Abstract
Canned bamboo shoots, a popular endurable storage product preserved by canning, can be used directly as a raw material for preparing dishes and processing many other downstream products. Fermentation and high temperature sterilization are decisive for product quality. During 3 days of fermentation at 25 °C, the protein and total amino acids of bamboo shoots increased remarkably and the total phenols changed a little. After steam sterilization, the total sugar decreased by 56.82%, and the protein of bamboo shoots decreased from 2.41 ± 0.04 g/100 g to 2.03 ± 0.30 g/100 g. The process significantly increased from zero the total sugar, protein and total amino acids in sterilization bamboo shoots soaking solution. GC-MS-ROAV was used for the detection of volatile flavor substances (VFCs) of bamboo shoots and soaking solution in the four processing stages. Fermented bamboo shoots after 72 h showed a strong aroma of orange oil, which was the evaluator’s preferred aroma. In the process of sterilization, Maillard reaction leads to the increase of pyrazines and furans in bamboo shoots and soaking solution, including dibenzofuran, furaneol, trimethyl-pyrazine and 2,3-dimethyl-pyrazine. Due to these volatile flavor components, the sterilized bamboo shoots spread a light caramel and cocoa flavor.
1. Introduction
As an indispensable part of Chinese cuisine culture, bamboo shoots are popular for their freshness, deliciousness and high nutritional value. In 2019, approximately 1.28 million tons of edible Phyllostachys edulis bamboo shoots were produced in China, 130,000 tons were processed into food, and canned bamboo shoots in clear water accounted for 70%, of which 13,900 tons were exported, ranking first in the world [1]. Provinces such as Hunan, Fujian, Zhejiang and Sichuan are the main production areas of bamboo shoots. In 2019, the processed output of bamboo shoots was approximately 64,300 tons, 41,700 tons, 19,100 tons and 10,500 tons, respectively. Due to the strong seasonal growth of bamboo shoots, the picking period is between March and April each year. Postharvest bamboo shoots are still living organisms, continuing to perform various forms of physiological activities, including respiration, transpiration and aging, so the quality of bamboo shoots is prone to severe deterioration during short-term storage. Generally, storage at room temperature cannot exceed 3 days, refrigeration any more than 7 days. To ensure the annual supply of bamboo shoot raw materials, bamboo shoots production enterprises must preserve the raw materials of bamboo shoots through various forms of processing and pretreatment. The main processing and preservation methods include drying, pickling, freezing, storage by canning after sterilization. The canned bamboo shoots in clear water can be stored at room temperature for 2 years and further processed into various products according to market demand. The main processing is to remove the shell of bamboo shoots, then the shoots are put into a metal tank, clean water is added for fermentation for 2–3 days to reduce the acidity, then the clean water is replaced and the tank is sealed and steam sterilized. Different bamboo shoots processing techniques will change the nutritional functional components and flavor substances of bamboo shoots, including carbohydrates, protein, free amino acids, methyl salicylate, nonanal, vitamins, phytosterols and polyphenol [2,3,4]. Many of the functional ingredients contained in bamboo shoots are proven to have antioxidant, hypolipidemic, prebiotic activity, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory and anti-hypertensive effects [5].
Many studies were conducted on the quality changes in the processing of dried bamboo shoots, frozen bamboo shoots and pickled bamboo shoots worldwide. However, there are few systematic studies on the migration of nutrients and changes in VFCs during the processing of canned bamboo shoots. Furthermore, factories treat all the soaking solution in the cans as waste water, which is required to be treated harmlessly and discharged before it meets the relevant national sewage discharge standards, but the subsequent treatment is costly. By analysis of the moisture, total sugar, reducing sugar, protein, total amino acids, total phenols, total sterols, sensory evaluation and VFCs, the article explores the influence on nutrition and flavor in processing canned bamboo shoots in clear water, and it is discovered that optimization of the production process will improve the product quality of canned clear water bamboo shoots.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys edulis) were provided by Hunan Jingshi Agricultural Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (Taojiang, China). Water, complies with GB 5749-2006 [6]. The production process is shown in Figure 1. Fresh bamboo shoots (BS1) were dug out of the mountains and stripped of their shells. Boiled bamboo shoots (BS2) were BS1 placed in a water bath at 80 °C for 30 min. After boiling, BS2 were put into a tin pot, added to water (m:m = 3:1), and then naturally fermented at 25 °C for 72 h. Sampling for fermented bamboo shoots and soaking solution for 36 h (BS3, BSJ3), fermented bamboo shoots and soaking solution for 72 h (BS4, BSJ4). All the water was poured out, and then fresh water was added again, steam sterilizing for 20 min which sampled for sterilization bamboo shoots and soaking solution (BS5, BSJ5). All the samples were transported to the laboratory and stored immediately at −80 °C for further analysis.
