Abstract
Food intake plays a pivotal role in human growth, constituting 45% of the global economy and wellbeing in general. The consumption of a balanced diet is essential for overall good health, and a lack of equilibrium can lead to malnutrition, prenatal death, obesity, osteoporosis and bone fractures, coronary heart diseases (CHD), idiopathic hypercalciuria, diabetes, and many other conditions. CHD, osteoporosis, malnutrition, and obesity are extensively discussed in the literature, although there are fragmented findings in the realm of kidney stone diseases (KSD) and their correlation with food intake. KSD associated with hematuria and renal failure poses an increasing threat to healthcare infrastructures and the global economy, and its emergence in the Indian population is being linked to multi-factorial urological disorder resulting from several factors. In this realm, epidemiological, biochemical, and macroeconomic situations have been the focus of research, even though food intake is also of paramount importance. Hence, in this article, we review the corollary associations with the consumption of diverse foods and the role that these play in KSD in an Indian context.
1. Introduction
Kidney stone diseases (KSD) and associated research have become widespread, with the correlation between genetic predisposition and calcium-based kidney stones being an early observation. Furthermore, in the USA, there was a sharp rise in KSD, i.e., nearly 200%, in the years between 1964 to 1972 [1]. In the same way, European countries, except Scotland (3.83% in 1977 to 3.5% in 1987), Germany, Spain, and Italy, have also shown an increasing trend in KSD prevalence in recent decades [2,3,4,5]. Along with these geographical boundaries, Japan and some parts of Iran, USA and other countries soon started investing money into research on KSD, focusing on general patterns relating to the age population of both men and women [6,7,8]. In conducting these studies, it was found that KSD is prevalent, with nearly 35% of the control group affected with hypercalcaemic nephrolithiasis disorder [9]. Along with this, reports have holistically demonstrated that monozygotic twins (32.4%) have approximately 15% higher rates in comparison to dizygotic twins (17.3%; P < 0.001) [10]. To further elaborate on this paradigm, reports have aptly depicted, in a Canadian context, that even though the presence of dent disease and hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria has been observed, there is still a strong relationship with ancestry and genetic patterns [11]. Furthermore, to conclude this hypothesis, they have to counteract several genetic analysis approaches, namely, encoding vitamin D receptor (VDR), calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR), 25(OH)D 1α-hydroxylase, osteocalcin, uromodulin, and osteopontin among others [12]. On the other hand, studies portraying gender and age as the principle parameters have revealed that Iran and USA are the peak KSD locations for people aged 40–49 years, while the greatest prevalence among people aged 50–59 years is shown in Japanese women [1]. The data illustrated a similar pattern in Japan and USA for the male group in the 40–49 age bracket, and Iran followed, with a different trend [13]. This initial investigation leads us to conclude that it is increasingly unscientific to extrapolate KSD patterns based on age and sex in different geographic locations. Therefore, the researchers were challenged to create a set of new parameters to fine-tune more realistic solutions in the realm of KSD and its prevalence.
Diet is an integral part of renal accumulation and thus filtration, which in turn affects the absorption and bodily homeostasis of renal stone occurrence [14,15]. The epidemiology differs in accordance with different geographical regions and social constructs. Within this context, food habits have been proposed as one of the major risk factors in renal stone formation, as a form of epidemiology for urine composition [16,17]. Food patterns are among the major factors for renal stone formation, and stone material deposition can be managed by regulating food intake. In the context of the Indian diet, there is a collection of many tastes and flavors, from the color-rich food of Rajasthan, to the spicy food of Punjab, and from the slightly sweet, oil-based food of Gujarat, to the southern, slightly sour seafood. All of these foods are found in this land of paradise. Several communities in the country are vegetarian, although there is still a large range of rich non-vegetarian recipes. Increases in urinary calcium excretion are strongly related to the consumption of animal proteins, with a consequent reduction in urinary pH and citrate excretion, which are the basis of stone formation. Due to this food pattern in Indian culture, we believe that it is of paramount interest to describe the nutritional factors causing renal stone formation and the immediate effects thereof.
2. Diverse Food Habits in India
The era of rapid globalization and packaged market products has shifted the equilibrium of nutrition in India. Urban areas in India have embraced more packaged foods, which have led to increased body mass and premature obesity. In this realm, Indian cooking reflects thousands of years of history, leading to the diversity of flavors and the innumerable regional dishes found in the country [18]. Diversified food habits range in different parts of India, with different geographical areas spanning from the Rajasthan desert to the Madhya Pradesh forest, or from the Maharashtra seashore to the Jammu and Kashmir Mountains [18]. For the ease of description, Indian cooking is classified principally into the North Indian, East Indian, West Indian, and South Indian cuisine, based on the similarity and differences in the nature of these cuisines. North Indian cuisines are distinguished by their heavy use of dairy products and the prevalence of flatbreads, such as roti and paratha, baked in clay ovens, over rice dishes. Even though parts of Western India, such as Gujarat and Rajasthan, are predominantly vegetarian, the remaining cuisines have their fair share of meat or animal proteins, owing to their associations with the Muslim incursion into India. South India can boast a bewildering range of regional cuisines. Therefore, with cuisines ranging from the rich northern style Mughlai cooking of the pre-dominantly Muslim dominated Hyderabad to the simple vegetarian dishes of Tamil Nadu, from the seafood, kebabs, and puris of Maharashtra to the strong Portuguese-influenced cuisine of Goa, from the coconut-based recipes of Kerala and the Malabar fish dishes to the unique cuisine of a shrinking Franco-Indian population in Pondicherry, South Indian food habits encompass a wide spectrum of culinary options [18]. Socio-demographic, macroeconomic, and lifestyle factors in the coastal part of Karnataka and Kerala illustrate the close proximity between observed dietary habits and food styles. The transition from South Indian to Eastern Indian food habits encompasses cuisines from the states of West Bengal and Orissa to the Northeastern states. The staple foods of this region are largely based on rice and wheat. East Indian food habits have a good balance of vegetarian and non-vegetarian dishes, with fish curries being the cornerstone of non-vegetarian dishes. Steaming and frying are popular methods of cooking. Therefore, to quantify the diversity of Indian food styles and their relationship with KSD, this review article investigates possible methods for curtailing the prevalence of KSD, which is associated, directly or indirectly, with food consumption.
