously evaluated using a multi-faceted approach, including read-depth uniformity analysis to detect potential coverage anomalies and assembly errors. The completeness and continuity will be further validated by examining the evenness of read coverage across the entire genome, ensuring the absence of significant drops or spikes that might indicate misassemblies or residual gaps. Specifically, PacBio HiFi sequencing combines long read lengths with high accuracy, enabling the generation of highly contiguous and precise mitogenome assemblies with minimal errors [8]. Successful applications of these technologies, either alone or in combination with other methods, have led to the assembly and annotation of numerous plant mitogenomes, revealing intricate phenomena such as interorganellar DNA transfer, recombination events [9,10], and the dynamics of transposable elements. Furthermore, long-read sequencing technologies enable direct detection of epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation patterns, thereby providing opportunities for comprehensive future studies of the mitochondrial epigenome [11,12].
The genus Quercus (oaks), a keystone group in the Northern Hemisphere’s forests, exhibits high ecological and economic importance due to its broad adaptability and roles in carbon sequestration and biodiversity [13]. Oaks exhibit high biological diversity and adaptability to varied climatic and edaphic conditions. Ecologically, they support biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and soil stabilization. Economically and culturally, they provide valuable timber, host diverse insects (including pollinators and pests), and hold cultural significance. These attributes have motivated extensive research on oak classification and evolution [14]. However, species delimitation remains challenging due to widespread hybridization and incomplete lineage sorting [15], but also due to the potential effects of incomplete lineage sorting. While chloroplast genomes have been widely used in phylogenetic studies (with over 174 published), their resolution remains limited for certain complexities [16]. In contrast, mitochondrial genomes are poorly characterized, with fewer than 20 complete mitogenomes available, representing a critical knowledge gap.
This study focuses on three closely related and taxonomically challenging oak species endemic to China: Quercus engleriana, Q. tungmaiensis, and Q. kongshanensis. Q. engleriana is an evergreen tree reaching 25 m, distinguished by yellowish-gray tomentose young branchlets and lanceolate to elliptic leaves. Q. tungmaiensis grows taller (up to 30 m), with young branches densely covered in gray-brown tomentum, sharply serrated leaf margins, and abaxial leaf surfaces bearing dense gray stellate hairs. Q. kongshanensis is characterized by long-elliptic leaves with acuminate tips, nearly rounded bases, and revolute margins. The taxonomic status of Q. kongshanensis is particularly contentious. Flora of China [17] treated it as a synonym of Q. engleriana, citing overlapping leaf morphology. Conversely, its specific status is based on diagnostic trichome and leaf margin characteristics [18]. Given this morphological ambiguity and subtle distinctions among the three species, molecular phylogenetic approaches are essential to clarify their evolutionary relationships and taxonomic boundaries [18,19]. Although plastid genomes are extensively employed in plant phylogenetic studies, their utility is often limited for resolving recent divergences owing to slow evolutionary rates and uniparental inheritance. In contrast, mitochondrial genomes typically display higher nucleotide substitution rates, undergo frequent structural rearrangements, and may experience occasional horizontal gene transfer. These characteristics can offer stronger phylogenetic signals and help clarify relationships within complex evolutionary groups affected by rapid radiation or hybridization [20]. Although no specific hybrid zones involving these three species have been explicitly reported, the prevalence of interspecific gene flow in oaks is widely recognized.
To address this taxonomic uncertainty and advance our understanding of oak mitogenomes, we assembled and characterized the complete mitogenomes of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis via high-fidelity PacBio HiFi sequencing. The primary objectives of this study were to: (1) analyze fundamental genomic features, including relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) and repetitive sequences; (2) detect potential structural rearrangements; (3) assess evidence for interorganellar gene transfer (particularly between chloroplasts and mitochondria); (4) identify putative RNA editing sites; and (5) explore sequence homology and reconstruct phylogenetic relationships among these species and related oaks. By leveraging the distinct evolutionary properties of mitochondrial genomes, this study aims to resolve the phylogenetic ambiguities that remain unresolved by plastome-based analyses. This comprehensive analysis of the mitogenomes of these three closely related and morphologically overlapping oaks is expected to provide a robust molecular framework for resolving their species boundaries and understanding their evolutionary history. Furthermore, the generated high-quality mitogenome resources will contribute significantly to the broader fields of molecular systematics, taxonomy, and evolutionary studies within Quercus and related genera.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Sequencing
Young leaves of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis were collected from multiple individuals in April 2023 by Min DENG at a cultivation site in Yunnan, China. The geographic coordinates for the cultivation site are approximately 26.05° N, 102.70° E, at an elevation of ~1900 m. As the plant material was obtained from a cultivated source, no field collection permits were required. Total genomic DNA extraction was extracted using TRIzol® Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., (formerly Invitrogen), Waltham, MA, USA). The obtained high-quality DNA was used for PacBio HiFi sequencing.
High-molecular-weight (HMW) genomic DNA was extracted from flash-frozen leaf tissue using a modified CTAB method, optimized for plant tissues rich in polysaccharides and polyphenols [21]. DNA integrity was assessed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (CHEF Mapper XA System, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA), which revealed a predominant fragment size exceeding 50 kb [22]. Fluorometric quantification (Qubit™ 4.0, dsDNA HS Assay; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) yielded a mean concentration of 4.2 ± 0.3 μg DNA per 100 mg tissue. Purity was evaluated spectrophotometrically (NanoDrop™ One; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), with absorbance ratios of A260/A280 = 1.85 ± 0.03 and A260/A230 = 2.20 ± 0.08, indicating minimal contamination. Fragment size distribution was further verified using the Agilent Femto Pulse™ System (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA), with over 85% of fragments longer than 30 kb. The resulting HMW DNA met all quality standards for PacBio HiFi sequencing and was suitable for the preparation of 15–20 kb SMRTbell™ libraries (Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc., Menlo Park, CA, USA) [23].
Library preparation utilized the SMRTbell prep kit 3.0 (PacBio #102-182-700) with 7 μg HMW DNA sheared to 15–20 kb (Megaruptor 3, Diagenode Corporation, Liège, Belgium), followed by 10–50 kb size selection (PippinHT, Sage Science, Inc., Beverly, MA, USA). Sequencing was performed on a Revio platform using one SMRT Cell tray (Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc., Menlo Park, CA, USA) (4 cells), Revio polymerase kit (Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc., Menlo Park, CA, USA) (#102-739-100), and 24 h runs. CCS analysis (SMRT Link v8.0; minPasses ≥ 3, minAccuracy ≥ 99%) generated 23 Gb, 72 Gb, and 68 Gb of raw data for Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis, respectively, with N50 values of 77,701 bp, 72,280 bp and 71,088 bp and mean accuracy ≥ Q20 (validated by reference genome alignment). These high-quality datasets provided the foundation for the subsequent assembly of highly accurate mitochondrial genomes.
