Long Non-Coding RNAs as Emerging Regulators of Pathogen Response in Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Origin and Database Development of Plant lncRNAs
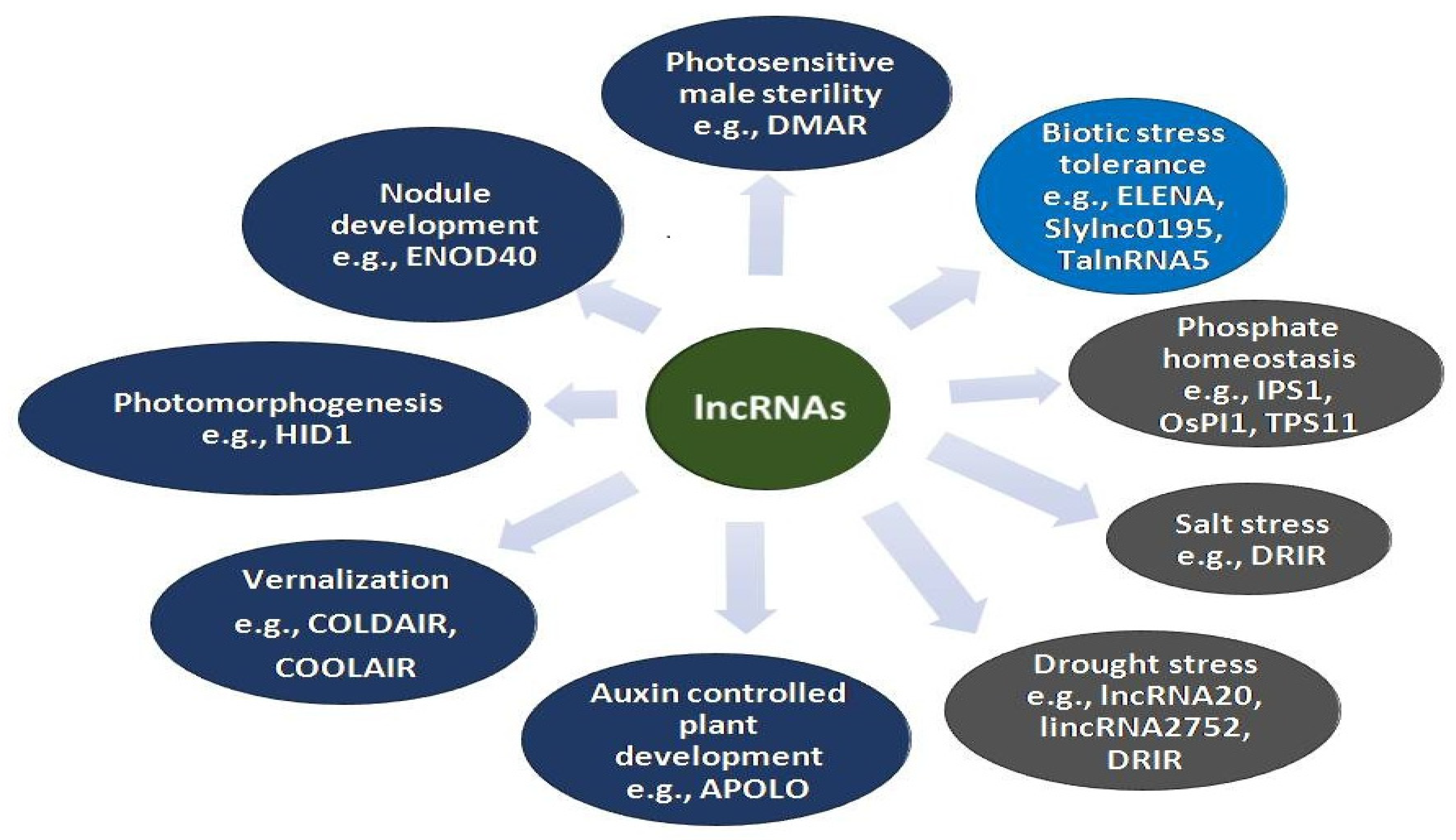
3. Involvement of lncRNAs in Various Biological Processes
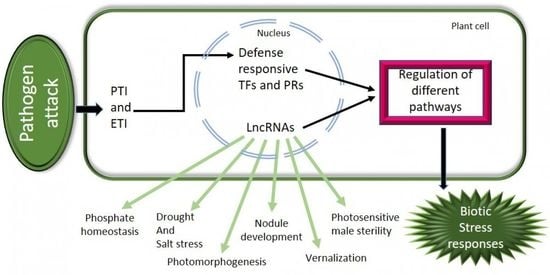
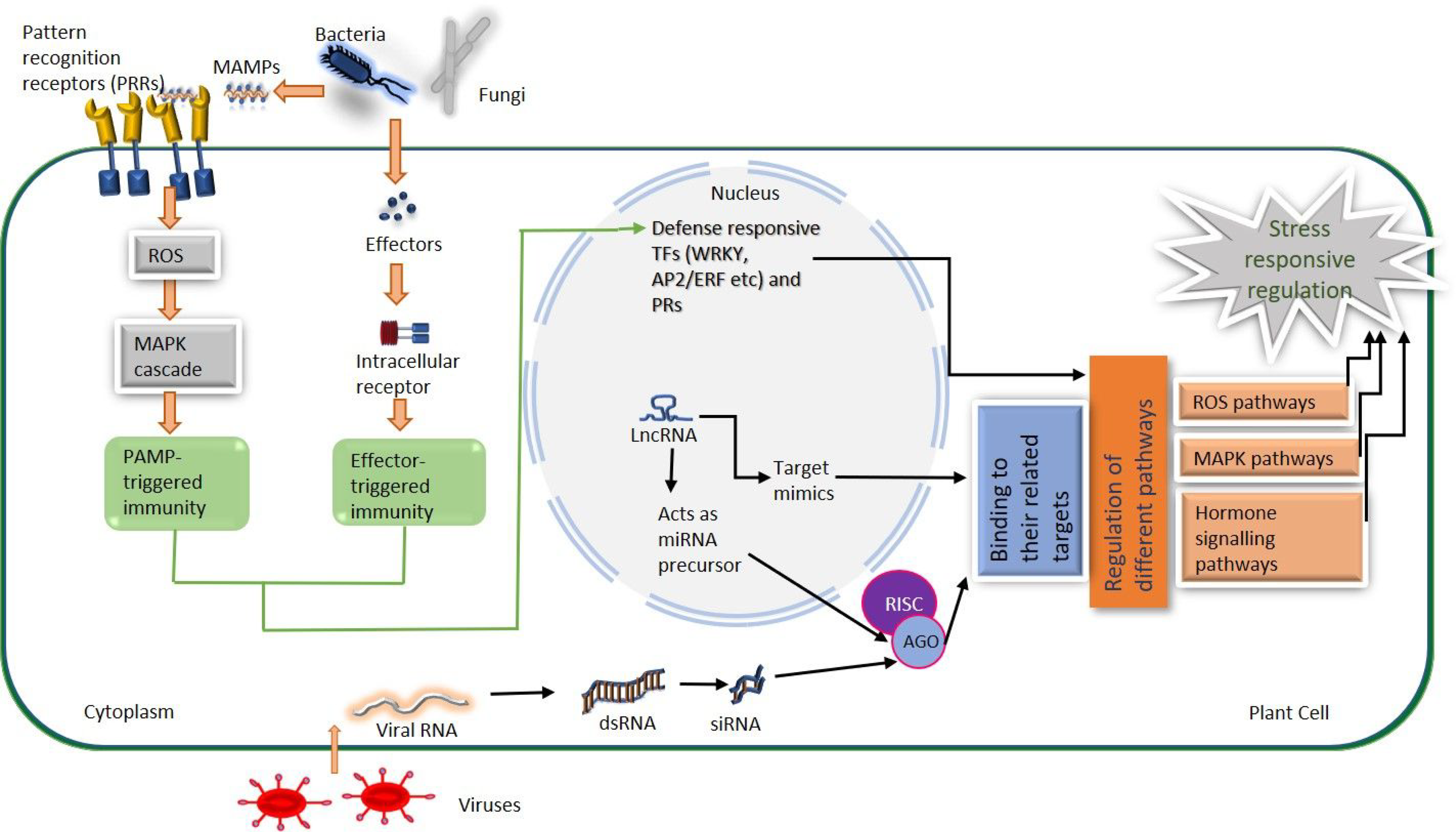
4. Roles of lncRNAs in Various Biotic Stress Responses
4.1. Long Non-Coding RNAs against Fungal Infection
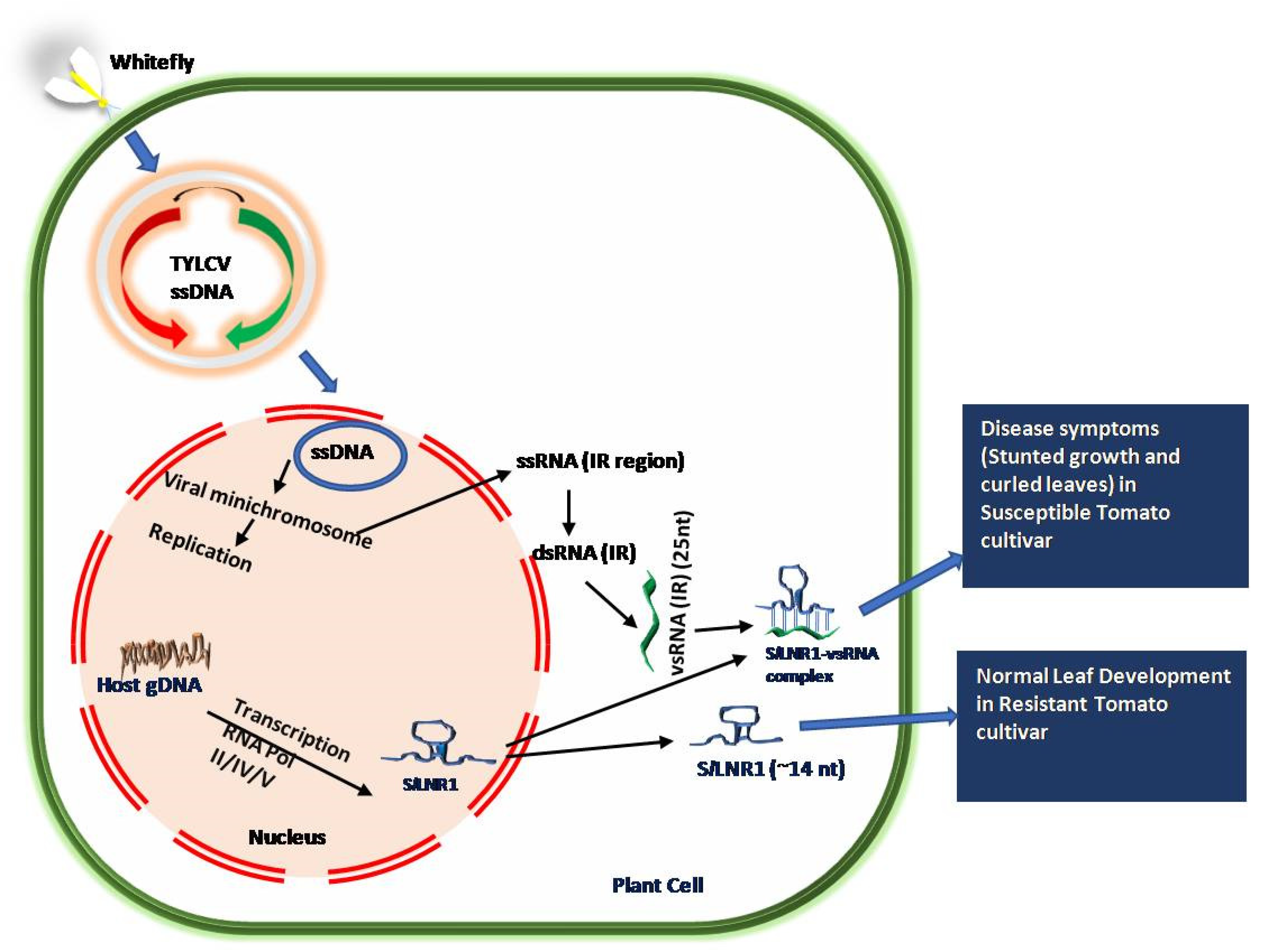
4.2. Long Non-Coding RNAs against Viral Infection
4.3. Long Non-Coding RNAs against Bacterial Infection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budak, H.; Kaya, S.B.; Cagirici, H.B. Long Non-coding RNA in Plants in the Era of Reference Sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urquiaga, M.C.O.; Thiebaut, F.; Hemerly, A.S.; Ferreira, P.C.G. From Trash to Luxury: The Potential Role of Plant LncRNA in DNA Methylation during Abiotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 603246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, A.; Upadhyay, S.K. Role of next-generation RNA-seq data in discovery and characterization of long non-coding RNA in plants. In Next Generation Plant Breeding; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Lin, F.; He, G.; Terzaghi, W.; Zhu, D.; Deng, X.W. Arabidopsis noncoding RNA mediates control of photomorphogenesis by red light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10359–10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Mathioni, S.M.; Yu, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Z.; Xu, C.; et al. PMS1T, producing Phased small-interfering RNAs, regulates photoperiod sensitive male sterility in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 15144–15149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, W.; Hao, J.; Lv, S.; Wang, C.; Tong, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ji, W. Genome-wide identification and functional prediction of novel and fungi-responsive lincRNAs in Triticum aestivum. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Sui, N. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals new lncRNAs responding to salt stress in sweet sorghum. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.K. Long Noncoding RNAs in Plants: Roles in Development and Stress; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachnis, V.; Belayew, A.; Tilghman, S.M. Locus unlinked to alpha-fetoprotein under the control of the murine raf and Rif genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5523–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Hu, W.; Ji, W. The Emerging Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Plant Defense against Fungal Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, M.E.; Pang, K.C.; Mercer, T.R.; Crowe, M.L.; Grimmond, S.M.; Mattick, J.S. NRED: A database of long noncoding RNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D122–D126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, A.T.; Haag, J.R.; Pikaard, C.S. Noncoding transcription by RNA polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V mediates transcriptional silencing of overlapping and adjacent genes. Cell 2008, 135, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, J.T.; Colognori, D.; Lee, J.T. Long noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics 2013, 193, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Rinn, J.L. Discovery and annotation of long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Diversity of Long Noncoding RNAs and Their Generation. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wong, L.; Chua, N.-H. PLncDB: Plant long non-coding RNA database. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, T.-T.; He, G.; Chen, R.; Terzaghi, W.; Zhu, D.; Deng, X.W. Genomic features and regulatory roles of intermediate-sized non-coding RNAs in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.B.; Sung, S. Vernalization-Mediated Epigenetic Silencing by a Long Intronic Noncoding RNA. Science 2011, 331, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-H.; Chekanova, J.A. Arabidopsis RRP6L1 and RRP6L2 function in FLOWERING LOCUS C silencing via regulation of antisense RNA synthesis. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.L.; Chen, C.L.; d’Aubenton-Carafa, Y.; Gourvennec, S.; Kwapisz, M.; Roche, V.; Bertrand, C.; Silvain, M.; Legoix-Né, P.; Loeillet, S.; et al. XUTs are a class of Xrn1-sensitive antisense regulatory non-coding RNA in yeast. Nature 2011, 475, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, D.; Schwalb, B.; Kiesel, A.; Baejen, C.; Torkler, P.; Gagneur, J.; Soeding, J.; Cramer, P. Transcriptome surveillance by selective termination of noncoding RNA synthesis. Cell 2013, 155, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.J.; Gao, H.; Smith-Kinnaman, W.R.; Liu, Y.; Mosley, A.L. The exosome component Rrp6 is required for RNA polymerase II termination at specific targets of the Nrd1-Nab3 pathway. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, R.A.; Almada, A.E.; Zamudio, J.R.; Sharp, P.A. Antisense RNA polymerase II divergent transcripts are P-TEFb dependent and substrates for the RNA exosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10460–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, J.; Duttke, S.H.; Benner, C.; Chory, J. Nascent RNA sequencing reveals distinct features in plant transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12316–12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necsulea, A.; Soumillon, M.; Warnefors, M.; Liechti, A.; Daish, T.; Zeller, U.; Baker, J.C.; Grützner, F.; Kaessmann, H. The evolution of lncRNA repertoires and expression patterns in tetrapods. Nature 2014, 505, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Song, T.; Wu, Y.; Fang, S.; Bu, D.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Pei, D.; et al. NONCODEV6: An updated database dedicated to long non-coding RNA annotation in both animals and plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D165–D171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, G.; Goyal, N.; Sharma, S.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Singh, K. Present Scenario of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Plants. Non-Coding RNA 2017, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ling, Y.; Xu, W.; Su, Z. PNRD: A plant non-coding RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D982–D989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paytuví Gallart, A.; Hermoso Pulido, A.; Anzar Martínez de Lagrán, I.; Sanseverino, W.; Aiese Cigliano, R. GREENC: A Wiki-based database of plant lncRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 4, D1161–D1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Krishnakumar, V.; Chan, A.P.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Schobel, S.; Town, C.D. Araport11: A complete reannotation of the Arabidopsis thaliana reference genome. Plant J. 2017, 89, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, L.; Meng, Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, M. PlantNATsDB: A comprehensive database of plant natural antisense transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1187–D1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szcześniak, M.W.; Rosikiewicz, W.; Makałowska, I. CANTATAdb: A collection of plant long non-coding RNAs. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Chakraborty, S. Roles of long non-coding RNAs in plant virus interactions. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jung, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Deng, S.; Bernad, L.; Arenas-Huertero, C.; Chua, N.H. Genome-wide analysis uncovers regulation of long intergenic noncoding RNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4333–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Taneja, M.; Tyagi, S.; Singh, K.; Upadhyay, S.K. Survey of high throughput RNA-seq data reveals potential roles for lncRNAs during development and stress response in bread wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Liao, J.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, Q.F.; Qu, L.H.; Shu, W.S.; Chen, Y.Q. Genome-wide screening and functional analysis identify a large number of long noncoding RNAs involved in the sexual reproduction of rice. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Eichten, S.R.; Shimizu, R.; Petsch, K.; Yeh, C.T.; Wu, W.; Chettoor, A.M.; Givan, S.A.; Cole, R.A.; Fowler, J.E.; et al. Genome-wide discovery and characterization of maize long non-coding RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Parker, B.J.; Weiller, G.F. In silico identification and characterization of mRNA-like noncoding transcripts in Medicagotruncatula. Silico Biol. 2007, 7, 485–505. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, G.; Sharma, S.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Singh, K. Long Non-coding RNAs Coordinate Developmental Transitions and Other Key Biological Processes in Grapevine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Paul, S. Long non-coding RNAs: Fine-tuning the developmental responses in plants. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Functions of plants long non-coding RNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Marquardt, S.; Lister, C.; Swiezewski, S.; Dean, C. Targeted 3’ processing of antisense transcripts triggers Arabidopsis FLC chromatin silencing. Science 2010, 327, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Csorba, T.; Skourti-Stathaki, K.; Proudfoot, N.J.; Dean, C. R-loop stabilization represses antisense transcription at the Arabidopsis FLC locus. Science 2013, 340, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultyaev, A.P.; Roussis, A. Identification of conserved secondary structures and expansion segments in enod40 RNAs reveals new enod40 homologues in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel, F.; Jegu, T.; Latrasse, D.; Romero-Barrios, N.; Christ, A.; Benhamed, M.; Crespi, M. Noncoding transcription by alternative RNA polymerases dynamically regulates an auxin-driven chromatin loop. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, K.; Zhang, H.; Scheres, B.; Dhonukshe, P. Retraction: CLASP-mediated cortical microtubule organization guides PIN polarization axis. Nature 2014, 508, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Valli, A.; Todesco, M.; Mateos, I.; Puga, M.I.; Rubio-Somoza, I.; Leyva, A.; Weigel, D.; García, J.A.; Paz-Ares, J. Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Lau, O.S.; Deng, X.W. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Lu, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Mao, H.; Zhang, P.; Yao, J.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q. A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, L.; Wu, P.; Lu, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejat, N.; Mantri, N. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Sun, H.-X.; Park, B.S.; Huang, C.-H.; Yeh, S.-D.; Jung, C.; Chua, N.-H. ELF18-INDUCED LONG-NONCODING RNA Associates with Mediator to Enhance Expression of Innate Immune Response Genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, C.; Huang, H. Whole transcriptome sequencing of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae-infected kiwifruit plants reveals species-specific interaction between long non-coding RNA and coding genes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; Feng, Y.Z.; He, H.; Lian, J.P.; Yang, Y.W.; Lei, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.Q. Transcriptional landscape of pathogen-responsive lncRNAs in rice unveils the role of ALEX1 in jasmonate pathway and disease resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 8, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Song, N.; Hu, Z.; Qin, D.; Xie, C.; Peng, H.; Ni, Z.; Sun, Q. Identification and characterization of wheat long non-protein coding RNAs responsive to powdery mildew infection and heat stress by using microarray analysis and SBS sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.K.; Megha, S.; Basu, U.; Rahman, M.H.; Kav, N.N. Genome Wide Identification and Functional Prediction of Long Non-Coding RNAs Responsive to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum Infection in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.H.; Stephen, S.; Taylor, J.; Helliwell, C.A.; Wang, M.B. Long noncoding RNAs responsive to Fusarium oxysporum infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Kang, Z.; Ji, W. Long non-coding genes implicated in response to stripe rust pathogen stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 6245–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, T.; Ma, N.; Yang, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, B. Genome-wide analysis of tomato long non-coding RNAs and identification as endogenous target mimic for microRNA in response to TYLCV infection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, M.; He, Y.; Guo, P. Genome-wide identification of long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs reveal their ceRNA networks in response to cucumber green mottle mosaic virus infection in watermelon. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogireddy, S.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.; Jain, A.; Budak, H.; Varshney, R.K.; Kudapa, H. Regulatory non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in regulation of plant biology. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2021, 21, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Luan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Ba, H.; Meng, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis between resistant and susceptible tomato allows the identification of lncRNA16397 conferring resistance to Phytophthora infestans by co-expressing glutaredoxin. Plant J. 2017, 89, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhier, N.; Lemaire, S.D.; Jacquot, J.P. The role of glutathione in photosynthetic organisms: Emerging functions for glutaredoxins and glutathionylation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, G.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Upadhyay, A.; Singh, K. Investigation of long non-coding RNAs as regulatory players of grapevine response to powdery and downy mildew infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, G.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Singh, K. Vitis vinifera (Grapevine) lncRNAs are potential regulators of response to necrotrophic fungus, Botrytis cinerea infection. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 112, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Ning, Y.; Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.L. Recent progress in understanding PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity against the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, P.N.; Rathjen, J.P. Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant–pathogen interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, T.; Kufer, T.A.; Schulze-Lefert, P. NLR functions in plant and animal immune systems: So far and yet so close. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, W.; Bhattacharjee, S. Effector-triggered immunity signaling: From gene-for-gene pathways to protein– protein interaction networks. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, R.; van Esse, H.P.; Maruthachalam, K.; Bolton, M.D.; Santhanam, P.; Saber, M.K.; Zhang, Z.; Usami, T.; Lievens, B.; Subbarao, K.V.; et al. Tomato immune receptor Ve1 recognizes effector of multiple fungal pathogens uncovered by genome and RNA sequencing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5110–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.Q.; Hartl, D.L.; Tian, D. Rapidly evolving R genes in diverse grass species confer resistance to rice blast disease. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18572–18577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Triplett, L.; Leach, J.E.; Wang, G.L. Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; Peck, S.C. Central roles and regulatory mechanisms of dual-specificity MAPK phosphatases in developmental and stress signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Shen, D.; Wang, J.; Ling, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, W.; et al. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus intergenic siRNAs target a host long noncoding RNA to modulate disease symptoms. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liang, Q.; Li, C.; Fu, S.; Kundu, J.K.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Transcriptome Analysis of Rice Reveals the lncRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Response to Rice Black-Streaked Dwarf Virus Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, L.C.; Rep, M.; Pieterse, C.M. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu. Rev.Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, P. Chemical warfare or modulators of defence responses—The function of secondary metabolites in plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Database | Features | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Plant long non-coding RNA database | This database consists of >13,000 lincRNAs and associated epigenetic markers | [18] |
| Plant ncRNA database | It consists of 11 different types of ncRNAs of 150 plant species | [30] |
| Green non-coding database | It consists of data of 37 plant species and algae with more than 120,000 lncRNAs | [31] |
| The Arabidopsis information resource | It also consists of data of various noncoding RNAs | [32] |
| Araportll | It consists of annotated lincRNA, NATs, and various other ncRNAs | [33] |
| Plant natural antisense transcripts database | It consists of NATs annotated data along with expression of small RNA of 70 plant species | [34] |
| CANTATAdb | It consists of data of 45,000 lncRNAs of 10 model plant species | [35] |
| Pathogen | Associated Stress | lncRNA | Mechanism | Plant | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Bacterial speck disease (Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000) | Up- ELENA1 | Directly interact with MED19a | Arabidopsis thaliana | [55] |
| Bacterial canker (Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae) | Up- TCONS_00202033, TCONS_0019494 & TCONS_00076221 | Unknown | Actinidi adeliciosa | [56] | |
| Bacterial leaf blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae) | Up- ALEX1 | Interacts with JA related genes | Oryza sativa | [57] | |
| Fungal | Powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) | Up- TalnRNA5, TapmlnRNA19 | Precursor of miR2004 | Triticum aestivum | [58] |
| Powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) | Up- TalnRNA9 | Signal recognition particle 7S RNA variant 1 | Triticum aestivum | [58] | |
| Powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) | Up- TapmlnRNA2, TapmlnRNA7 | Precursor of siRNA | Triticum aestivum | [58] | |
| White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) | Up- TCONS_00012499, TCONS_00004577, TCONS_00004034, TCONS_00009614, TCONS_00015411 | Precursor of mi156 | Brassica napus | [59] | |
| White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) | Up- TCONS_00006568, TCONS_00018692, TCONS_000017152, TCONS_00008591, TCONS_00001092 | Precursor of mi169 | Brassica napus | [59] | |
| Wilt disease (Fusarium oxysporum) | Up- TAR-66 (lincRNA) | Co-induction with neighboring defense-related gene | Arabidopsis thaliana | [60] | |
| Wilt disease (Fusarium oxysporum) | Up- TAR- 67,-191,- 197,-224 | Unknown | Arabidopsis thaliana | [60] | |
| Stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) | Up- TalncRNA18, 106 | Unknown | Triticum aestivum | [61] | |
| Stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) | Up & Dp at different dpi- TalncRNA73, 108 | Unknown | Triticum aestivum | [61] | |
| Viral | TYLCV Infection | Up- Slylnc0195 | Target mimicry of miR166 | Solanum lycopersicum | [62] |
| TYLCVInfection | Dn- Slylnc1077 | Target mimicry of miR399 | Solanum lycopersicum | [62] | |
| CGMMV infection | Up- lncRNALNC_1497 | Target mimicry of MIR4995-p5_Iss19GC | Citrullus lanatus | [63] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, Y.; Sharma, A.; Madhu; Shumayla; Singh, K.; Upadhyay, S.K. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Emerging Regulators of Pathogen Response in Plants. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010004
Sharma Y, Sharma A, Madhu, Shumayla, Singh K, Upadhyay SK. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Emerging Regulators of Pathogen Response in Plants. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Yashraaj, Alok Sharma, Madhu, Shumayla, Kashmir Singh, and Santosh Kumar Upadhyay. 2022. "Long Non-Coding RNAs as Emerging Regulators of Pathogen Response in Plants" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010004
APA StyleSharma, Y., Sharma, A., Madhu, Shumayla, Singh, K., & Upadhyay, S. K. (2022). Long Non-Coding RNAs as Emerging Regulators of Pathogen Response in Plants. Non-Coding RNA, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010004