2.1. Stone Forming Area in India
In the context of India, KSD is prevalent, with an expectancy of 12% in a total population reported to be prone to urinary stones [19]. Of this 12%, 50% of the population are severely affected by renal damage, which even leads to a loss of kidneys [19]. Unlike in South India, where a few reported percentages affected by Urolithiasis, in North India, there is a steep 15% of the population within the realm of KSD [20]. Thus, considering the prospects of the kidney stone belt, which are affected by KSD in India, a proper corollary needs to be established [20]. This stone belt occupies areas of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal (Figure 1). In these regions, the frequency of the prevalence and recurrence rate of renal stone is high in most of the members of a family.
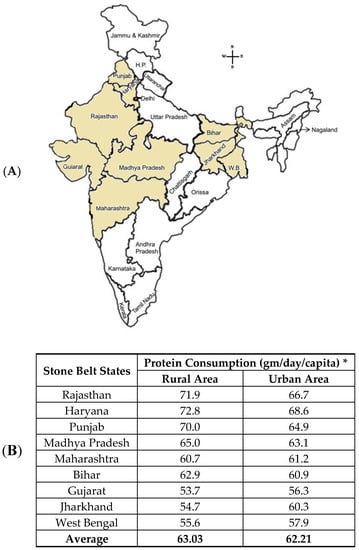
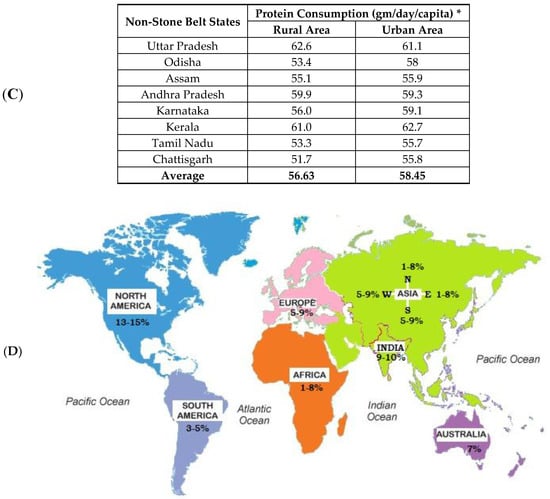
Figure 1.
Stone belt Area: (A) Major kidney stone prevalent states in the Indian continent. (B) Animal protein consumption per gram per day per capita in stone belt Indian states, which leads to KSD (* Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation 2012). (C) Non-stone belt Indian states are also depicted with the rural and urban population and the animal protein consumption per gram per day per capita. (D) Prevalence rates of kidney stones in a global platform, for comparison.
2.2. Food Habits with Stone Formation
The Indian food habit has been considered a widely recognized risk factor of kidney stone formation [21]. An increase in calcium excretion after a load of protein was stated by many studies [22,23]. The increased consumption of animal products leads to higher calcium, oxalate, and phosphorous in the urinary tract [24,25,26]. These are the reasons for stone formation, initially in the form of insoluble calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate crystals. Proteins also increase uric acid generation, which may end up in stone formation [25,26]. High carbohydrate and lipid consumption has been shown to have similar changes [27]. The presence of a high amount of salt in fast food, especially in industrialized countries, causes higher calcium in the kidneys [28]. Conversely, a low calcium diet is considered to be a risk factor, as it increases the intestinal absorption of oxalate [29]. Citric acid, potassium, and magnesium act as negative regulators of stone synthesis [25]. For this reason, the inadequate intake of fruits and vegetables are considered as risk factors for stone synthesis, although some oxalate-rich fruits, such as berries, chikoos, and vegetables, such as tomatoes, spinach, and beets, are still of some risk [30,31]. Vitamin C, when administered in higher quantities into the human body, is reported to cause kidney stones in some cases [32]. It is inferred that Vitamin C gets converted to oxalates [33]. However, some studies reported that oxalate excretion is not closely related to dietary intake [34]. There are a number of comparative studies of stone formers and the healthy control of dietary habits [27,29], but the results are contradictory. Most of these studies support the relation between food habits and kidney stones, although the opposite result has also been found [35]. Thus, the development and progress of the disease is not clear. In this connection, Table 1 corresponds to reports conducted in the different geographical study populations to strengthen the correlation of food intake and its impact on KSD.

Table 1.
Impact of food content and the prevalence of kidney stone diseases (KSD) in some different zones.
2.2.1. Protein
A high intake of protein, especially animal protein, is responsible for the relatively high prevalence of stones [23,49,53]. Animal protein containing purines are precursors of uric acid stones [54]. Amino acids, such as glycine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, convert into oxalate, which is a very common component of kidney stones [55]. It also causes renal acid excretion, calcium reabsorption, increased urinary calcium excretion, and an increased renal reabsorption of citrate, which ultimately leads to kidney stone formation [49]. This protein makes a good contribution to forming a bridge between calcium (increased calcium) and uric acid (decreased citrate) stones by its activity. While a balanced amount of protein intake is required to ignite metabolism, greater consumption, on the other hand, increases the burden in the kidney and liver [56]. To support the fact of protein consumption and associated kidney stones, reports have shown that meat consumption in the developed nation is three times higher than that in developing ones, such as Asia between 1970 and 1990 [57].
2.2.2. Calcium-Rich Food
Nishiura (2002) demonstrated a comparative study of the control individuals and stone former individuals in relation to the oral consumption of a calcium diet, with urinary excretion. In stone formers, there is a dependency of urinary calcium excretion on diet, whereas in controls, there is a variation in calcium excretion corresponding to diet [34]. On the contrary, it has been shown that lower calcium intake provides a higher risk of stone formation than higher calcium intake [58]. Calcium-rich cereals, such as ragi, rajma, soybeans, or dairy products, are the main ingredients of a regular diet in India, especially in the stone belt region [18]. Conversely, the intake of calcium supplements outside meals causes an increased risk of stone formation in patients taking calcium supplements [34]. Calcium intake outside meals results in a different effect than does calcium intake with other nutrients [45].
2.2.3. Carbohydrate-Rich Food
Calcium stone formers exhibit an enhanced urinary calcium excretion of dietary content containing high carbohydrates in comparison to healthy controls [59]. Carbohydrates reduce the reabsorption of calcium at the level of the distal tubule, but subsequent studies have shown that glucose in a high concentration can enhance the intestinal absorption of calcium [60]. In addition, fructose increases the urinary excretion of calcium and oxalate, both of which are important risk factors for calcium stones. Low urinary pH, which is a major reason behind uric acid formation, is the trailing step of insulin resistance due to excessive fructose intake [61]. It was reported that uric acid synthesis is upregulated due to a single carbohydrate component, fructose [62]. In India, the diet of northern and eastern regions contains the maximum sucrose content of everyday life [63].
2.2.4. Sodium and Potassium
The modification of sodium by cutting down the daily intake of salt is advised for reducing kidney stone recurrence [64]. Changes in the composition of urine, i.e., increased calcium or decreased citrate, is attributed to increased sodium in the diet [14]. It is shown that sodium can greatly affect the urinary excretion of calcium, i.e., 25 mmol/day increases in urinary sodium cause an increase of 0.6 mmol/ day in urinary calcium [65]. Sodium and calcium excretion in the urine are well correlated, and this is shown in some studies [52,66]. Potassium also regulates the value of urinary calcium in the body [67]. In one study, it was reported that in healthy subjects’ diet, with normal sodium quantity, dietary potassium deprivation is associated with an increase in urinary calcium excretion [68]. The regular salty food pattern is one of the reasons behind kidney stone formation in India [69,70]. In contrast, sodium and potassium also increase urinary volume and pH, which is required in cystine lithiasis [71].
2.2.5. Oxalate-Rich Food
The dietary oxalate and the metabolism of vitamin C both cause oxalate [38,39,40]. Urinary oxalate excretion derives from metabolism, but 10–50% comes from dietary oxalate [38]. In Western countries, the intake of oxalate ranges between 100–300 mg/day, and approximately 5–10% of the total is absorbed in the intestine [72]. Intestinal absorption depends on the form in which it is consumed, i.e., soluble or insoluble, and on its interaction with other food materials [73]. The main sources of dietary oxalate are relatively few: spinach (45%), potatoes (10%), cold cereal (4%), nuts, coffee, and tea account for about 70% of all dietary oxalate [30,31]. Some studies claim that renal stone formers consume more oxalate than healthy controls, and there are some studies where the oxalate quantity of the diets is not the only reason for renal stone formation [34]. In Table 2, we compiled diverse food intake in different Indian regions, i.e., central (Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh), eastern (West Bengal, Tripura, Sikkim, Odisha, Nagaland, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur, Jharkhand, Bihar, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh), northern (Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana), western (Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Goa) and southern (Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh) regions, and the macromolecular content related to KSD (Table 3).

Table 2.
Different geographic regions and food habits of India.

Table 3.
Various macromolecules/nutrients and their effect on the level of KSD.
3. Mechanism of Different Types of Stones According to Food Habits
3.1. Impact of Food on the Mechanism of Stone Formation
Kidney stones are named according to the names of the crystals that make up the hard part of the stones: calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, cysteine, and struvite. In India, calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate stones are predominant, whereas reports of uric acid and cystine stone are very few [74]. Struvite stones are not under consideration, as they are formed by bacteria in urinary tract infections and are generally not found in the Indian population [21].
3.1.1. Calcium Stone
Calcium is the major element of about 80–90% of all urinary stones [75]. They are usually made of calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate or mixtures of them detected in chemical or infrared spectrometric analysis [76]. Calcium phosphate may solidify in the renal interstitium and, later, on a papillary surface along with calcium oxalate [77]. Many studies reported a derivation of 10–50% of the urinary oxalate in diets rich in dark-green leafy vegetables, spinach, beets, beans, cereals, dietary ascorbic acid, glycine-rich food, such as animal proteins, chocolate, black tea, etc. [2,38,39,40,73,78]. The protein breakdown product, glycine, oxidizes to glyoxylate in a metabolic pathway, which is the precursor of oxalate, a major stone component [79]. It has been shown that the overconsumption of animal protein creates an observable increased rate of urinary calcium (23%) and oxalate (24%) [80]. High fructose consumption from soft drinks is associated with an increased risk of hypercalciuria, hyperoxaluria, and hyperuricosuria [39,81]. In an experiment, higher urinary calcium excretion occurred in rats fed high-fructose diets, unlike in rats fed high-starch diets [82,83]. An insufficient supply of dietary calcium is also a notable risk factor for both calcium oxalate and phosphate stone formation [34,45]. High salt intake has been associated with elevated urinary calcium excretion, because it reduces tubular reabsorption, which is an output of the free particle model on crystallization [84]. These high concentrations of calcium in the urine combines with oxalate and phosphorus to form stones (Figure 2).
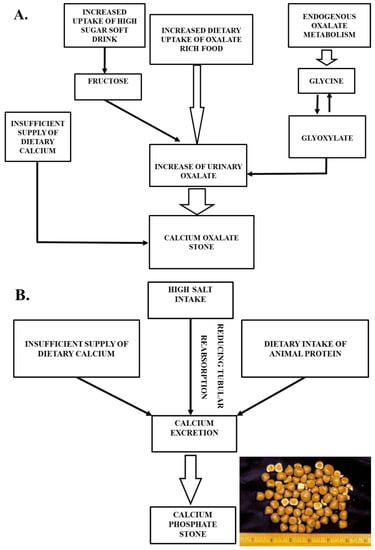
Figure 2.
Calcium stone formation with food habits: (A) Calcium oxalate stone formation, and (B) calcium phosphate stone aggregation.
KSD is mostly accompanied with hypercalciuria in 30–60% patients due to high intestinal calcium absorption [85]. In hypercalciuria, calcium stimulates the supersaturation of mineral crystallization and makes the obstacles of stone inhibitory factors (citrate, glycosaminoglycans) by binding with them [86]. Other events, such as bone resorption and renal leakage, play a positive role in implicating hypercalciuria manifestation [87]. By reducing calcium intake, the heights of calcium excretion are manageable at a certain level [88]. Thus, dietary management should be required for the regulation of hypercalciuria. A diet-based study demonstrated that a lower intake of animal proteins and salts, with optimum calcium intake, have a great impact on reducing the chance of stone recurrence [52,66]. Overtaking salts and proteins increases urinary calcium excretion by nearly 23%, and the outcome is kidney stone formation [52]. From a rat model experiment with elevated urinary calcium excretion, fructose was also found to have a significant role [89].
3.1.2. Uric Acid
Uric acid stones constitute nearly 5–10% of urinary stones [90]. Low urine pH is often associated with this type of stone [22]. Urinary uric acid solubility decreases by approximately 185 mg/dL when urine pH drops from 7 to 5. At a higher pH, 95% of uric acid is in its soluble urate form, and at a lower pH solubility, it decreases in most of the uric acid [91]. Excess uric acid is excreted through urine, and hyperuricosuria is caused by a purine-rich diet, a precursor of uric acid (Figure 3) [90]. Foods containing high protein, especially animal protein, such as poultry things, eggs, meat, sea fish, and some plant products, such as seeds and nuts, are the highest sources of purines [92]. It was reported that a daily increase of animal protein significantly increased uric acid excretion by 48% [93]. Another factor, sweet drinks with a high fructose level, is related to an increased risk of renal stones. In one study, it was shown that the overconsumption of fructose results in a rapid rise in serum uric acid through increased purine synthesis [89]. In the metabolism pathway, fructose breaks into insonine and xanthine with the help of energy driver ATP. This xanthine ultimately promotes uric acid formation using ADP as a substrate [94].
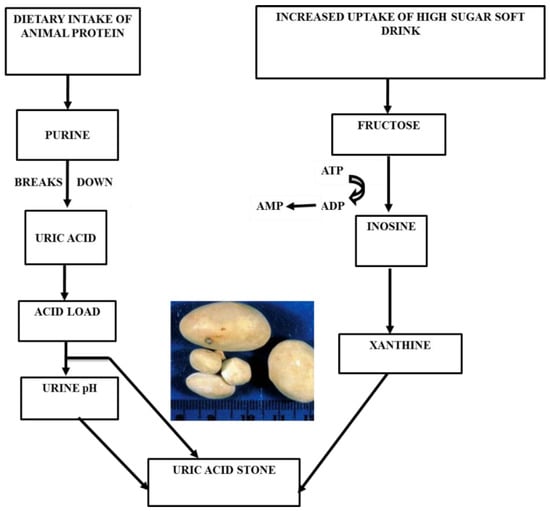
Figure 3.
Uric acid stone formation with food habits.
3.1.3. Cystine Stone
Cystine stones are very rare, constituting only 1–2% of urinary calculi [95]. These are formed in people who have a tendency of excessive cystine leakage from the kidneys into the urine [96]. Maintaining cystine concentration in urine below 200 to 300 mg/L is the best medical method for avoiding this type of stone [97]. A high liquid substance is required for producing at least 3 L of urine a day to decrease the high level of urinary cystine [98]. In addition, potassium citrate is usually taken as a drug for reducing renal acidosis [99]. In food, animal proteins containing methionine, such as meat, break down into cystines, which increases the urinary cystine level in the body [100]. It has been shown that urinary cystine excretion can be reduced to 34% by consuming a very low protein diet (nearly 20 g/day) [101]. Overtaking sodium has a high impact on the manifestation of this disease, since it promotes the excretion of cystines (Figure 4) [102].
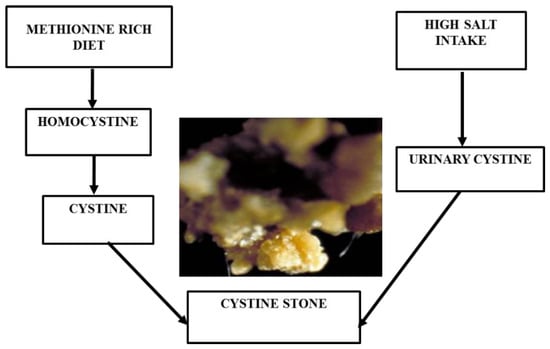
Figure 4.
Cystine stone formation with food habits.
4. Food Diversity and Nutritional Effects in Indian Population
Over-nourishment and undernourishment are both great burdens for society. On the one hand, the excess intake of proteins, carbohydrates, and oxalate-rich foods enhances the occurrence of renal stones [23,59,61,62,72]. On the other hand, increased protein breakdown and protein undernutrition are familiar in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients [103]. Thus, it is evident that the presence or absence of protein has an observable influence on these two kidney diseases. Several studies have suggested that CKD is a recognized issue among stone formers [104,105,106]. Renal stone is a risk factor of an impaired kidney function, and an important clinical parameter, the serum creatinine level, should be monitored in the follow-up [107]. In a population study from the US, it was indicated that elevated serum creatinine levels cause a nearly 25–44% increased risk of CKD in stone formers [108]. Recurrent stone formers might accumulate incremental kidney injuries with each stone event. Therefore, treatments to prevent kidney stone recurrence may be beneficial for delaying CKD progression, especially because kidney stone events are associated with reductions in glomerular filtration rates and increases in proteinuria [105,106,107]. During a mean of 8.6 years of follow-up, stone formers had an increased risk of being clinically diagnosed with CKD [108]. A protein-rich diet may increase serum creatinine levels, which has an impact on changes in the glomerular filtration rate [109]. Interestingly, there are multiple reports on protein energy malnutrition, which occurs during the CKD, especially in the mature stages (3–5), and the risks of mortality are high due to the occurrence of protein malnutrition at the time of dialysis [110]. Many studies have also shown that CKD patients have a lot of resting energy expenditure in comparison to normal individuals, and during dialysis, this expenditure is further increased [111,112]. For this reason, they require more energy, especially protein. In conclusion, food management is a very important tool for maintaining the health of the kidney.
In the Indian scenario, where mostly there are people under the poverty line, income plays a major role in determining the status of life and food intake in general [101]. This poor socioeconomic position is associated with chronic malnutrition, since it inhibits the purchase of essential nutritious foods for growth and development, as the price rates are not increasing with income proportionately [113]. Thus, there are many indirect pathways, such as poor healthcare, malnutrition, abstemious food intake, that lead to a CKD and many other medical conditions (Figure 5) [114]. Prenatal cases, where calcium intake and nutritional levels need to be properly maintained, have frequently been the underprivileged. In this section, we have given an introductory causality model, revealing causes that very much exist in India, in the realm of nutrition, food intake, and their impact on human lives.
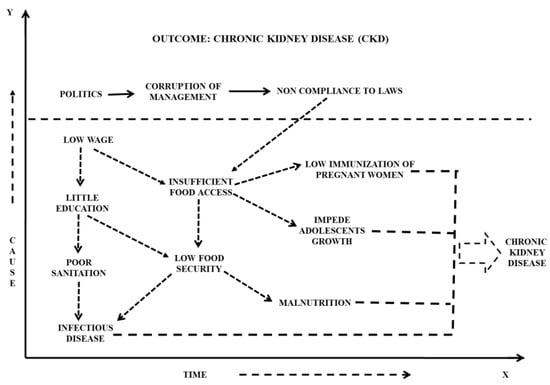
Figure 5.
Diagrammatic representation of a causal conceptual model in the Indian scenario. An example where societal factors, such as economy, political view, and education, affect the health and wellbeing of the poorer class of the Indian population.
5. Concluding Remarks
KSD is a rising concern, a major healthcare burden, and is associated with hematuria and renal failure. The risk of renal stone varies from 1–5% in Asia, 5–9% in Europe, 10–15% in the USA, and 20–25% in the Middle East [115]. Dietary therapy can be one of the promising solutions for minimizing the cases of recurring kidney stone formation and hence a better quality of life. Protein and carbohydrates are the most dominant food contents in India. Rural as well as urban areas of the stone belt region consume a high amount of protein in comparison to other regions. These food habits are one of the main reasons behind the prevalence of KSD in India. Thus, awareness of the health concern and optimized food therapy can potentially curtail the cost of hospitalization and enhance compliance in general. Vis-à-vis dietary control and the insufficient understanding of the molecular and genetic basis of pathogenic mechanisms remains a critical barrier to early detection and treatment. Stone formation is mostly attributed to two mechanisms: (1) renal calcium leak, excessive absorption, bone resorption/formation imbalance; and (2) mineralization. Dietary factors have been widely recognized as one of the primary risk factors of kidney stone formation [59]. On the other hand, the parathyroid hormone primarily modulates calcium balance. It increases calcium excretion in the kidney. VDR regulates calcium homeostasis by affecting bone resorption and calcium absorption. CLDN-14, a tight junction protein, decreases Ca2+ permeability, whereas matrix gla protein (MGP) regulates calcification [76]. Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) prevents renal stone formation by decreasing the aggregation of crystals and binding to the renal epithelial cells [115]. These genes are significantly associated with KSD in the Indian population [76]. These are the reasons for the initial stone formation in the form of insoluble calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate crystals. Most of these genetically inspired reports support the relation between food habits and kidney stones, although stratified contradictory reports also exist. Thus, conclusively, there is a high demand for a better understanding of the correlation between food intake and CKD, and hence quantified research and associated case studies need to be established in the near future.
Author Contributions
M.D. provided the outline for the draft and critical revision. M.G., P.M. and H.B. conducted the literature search. M.G. and H.B. collected the data for the tables and figures and drafted the manuscript.
Funding
No funding is associated with this work.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the Department of Zoology, University of Calcutta, Kolkata and the National University of Singapore for their support with the available Library resources during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare that no conflict of interest existed while this manuscript was produced.
References
- Romero, V.; Akpinar, H.; Assimos, D.G. Kidney stones: A global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev. Urol. 2010, 12, e86–e96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesse, A.; Siener, R.; Heynck, H.; Jahnen, A. The influence of dietary factors on the risk of urinary stone formation. Scanning Microsc. 1993, 7, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serio, A.; Fraioli, A. Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis. Nephron 1999, 81, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, M.; Lusini, M.L.; Nelli, F. Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis today. Urol. Int. 2004, 72, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Martín, F.M.; Millán Rodríguez, F.; Esquena Fernández, S.; Segarra Tomás, J.; Rousaud Barón, F.; Martínez-Rodríguez, R.; Villavicencio Mavrich, H. Incidence and prevalence of published studies about urolithiasis in Spain: A review. Actas Urol. Esp. 2007, 31, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieske, J.C.; Peña de la Vega, L.S.; Slezak, J.M.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Leibson, C.L.; Ho, K.L.; Gettman, M.T. Renal stone epidemiology in Rochester, Minnesota: An update. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarinejad, M.R. Adult urolithiasis in a population-based study in Iran: Prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Urol. Res. 2007, 35, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Iguchi, M.; Suzuki, S.; Kohri, K. Prevalence and epidemiological characteristics of urolithiasis in Japan: National trends between 1965 and 2005. Urology 2008, 71, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stechman, M.J.; Loh, N.Y.; Thakker, R.V. Genetic causes of hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 2321–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, D.S.; Fischer, M.E.; Keich, Y.; Goldberg, J. A twin study of genetic and dietary influences on nephrolithiasis: A report from the Vietnam Era Twin (VET) Registry. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devuyst, O.; Pirson, Y. Genetics of hypercalciuric stone forming diseases. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Chonchol, M.B. Vitamin D and kidney stone disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchene, D.A.; Pearle, M.S. Stones and Endourology in Older Adults. In Geriatric Urology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- Borghi, L.; Schianchi, T.; Meschi, T.; Guerra, A.; Allegri, F.; Maggiore, U.; Novarini, A. Comparison of two diets for the prevention of recurrent stones in diopathic hypercalciuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.N.; Fung, T.T.; Curhan, G.C. DASH-style diet associates with reduced risk for kidney stones. JASN 2009, 20, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, A. Epidemiology of urolithiasis. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 1996, 68, 203–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, W.G. Renal stones in the tropics. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosambi, D.D. The Culture and Civilisation of Ancient India in Historical Outline; Routledge and K. Paul: London, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sofia, N.H.; Manickavasakam, K.; Walter, T.M. Prevalence and risk factors of kidney stone. GJRA 2016, 5, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesamoni, R.; Singh, S.K. (Eds.) Epidemiology of stone disease in Northern India. In Urolithiasis; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mikawlrawng, K.; Kumar, S.; Vandana, R. Current scenario of urolithiasis and the use of medicinal plants as antiurolithiatic agents in Manipur (North East India): A review. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2014, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Maalouf, N.M.; Moe, O.W.; Adams-Huet, B.; Sakhaee, K. Hypercalciuria associated with high dietary protein intake is not due to acid load. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 3733–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, E.; Hospers, F.A.; Navis, G.; Engberink, M.F.; Brink, E.J.; Geleijnse, J.M.; van Baak, M.A.; Gans, R.O.; Bakker, S.J. Dietary acid load and rapid progression to end-stage renal disease of diabetic nephropathy in Westernized South Asian people. J. Nephrol. 2011, 24, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, W.G.; Peacock, M.; Baker, M.; Marshall, D.H.; Pearlman, B.; Speed, R.; Sergeant, V.; Smith, A. Studies on the prevalence and epidemiology of urinary stone disease in men in Leeds. BJU Int. 1983, 55, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslau, N.A.; Brinkley, L.; Hill, K.D.; Pak, C.Y. Relationship of animal protein-rich diet to kidney stone formation and calcium metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 66, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekcharoensuk, C.; Osborne, C.A.; Lulich, J.P.; Pusoonthornthum, R.; Kirk, C.A.; Ulrich, L.K.; Koehler, L.A.; Carpenter, K.A.; Swanson, L.L. Association between dietary factors and calcium oxalate and magnesium ammonium phosphate urolithiasis in cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meschi, T.; Nouvenne, A.; Ticinesi, A.; Prati, B.; Guerra, A.; Allegri, F.; Pigna, F.; Soldati, L.; Vezzoli, G.; Gambaro, G.; et al. Dietary habits in women with recurrent idiopathic calcium nephrolithiasis. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, D.S.; Coe, F.L. Prevention of recurrent nephrolithiasis. Am. Fam. Physician 1999, 60, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finkielstein, V.A.; Goldfarb, D.S. Strategies for preventing calcium oxalate stones. CMAJ 2006, 174, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traxer, O.; Huet, B.; Poindexter, J.; Pak, C.Y.; Pearle, M.S. Effect of ascorbic acid consumption on urinary stone risk factors. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschi, T.; Maggiore, U.; Fiaccadori, E.; Schianchi, T.; Bosi, S.; Adorni, G.; Ridolo, E.; Guerra, A.; Allegri, F.; Novarini, A.; et al. The effect of fruits and vegetables on urinary stone risk factors. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.D.; Elinder, C.G.; Tiselius, H.G.; Wolk, A.; Åkesson, A. Ascorbic acid supplements and kidney stone incidence among men: A prospective study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, J.; Nair, R.; Peguero, A.; Courville, C. Vitamin C-induced oxalate nephropathy. Int. J. Nephrol. 2011, 2011, 146927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, J.L.; Martini, L.A.; Mendonça, C.O.G.; Schor, N.; Heilberg, I.P. Effect of calcium intake on urinary oxalate excretion in calcium stone-forming patients. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2002, 35, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curhan, G.C.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J. A prospective study of dietary calcium and other nutrients and the risk of symptomatic kidney stones. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendse, A.K.; Singh, P.P. The etiology of urolithiasis in Udaipur (Western part of India). Urol. Res. 1986, 14, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siener, R.; Ebert, D.; Nicolay, C.; Hesse, A. Dietary risk factors for hyperoxaluria in calcium oxalate stone formers. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, R.P.; Goodman, H.O.; Assimos, D.G. Contribution of dietary oxalate to urinary oxalate excretion. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.N.; Curhan, G.C. Oxalate intake and the risk for nephrolithiasis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urivetzky, M.; Kessaris, D.; Smith, A.D. Ascorbic acid overdosing: A risk factor for calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchieri, A.; Nespoli, R.; Ostini, F.; Rovera, F.; Zanetti, G.; Pisani, E. A study of dietary calcium and other nutrients in idiopathic renal calcium stone formers with low bone mineral content. J. Urol. 1998, 159, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, L.K.; Liebman, M.; Kynast-Gales, S.A. Ascorbate increases human oxaluria and kidney stone risk. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, P.M.; Curhan, G.C.; Gambaro, G.; Taylor, E.N. Total, dietary, and supplemental vitamin C intake and risk of incident kidney stones. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, P.; Charransol, G.; Gregoire, I.; Daigre, J.L.; Coevoet, B.; Makdassi, R.; Pruna, A.; Locquet, P.; Sueur, J.P.; Fournier, A. Effect of calcium restriction on renal excretion of oxalate and the probability of stones in the various pathophysiological groups with calcium stones. J. Urol. 1983, 130, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curhan, G.C.; Willett, W.C.; Speizer, F.E.; Spiegelman, D.; Stampfer, M.J. Comparison of dietary calcium with supplemental calcium and other nutrients as factors affecting the risk for kidney stones in women. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 126, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, R.P.; Rafferty, K. Carbonated beverages and urinary calcium excretion. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselman, M.; Verkoelen, C.F. Fructose intake as a risk factor for kidney stone disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, T.M.; Basso, O.; Darden, R.; Sandler, D.P. Carbonated beverages and chronic kidney disease. Epidemiology (Camb. Mass.) 2007, 18, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.T.; Wang, C.Y.; Sakhaee, K.; Brinkley, L.; Pak, C.Y. Effect of low-carbohydrate high-protein diets on acid-base balance, stone-forming propensity, and calcium metabolism. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 40, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.U.; Dumoulin, G.T.H.M.; Henriet, M.T.; Regnard, J. Increase in urinary calcium and oxalate after fructose infusion. Horm. Metab. Res. 1995, 27, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.; Malhotra, S.R. Assessment of mineral intake by kidney stone patients of Kangra District, Himachal Pradesh with respect to their gender, age and income. Indian J. Pediatr. 2013, 80, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Jee, J.; Joung, J.Y.; Cho, Y.Y.; Sohn, S.Y.; Jin, S.; Hur, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Chung, J.H.; et al. High dietary sodium intake assessed by 24-hour urine specimen increase urinary calcium excretion and bone resorption marker. J. Bone Metab. 2014, 21, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzel, U.S.; Massey, L.K. Excess dietary protein can adversely affect bone. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, S.; Nobile, M.; Sartori, L.; Dalle Carbonare, L.; Ciuffreda, M.; Corrò, P.; D'Angelo, A.; Calò, L.; Crepaldi, G. Acute effects of moderate dietary protein restriction in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria and calcium nephrolithiasis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z. The change of human Na+/dicarboxylate co-transporter 1 expression in the kidney and its relationship with pathogenesis of nephrolithiasis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2001, 81, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambühl, P.M. Protein intake in renal and hepatic disease. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2011, 81, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speedy, A.W. Global production and consumption of animal source foods. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 4048S–4053S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, M.D. Calcium intake and urinary stone disease. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2014, 3, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nouvenne, A.; Meschi, T.; Guerra, A.; Allegri, F.; Prati, B.; Borghi, L. Dietary treatment of nephrolithiasis. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2008, 5, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Klett, D.E.; Littleton, R.; Elder, J.S.; Sammon, J.D. Role of insulin resistance in uric acid nephrolithiasis. World J. Nephrol. 2014, 3, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.L.; Stanhope, K.L.; Schwarz, J.M.; Graham, J.L.; Hatcher, B.; Griffen, S.C.; Bremer, A.A.; Berglund, L.; McGahan, J.P.; Keim, N.L.; et al. Consumption of fructose- but not glucose sweetened beverages for 10 weeks increases circulating concentrations of uric acid, retinol binding protein-4, and gamma-glutamyl transferase activity in overweight/obese humans. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Misra, A. Sugar intake, obesity, and diabetes in India. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5955–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouvenne, A.; Meschi, T.; Prati, B.; et al. Effects of a low-salt diet on idiopathic hypercalciuria in calcium-oxalate stone formers: A 3-mo randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemann, J., Jr. Pathogenesis of idiopathic hypercalciuria and nephrolithiasis. In Disorders of Bone and Mineral Metabolism; Coe, F.L., Favus, M.J., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 685–706. [Google Scholar]
- Sabto, J.; Powell, M.J.; Breidahl, M.J.; Gurr, F.W. Influence of urinary sodium on calcium excretion in normal individuals. A redefinition of hypercalciuria. Med. J. Aust. 1984, 140, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaine, J.; Chonchol, M.; Levi, M. Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemann, J.; Pleuss, J.A.; Gray, R.W.; Hoffmann, R.G. Potassium administration increases and potassium deprivation reduces urinary calcium excretion in healthy adults. Kidney Int. 1991, 39, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldowney, F.P.; Freaney, R.; Moloney, M.F. Importance of dietary sodium in the hypercalciuria syndrome. Kidney Int. 1982, 22, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, J.; Rubinger, D.; Friedlaender, M.M.; Popovtzer, M.M. Sodium dependent idiopathic hypercalciuria in renal-stone formers. Lancet 1983, 322, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zisman, A.L.; Coe, F.L.; Worcester, E.M. Kidney stones: An update on current pharmacological management and future directions. Exp. Opin. Pharmacother. 2013, 14, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.; Jiang, J.; Wood, K.D.; Holmes, R.P.; Assimos, D.G. Oxalate and sucralose absorption in idiopathic calcium oxalate stone formers. Urology 2011, 78, 475.e9–475.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, L.K.; Roman-Smith, H.; Sutton, R.A. Effect of dietary oxalate and calcium on urinary oxalate and risk of formation of calcium oxalate kidney stones. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 1993, 93, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.C.; Assimos, D.G. Uric acid nephrolithiasis: Recent progress and future directions. Rev. Urol. 2007, 9, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, A.; Siener, R. Current aspects of epidemiology and nutrition in urinary stone disease. World J. Urol. 1997, 15, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, M.; Bankura, B.; Ghosh, S.; Pattanayak, A.K.; Ghosh, S.; Pal, D.K.; Puri, A.; Kundu, A.K.; Das, M. Polymorphisms in CaSR and CLDN14 genes associated with increased risk of kidney stone disease in patients from the eastern part of India. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evan, A.P. Physiopathology and etiology of stone formation in the kidney and the urinary tract. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, A.; Mandressi, A.; Luongo, P.; Longo, G.; Pisani, E. The influence of diet on urinary risk factors for stones in healthy subjects and idiopathic renal calcium stone formers. BJU Int. 1991, 67, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolbert, N.E. Microbodies-peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1971, 22, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Segal, A.M.; Seifter, J.L.; Dwyer, J.T. Nutritional management of kidney stones (nephrolithiasis). Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.V.; Kälin, A.; Drouve, U.; Casez, J.P.; Jaeger, P. Sensitivity to meat protein intake and hyperoxaluria in idiopathic calcium stone formers. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.T.; Reiser, S.; Fields, M. Dietary fructose as compared to glucose and starch increases the calcium content of kidney of magnesium-deficient rats. J. Nutr. 1989, 119, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.T.; Min, K.W. Fructose precipitates calcium phosphate in the kidneys of female rats fed magnesium-deficient diets. