Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Extraction Method
2.3. Detection Method
2.4. Quality Assurance and Control
2.5. Source Apportionment by the PMF Model
2.6. Risk Assessment of Antibiotics
3. Results and Discussion
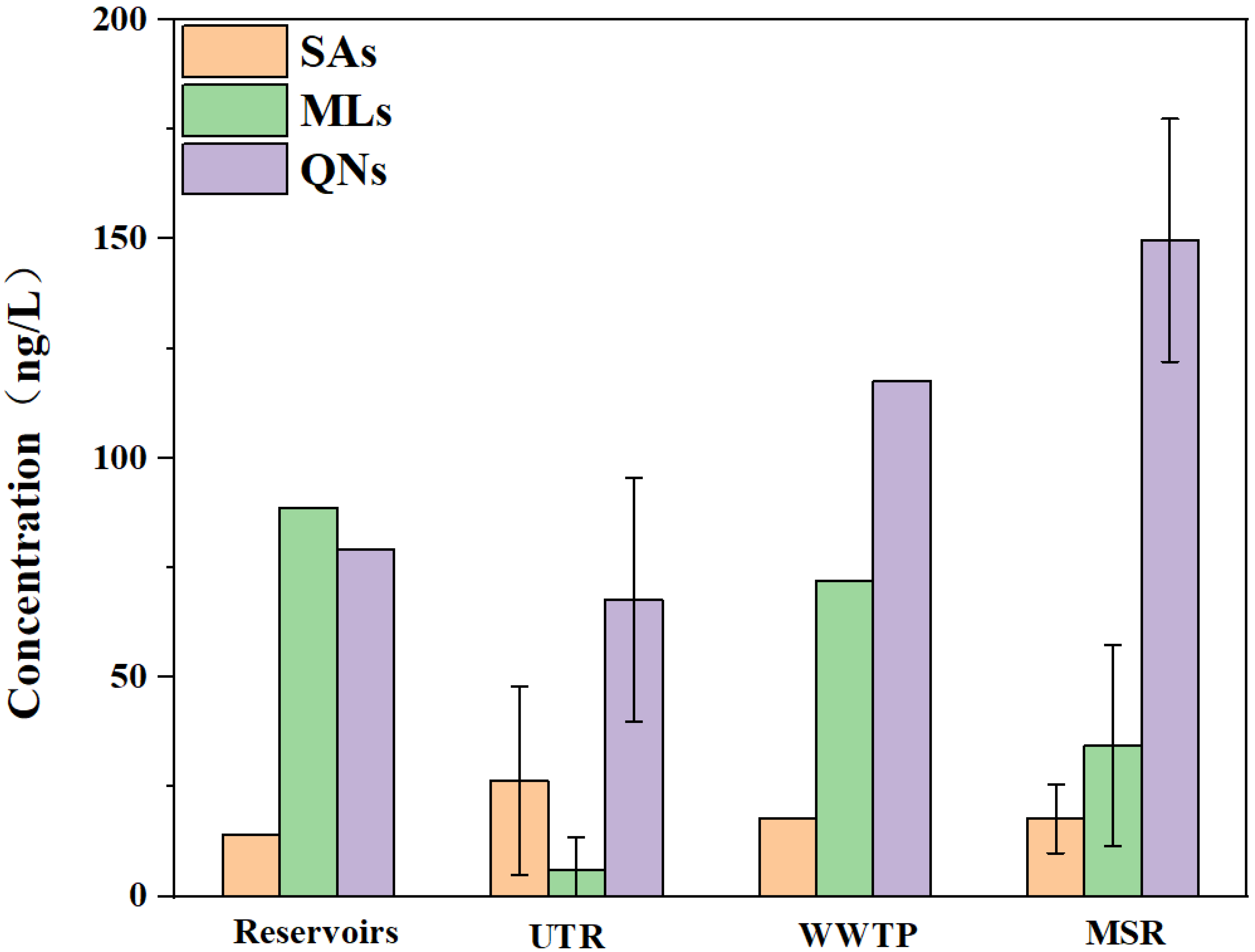
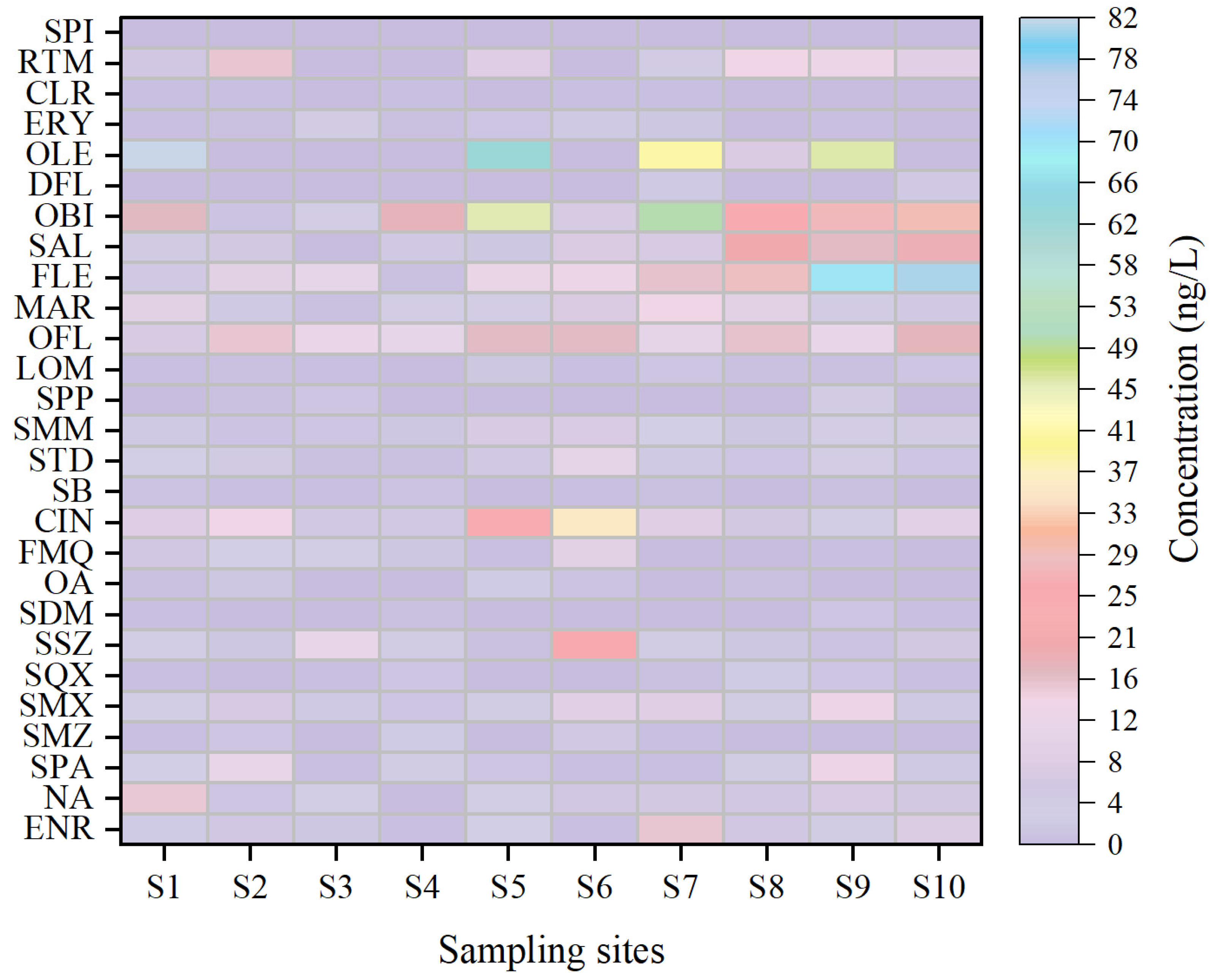
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Antibiotics in Surface Water
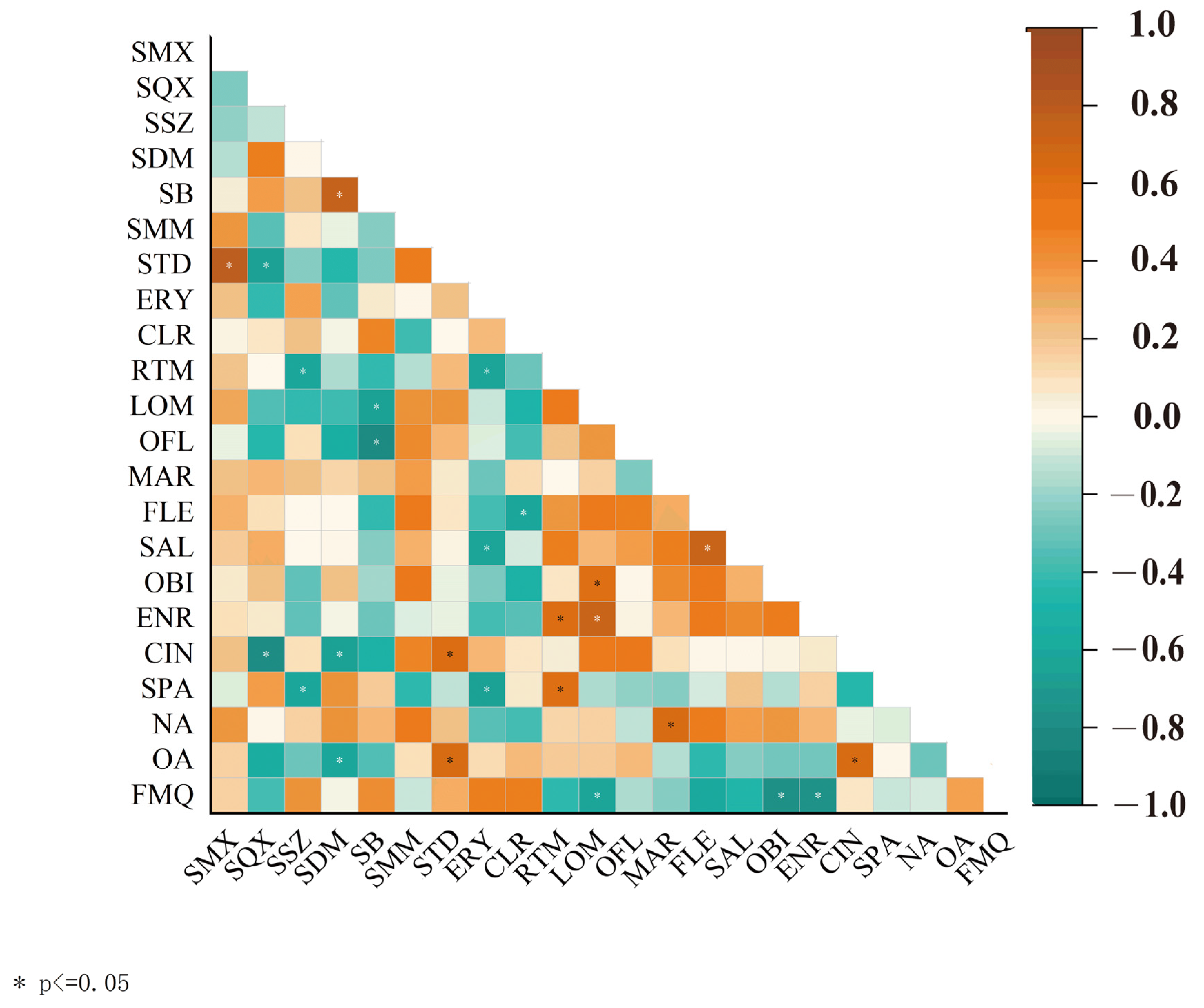
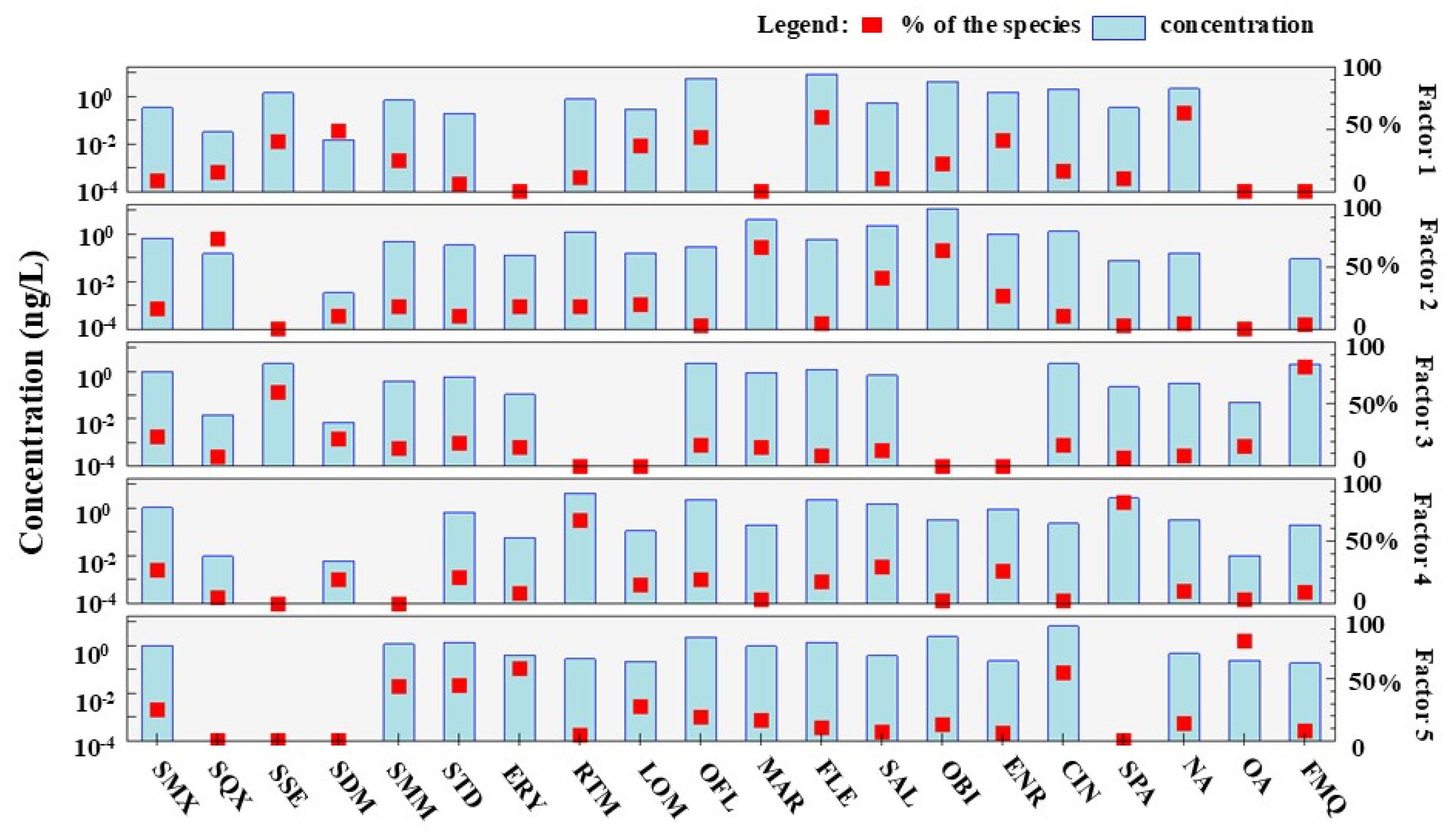
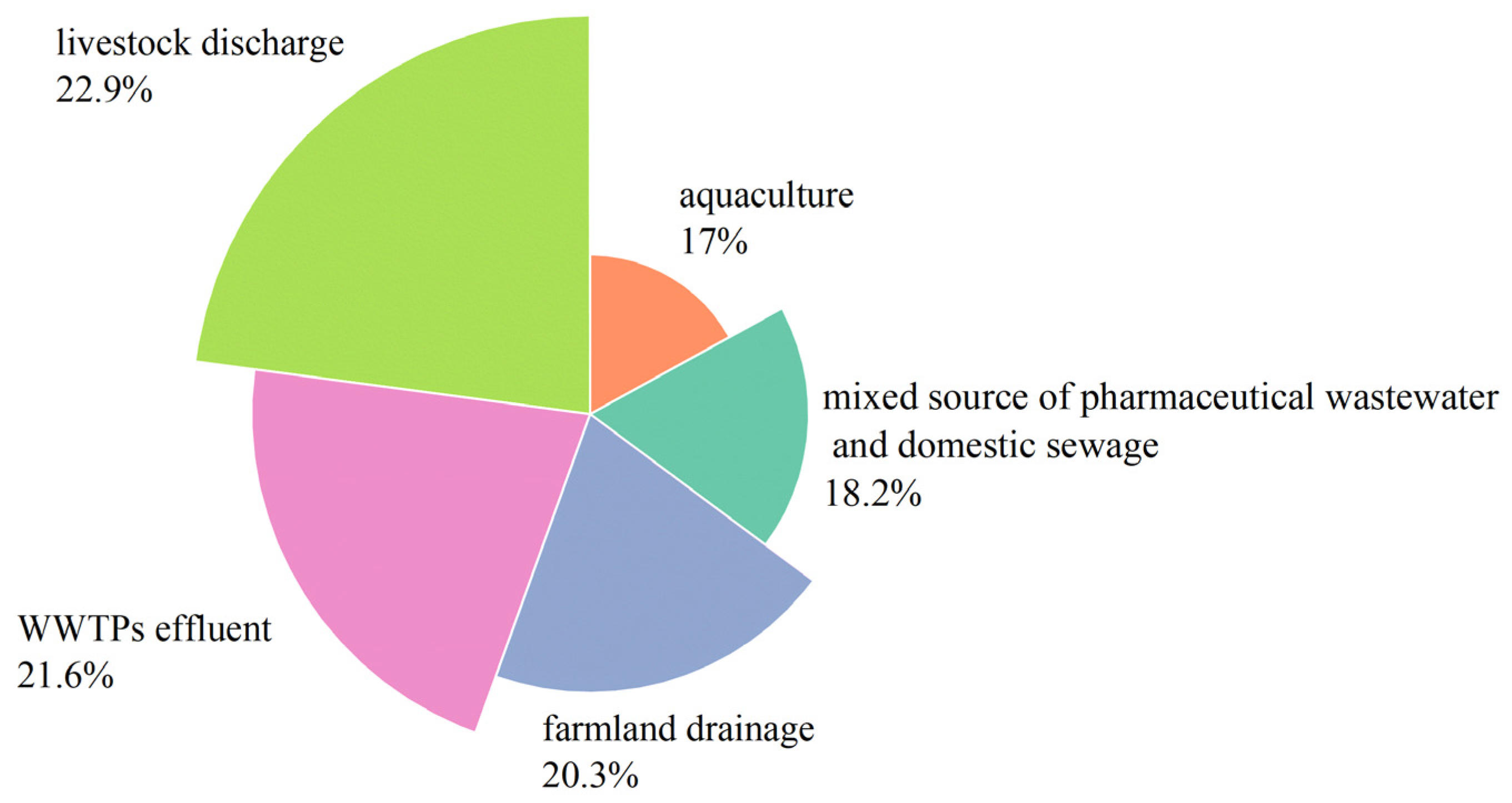
3.2. Source Apportionment of Antibiotics
3.3. Antibiotic Risk Assessments in the Zhuozhang River
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuemmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Song, W.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Du, L.; Xing, W. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Lu, S.Y.; Guo, W.; Xi, B.D.; Wang, W.L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of lakes, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhong, Q.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y. Global Supply Chain Drivers of Agricultural Antibiotic Emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5860–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Ying, G.-G.; Pan, C.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Emission and Fate in the River Basins of China: Source Analysis, Multimedia Modeling, and Linkage to Bacterial Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Mao, D.; Rysz, M.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Trends in Antibiotic Resistance Genes Occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7220–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Minh, N.; Khan, S.J.; Drewes, J.E.; Stuetz, R.M. Fate of antibiotics during municipal water recycling treatment processes. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4295–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shi, T.; Wu, X.; Cao, H.; Li, X.; Hua, R.; Tang, F.; Yue, Y. The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: Seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, M.