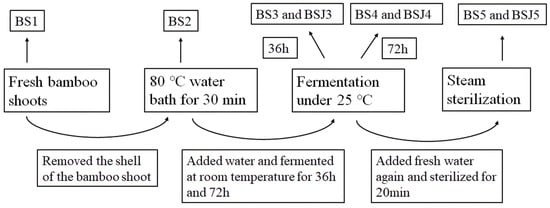
Figure 1.
Processing flow chart of canned bamboo shoots in clear water.
2.2. Nutritional Ingredients Assay and Sensory Evaluation
Nutritional ingredients, including moisture, total sugar, reducing sugar, protein, total amino acids, total phenols and total sterols were determined by the national standard of China. Moisture content was analyzed by using the dry oven method to measure moisture evaporation. Sugar and protein contents were determined using the methods described in GB/T 9695.31-2008 [7] and GB 5009.5-2016 [8], respectively. The total amino acids, total phenols and total sterols were improved based on these references [3,9,10]. All the samples were calculated on a wet basis. The nutritional ingredients were determined in triplicate.
According to Yao et al [11], the samples were evaluated by 20 professional sensory assessors (10 females and 10 males, mean age 22). The bamboo shoots were cut into cubes (1 cm) and bamboo shoots soaking solution was filled in cups (5 mL), and presented to the assessors in the laboratory (25 °C) for sensory analyses. The assessors were asked to evaluate the overall acceptance and flavors concentration on a scale ranging from 0 to 5 with five replicates of each group.
2.3. VFCs Analysis
The sample analysis of VFCs was performed by using HS-SPME-GC-MS analysis. The PDMS/DVB/65 µm fiber was headed into the headspace of a 20 mL glass vial containing 2 g respective of sample sealed with a Teflon cover and kept at 80 °C for 30 min. It was then desorbed for 5 min at 280 °C into the GC inlet with the automatic auto-sampler. Volatile components analysis was carried out by using a GC-MS (Agilent Technologies Inc., 7000 D, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with an HP-5 MS Ultra Inert column (30 m × 250 µm × 0.25 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) attached to a mass spectrometer. The GC operation conditions were as follows: an inlet temperature of 280 °C, split ratio of 5:1, Helium (purity: 99.999%) carrier gas flow of 1 mL/min. The oven temperature setting was as follows: 50 °C (2 min), 10 °C/min to 180 °C, 5 °C/min to 220 °C (2 min), 20 °C/min to 280 °C (5 min). The ion energy for the electron impact (EI) was kept at 70 eV. The chromatograms were recorded by monitoring the total ion currents in the 40–300 mass range. The VFCs in samples were identified by matching the mass spectra and retention index (RI) with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) library database (Nist2008/Wiley275) and the retention index with relevant references were compared. The compounds with a matching degree greater than 80% were extracted and analyzed. The peak area normalization method was used to calculate the relative content of each component.
The Relative odor activity value (ROAV) was used to study the characteristic VFCs and evaluate their contributions to the whole flavor perception [12]. The ROAV was calculated based on odor activity value (OAV) according to the following formula
where Ti and Ci are the threshold and percentage of an arbitrary flavor component; Tmax and Cmax are the threshold and percentage of the volatile component with the highest OAV, respectively. The substance with ROAV ≥ 1 is divided into the key flavor compounds of the analyzed samples.
ROAVi = 100 (Ci/Cmax) (Tmax/Ti),
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data of the physicochemical properties were obtained in triplicate and reported as averages. Statistical analyses were performed to determine the significant differences (p < 0.05) among the obtained results using ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test. All data were analyzed using SPSS 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and figures by GraphPad Prism 6.01 (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in the Migration of Nutrients
Figure 2 shows the changes in the contents of total sugar, reducing sugar, protein, total amino acids, total phenols and total sterols during the processing of canned clear water bamboo shoots. BS1 has a moisture content of 90.42 ± 0.43 g/100 g, total sugar content of 1.97 ± 0.05 g/100 g and reducing sugar content of 0.85 ± 0.03 g/100 g. The presence of carbohydrates can lay solid nutrients for the growth of bamboo shoots into bamboo. Fresh bamboo shoots are a rich source of protein, with a crude protein content of 2.45 ± 0.03 g/100 g and a total amino acid content of 0.85 ± 0.01 g/100 g. The total phenol content of secondary metabolites was 48.36 ± 0.18 mg/100 g, and the total sterol content was 74.89 ± 2.77 mg/100 g. The basic nutrient content of fresh bamboo shoots varies greatly due to different varieties, growth environments and analysis methods [13].
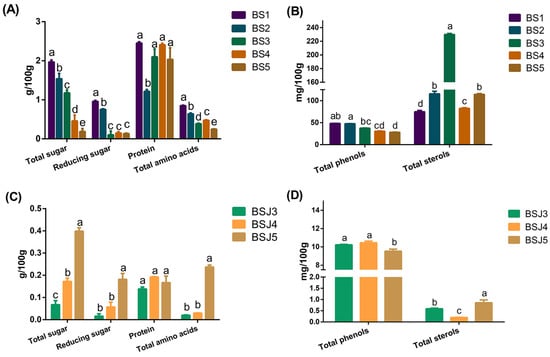
Figure 2.
Histogram of changes in nutrients during processing. a, b, c, d indicate significant differences (p < 0.05), and all data are calculated on a wet basis; (A,B) were the changes of main nutrients in bamboo shoots during processing; (C,D) were the changes of main nutrients in bamboo shoots soaking solution during processing.
Figure 2A,B are bar graphs of the nutrient content of fresh bamboo shoots after boiling, fermentation and sterilization. After boiling, the total sugar, reducing sugar, protein and total amino acid content of fresh bamboo shoots decreased significantly (p < 0.05). Boiling for 30 min at 80 °C resulted in the dissolution of water-soluble nutrients from the bamboo shoots. The protein content decreased after boiling the bamboo shoots at high temperature, the content decreased sharply to 1.22 ± 0.05 g/100 g. The previous study also showed that the protein content of bamboo shoots after boiling (1.45 g/100 g wet basis) is lower than that of fresh bamboo shoots (2.08 g/100 g wet basis), and the carbohydrate loss is about 46% [14]. This is consistent with changes in the BS5. The test result of the nutrient content of the BSJ5 can also partially explain the reason for the decrease of such substances in the bamboo shoots. The total sugar, reducing sugar, protein and total amino acids in BSJ5 all increase significantly from zero. Both the boiling and sterilization processes are heat treatment, by which the total content of sugar and protein in the bamboo shoots is reduced and leaks into the bamboo shoots soaking solution. On the contrary, total sterols show an upward trend after boiling and steam sterilization. Phytosterols are a kind of secondary metabolites, which are slightly soluble in water and easily soluble in organic matter. Therefore, sterols are less dissolved in BSJ5. There is no significant change in total phenols during the whole process, and even the fermentation process cannot increase its content. Contrary to the conclusions of other researchers, the reason is probably due to the different microorganisms mainly acting in the fermentation process [15]. Further research is necessary.
During the fermentation process, the microorganisms grow and reproduce by using the sugar, protein and amino acids in the bamboo shoots. The total sugar content is significantly reduced because of the activity of microorganisms (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, the total sugar content of the bamboo shoots is dissolved into the bamboo shoots soaking solution, which increases the total sugar content of the bamboo shoots soaking solution. However, due to the long carbon chain of the polysaccharide structure and poor hydrophilicity [16], the sugars dissolved in bamboo shoots are mostly low-molecular-weight sugars (reducing sugars). While using protein to break down into short peptides and amino acids, microorganisms also produce a large number of enzymes for metabolism, as well as the high protein content of the microorganisms itself [17], making the protein content of the BS4 reach the level of BS1, nearly doubled with unfermented. After fermentation, bamboo shoot protein has more nutritional value. This is consistent with the results of [18,19]. This may be due to the increase in essential amino acid content during fermentation. For example, phenylalanine and leucine in fermented milk will increase significantly during lactic acid fermentation [20]. This can improve the biological potency of protein. Phytosterols increased first and then decreased during the fermentation process of bamboo shoots (p < 0.05). The content in BS3 was as high as 229.94 ± 1.49 mg/100 g, which may be caused by changes in the microbial community structure. Studies have shown that Aspergillus niger can promote the accumulation of phytosterols in bamboo shoot residues during fermentation [3], and at the same time, the microorganism grows and reproduces rapidly, and the sterol existing in microbial lipid droplets and cell membrane increases the total sterols of BS3 [21]. Mycobacteria convert plant sterols into steroid hormone precursors [22,23], which reduces the sterol content of BS4 after 72 h of fermentation. The same trend is also observed in bamboo shoots soaking solution. If fermentation continues, the total sugar and sterol content will decrease greatly, and there is no significant increase in protein content, which can also increase time cost and inefficiency of nutrient retention.
3.2. Sensory Characteristics Analysis
As is shown in Table 1, Fresh bamboo shoots demonstrated a high level of satisfaction in flavor, color, taste and histomorphology, which explains why fresh bamboo shoots are widely loved by consumers. The scores of the four sensory indicators during the fermentation of the samples exhibited an increasing trend. This indicates that all bamboo shoots samples fermented for 0–72 h were acceptable to consumers, and the quality of the BS4 was better than that of fermented ones for shorter periods. The BSJ5 was the most acceptable to the evaluators among the bamboo shoots soaking solutions.

Table 1.
Sensory characteristics analysis of samples.
3.3. Composition of VFCs
The GC-MS histogram of the flavor of bamboo shoots and bamboo shoots soaking solution are shown in Figure 3. From the results of GC-MS analysis, 115 major volatile compounds in bamboo shoots and 56 in bamboo shoots soaking solution are identified. Only 65 volatile compounds meet the odor threshold, as can be seen in Table S1. A total of 42 VFCs were detected in BS1, including esters (13 components), aldehydes (11 components), acid (1 component) and ketone (1 component); a total of 44 kinds of VFCs were detected in BS2. Alcohols, acids and ketones increased significantly (p < 0.05). The content of alcohols accounted for the largest proportion (30%), and types of esters and aldehydes decreased; VFCs contained in BS3 are slightly reduced (39 components), which are mainly reflected in alcohol compounds. Compared with unfermented bamboo shoots (BS2), BS3 reduces 4 types of alcohol compounds; The total VFCs are on the rise in BS4 (46 components), due to the activity of microbial fermentation, various compounds are increased [18]. After steam sterilization, the structure of bamboo shoots’ VFCs changes significantly. When esters, alcohols, acids and ketones are all reduced, aldehyde compounds slightly increase. In the bamboo shoots soaking solution samples, there are few VFCs and no obvious changes; 44 kinds of VFCs were detected in BSJ5, including 3 esters, 5 alcohols, 5 acids, 3 aldehydes, 10 species of ketones and 18 other alkane compounds, indicating that when the bamboo shoots are heat-treated during the sterilization process, BS5 produces a special flavor because of the chemical reaction.
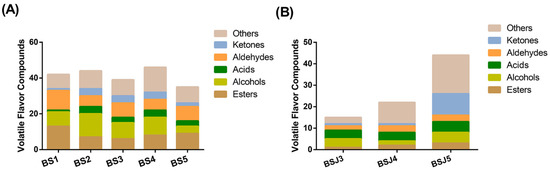
Figure 3.
Diagram of classification of volatile flavor substances. (A) was volatile flavor substance contents of bamboo shoots; (B) was volatile flavor substance contents of bamboo shoots soaking solution. Others contain hydrocarbons, ethers and phenol, etc.
3.4. Odor Activity Value Analysis
Figure 4 classifies the VFCs detected in bamboo shoots and bamboo shoots soaking solution according to [24], including citrus, fruity, floral, vanilla and others. To have better control of the quality of bamboo shoots and enhance the aroma appropriately, it is necessary to study the composition and dynamics of aroma active volatiles in bamboo shoots. The determination of food flavor is complicated, because not every ingredient has the same contribution to the overall feeling and some interactions may combine flavor compounds, so the introduction of the ROAV is particularly necessary.
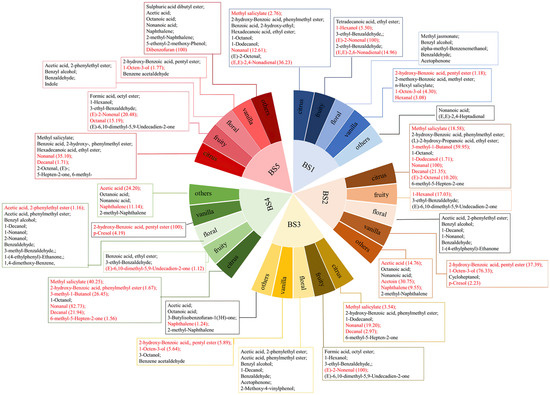
Figure 4.
Classification of volatile flavor substances. Volatile flavor substances with a relative odor activity value greater than or equal to 1 are marked in red, and the number in parentheses indicates their relative odor activity value. The darker the graphic color, the greater the contribution of this flavor.
With (E)-2-nonenal having the maximum ROAV control (ROAVmax), other key VFCs in BS1were (E,E)-2,4-nonadienal, (E,E)-2,6-nonadienal, nonanal, 1-hexanol, 1-octen-3-ol, hexanal, methyl salicylate and 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, pentyl ester (ROAV ≥ 1). Among them, (E)-2-nonenal and 1-hexanol are common and important flavor components in vegetables and fruits, and are precursors of linear ester compounds, which are common in apricots and wheat [25,26]. Zhen et al. [27] have shown that 1-hexanol is the most abundant alcohol compound in fresh bamboo shoots. (E)-2-nonenal was proved to be 13-(S)-hydroperoxide formed by γ-linolenic acid enzymatically during the division of plant tissues, and it has been detected in Phyllostachys pubescens and speculated to have bamboo fragrance [28]. (E,E)-2,4-nonadienal, nonanal, methyl salicylate has the smell of citrus fat, Takahashi had reported that (E,E)-2,4-nonadienal and nonanal exhibited the bamboo-like odor and plays an important role in the aroma of fresh bamboo shoots [28]. Methyl salicylate is the highest content of ester compounds in spring bamboo shoots, and when the odor is emitted, it can prevent insects during the growth of bamboo shoots [4]. 1-octen-3-ol, hexanal, 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, pentyl ester have a grassy smell. Hexanal naturally exists in many fruits and vegetables, which process volatile substances that contribute the most to the aroma of the BS1 [29].
The presence of 1-dodecanol, decanal and (E)-2-octenal increases the citrus oil aroma alcohol and aldehyde compounds after boiling bamboo shoots, while the content of olefinic compounds in the fruit aroma decreases. Probably, it is during the heat treatment process that the aldehydes react with oxygen to form alcohols. Similarly, after steam sterilization heat treatment, six key VFCs in BS5 including dibenzofuran, nonanal, (E)-2-nonenal, octanal, 1-octen-3-ol and decanal (ROAV ≥ 1) were found. Compared with BS4, methyl salicylate, 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, phenylmethyl ester, 3-methyl-1-butanol and 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one with citrus oil aroma in BS5 were not detected, but 1-octen-3-ol with grassy fragrance and (E)-2-nonenal and octanal with fruity fragrance increased.
