Prenatal Bisphenol B Exposure Induces Adult Male Offspring Reproductive Dysfunction via ERα Inhibition-Triggered MHC I-Mediated Testicular Immunological Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Maternal BPB Exposure
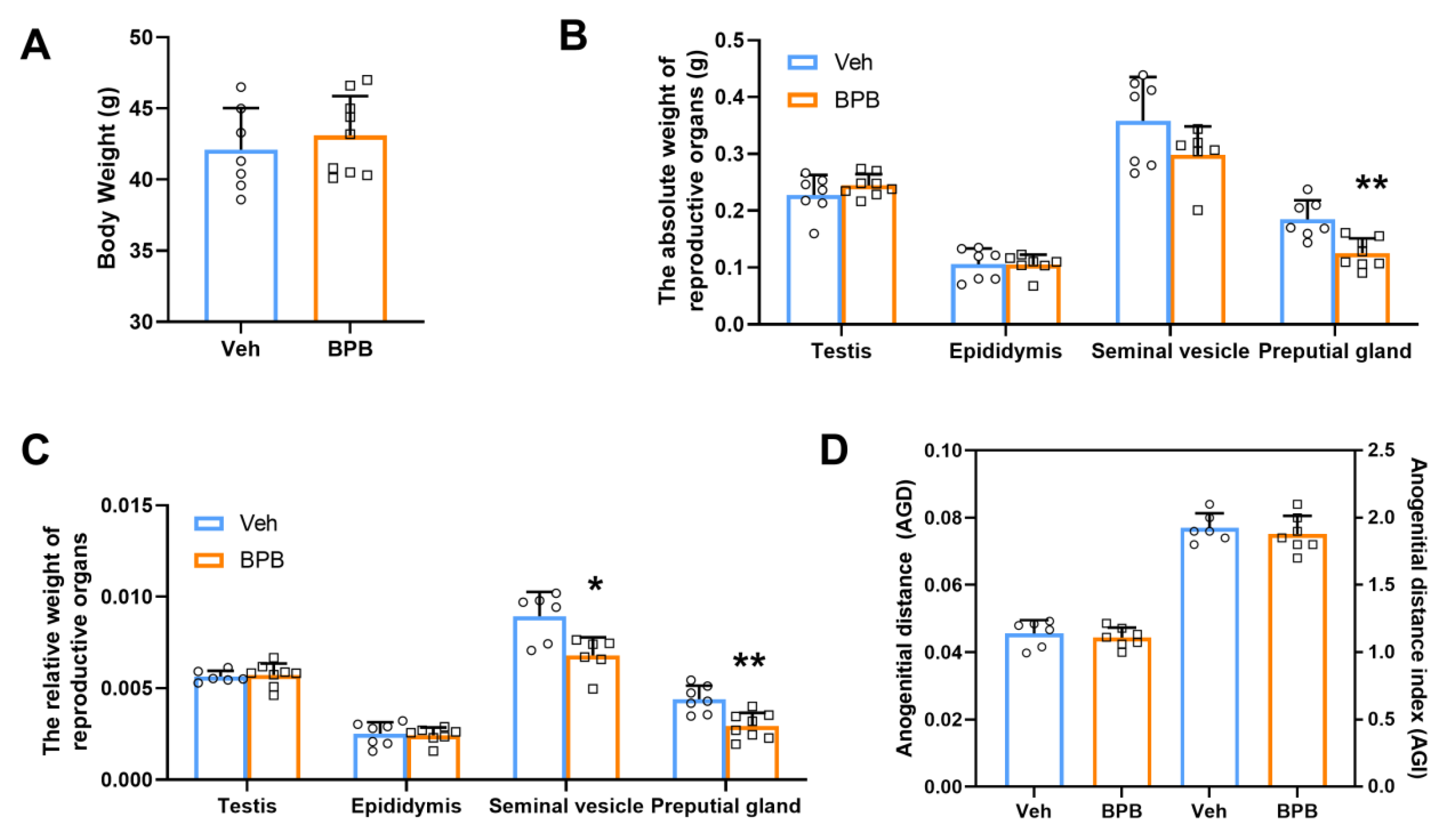
2.2. Body Weight and Reproductive Organ Indices Test
2.3. Histological Analyses
2.4. Sperm Count Test
2.5. Hormone Measure
2.6. Total Testicular RNA-seq and Data Analysis
2.7. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription PCR
2.8. Immunostaining and Analyses
2.9. Molecular Docking
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Maternal BPB Exposure Disrupts Reproductive Organ Indices in Adult Male Offspring
3.2. Maternal BPB Exposure Impairs Testicular Morphology in Adult Male Offspring
3.3. Maternal BPB Exposure Reduces Sperm Count and Testosterone Synthesis in Adult Male Offspring
3.4. Maternal BPB Exposure Alters Immunological Response-Related Biological Processes in the Testis of Adult Male Offspring
3.5. Maternal BPB Exposure Induces Testicular MHC I Overexpression, Immunological Dysregulation, and ERα Downregulation in Adult Male Offspring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnich, N.; Canivenc-Lavier, M.C.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Coffigny, H.; Cravedi, J.P.; Grob, K.; Macherey, A.C.; Masset, D.; Maximilien, R.; Narbonne, J.F.; et al. Conclusions of the French Food Safety Agency on the toxicity of bisphenol A. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Guo, M.; Yin, X.; Huang, C.; Qian, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Ji, G. A systematic comparison of neurotoxicity of bisphenol A and its derivatives in zebrafish. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 805, 150210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladak, S.; Grisin, T.; Moison, D.; Guerquin, M.J.; N’Tumba-Byn, T.; Pozzi-Gaudin, S.; Benachi, A.; Livera, G.; Rouiller-Fabre, V.; Habert, R. A new chapter in the bisphenol A story: Bisphenol S and bisphenol F are not safe alternatives to this compound. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, H.; Beausoleil, C.; Habert, R.; Minier, C.; Picard-Hagen, N.; Michel, C. Evidence for Bisphenol B Endocrine Properties: Scientific and Regulatory Perspectives. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ma, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, L. Bisphenol B induces developmental toxicity in zebrafish via oxidative stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobellis, L.; Colacurci, N.; Trabucco, E.; Carpentiero, C.; Grumetto, L. Measurement of bisphenol A and bisphenol B levels in human blood sera from healthy and endometriotic women. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Quantification of free and total bisphenol A and bisphenol B in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (MD-GC/MS). Talanta 2010, 83, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhuang, T.; Shi, W.; Liang, Y.; Liao, C.; Song, M.; Jiang, G. Serum concentration of bisphenol analogues in pregnant women in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Casero, N.; Lunar, L.; Rubio, S. Analytical methods for the determination of mixtures of bisphenols and derivatives in human and environmental exposure sources and biological fluids. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 908, 22–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.; Wignall, J.A.; Goldstone, A.E.; Ross, P.K.; Blain, R.B.; Shapiro, A.J.; Holmgren, S.D.; Hsieh, J.H.; Svoboda, D.; Auerbach, S.S.; et al. A scoping review of the health and toxicological activity of bisphenol A (BPA) structural analogues and functional alternatives. Toxicology 2019, 424, 152235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Phedonos, A.; Arno, M.; Balu, S.; Corton, J.C.; Antoniou, M.N. Editor’s Highlight: Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Bisphenol A Alternatives Activate Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 158, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.V.; Liu, J.H.; Liao, C.S. Aerobic degradation of bisphenol-A and its derivatives in river sediment. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gély, C.A.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Morin, M.; Vayssière, C.; Gayrard, V.; Picard-Hagen, N. Comparison of the materno-fetal transfer of fifteen structurally related bisphenol analogues using an ex vivo human placental perfusion model. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijngaard, R.R.; van der Perk, M.; van der Grift, B.; de Nijs, T.C.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. The Impact of Climate Change on Metal Transport in a Lowland Catchment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Qiang, L.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L. Toxicokinetics and bioaccumulation characteristics of bisphenol analogues in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Chahoud, I.; Padmanabhan, V.; Paumgartten, F.J.; Schoenfelder, G. Biomonitoring studies should be used by regulatory agencies to assess human exposure levels and safety of bisphenol A. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; Drury, B.; Rottinghaus, G.; Hunt, P.A.; Toutain, P.L.; Laffont, C.M.; VandeVoort, C.A. Similarity of bisphenol A pharmacokinetics in rhesus monkeys and mice: Relevance for human exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hunt, P.A.; Myers, J.P.; Vom Saal, F.S. Human exposures to bisphenol A: Mismatches between data and assumptions. Rev. Environ. Health 2013, 28, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, P.; Ji, X.; Qin, G.; Sang, N. Fetal Origin of Abnormal Glucose Tolerance in Adult Offspring Induced by Maternal Bisphenol A Analogs Exposure. Environ. Sci Technol. 2024, 58, 10910–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yue, H.; Ji, X.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Prenatal NO2 exposure and neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring mice: Transcriptomics reveals sex-dependent changes in cerebral gene expression. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongkorn, S.; Kanlayaprasit, S.; Kasitipradit, K.; Lertpeerapan, P.; Panjabud, P.; Hu, V.W.; Jindatip, D.; Sarachana, T. Investigation of autism-related transcription factors underlying sex differences in the effects of bisphenol A on transcriptome profiles and synaptogenesis in the offspring hippocampus. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Cheng, C.Y.; Liu, Y.X. Development, function and fate of fetal Leydig cells. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 59, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, S.; Meinhardt, A. The macrophages in testis function. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 119, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, J.; Leufgen, A.; Hager, F.T.; Pabst, O.; Cerovic, V. MHCII expression on gut macrophages supports T cell homeostasis and is regulated by microbiota and ontogeny. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Orozco, N.; Isibasi, A.; Ortiz-Navarrete, V. Macrophages present exogenous antigens by class I major histocompatibility complex molecules via a secretory pathway as a consequence of interferon-gamma activation. Immunology 2001, 103, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.H.; Kim, Y.A.; Heo, S.H.; Bang, W.S.; Park, H.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, H.; Seo, J.H.; Cho, Y.; Jung, S.W.; et al. The Association of Estrogen Receptor Activity, Interferon Signaling, and MHC Class I Expression in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO/IPCS. Global Assessment of State-Of-The-Science of Endocrine Disrupters; Damstra, T., Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski, P.; Romano, R.M.; Kizys, M.M.; Oliveira, K.C.; Kasamatsu, T.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Dias-da-Silva, M.R.; Romano, M.A. Adult exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) in Wistar rats reduces sperm quality with disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis. Toxicology 2015, 329, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombó, M.; Fernández-Díez, C.; González-Rojo, S.; Herráez, M.P. Genetic and epigenetic alterations induced by bisphenol A exposure during different periods of spermatogenesis: From spermatozoa to the progeny. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.; Molangiri, A.; Kona, S.R.; Ibrahim, A.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Basak, S. Fetal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting-Bisphenol A (BPA) Alters Testicular Fatty Acid Metabolism in the Adult Offspring: Relevance to Sperm Maturation and Quality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv-Gal, A.; Flaws, J.A. Evidence for bisphenol A-induced female infertility: A review (2007–2016). Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 827–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cull, M.E.; Winn, L.M. Bisphenol A and its potential mechanism of action for reproductive toxicity. Toxicology 2025, 511, 154040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Han, C.; Geng, Y.; Cui, Y.; Bao, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhong, X. Maternal exposure to bisphenol A during pregnancy interferes testis development of F1 male mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23491–23504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivonello, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Nardone, A.; Garifalos, F.; Provvisiero, D.P.; Verde, N.; de Angelis, C.; Conforti, A.; Piscopo, M.; Auriemma, R.S.; et al. Bisphenol A: An emerging threat to female fertility. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2020, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Pirzada, M.; Jahan, S.; Ullah, H.; Shaheen, G.; Rehman, H.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Butt, M.A. Bisphenol A and its analogs bisphenol B, bisphenol F, and bisphenol S: Comparative in vitro and in vivo studies on the sperms and testicular tissues of rats. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlas, S.; Ahmad, M. Acute and sub-acute bisphenol-B exposures adversely affect sperm count and quality in adolescent male mice. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, S.; Ullah, A.; Shaheen, G.; Jahan, S. Exposure of BPA and its alternatives like BPB, BPF, and BPS impair subsequent reproductive potentials in adult female Sprague Dawley rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Zheng, C.; Wang, K.J. The comparative toxicities of BPA, BPB, BPS, BPF, and BPAF on the reproductive neuroendocrine system of zebrafish embryos and its mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, C.J.; Jiao, X.F.; Ding, Z.M.; Zhang, S.X.; Miao, Y.L.; Huo, L.J. Bisphenol AF compromises blood-testis barrier integrity and sperm quality in mice. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Liu, L.; Dong, M.; Xue, W.; Zhou, S.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Yan, W. Prenatal exposure to bisphenol AF induced male offspring reproductive dysfunction by triggering testicular innate and adaptive immune responses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 115030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, H.; Takeda, S.; Kakizoe, K.; Taniguchi, A.; Tokuyasu, M.; Himeno, T.; Ishii, H.; Kohro-Ikeda, E.; Haraguchi, K.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Bisphenol AF as an Inducer of Estrogen Receptor β (ERβ): Evidence for Anti-estrogenic Effects at Higher Concentrations in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreau, S.; Bois, C.; Zanatta, L.; Silva, F.R.; Bouraima-Lelong, H.; Delalande, C. Estrogen signaling in testicular cells. Life. Sci. 2011, 89, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenmai, A.K.; Dybdahl, M.; Pedersen, M.; Alice van Vugt-Lussenburg, B.M.; Wedebye, E.B.; Taxvig, C.; Vinggaard, A.M. Are structural analogues to bisphenol a safe alternatives? Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 139, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desdoits-Lethimonier, C.; Lesné, L.; Gaudriault, P.; Zalko, D.; Antignac, J.P.; Deceuninck, Y.; Platel, C.; Dejucq-Rainsford, N.; Mazaud-Guittot, S.; Jégou, B. Parallel assessment of the effects of bisphenol A and several of its analogs on the adult human testis. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, S.; Theas, M.S.; Guazzone, V.A.; Jacobo, P.; Wang, M.; Fijak, M.; Meinhardt, A.; Lustig, L. Immune Cell Subtypes and Their Function in the Testis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, P.M.; Timms, R.T.; Abdelfattah, N.S.; Leng, Y.; Lelis, F.J.N.; Wesemann, D.R.; Yu, X.G.; Elledge, S.J. High-throughput, targeted MHC class I immunopeptidomics using a functional genetics screening platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, S.Y.; Matsuyama, S.; DeFalco, T. Immune Cells as Critical Regulators of Steroidogenesis in the Testis and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 894437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Byemerwa, J.; Krebs, T.; Lim, F.; Chang, C.Y.; McDonnell, D.P. Estrogen Receptor Signaling in the Immune System. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Byemerwa, J.; Shepherd, J.; Haines, C.N.; Baldi, R.; Gong, W.; Liu, W.; Mukherjee, D.; Artham, S.; Lim, F.; et al. Inhibition of estrogen signaling in myeloid cells increases tumor immunity in melanoma. J. Clin Investig. 2021, 131, e151347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Cheng, Y.; Du, W.; Fu, L.; Wei, Z.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mei, C.; Hao, C.; Chen, M.; et al. Activation of GPER1 in macrophages ameliorates UUO-induced renal fibrosis. Cell Death. Dis. 2023, 14, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| H2-T24 (histocompatibility 2, T region locus 24) | GTCGCACTCTCTGCATTACTG | CTGCTGTCGTAGTGGATGAAG |
| H2-T22 (histocompatibility 2, T region locus 22) | GCCTTGGATTTGGATTGTTGC | AAGACTCGCCAACTGAAGTTC |
| H2-DMB1 (histocompatibility 2, class II, locus Mb1) | ACCCCACAGGACTTCACATAC | GGATACAGCACCCCAAATTCA |
| H2-K1 (histocompatibility 2, K1, K region) | CGTTCCAGGGGATGTACGG | GCTCCCACTTGTGTTTGGTGA |
| H2-OB (histocompatibility 2, O region beta locus) | AGGCGGACTGTTACTTCACC | ATCCAGGCGTTTGTTCCACTG |
| TAP1 (transporter 1, ATP binding cassette subfamily B member) | GGACTTGCCTTGTTCCGAGAG | GCTGCCACATAACTGATAGCGA |
| H2-Q2 (histocompatibility 2, Q region locus 2) | ACGCGGAGAAACCGAGGTA | CCGTCCGATCCCACATCAC |
| H2-D1 (histocompatibility 2, D region locus 1) | TGGTGCTGCAGAGCATTACA | TGTGCCTTTGGGGAATCTGT |
| ERα (estrogen receptor alpha) | TTGAACCAGCAGGGTGGC | AGGCTTTGGTGTGAAGGGTC |
| TNFα (tumor necrosis factor alpha-like) | CATCTTCTCAAAATTCGAGTGACAA | TGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| IL-10 (interleukin 10) | CTTACTGACTGGCATGAGGATCA | GCAGCTCTAGGAGCATGTGG |
| IL-1β (interleukin 1 beta) | CAACCAAAAGTGATATTCTCCATG | GATCCACACTCTCCAGCTGCA |
| TGF-β (transforming growth factor, beta receptor I) | CCACCTGCAAGACCATCGAC | CTGGCGAGCCTTAGTTTGGAC |
| IL-2 (interleukin 2) | ACACCTTTAATTGGTCAACACGA | CCTGCTACGTTCTCTACCTCT |
| Gapdh | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, N.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Peng, X.; Xue, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yan, W. Prenatal Bisphenol B Exposure Induces Adult Male Offspring Reproductive Dysfunction via ERα Inhibition-Triggered MHC I-Mediated Testicular Immunological Responses. Toxics 2025, 13, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060423
Chen N, Li X, Zhou S, Peng X, Xue S, Liu Y, Jiang T, Yan W. Prenatal Bisphenol B Exposure Induces Adult Male Offspring Reproductive Dysfunction via ERα Inhibition-Triggered MHC I-Mediated Testicular Immunological Responses. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060423
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Nannan, Xiaotian Li, Shenrui Zhou, Xin Peng, Senlin Xue, Yuetong Liu, Tingwang Jiang, and Wei Yan. 2025. "Prenatal Bisphenol B Exposure Induces Adult Male Offspring Reproductive Dysfunction via ERα Inhibition-Triggered MHC I-Mediated Testicular Immunological Responses" Toxics 13, no. 6: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060423
APA StyleChen, N., Li, X., Zhou, S., Peng, X., Xue, S., Liu, Y., Jiang, T., & Yan, W. (2025). Prenatal Bisphenol B Exposure Induces Adult Male Offspring Reproductive Dysfunction via ERα Inhibition-Triggered MHC I-Mediated Testicular Immunological Responses. Toxics, 13(6), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060423