2.2. Genome Assembly and Annotation
Mitogenomes were reconstructed using a tiered assembly strategy (Supplementary Materials). PacBio HiFi reads were de novo assembled with SmartDenovo v5.34.0 [24], and resulting contigs were aligned to the Arabidopsis thaliana reference mitogenome (NC_037304.1) via BLAST+ v2.12.0+ [25] (identity ≥ 70%, E-value ≤ 1 × 10−5) to identify mitochondrial-derived sequences [26]. Target contigs were extracted using SeqKit v2.8.2 [27]. and polished iteratively with Minimap2 v2.22 [28] and Racon v1.4.20 [29]. High-confidence reads were isolated using SAMtools v1.13 [30,31] and reassembled with Flye v2.8.1 [32] under organelle-optimized parameters. Coverage uniformity was assessed using Minimap2 [22] and BBMap v39.33 [33]. The resulting mitogenome assembly was visualized via Bandage v0.8.1 [34]. Contaminants were removed based on alignment divergence and coverage depth. Annotation was performed with GeSeq v2.03 [35] using A. thaliana as a reference. tRNA and rRNA genes were predicted using tRNAscan-SE v2.0.7 [36] and BLASTN against the NCBI nt database, respectively. All annotations were manually verified. Final genomes were visualized with OGDRAW v1.3.1 [37]. The detailed assembly and annotation process has been added to the Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Analysis of RSCU and RNA Editing Prediction
Mitochondrial Protein-Coding Genes (PCGs) were extracted from the assembled genomes via PhyloSuite v1.2.3 [38]. Codon usage bias was analyzed for these PCGs via MEGA11 v11.0.13 [39]. RSCU values were calculated, with codons exhibiting RSCU values > 1 considered preferentially used. The RSCU results were visualized via R v4.3.0 with the ggplot2 v4.4.3 package [40]. and aplot v4.4.3 [41]. In silico C-to-U RNA editing sites were predicted via the PREPACT3 [42], with the following parameters: a cutoff E-value of 0.001, BLASTX reference to the Amborella trichopoda mitochondrial genome (GenBank: KF754799.1)—selected as it represents the closest available relative to our study species within the database—with an amino acid result extension value of 2 and a filter threshold of 30%. The predicted RNA editing sites were visualized with Plotly v6.1.1 in Python v3.10.
2.4. Repeated Sequences
The following mitochondrial simple sequence repeats (SSRs) were identified via MISA v2.1 [43] with minimum repeat thresholds: mononucleotides (≥10 repeats), dinucleotides (≥5 repeats), trinucleotides (≥4 repeats), and tetra-/penta-/hexanucleotides (≥3 repeats each). To minimize the inclusion of homopolymer sequencing artifacts, mononucleotide SSRs were further filtered to exclude those likely resulting from sequencing errors. Tandem and interspersed repeats (≥30 bp) were detected via the REPuter [44] web server with the following parameters: Hamming distance = 3 (allowing nucleotide substitutions) and minimal repeat size = 30 bp. Overlapping and redundant repeats were merged to ensure non-redundancy, and repeats located within mitochondrial pseudogene (IGT) regions were annotated and analyzed separately to avoid potential nuclear-derived artifacts. The results were visualized via Ploty v6.1.1 in Python v3.10.
2.5. Chloroplast to Mitochondrion DNA Transfer
To detect intracellular gene transfer (IGT), the assembled mitochondrial genomes were compared to their corresponding species-specific chloroplast reference genomes using BLAST+ v2.12.0+ [45]. The chloroplast genomes of Q. engleriana and Q. tungmaiensis were downloaded from NCBI (MW829653.1 for Q. engleriana, NC_036936.1 for Q. tungmaiensis). On the basis of available online datasets and our sequencing results, no published chloroplast genome data exist for Q. kongshanensis. Therefore, the chloroplast genome sequence assembled for Q. kongshanensis in this study utilized high-depth sequencing reads, a high-fidelity chloroplast genome was de novo assembled using PacBio HiFi reads (≥100× coverage) with Flye v2.8.1, and validated for core gene completeness (≥99% BUSCO score, embryophyta_odb10). Following annotation verification confirming the integrity of all core chloroplast genes, this newly assembled sequence served as the definitive genomic data source for subsequent analyses. The alignments were filtered using an E value threshold of ≤1 × 10−5 and a minimum sequence identity of 70%. Mitogenome lengths were calculated via TBtools-II v2.154 [46]. The identified IGT sequences were extracted and annotated to characterize the transferred functional elements and chloroplast-derived gene fragments. Visualization of IGT distributions and genomic features was performed via the Circos module [47] within TBtools-II v2.154 [46].
2.6. Genome Collinearity and Visualization
Mitogenome collinearity was assessed via TBtools-II v2.154 [46] and LINKVIEW2 v2.0 (https://yangjianshun.github.io/LINKVIEW2/; accessed on 11 March 2025). Reference mitochondrial genome sequences were selected to represent major phylogenetic clades, including members of Fagaceae: Q. acutissima (MZ636519.1), Q. variabilis (CP129458.1), Castanopsis carlesii (PP853255.1), and Fagus sylvatica (MT446430.1), with A. thaliana (NC_037304.1) included as the outgroup. The mitogenomes newly assembled in this study—Q. engleriana (PX132616–PX132617), Q. kongshanensis (PX118870–PX118871), and Q. tungmaiensis (PX118879–PX118881)—were also incorporated into the analysis. All reference sequences were obtained from NCBI. Pairwise alignments were performed via the two-sequence files module in TBtools-II [46] with default parameters. To enhance the reliability of collinearity detection by minimizing spurious alignments caused by repetitive elements, a filtration step was implemented to exclude regions with high repetition (e.g., tandem or dispersed duplicates) and low sequence complexity (e.g., homopolymer tracts or SSRs) prior to collinearity block construction. The resulting collinearity data (exported in TXT format) were processed through LINKVIEW2 (https://yangjianshun.github.io/LINKVIEW2/) via a circular layout configuration. Syntenic relationships were visualized with hierarchical coloring and a minimum alignment identity threshold of 70%, generating vector graphics.
For nuclear genome collinearity analysis, we employed MUMmer v4.0 to identify large-scale syntenic blocks between Q. Tungmaiensis and Q. acutissima. Whole-genome alignments were performed using nucmer with the -maxmatch parameter to enable all-to-all matching. Resulting alignments were filtered using delta-filter with stringent criteria (minimum identity: 95%; minimum alignment length: 1000 bp; requiring both reference and query coverage with -r, -qoptions) to obtain high-confidence collinear regions.
2.7. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
Putatively orthologous mitochondrial PCGs shared across all the taxa were identified via PhyloSuite v1.2.2 [48]. The taxa included in this phylogenetic analysis comprise both newly assembled and publicly available sequences: Q. engleriana (PX132616–PX132617), Q. kongshanensis (PX118870–PX118871), Q. tungmaiensis (PX118879–PX118881), Q. variabilis (CP1294581), Q. chenii (PQ778323), Q. acutissima (MZ636519), F. sylvatica (NC050960), Juglans mandshurica (MZ900994), Pisum abyssinicum (NCO59791), Cucurbita maxima (OL350846), and Luffa acutangula (NC050067). Following the removal of paralogous sequences, coding DNA sequences (CDSs) were extracted. To preserve correct reading frames and evolutionary signal, nucleotide sequences were first translated to amino acids, aligned using MAFFT v7.313 (-auto strategy), and then back-translated to codon-aligned nucleotides. Nucleotide sequences were aligned using MAFFT v7.313 [49] with subsequent refinement via Gblocks v0.91b to remove poorly aligned positions. Parameters were set to allow for less stringent selection while preserving the phylogenetic signal: minimum number of sequences for a conserved/flanking position = 85% of all taxa, maximum number of contiguous nonconserved positions = 8, minimum length of a block = 10, and allowed gap positions = “with half”. This balanced approach aims to reduce alignment ambiguity without excluding an excessive number of informative sites [50]. Maximum likelihood trees were reconstructed from the trimmed alignments via IQ-TREE v1.6.8 (-m MFP -bb 10000 -alrt 1000 options) [51,52]. The optimal nucleotide substitution model was selected using ModelFinder (v2.2.0) [53] within the IQ-TREE framework. Branch support was evaluated with 50,000 ultrafast bootstrap (UFBoot) replicates and 1000 SH-like approximate likelihood ratio test replicates. Clades with UFBoot ≥ 95% and SH-aLRT ≥ 80% were considered strongly supported [51]. The final phylogenetic trees were generated via Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) version 6 [54].
3. Results
3.1. Mitogenomic Genome Features
This study revealed that the mitochondrial genomes of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis exhibit a branched structure (characterized by 1 circular and 1–2 linear molecules) with duplicated regions (Figure 1). After removing the duplicated regions, the assembly results revealed two contigs (total 445,351 bp; GC 45.81%) in Q. engleriana, comprising a circular molecule 1 (341,964 bp; GC 45.80%) and linear molecule 2 (103,387 bp; GC 45.90%) (Figure 2a); Q. kongshanensis yielded two contigs (total 538,610 bp; GC 45.90%), including a circular molecule 1 (365,564 bp; GC 45.70%) and linear molecule 2 (173,046 bp; GC 46.20%) (Figure 2b); and Q. tungmaiensis yielded three contigs (total 479,938 bp; GC 45.63%), featuring a circular molecule 1 (206,471 bp; GC 45.70%), linear molecule 2 (42,332 bp; GC 46.20%), and linear molecule 3 (231,135 bp; GC 46.20%) (Figure 2c). The read-depth uniformity plots generated from the binning coverage analysis confirmed the high continuity and absence of large-scale assembly errors in the final mitogenomes, while the base-level coverage profiles validated the absence of significant coverage drops or extreme outliers, further supporting the reliability of the assembly and the effective removal of contaminating sequences. Structural configurations were inferred computationally and require further validation via long-read sequencing (Figure S1). After gene annotation refinement and removal of redundant duplicates, all species were found to contain 24 conserved core (atp1, atp4, atp6, atp8, atp9, ccmB, ccmC, ccmFC, ccmFN, cob, cox1, cox2, cox3, matR, mttB, nad1, nad2, nad3, nad4, nad4L, nad5, nad6, nad7, nad9) mitochondrial genes. There were 31 PCGs in Q. engleriana, 33 in Q. kongshanensis, and 38 in Q. tungmaiensis, with 7, 9, and 14 noncore genes, respectively. The core genes spanned seven functions. All the species conserved three large ribosomal subunit genes (rpl2, rpl5, and rpl16) in noncore elements, whereas the small ribosomal subunit genes exhibited species divergence: Q. engleriana maintained two genes (rps3 and rps4) versus three genes (rps3, rps4, and rps12) in Q. kongshanensis and Q. tungmaiensis. All the species lacked succinate dehydrogenase genes but contained Mitovir RNA polymerase. The tRNA counts were 21 (Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis) and 24 (Q. tungmaiensis), with multicopy tRNAs specified per species (Table 1). Each mitogenome conserved 3 rRNAs. The number of introns were 10 (Q. engleriana), 12 (Q. kongshanensis), and 14 (Q. tungmaiensis). BLAST analysis confirmed that the viral sequences represent authentic coding regions within the genome, ruling out their classification as anomalous annotations or contaminants.
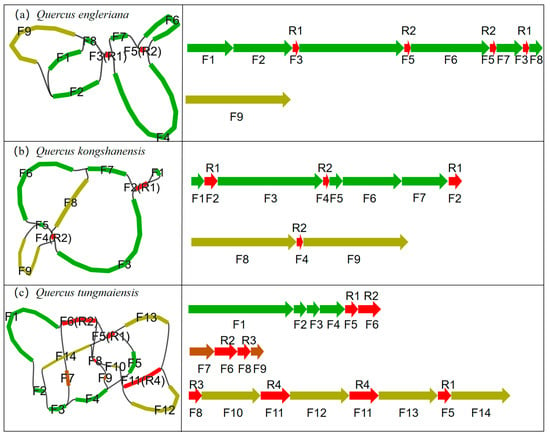
Figure 1.
Mitogenome structural variation in (a) Q. engleriana, (b) Q. kongshanensis, and (c) Q. tungmaiensis. Each panel depicts major assembly configurations with annotated feature positions (F1–F14 denote conserved functional elements; R1–R4 represent repeat regions), for which a consistent color scheme is maintained between the circular diagrams and linear maps. The red color represents repetitive regions, and the green, dark green, and brown colors represent non-repetitive regions. Key structural configurations include: (a) one circular and one linear molecule; (b) one circular and one linear molecule; (c) one circular and two linear molecules.
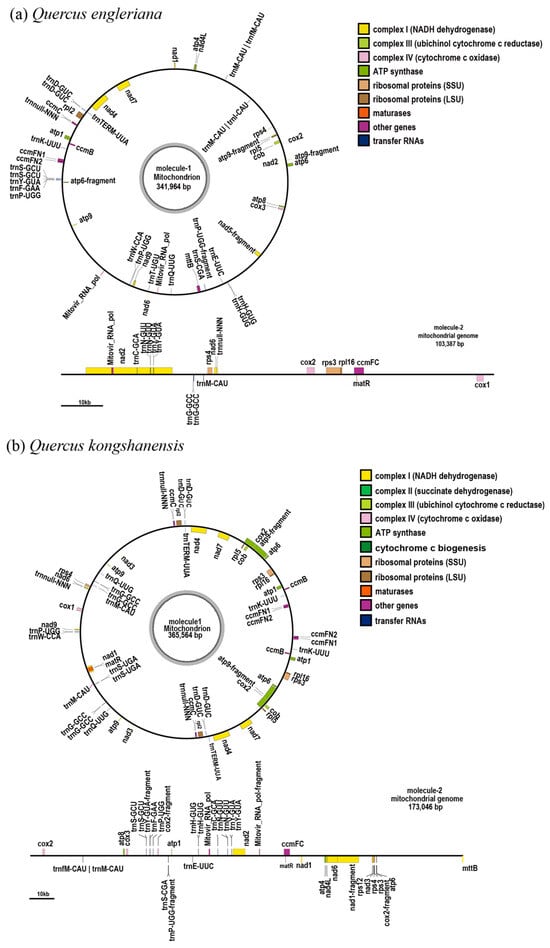
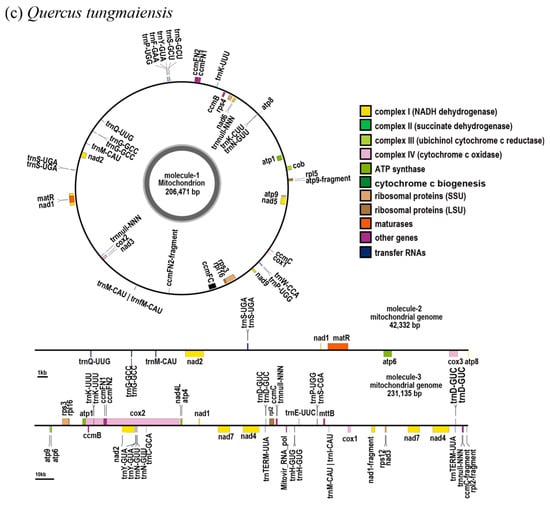
Figure 2.
Gene maps of the mitochondrial genomes for (a) Q. engleriana, (b) Q. kongshanensis, and (c) Q. tungmaiensis. Genes located on the outer and inner rings are transcribed in the clockwise and counterclockwise directions, respectively.

Table 1.
Gene content variation in mitochondrial genomes.
3.2. PCG Condon Usage Analysis
The mitochondrial PCGs revealed that the interspecific codon count diverged interspecifically: 9368 (Q. engleriana), 15,091 (Q. kongshanensis), and 14,056 (Q. tungmaiensis) (Figure 3). Among the codons with a neutral frequency of use (RSCU = 1), the start codons AUG and UGG had RSCU values of 1, with Q. tungmaiensis being more specific. All the other codons showed some preference. Among them, Q. engleriana had 31 codons with high preference and 31 codons with low preference. It showed the strongest preference for GCU (RSCU = 1.61) and the lowest preference for UAC (RSCU = 0.45); Q. kongshanensis had 30 codons with high preference and 32 codons with low preference. It showed the strongest preference for GCU (RSCU = 1.52) and the lowest preference for UAC (RSCU = 0.53); Q. tungmaiensis had 30 codons with high preference and 32 codons with low preference. It showed the strongest preference for CAA (RSCU = 1.47) and the lowest preference for both CUG and CAG (RSCU = 0.53). The codon preferences of Q. engleriana and Q. kongshanensis were similar.
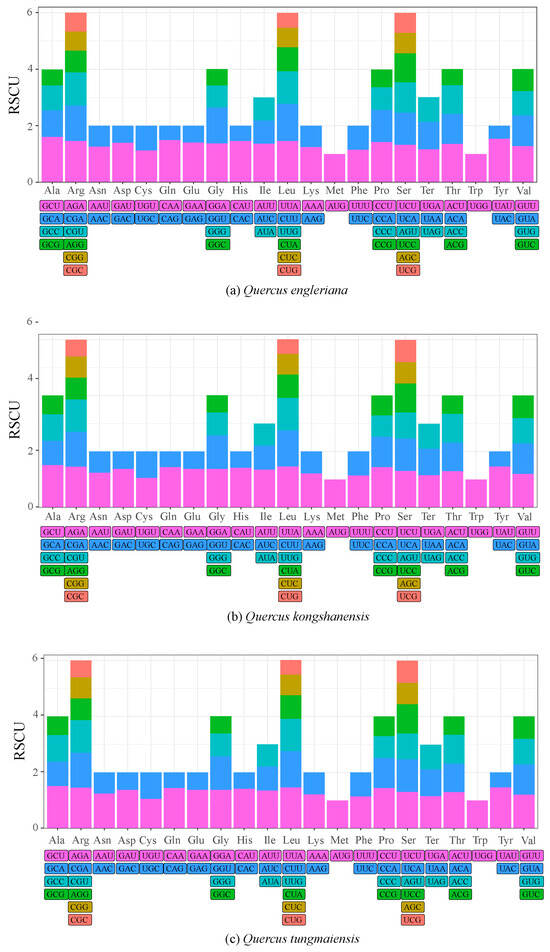
Figure 3.
Relative synonymous codon usage in the mitochondrial protein-coding genes of (a) Q. engleriana, (b) Q. kongshanensis, and (c) Q. tungmaiensis.
3.3. Mitogenome Repeat Analysis
SSR analysis was performed on the final mitogenome assemblies after rigorous filtering to remove potential sequences of nuclear and plastid origin (NUMTs/MTPTs) (Tables S1 and S2). SSR analysis revealed 154, 176, and 160 SSRs in the mitogenomes of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis, respectively (Figure 4a). Mononucleotide SSRs represented 19.48%, 19.21%, and 25.63% of the total SSRs across these species, whereas dinucleotide SSRs constituted 20.78%, 22.03%, and 21.25%, respectively. Compositional analysis revealed that thymine (T)-based mononucleotide repeats dominated this category, representing 30% (9/30) of the mononucleotide SSRs in Q. engleriana, 32.35% (11/34) in Q. kongshanensis, and 36.62% (15/41) in Q. tungmaiensis. Among dinucleotide SSRs, TA/AT motifs were predominant, accounting for 34.38% (Q. engleriana), 28.21% (Q. kongshanensis), and 32.35% (Q. tungmaiensis) of this subtype. Notably, higher-order repeats were exceptionally rare: hexanucleotide SSRs were detected only in Q. engleriana (n = 1). Additionally, the longest SSR identified—a cytosine (C) mononucleotide tract—occurred in Q. kongshanensis.
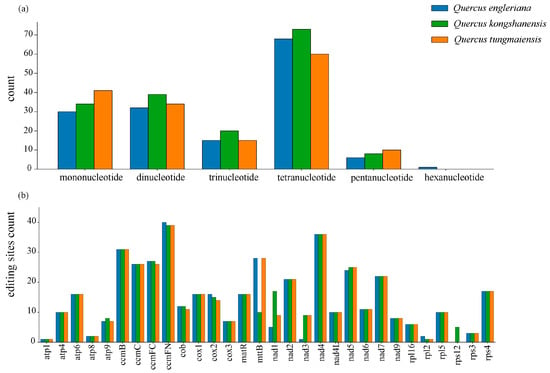
Figure 4.
Analyses of nucleotide repeats and RNA editing in three Quercus mitogenomes. (a) Counts of different types of nucleotide repeat sequences (mono- to hexanucleotide repeats). (b) Number of predicted RNA editing sites for each protein-coding gene.
3.4. Prediction of RNA Editing
RNA editing analysis predicted 431, 437, and 438 mitochondrial C-to-U editing sites in Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis, respectively, indicating minimal interspecific variation in total predicted editing frequency (Figure 4b). Five genes (ccmB, ccmC, ccmFC, ccmFN, and nad4) were consistently predicted to contain > 25 editing sites across all species. Significant interspecific divergence was observed in specific genes: mttB was predicted to contain only 10 editing sites in Q. kongshanensis versus 28 in both Q. engleriana and Q. tungmaiensis, whereas the number of predicted editing sites in nad1 ranged from 5 (Q. engleriana) to 17 (Q. kongshanensis). Notably, the species-specific rps12 gene in Q. kongshanensis was predicted to contain five editing sites. Functionally conserved editing events generated start codons (ACG → AUG) in nad1, nad5, cox2, and rps3, and stop codons (CGA → UGA) in ccmFC across all three species (Table 2).

Table 2.
Summary Statistics of RNA Editing Sites.
3.5. Chloroplast-to-Mitochondrion DNA Transfer
The mitochondrial genomes of the three Quercus species contained 19 (Q. engleriana), 29 (Q. kongshanensis), and 24 (Q. tungmaiensis) chloroplast-derived sequences (IGTs), which constituted 1.39% to 2.24% of their respective mitogenome lengths (Figure 5, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). Among these, Q. engleriana had two fragments > 1 kb (longest: 1149 bp), Q. kongshanensis contained one fragment > 1 kb (1012 bp), and Q. tungmaiensis contained three fragments > 1 kb (longest: 1866 bp). By annotating these homologous sequences, Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis identified 10, 8, and 12 complete genes, respectively; all annotations included the shared genes: two PCGs (petL, petG) and five tRNA genes (trnW-CCA, trnH-GUG, trnD-GUC, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU), all annotated as complete tRNAs. Species-specific tRNA genes were also identified: Q. engleriana possessed trnP-GGG, trnI-CAU and trnT-GGU; Q. kongshanensis possessed trnP-UGG; and Q. tungmaiensis possessed trnP-GGG, trnI-CAU, trnT-GGU, trnP-UGG and trnA-UGC.
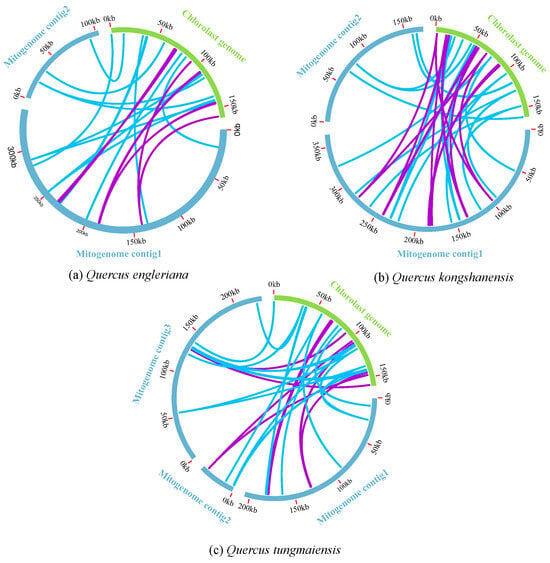
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of gene transfer between the chloroplast and mitogenomes of (a) Q. engleriana, (b) Q. kongshanensis, and (c) Q. tungmaiensis. The blue and green arcs represent the mitogenome and chloroplast genomes, respectively. Lines connect homologous regions between the mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. The purple lines indicate sequences with 70–90% similarity, and the blue lines represent those with higher than 90% similarity.

Table 3.
Fragments transferred from chloroplasts to mitochondria in Quercus engleriana.

Table 4.
Fragments transferred from chloroplasts to mitochondria in Quercus kongshanensis.

Table 5.
Fragments transferred from chloroplasts to mitochondria in Quercus tungmaiensis.
3.6. Collinearity Analysis
Comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genomes of Q. tungmaiensis and Q. acutissima revealed 13 repeat regions larger than 10 kb (Figure 6). Similarly, 13 such repeats were detected between Q. kongshanensis and Q. acutissima. Fourteen repeats larger than 10 kb were found between Q. kongshanensis and Q. variabilis, whereas eleven were identified between Q. engleriana and Q. variabilis. Notably, the largest repeat region (24,462 bp) within Quercus species was found between Q. kongshanensis and Q. variabilis. Moreover, an even larger repeat (35,561 bp) was identified in the comparison between Q. engleriana and C. carlesii, although only 6 repeats larger than 10 kb were detected between these two species. In addition to repeat the analysis, we quantitatively characterized structural rearrangements including inversions, translocations, duplications, and deletions across all species pairs (Table S3). These results indicate variations in the arrangement order of collinear blocks among different mitochondrial genomes. Specifically, the mitochondrial genomes of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis have undergone significant structural reorganization during evolution relative to closely related species, demonstrating highly nonconserved genome architectures.
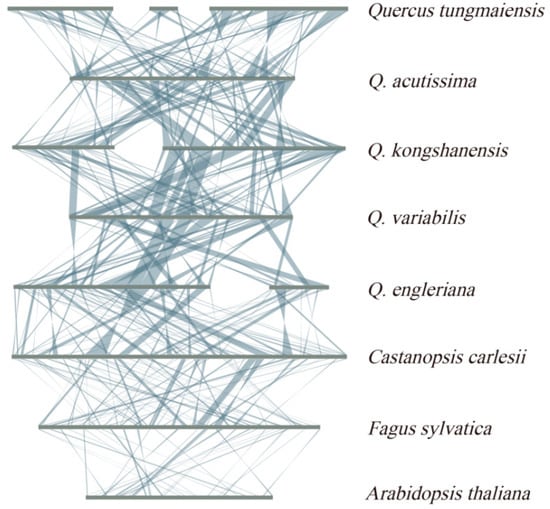
Figure 6.
Mitogenome synteny. The bars indicate the mitogenomes, and the ribbons represent the homologous sequences between adjacent species.
Furthermore, whole-genome collinearity analysis of nuclear genomes identified large-scale syntenic regions, which were subsequently filtered using delta-filterto retain high-confidence alignments (minimum identity: 95%; minimum length: 1000 bp; requiring both query and reference coverage). The results revealed extensive collinearity blocks between the two nuclear genomes, with clear patterns of both conserved and rearranged segments. Visualization of alignments further supported the presence of macro-synteny alongside structural variations, consistent with the dynamic evolutionary trajectory observed in the mitochondrial genomes (Figure S2).
3.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
To confirm and comprehensively analyze the phylogenetic relationship, a maximum-likelihood (ML) tree was reconstructed based on 39 conserved mitochondrial PCGs from 11 angiosperm species (6 Quercus species + 5 outgroups), with the optimal substitution model being K3Pu+F+I+G4 (Figure 7). As shown in the tree, outgroup species were positioned at the basal clade, showing a clear divergence from Quercus species. Within Quercus, Q. kongshanensis and Q. tungmaiensis formed a sister-species relationship, and all target Quercus species involved in this study clustered into a monophyletic clade, which was distinctly separated from Q. chenii and Q. variabilis.
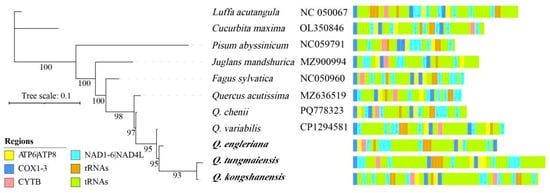
Figure 7.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of representative angiosperm species on the basis of mitochondrial genome sequences, with branch lengths scaled to nucleotide substitutions per site. Species are annotated with GenBank accession numbers.
4. Discussion
The mitochondrial genome is essential for eukaryotic energy metabolism, biosynthesis, stress response, and nuclear coordination via encoded proteins and RNA [55,56,57,58]. While often depicted as circular, plant mitogenomes typically exist as heterogeneous molecular populations [59,60,61]. Higher plant mitogenomes exhibit remarkable structural diversity, as seen in F. sylvatica with a single circular chromosome [62], Broussonetia kaempferi with two independent molecules [63], and Populus deltoides with three circular chromosomes [64]. Similarly, our study reveals considerable interspecific heterogeneity in mitochondrial architecture within Quercus, which is consistent with the structural plasticity previously reported in this genus, for example, Q. dentata has been assembled either as a single circle or as two smaller circular molecules [20]. Specifically, we observed that Q. engleriana and Q. kongshanensis each possess two molecules (one circular and one linear), while Q. tungmaiensis has three (one circular and two linear), with species-specific differences in molecule size and total genome length. Such architectural variation may influence mitochondrial recombination, inheritance, and gene regulation, and could potentially contributing to lineage-specific adaptations throughout oak evolution [65]. This structural plasticity aligns with the broad structural dynamism of plant mitogenomes [66], which include size variation, diverse conformations (multicircular/linear), altered gene density, recurrent gene loss or transfer, and extensive RNA editing [58,59,60].
Abundant repetitive sequences, a hallmark of plant mitogenomes, facilitate homologous recombination and structural reorganization, contribute to the structural plasticity [67]. SSRs serve as effective molecular markers because of their polymorphism, codominant inheritance, and broad genomic distribution [62,63,64]. In the studied Quercus species, mononucleotide, dinucleotide, and tetranucleotide repeats dominated (>60% of total SSRs), which is consistent with patterns in other angiosperms [68,69]. Thymine (T) mononucleotide repeats (30.0–36.6%) reflect the general AT enrichment of mitogenomes. TA/AT dinucleotides were most common (28.2–34.4% across species), demonstrating a pronounced A/T bias similar to that of other oaks [70]. Species-specific patterns emerged: Q. tungmaiensis had the highest proportion and number of mononucleotide SSRs, whereas dinucleotide SSRs predominated in Q. kongshanensis. These repetitive elements may promote mitogenome rearrangements that could influence hybrid compatibility and contribute to the genomic divergence observed among oak species [71].
MtPt constitutes a significant portion of plant mitogenomes [72]. We detected prevalent chloroplast-to-mitochondrion DNA transfer in the Quercus species. Quercus tungmaiensis presented the most extensive transfer/retention, as evidenced by the highest number of IGT, longest cumulative length, largest proportion, most frequent large fragments), and greatest diversity of intact tRNA genes. Functional elements, particularly a subset of tRNA genes and the petL and petG protein-coding genes, were selectively retained after integration. Notably, petL contributes to photosynthetic cold adaptation in plants [73], whereas petG maintains the structural stability of the cytochrome b6f complex [74]. Similar transfer of photosynthesis-related genes to mitogenomes occurs in Orobanchaceae species, suggesting conserved interorganellar DNA mobilization mechanisms [75,76]. All the species retained five identical, intact tRNA genes (trnW-CCA, trnH-GUG, trnD-GUC, trnM-CAU, and trnN-GUU). Previous studies have demonstrated that chloroplast-to-mitochondrion tRNA gene transfer is a widespread phenomenon in angiosperms [77,78]. For example, 18 intact tRNA genes were translocated from the chloroplast genome to the mitogenome in Curcuma amarissima [79]. The integrity of these transferred sequences suggests selective retention for functional purposes [77], potentially supporting mitochondrial translation given the essential role of tRNAs [80,81]. Species-specific tRNA retentions were identified across the three oaks, with distinct complements of functional tRNA genes retained in each species—particularly reflected in the differential retention of trnP isotypes, highlighting lineage-specific evolutionary trajectories in DNA transfer and sequence retention [78]. The exceptional tRNA diversity of Q. tungmaiensis corresponds to its extensive IGT enrichment. Large transferred fragments with intact genes may indicate mechanisms enabling substantial DNA mobilization [82]. Together, these findings underscore the dynamic nature of organellar genomes and enhance our understanding of the evolutionary mechanisms contributing to genomic complexity in plants. Future studies should focus on validating the functionality and retention mechanisms of these transferred genes within mitochondria.
Codon usage is fundamental to genetic expression and translational efficiency, reflects evolutionary adaptation under various selective pressures [83]. In particular, natural selection for translational efficiency serves as a major driver of codon usage bias [69], which can constrain the evolutionary rate of synonymous sites [84,85]. The mitochondrial protein-coding genes of the three Quercus species exhibit both shared and divergent patterns in RSCU. Specifically, the start codon AUG and tryptophan codon UGG had RSCU values of 1, indicating neutral usage without significant bias, which is a conserved trait across species. Quercus engleriana and Q. kongshanensis display highly similar codon preference patterns, whereas Q. tungmaiensis exhibits a distinct pattern. These similarities and differences may provide insights into the evolutionary divergence within the genus. Codon usage bias is shaped by selective pressures such as optimization for translational efficiency and adaptation to metabolic demands. The pronounced preference for GCU (alanine) in Q. engleriana and Q. kongshanensis may be associated with selection for efficient translation of mitochondrial proteins rich in alanine, such as subunits of oxidative phosphorylation complexes [86]. Similarly, the marked preference for CAA (glutamine) in Q. tungmaiensis could reflect adaptive optimization for the synthesis of glutamine-related proteins under specific physiological conditions, such as high energy demand or stress resistance [87,88]. Divergent codon usage profiles among these oaks may reflect adaptations to distinct ecological niches and could contribute to metabolic specialization during speciation. It is important to note, however, that in the absence of empirical transcriptomic or proteomic data, directly linking codon usage patterns to complex biological functions remains speculative. Future studies should prioritize comparative transcriptomics across Quercus species to correlate codon usage patterns with gene expression levels and experimentally validate the effects of codon usage on protein expression and function.
Mitochondrial RNA editing modifies mRNAs in higher plants, regulating organellar gene expression [69,70]. Characterization of RNA editing sites provides insights into organellar gene expression regulation [89]. We observed both conserved and species-specific editing patterns. The genes nad1 and cox1 presented conserved editing site numbers across species, suggesting purifying selection [70,90]. Quercus engleriana presented greater editing site density in key energy metabolism genes (ccmFC, nad4L), whereas Q. kongshanensis presented more editing sites in cox3. Notably, Q. kongshanensis exhibits a species-specific RNA editing pattern in its rps12 gene. As rps12 encodes a small subunit ribosomal protein essential for mitochondrial translation, these edits could potentially alter the amino acid sequence of rps12 and influence its structural interaction within the ribosome [91]. Such modifications might contribute to enhanced mitochondrial translational efficiency, possibly supporting the expression of energy metabolism or stress-responsive genes [92,93]. Ecologically, this distinctive editing profile might reflect an adaptive response to fluctuating environmental conditions such as temperature variation or nutrient availability. For Q. kongshanensis, which occurs at elevations of 2400–3000 m, this editing pattern may help stabilize ribosome structure under diurnal temperature fluctuations, thereby supporting sustained OXPHOS activity. Q. tungmaiensis presented an intermediate editing density, with convergence toward Q. engleriana in specific genes (e.g., ccmFN). We hypothesize that these distinct editing patterns may reflect lineage-specific adaptations associated with ecological niches and the functional specialization of mitochondrial genes. Genes with high editing density (>20 sites), predominantly involved in core energy pathways (ccmFC, ccmFN, nad4L, cox3), reached up to 40 sites (e.g., ccmFC). Ccm-type genes (e.g., ccmFN) are crucial for cytochrome c maturation and complex III assembly. The prevalence of RNA editing in these genes may optimize encoded proteins via posttranscriptional modification, potentially maintaining mitochondrial proteostasis during fluctuating metabolic demands [73,74,75]. The interspecific variation in RNA editing sites may underlie metabolic diversification and ecological adaptation [94]. For example, the increased editing in ccmFC and nad4L observed in Q. engleriana might represent a metabolic adaptation that enhances energy efficiency in complex habitats [95]. Collectively, these findings highlight how RNA editing represents a versatile molecular mechanism contributing to mitochondrial functional diversification and environmental adaptation in oaks. The species-specific editing patterns observed in this study may have implications for understanding the evolutionary dynamics of Quercus species.
Our mitogenomic phylogenetic analysis strongly supports that Q. tungmaiensis and Q. kongshanensis form a sister clade, which is relatively distantly related to Q. engleriana. Based on both morphological and phylogenetic evidence [96], Q. tungmaiensis is placed within Quercus, subgenus Cerris, section Ilex, subsection Cocciferae. This classification is consistent with its leaf traits—thin-coriaceous texture, glabrous or partly pubescent abaxial surface along veins, and spinose teeth—which align with Menitsky’s [97] delineation for subsection Cocciferae. In contrast, Q. engleriana, a widespread East Asian species, belongs to subsection Ilex and typically exhibits fasciculate trichomes and leaves mostly lacking spinose teeth. Although Q. tungmaiensis shares similarities in leaf shape and acorn structure with Q. engleriana, it differs significantly in its oblong-lanceolate leaves (10–20 cm long, with 14–17 pairs of lateral veins), sharply serrate margins in the apical half, and spinose-toothed edges. These distinctions, along with its hemispherical cupule covering one-third to half of the acorn, further support the placement of Q. tungmaiensis within subsection Cocciferae, while highlighting convergent morphological evolution between these taxonomically proximate but phylogenetically distinct lineages.
Several limitations of this study warrant mention. As the structural and functional inferences are based primarily on assembly data, in vivo conformation and molecular activity remain unverified. Future work incorporating transcriptomic, proteomic, and long-read sequencing will be essential to validate the proposed mechanisms and functional implications of the observed genomic features.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we assembled and annotated the mitochondrial genomes of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis, and Q. tungmaiensis and carried out in-depth analyses on the basis of the DNA and amino acid sequences of the annotated genes. The total lengths of the annotated mitochondrial genomes were 445,351 bp (45.81%), 538,610 bp (45.90%), and 479,938 bp (45.63%), respectively. The primary structures of these species all showed branching features, with Q. engleriana and Q. kongshanensis containing two molecules (cyclic molecule 1 and linear molecule 2), whereas Q. tungmaiensis contained three molecules (1 cyclic molecule and 2 linear molecules); however, whether these molecules coexist still needs further investigation. We identified 31, 33, and 38 PCGs in each of the three species. All the species presented 24 core mitochondrial genes, with 31, 33, and 38 total PCGs, respectively. In addition, features such as codon usage preferences, repetitive sequences, chloroplast-to-mitochondrial DNA conversion, RNA editing, and isolinearity were analyzed. Our findings reveal substantial mitogenomic divergence among these three oak species, which may underlie functional adaptations to their respective ecological niches. The structural variations, editing patterns, and IGT profiles provide new insights into the mechanisms driving speciation and adaptation in Quercus. The phylogenetic trees constructed on the basis of the mitochondrial genomes of the 11 species provided a basis for the scientific classification of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis and Q. tungmaiensis. This study not only reveals the genetic characteristics, phylogenetic relationships, and evolutionary history of Q. engleriana, Q. kongshanensis and Q. tungmaiensis but also lays an important foundation for the species identification and biological study of Quercus.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11101231/s1, Table S1. Distribution of simple sequence repeat types in the mitochondrial genomes of three Quercus species. Table S2. Removed SSRs overlapping with IGT regions in the three Quercus species. Table S3. Summary of detectable structural rearrangements in mitochondrial genomes across species comparisons. Figure S1. Coverage depth analysis of mitochondrial genomes in the three Quercus species. Figure S2. Mitochondrial genome collinearity analysis across Fagaceae species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.-L.J., X.-S.L. and M.D.; methodology, Z.-T.X., Y.S. and L.-T.L.; software, Z.-T.X., B.C. and Y.X.; data curation, X.-L.J., X.-S.L. and M.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.-T.X., X.-L.J. and Y.S.; writing—review and editing, X.-L.J., H.L., L.-J.H., Y.S. and Z.-T.X.; supervision, X.-L.J.; funding acquisition, Z.-T.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Hunan Province Undergraduate Innovation Training Program, grant number S202510538090.
Data Availability Statement
The genomic datasets generated in this study have been submitted to the NCBI BioProject database with the accession numbers PRJNA1330756 (Q. engleriana), PRJNA1330775 (Q. kongshanensis), and PRJNA1330779 (Q. tungmaiensis). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Q. kongshanensis assembled in this study has been deposited and is publicly available at Figshare via https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30196444.v1. The complete mitochondrial genome sequences have been deposited in GenBank under accessions PX132616–PX132617 (Q. engleriana), PX118870–PX118871 (Q. kongshanensis), and PX118879–PX118881 (Q. tungmaiensis). The resulting phylogenetic tree file generated in this study has been deposited in the Figshare repository under the DOI https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30196426.v1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fuchs, P.; Bohle, F.; Lichtenauer, S.; Ugalde, J.M.; Feitosa Araujo, E.; Mansuroglu, B.; Ruberti, C.; Wagner, S.; Müller-Schüssele, S.J.; Meyer, A.J. Reductive stress triggers ANAC017-mediated retrograde signaling to safeguard the endoplasmic reticulum by boosting mitochondrial respiratory capacity. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermann, B. Mitochondrial fusion and fission in cell life and death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.D.; Herbon, L.A. Unicircular structure of the Brassica hirta mitochondrial genome. Curr. Genet. 1987, 11, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, P.D.; Weber, M.M.; Waneka, G.; Broz, A.K.; Sloan, D.B. Chromosome-level genome assembly for the angiosperm Silene conica. Genome Biol. Evol. 2023, 15, evad192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kan, S.L.; Liao, X.Z.; Zhou, J.W.; Tembrock, L.R.; Daniell, H.; Jin, S.X.; Wu, Z.Q. Plant organellar genomes: Much done, much more to do. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alverson, A.J.; Rice, D.W.; Dickinson, S.; Barry, K.; Palmer, J.D. Origins and recombination of the bacterial-sized multichromosomal mitochondrial genome of cucumber. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Pongpanich, M.; Porntaveetus, T. Unraveling metagenomics through long-read sequencing: A comprehensive review. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jia, P.; Gao, S.H.; Zhao, H.H.; Zheng, G.Y.; Xu, L.F.; Ye, K. Long and accurate: How HiFi sequencing is transforming genomics. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2025, 23, qzaf003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Norbu, N.; Bonjor, N.; Tan, X.; Zhang, S.T.; Tso, N.; Wang, J.W.; Qiong, L. Comprehensive Analysis of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Paeonia ludlowii Reveals a Dual-Circular Structure and Extensive Inter-Organellar Gene Transfer. Biology 2025, 14, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bradley, R.K.; Sugumaran, M.; Marx, C.J.; Rest, J.S.; Davis, C.C. Massive mitochondrial gene transfer in a parasitic flowering plant clade. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.H.; Brendel, O.; Deng, M.; Hipp, A.L.; Kremer, A.; Kua, C.-S.; Plomion, C.; Romero-Severson, J.; Sork, V.L. Gaining a global perspective on Fagaceae genomic diversification and adaptation. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, I.; Sousa, V.; Ferreira, J.; Pereira, H. Chemical characterization and extractives composition of heartwood and sapwood from Quercus faginea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.B.; Liu, H.S.; Wu, S.R.; Yuan, Y.C.; Li, H.J.; Dong, J.S.; Liu, Z.H.; An, C.Z.; Su, Z.H.; Li, B. Species identification of oaks (Quercus L., Fagaceae) from gene to genome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.J.; Fu, J.; Fang, Y.; Xiang, J.P.; Dong, H.J. Complete chloroplast genomes of Rubus species (Rosaceae) and comparative analysis within the genus. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Bartholomew, B. Fagaceae. In Flora of China; Wu, C.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; MissouriBotanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1999; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.C.; Zhou, T.; Qian, Z.Q.; Zhao, G.F. Phylogenetic relationships in Chinese oaks (Fagaceae, Quercus): Evidence from plastid genome using low-coverage whole genome sequencing. Genomics 2021, 113, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, T.; Grimm, G.W.; Manos, P.S.; Deng, M.; Hipp, A.L. An Updated Infrageneric Classification of the Oaks: Review of Previous Taxonomic Schemes and Synthesis of Evolutionary Patterns. In Oaks Physiological Ecology. Exploring the Functional Diversity of Genus Quercus L.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 7, pp. 13–38. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Pan, S.-J.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z.-T.; Huang, K.-R.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.-L. Structural variations and phylogenetic implications of mitochondrial genomes in oaks. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 235, 121817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porebski, S.; Bailey, L.G.; Baum, B.R. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 1997, 15, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.C.; Cantor, C.R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell 1984, 37, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.M.; Peluso, P.; Rowell, W.J.; Chang, P.C.; Hunkapiller, M.W. Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Wu, S.G.; Li, A.L.; Ruan, J. SMARTdenovo: A de novo assembler using long noisy reads. Gigabyte 2021, 2021, gigabyte15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Farrell, C.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Fine, A.M.; Funk, K.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D29–D38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alverson, A.J.; Wei, X.; Rice, D.W.; Stern, D.B.; Barry, K.; Palmer, J.D. Insights into the evolution of mitochondrial genome size from complete sequences of Citrullus lanatus and Cucurbita pepo (Cucurbitaceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro, C.; Pichel, J.C. BigSeqKit: A parallel Big Data toolkit to process FASTA and FASTQ files at scale. GigaScience 2023, 12, giad062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senol Cali, D.; Kim, J.S.; Ghose, S.; Alkan, C.; Mutlu, O. Nanopore sequencing technology and tools for genome assembly: Computational analysis of the current state, bottlenecks and future directions. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1542–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelkunov, M.I. Mabs, a suite of tools for gene-informed genome assembly. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G.; et al. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq–versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3. 1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.Y.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Lei, H.P.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, H.; Wang, G.T.; Zhang, D. Using PhyloSuite for molecular phylogeny and tree-based analyses. Imeta 2023, 2, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koichiro, T.; Glen, S.; Sudhir, K. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 7, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, L.; Hadavand, A.; Jager, L.; Leek, J. Comparison of beginning R students’ perceptions of peer-made plots created in two plotting systems: A randomized experiment. J. Stat. Educ. 2020, 28, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.B.; Wang, Q.W.; Wen, S.D.; Li, J.R.; He, N.; Li, M.; Hackl, T.; Wang, R.; Zeng, D.Q.; Wang, S.X. aplot: Simplifying the creation of complex graphs to visualize associations across diverse data types. Innovation 2025, 6, 100958. [Google Scholar]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Xia, R. A painless way to customize Circos plot: From data preparation to visualization using TBtools. Imeta 2022, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.L.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, R.; Marine, J.C.; Leucci, E. Non-coding RNA s: The dark side of nuclear–mitochondrial communication. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, I.M.; Rasmusson, A.G.; Van Aken, O. Plant mitochondria–past, present and future. Plant J. 2021, 108, 912–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, P.; Koltun, A.; Nonato, J.; Yassitepe, J.; Maia, I.D.G.; Arruda, P. Metabolism and signaling of plant mitochondria in adaptation to environmental stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, M.; Shirihai, O.S. Mitochondrial signal transduction. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1620–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozik, A.; Rowan, B.A.; Lavelle, D.; Berke, L.; Schranz, M.E.; Michelmore, R.W.; Christensen, A.C. The alternative reality of plant mitochondrial DNA: One ring does not rule them all. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-X.; Dierckxsens, N.; Bai, M.-Z.; Guo, Y.-Y. Multichromosomal mitochondrial genome of Paphiopedilum micranthum: Compact and fragmented genome, and rampant intracellular gene transfer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.J.; Ni, Y.; Lin, Z.B.; Yang, L.B.; Chen, G.T.; Nijiati, N.; Hu, Y.Z.; Chen, X.Y. De novo assembly of the complete mitochondrial genome of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam) revealed the existence of homologous conformations generated by the repeat-mediated recombination. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, M.; Schroeder, H.; Schott, T.; Schöning-Stierand, K.; Leite Montalvao, A.P.; Liesebach, H.; Liesebach, M.; Fussi, B.; Kersten, B. Mitochondrial genome of Fagus sylvatica L. as a source for taxonomic marker development in the fagales. Plants 2020, 9, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.J.; Wang, J.; Kan, S.L.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Reeve, W.G.; Wu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.H. Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes of Broussonetia spp. (Moraceae) reveals heterogeneity in structure, synteny, intercellular gene transfer, and RNA editing. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1052151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.S.; Zhou, P.Y.; Tong, C.F.; Bi, C.W.; Xu, L.A. Assembly and analysis of the Populus deltoides mitochondrial genome:the first report of a multicircular mitochondrial conformation for the genus Populus. J. For. Res. 2023, 34, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.J.; Wang, J.; Nie, L.Y.; Tembrock, L.R.; Zou, C.S.; Kan, S.L.; Ma, X.F.; Wendel, J.F.; Wu, Z.Q. Evolutionary dynamics of mitochondrial genomes and intracellular transfer among diploid and allopolyploid cotton specie. BMC Biol. 2025, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Liao, X.Z.; Zhang, X.N.; Tembrock, L.; Broz, A. Genomic architectural variation of plant mitochondria—A review of multichromosomal structuring. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 60, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qu, K.; Yuan, Y.C.; Zhao, Z.H.; Chen, Y.; Han, B.; Li, W.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Yin, Y.Y.; Xie, X.M. Complete sequence and comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genome of the rare and endangered Clematis acerifolia, the first clematis mitogenome to provide new insights into the phylogenetic evolutionary status of the genus. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1050040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Ran, Z.H.; Yan, C.; Gu, W.H.; Li, Z. Mitochondrial genome assembly of the Chinese endemic species of Camellia luteoflora and revealing its repetitive sequence mediated recombination, codon preferences and MTPTs. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ran, Z.H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, C.; Xu, J.; Tang, M.T.; An, M. Comparative analysis of the whole mitochondrial genomes of four species in sect. Chrysantha (Camellia L.), endemic taxa in China. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 955. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Li, B.Y.; Zhang, X.M. Comparison of chloroplast genomes and phylogenetic analysis of four species in Quercus section Cyclobalanopsis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, Q.M.; Li, A.X.; Hou, F.Y.; Zhang, L.M. Evolution Analysis of Simple Sequence Repeats in Plant Genome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Hou, S.Y.; Shi, J.; Guo, S. Research progress on mitochondrial genome of higher plant. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 13, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Thiele, W.; Saleh, O.; Scossa, F.; Arabi, F.; Zhang, H.; Sampathkumar, A.; Kühn, K.; Fernie, A.; Bock, R. Chloroplast translational regulation uncovers nonessential photosynthesis genes as key players in plant cold acclimation. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 2056–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkert, S.; Legen, J.; Takami, T.; Shikanai, T.; Herrmann, R.G.; Meurer, J.R. Role of the low-molecular-weight subunits PetL, PetG, and PetN in assembly, stability, and dimerization of the cytochrome b6f complex in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cusimano, N.; Wicke, S. Massive intracellular gene transfer during plastid genome reduction in nongreen Orobanchaceae. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.-S.; Park, S. Complete plastid and mitochondrial genomes of Aeginetia indica reveal intracellular gene transfer (IGT), horizontal gene transfer (HGT), and cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.W.; Paterson, A.H.; Wang, X.L.; Xu, Y.Q.; Wu, D.Y.; Qu, Y.L.; Jiang, A.N.; Ye, Q.L.; Ye, N. Analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii by comparative genomics approaches. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5040598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knie, N.; Polsakiewicz, M.; Knoop, V. Horizontal gene transfer of chlamydial-like tRNA genes into early vascular plant mitochondria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Deng, J.B.; Wang, Y.D.; Gao, G.W.; Yang, R. The first complete mitochondrial genome of Curcuma amarissima (Zingiberaceae): Insights into multi-branch structure, codon usage, and phylogenetic evolution. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, P. The emerging complexity of the tRNA world: Mammalian tRNAs beyond protein synthesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Baranwal, A.K.; Maerkl, S.J. Continuous in situ synthesis of a complete set of tRNAs sustains steady-state translation in a recombinant cell-free system. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6212. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, L.T.; Olofsson, J.K.; Parisod, C.; Choudhury, R.R.; Moreno-Villena, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Dionora, J.; Quick, W.P.; Park, M.; Bennetzen, J.L. Lateral transfers of large DNA fragments spread functional genes among grasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4416–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wei, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, C.B.; Qu, X.Y. Assembly and comparative analysis of the first complete mitochondrial genome of a traditional Chinese medicine Angelica biserrata (Shan et Yuan) Yuan et Shan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasovec, M.; Filatov, D.A. Codon usage bias in phytoplankton. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Qi, L.P.; Yang, L.J.; Lu, X.X.; Liu, J.Q.; Wang, J.L. Natural Selection as the Primary Driver of Codon Usage Bias in the Mitochondrial Genomes of Three Medicago Species. Genes 2025, 16, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.X.; Li, Y.F.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Fang, Y.M. Mitochondrial genome of Quercus chenii: Genomic features and evolutionary implications. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-T.; Liao, H.-S.; Hsieh, M.-H. Glutamine metabolism, sensing and signaling in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 1466–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matés, J.M.; Segura, J.A.; Campos-Sandoval, J.A.; Lobo, C.; Alonso, L.; Alonso, F.J.; Márquez, J. Glutamine homeostasis and mitochondrial dynamics. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2051–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, H.; Luo, H.; Tang, J.; Zhong, N.; Xiao, L.Z. Complete mitochondrial genome assembly and comparison of Camellia sinensis var. Assamica cv. Duntsa. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrini, A.M.; Snyder, K.E.; Purow-Ruderman, R.; Seiblitz, I.G.; Hoang, J.; Floerke, N.; Ramos, N.I.; Wirshing, H.H.; Rodriguez, E.; McFadden, C.S. Mito-nuclear discordance within Anthozoa, with notes on unique properties of their mitochondrial genomes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimov, E.; Rudenskaya, Y.A.; Bryushkova, E.; Korzhavina, O.; Kolesnikov, A. Analysis of RNA Editing in Conserved Sequence Blocks of the Trypanosomatid RPS12 Gene. Biophysics 2024, 69, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phreaner, C.G.; Williams, M.A.; Mulligan, R.M. Incomplete editing of rps12 transcripts results in the synthesis of polymorphic polypeptides in plant mitochondria. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Wilson, R.K.; Phreaner, C.G.; Mulligan, R.M.; Hanson, M.R. Protein polymorphism generated by differential RNA editing of a plant mitochondrial rps12 gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, H. The complete nucleotide sequence and RNA editing content of the mitochondrial genome of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): Comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genomes of rapeseed and Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5907–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.J.; Zhang, Q.X.; Yin, P. RNA editing machinery in plant organelles. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Coombes, A.; Li, Q.S. Reinstatement of Quercus tungmaiensis Y.T. Chang (Fagaceae) and supplementation of its anatomic features. Phytotaxa 2015, 239, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menitsky, Y.L.; Menitskii, I.L.; Fedorov, A.A. Oaks of Asia; Science Pub Inc.: Albany, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).