Among the three major types of flavor compounds produced by the Maillard reaction, furan compounds are oxygen-containing compounds, the other two are nitrogen-containing compounds such as pyrazine, pyrrole and oxazoline, and sulfur compounds such as thiazole and furan mercaptan. All of them impart caramel, meat, cocoa and other aromas in the Maillard reaction [30]. In the process of steam sterilization of bamboo shoots, heat treatment for a long time leads to the interaction of protein and carbohydrates, and Maillard reaction occurs to form characteristic flavor. During the heat treatment of bamboo shoots, a large number of ester compounds are reduced to alcohols and aldehydes, which is consistent with the boiling process. Dibenzofuran is the biggest contributor to the flavor of BS5, and the sweet aroma of caramel and honey are the representatives of furan compounds.
With (E)-2-nonenal having the maximum ROAV control (ROAVmax), other key VFCs in BS3 were nonanal, 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, pentyl ester, 1-octen-3-ol, 1-methyl salicylate, decanal and naphthalene (ROAV ≥ 1). The BS3 have fewer VFCs, which were mainly reflected in the (E)-2-nonenal effect of the fruit aroma, and the ROAV values of compounds with other flavors were lower. Compared with BS2, 3-methyl-1-butanol, 1-dodecanol and (E)-2-octenal with citrus oil aroma are less. In other studies, among the bamboo shoots fermented with acetic acid, 2,3-butanediol, linalool, octanal and benzene acetaldehyde enhanced the odor intensity of samples; The important flavor effects in the bamboo shoots fermented with water are cis-2-nonen-1-ol and ethyl benzene, which is the product of fermentation and fat oxidation by lactic acid bacteria [31]. In this experiment, clean water was used for fermentation, the pH value in the early stage of fermentation was neutral, and the VFCs produced by microbial fermentation was not prominent. After 72 h of fermentation, the pH value of BS4 decreases. The 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, pentyl ester acts as ROAVmax. Grass aroma contributes to the main flavor of bamboo shoots, followed by nonanal, methyl salicylate, 3-methyl-1-butanol, acetic acid, decanal, naphthalene, p-cresol, 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, phenylmethyl ester, 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one, acetic acid, 2-phenylethyl ester and (E)-6,10-dimethyl-5,9-undecadien-2-one. As is shown in Figure 4, due to the fermentation of microorganisms in BS4, the VFCs of esters and alcohols have changed, which is reflected in the 3-methyl-1-butanol, nonanal and methyl salicylate ROAV value increased significantly and has an oily aroma. Studies have shown that p-cresol is the main aroma active compound of fermented bamboo shoots and has a grassy aroma, which is probably produced by the degradation of amino acids containing benzene rings such as phenylalanine and tyrosine [31]. Tyrosine is the most abundant amino acid in fresh bamboo shoots [5]. After microbial fermentation, tyrosine is degraded into phenolic compounds, giving the bamboo shoots a grassy smell.
The main VFCs in BSJ3 and BSJ4 are acetic acid, which is due to the large amount of acid and carbon dioxide produced during the fermentation of bamboo shoots, while the ROAV value of other flavor compounds is lower than 1 and is not the main flavor contributor. In BSJ5, acetic acid is ROAVmax, and other contributors to strong flavor bamboo shoots soaking solution are: 2-methyl-propanal, butanal, methyl-pyrazine, furaneol and 4-ethyl-phenol, among which methyl-pyrazine and furaneol present a caramel flavor. Although the ROAV value of many other pyrazine compounds is less than 1, they still have a caramel flavor contribution to the BSJ5. These substances are common in coffee and nuts [32]. The increase in caramel aroma compounds in BSJ5 is probably due to the Maillard reaction of protein, amino acid and reducing sugar in bamboo shoots at higher temperatures and longer reaction time. Studies have shown that adding 1.5 g Cysteine and 0.3 g xylose in flaxseed protein hydrolysate can increase its meat flavor through the Maillard reaction [33,34]. Bamboo shoots after 72 h of fermentation contain high content of amino acids and protein which, in the steam sterilization process, strengthen Maillard reaction to form caramel-flavored compounds, such as pyrazine and pyrrole, giving the bamboo shoot soaking solution a special flavor after sterilization.
4. Conclusions
Canned bamboo shoots in clear water prove to be a good way to ensure the supply of fresh bamboo shoots throughout the year. The processing of canned bamboo shoots includes boiling, shaping, fermentation and sterilization. The changes of nutrients and VFCs in the processing are worthy of in-depth study.
It was discovered that boiling, fermentation and sterilization could reduce the total sugar and reduce sugar in bamboo shoots, thus significantly increasing the total sugar in bamboo shoots soaking solution. The total amino acid in bamboo shoots soaking solution increased approximately 8 times by sterilization process. The primary cause of protein loss in bamboo shoots was the boiling process, decreasing protein from 2.45 ± 0.03 g/100 g to 1.22 ± 0.05 g/100 g. During the early fermentation process (BS3), the microorganisms made use of sugar for growth and reproduction, thus increasing protein content and biological value. Moreover, the total sterols in bamboo shoots could be accumulated by fermentation for 36 h and reached the peak (229.94 ± 1.49 mg/100 g). There are few studies on sterol accumulation during bamboo shoots fermentation, and this will be continuously studied.
The bamboo shoots fermented for 72 h (BS4) were more acceptable for sensory evaluators, because of the prominent citrus oily aroma of nonanal and methyl salicylate, and with the aroma of grass of 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, pentyl ester also contributing to the flavor. Having been sterilized, the bamboo shoots and soaking solution had a special caramel aroma due to the pyrazine, furan, furanone, imidazole and pyrrole compounds produced by the Maillard reaction.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation7040293/s1, Table S1: Relative odor activity value of bamboo shoots and soaking solution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing-Original Draft, Writing-Reviewing and Editing: J.T.; Supervision, Writing-Reviewing and Editing, Project administration: K.L.; Resources, Funding acquisition: Z.L.; Visualization, Data Curation: Z.Z.; Formal analysis: S.Z.; Visualization, Software: N.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by “Science and Technology Program of Hunan Province, grant number 2018XK2006”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable to this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable to this study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge and thank the generous support and participation of Hunan Jingshi Agricultural Science and Technology Co., Ltd. during experimental design, sample collection, and handling.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- International Bamboo and Rattan Organisation. Available online: https://www.inbar.int/cn/ (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Bajwa, H.K.; Nirmala, C.; Koul, A.; Bisht, M.S. Changes in Organoleptic, Physicochemical and Nutritional Qualities of Shoots of an Edible Bamboo Dendrocalamus hamiltonii Nees and Arn. Ex Munro During Processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 40, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.X.; Chen, R.S.; Shen, Y.; Yin, Z.Y. Phytosterols Elevation in Bamboo Shoot Residue through Laboratorial Scale Solid-State Fermentation Using Isolated Aspergillus niger CTBU. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 4078–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Cheng, S.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, S.T. Profiling of volatile compounds of Phyllostachys pubescens shoots in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.M.; Ye, F.Y.; He, Y.L.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhao, G.H. A systematic review on the composition, storage, processing of bamboo shoots: Focusing the nutritional and functional benefits. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 71, 104015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2006. Standard for Drinking Water Quality; China National Standard: Shenzhen, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 9695.31-2008. Determination of Total Sugar Content in Meat Products; China National Standard: Shenzhen, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009. 5-2016. Determination of Protein in Foods; China National Standard: Shenzhen, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.C.; Yuan, K. Studies on the Functional Components and Bioactivity and the Relativity of Bamboo Shoots and Shells. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 108, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, F.S.; Zhou, C.H.; Chen, G.J.; Lin, M.; Kan, J.Q. Changes in amino acid contents, texture and microstructure of bamboo shoots during pickling process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Mo, Y.; Chen, D.; Feng, T.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, M. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Xinjiang dried figs (Ficus carica L.) by GC–MS, GC–olfactometry, odor activity values, and sensory analyses. LWT 2021, 150, 111982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Long, X.; Wei, X. Effects of 3 Feeding Modes on the Volatile and Nonvolatile Compounds in the Edible Tissues of Female Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, S968–S981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, P.; Bal, L.M.; Satya, S.; Sudhakar, P.; Naik, S.N. Bamboo Shoots: A Novel Source of Nutrition and Medicine. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2013, 53, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Ojha, V. Precooking processing of bamboo shoots for removal of anti-nutrients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badwaik, L.S.; Borah, P.K.; Borah, K.; Das, A.J.; Deka, S.C.; Sharma, H.K. Influence of Fermentation on Nutritional Compositions, Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic and Microbial Load of Bamboo Shoot. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 20, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, S.; Li, J.; Fei, P. Hydrophobic edible composite packaging membrane based on low-methoxyl pectin/chitosan: Effects of lotus leaf cutin. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.A.; de Carvalho, G.G.P.; Azevedo, J.A.G.; Zanetti, D.; Santos, E.M.; Pereira, M.L.A.; Pereira, E.S.; Pires, A.J.V.; Valadares Filho, S.C.; Teixeira, I.; et al. Metabolizable Protein: 1. Predicting Equations to Estimate Microbial Crude Protein Synthesis in Small Ruminants. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 650248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Sahu, J.K.; Sharma, G.D. Bamboo shoot: Microbiology, Biochemistry and Technology of fermentation—A review. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2012, 11, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Agrahar-Murugkar, D.; Subbulakshmi, G. Preparation Techniques and Nutritive Value of Fermented Foods From the Khasi Tribes of Meghalaya. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2006, 45, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, J.; Cais-Sokolińska, D.; Bielska, P.; Danków, R.; Chudy, S.; Kaczyński, Ł.K.; Biegalski, J. Milk fermentation affects amino acid and fatty acid profile of mare milk from Polish Coldblood mares. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 121, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holert, J.; Brown, K.; Hashimi, A.; Eltis, L.D.; Mohn, W.W. Steryl Ester Formation and Accumulation in Steroid-Degrading Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02353-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X.; Khaletski, V. Study on optimum technological conditions for producing androstenedione by microbial method. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 136, 06025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, S.; Ajibise, F. Evaluation of C19 Steroid Intermediates during Microbial Transformation of Phytosterol. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 2017, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, G.; Tu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Wu, X.; Ren, H.; Huang, K.; He, X.; et al. Evolution analysis of flavor-active compounds during artificial fermentation of Pu-erh tea. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Piao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y.; Shi, Z. Analysis of volatile compounds from a malting process using headspace solid-phase micro-extraction and GC–MS. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokbulut, I.; Karabulut, I. SPME–GC–MS detection of volatile compounds in apricot varieties. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Zhan, F.S.; Zhou, C.H.; Kan, J.Q. Comparison of Flavor Compounds in Fresh and Pickled Bamboo Shoots by GC-MS and GC-Olfactometry. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 20, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, T.; Mizui, K.; Miyazawa, M. Volatile compounds with characteristic odour in moso-bamboo stems (Phyllostachys pubescens Mazel ex Houz. De ehaie). Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeš, D.; Kantar, D.; Kreft, S.; Prosen, H. Identification of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) aroma compounds with GC–MS. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Zieliński, H. How Maillard Reaction Influences Sensorial Properties (Color, Flavor and Texture) of Food Products? Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.C.; Yu, F.T.; Wang, C.H.; Jiang, H.R.; Yu, L.; Zhao, M.M.; Liu, X.L. Determination of the Volatiles in Fermented Bamboo Shoots by Head Space—Solid-Phase Micro Extraction (HS-SPME) with Gas Chromatography—Olfactory—Mass Spectrometry (GC-O-MS) and Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis (AEDA). Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 1162–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortzfeld, F.B.; Hashem, C.; Vranková, K.; Winkler, M.; Rudroff, F. Pyrazines: Synthesis and Industrial Application of these Valuable Flavor and Fragrance Compounds. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 2000064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikusuma, M.; Paravisini, L.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of aroma compounds in pea protein UHT beverages. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-K.; Ni, Z.-J.; Thakur, K.; Liao, A.-M.; Huang, J.-H.; Wei, Z.-J. Color and flavor of flaxseed protein hydrolysates Maillard reaction products: Effect of cysteine, initial pH, and thermal treatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).