-C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Kang, J.; Lin, C.; Xu, Q.; Yang, W.; Fan, K.; Li, J. Antibiotics in Surface Sediments from the Anning River in Sichuan Province, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Risk Assessment. Toxics 2024, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: A global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, W.; Yang, C.; Li, E.; Du, Y.; Wang, X. Inconsistent seasonal variation of antibiotics between surface water and groundwater in the Jianghan Plain: Risks and linkage to land uses. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 109, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetan, S.K.; Collins, T.J. Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A challenge to green chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2319–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.-Z.; Zou, H.-Y.; Wu, D.-L.; Chen, S.; He, L.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Bai, H.; Ying, G.-G. Swine farming elevated the proliferation of Acinetobacter with the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in the groundwater. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M. Stop the killing of beneficial bacteria. Nature 2011, 476, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Wang, X.; Melching, C.S.; Guo, H.; Li, W. Identification of multilevel priority management areas for diffuse pollutants based on streamflow continuity in a water-deficient watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Cao, L.; Jiao, L.; Xia, X. Source-specific risk apportionment and critical risk source identification of antibiotic resistance in Fenhe River basin, China. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruti, A.; Fernandez-Olmo, I.; Irabien, A. Impact of the global economic crisis on metal levels in particulate matter (PM) at an urban area in the Cantabria Region (Northern Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polissar, A.V.; Hopke, P.K.; Paatero, P. Atmospheric aerosol over Alaska—2. Elemental composition and sources. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1998, 103, 19045–19057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, B.; Liang, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, L. Occurrence, spatial distribution, source apportionment, and risk assessment of antibiotics in Yangtze river surface water. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Trace elements in PM2.5 in Shandong Province: Source identification and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.Z.; Li, H.M.; Xu, N.; Zhang, R.J.; Chen, X.J.; Sun, W.L.; Wen, D.H.; He, S.L.; Pan, J.G.; et al. Antibiotics in water and sediments of rivers and coastal area of Zhuhai City, Pearl River estuary, south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemicals Bureau. Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances, Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substance, and Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market. Part II; EUR 20418 EN/2; European Commission Joint Research Centre: Brussels, Belgium, 2003; pp. 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J. Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, L. Analysis of the Distribution and Influencing Factors of Antibiotic Partition Coefficients in the Fenhe River Basin. Water 2024, 16, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Long, S.; Wang, L.; Tang, C.; Tam, N.F.; Yang, Y. Predicting distribution coefficients for antibiotics in a river water-sediment using quantitative models based on their spatiotemporal variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.; You, M.; Zhang, R.; Kuang, Y.; Dang, C.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Ni, J. Antibiotics in water and sediments of Danjiangkou Reservoir, China: Spatiotemporal distribution and indicator screening. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ci, M.; Zhang, G.; Yan, X.; Dong, W.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in the Xiaoqing River basin and antibiotic source contribution-a case study of Jinan city, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 25241–25254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liang, H.; Gao, D. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the Songhua River in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19282–19292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Jia, A.; Wan, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.P.; Peng, H.; Dong, Z.M.; Hu, J.Y. Occurrences of Three Classes of Antibiotics in a Natural River Basin: Association with Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14317–14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.F.; Jelic, A.; Lopez-Serna, R.; Mozeto, A.A.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in surface water, suspended solids and sediments of the Ebro river basin, Spain. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar. Occurrence of High Levels of Fluoroquinolones in Aquatic Environment due to Effluent Discharges from Bulk Drug Manufacturers. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 05016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Hoang, L.; Nghiem, L.D.; Nguyen, N.M.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Trinh, Q.T.; Mai, N.H.; Chen, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of multiple classes of antibiotics in urban canals and lakes in Hanoi, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, F.; Huang, Y. Reaction of fleroxacin with chlorine and chlorine dioxide in drinking water distribution systems: Kinetics, transformation mechanisms and toxicity evaluations. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zha, R.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Y. Occurrence and removal prediction of pharmaceuticals positively correlated with antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Chatterjee, S. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Occurrence, mode of action, resistance, environmental detection, and remediation—A comprehensive review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtam, F.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B.; Eurin, J.; Tuc Dinh, Q.; Clement, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Seine River in various hydrological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Jiang, H.; Ma, Y.; Cai, H.; Fu, H.; Li, Z. A nationwide probabilistic risk assessment and a new insight into source-specific risk apportionment of antibiotics in eight typical river basins in China: Human health risk and ecological risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.-Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zou, G.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z. Inhomogeneous antibiotic distribution in sediment profiles in anthropogenically impacted lakes: Source apportionment, fate drivers, and risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Profumo, A.; Pretali, L.; Fasani, E.; Albini, A. Sunlight-induced degradation of soil-adsorbed veterinary antimicrobials Marbofloxacin and Enrofloxacin. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.L.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.R.; Hu, T.; Zhou, B.B. Factors that affect the occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in soils from livestock and poultry farms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Davis, J.G.; Truman, C.C.; Ascough, J.C.; Carlson, K. Simulated rainfall study for transport of veterinary antibiotics—Mass balance analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.E.; Sun, Z.L.; Zheng, S.Y.; Yu, J.; Liang, X.Q. An Integrated Approach to Identify Critical Source Areas of Agricultural Nonpoint-Source Pollution at the Watershed Scale. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Yuan, Z. Vertical migration of typical sulfonamide antibiotics in paddy soil. Huanjing Huaxue-Environ. Chem. 2018, 37, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yin, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, D.; Cui, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wen, L. Distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment of quinotone antibiotics in the surface sediments from Jiaozhou Bay wetland, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, R. Occurrence, source apportionment and source-specific risk assessment of antibiotics in a typical tributary of the Yellow River basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.M.; Ji, M.; Zhai, H.Y.; Guo, Y.J.; Liu, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in WWTP effluent-receiving water bodies and reclaimed wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, B.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Tang, W. Source apportionment and specific-source-site risk of quinolone antibiotics for effluent-receiving urban rivers and groundwater in a city, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 144, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Pretali, L.; Ferri, E.N.; Profumo, A. Sunlight-induced degradation of fluoroquinolones in wastewater effluent: Photoproducts identification and toxicity. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, G.; Meng, G.; Xing, L. Evaluation of non-point source pollution load in Fenhe Irrigation District based on SWAT model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 44, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.H.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.D.; Zou, S.C.; Li, P.; Hu, Z.H.; Li, J. Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckowski, A.; Mioduszewska, K.; Lukaszewicz, P.; Borecka, M.; Caban, M.; Maszkowska, J.; Stepnowski, P. Bioaccumulation and analytics of pharmaceutical residues in the environment: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 127, 232–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in the Haihe River in China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golet, E.M.; Strehler, A.; Alder, A.C.; Giger, W. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents in sewage sludge and sludge-treated soil using accelerated solvent extraction followed by solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5455–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, B.; Marti, E.; Gros, M.; Lopez, P.; Pompeo, M.; Armengol, J.; Barcelo, D.; Luis Balcazar, J.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Marce, R. Exploring the links between antibiotic occurrence, antibiotic resistance, and bacterial communities in water supply reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Shi, Y.L.; Gao, L.H.; Liu, J.M.; Cai, Y.Q. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Chaemfa, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Song, M.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Antibiotics in the offshore waters of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea in China: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 78, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, X. Occurrence, seasonal variation and risk assessment of antibiotics in the reservoirs in North China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Pascarella, L.; Parrella, A. Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, C.; Muehlbauer, V.; Krebs, P.; Kuehn, V. Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics including synergistic and antagonistic combination effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Jing, L.J.; Teng, Y.G.; Wang, J.S. Characterization of antibiotics in a large-scale river system of China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Qiu, X.; Chen, B.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, G.; Huang, H.; et al. Antibiotics pollution in Jiulong River estuary: Source, distribution and bacterial resistance. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.G.H.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Baker-Austin, C. Aquatic systems: Maintaining, mixing and mobilising antimicrobial resistance? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, C.; Lian, M.; Wang, A.; He, M.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, W. Riverine antibiotic occurrence and potential ecological risks in a low-urbanized and rural basin of the middle Yangtze River: Socioeconomic, land use, and seasonal effects. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.J.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhong, J.Y.; Lou, Q.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y.Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaidi, V.S.; Stasinakis, A.S.; Borova, V.L.; Thomaidis, N.S. Is there a risk for the aquatic environment due to the existence of emerging organic contaminants in treated domestic wastewater? Greece as a case-study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger, W.; Alder, A.C.; Golet, E.M.; Kohler, H.P.E.; McArdell, C.S.; Molnar, E.; Siegrist, H.; Suter, M.J.F. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics as trace contaminants in wastewaters, sewage sludges, and surface waters. Chimia 2003, 57, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.W.; Minh, T.B.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, J.C.W.; So, M.K.; Martin, M.; Lam, P.K.S.; Richardson, B.J. Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z. High-Throughput Screening of New Pollutants in Water Based on Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction; Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China; pp. 17–30.
- Lützhoft, H.C.H.; Halling-Sorensen, B.; Jorgensen, S.E. Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents applied in Danish fish farming. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialk-Bielinska, A.; Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Uebers, U.; Boeschen, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Matzke, M. Ecotoxicity evaluation of selected sulfonamides. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, B.; Mons, R.; Vollat, B.; Fraysse, B.; Paxéus, N.; Lo Giudice, R.; Pollio, A.; Garric, J. Environmental risk assessment of six human pharmaceuticals:: Are the current environmental risk assessment procedures sufficient for the protection of the aquatic environment? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Liguoro, M.; Fioretto, B.; Poltronieri, C.; Gallina, G. The toxicity of sulfamethazine to Daphnia magna and its additivity to other veterinary sulfonamides and trimethoprim. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brain, R.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Richards, S.M.; Sanderson, H.; Sibley, P.K.; Solomon, K.R. Effects of 25 pharmaceutical compounds to Lemna gibba using a seven-day static-renewal test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ke, J.; Show, P.L.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Antibiotics: An overview on the environmental occurrence, toxicity, degradation, and removal methods. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7376–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Jeong, D.-H.; Choi, K. Environmental levels of ultraviolet light potentiate the toxicity of sulfonamide antibiotics in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pro, J.; Ortiz, J.A.; Boleas, S.; Fernández, C.; Carbonell, G.; Tarazona, J.V. Effect assessment of antimicrobial pharmaceuticals on the aquatic plant Lemna minor. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 70, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, H.; Dong, H.; Ma, B.; Sun, H.; Pan, T.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, R.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of organic micropollutants in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China: A case study of water diversion. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-H.; Ying, G.-G.; Su, H.-C.; Stauber, J.L.; Adams, M.S.; Binet, M.T. Growth-inhibiting effects of 12 antibacterial agents and their mixtures on the freshwater microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sorensen, B. Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents used in intensive farming. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Huang, H.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Luo, Q. Occurrence and ecological risk of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and pesticides in typical surface watersheds, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.A.; Belden, J.B.; Lydy, M.J. Toxicity of fluoroquinolone antibiotics to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kergaravat, S.V.; Hernandez, S.R.; Maria Gagneten, A. Second-, third- and fourth-generation quinolones: Ecotoxicity effects on Daphnia and CerioDaphnia species. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wei, D.; Du, Y. Acute toxicity evaluation for quinolone antibiotics and their chlorination disinfection processes. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus, T.; Scholze, M.; Grimme, L.H. The single substance and mixture toxicity of quinolones to the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munch Christensen, A.; Ingerslev, F.; Baun, A. Ecotoxicity of mixtures of antibiotics used in aquacultures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2208–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| River | ng/L | SAs | MLs | QNs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhuozhang River, China | Radius | 10.1–58.5 | 1.1–88.6 | 41.7–184.3 | This study |
| Average | 20.8 | 32.3 | 106.6 | This study | |
| Liuxi River, China | Radius | 55.1–778.0 | 22.8–216.0 | 17.0–161.8 | [31] |
| Danjiangkou, China | Radius | ND–149 | ND–3.48 | ND–9.17 | [32] |
| Xiaoqing River, China | Average | 81.64 | 138.8 | 86.97 | [33] |
| The main stream of the Songhua River | Radius | ND-73.1 | ND-11.5 | ND-4.21 | [34] |
| Wenyu River | Average | 1046.7 | 400.4 | [35] | |
| Rivers in Southeast Queensland, Australia | Average | 8 | 10 | 80 | [36] |
| Ebro River Basin, Spain | Average | 4.54 | / | / | [37] |
| Musi River, India | Radius | / | / | 35,420–6,278,000 | [38] |
| Urban canals, Vietnam | Average | 7940 | 6794 | 800 | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Wu, X.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Chai, B. Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions. Toxics 2025, 13, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060422
Yan J, Wu X, Dong K, Zhang Z, Sun X, Gao S, Liu J, Chai B. Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060422
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Juping, Xiayang Wu, Ke Dong, Zhiyuan Zhang, Xuejun Sun, Shaopeng Gao, Jinxian Liu, and Baofeng Chai. 2025. "Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions" Toxics 13, no. 6: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060422
APA StyleYan, J., Wu, X., Dong, K., Zhang, Z., Sun, X., Gao, S., Liu, J., & Chai, B. (2025). Occurrence, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Zhuozhang River, China: A Specific Investigation in Water-Scarce and Human Activity-Intensive Regions. Toxics, 13(6), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060422







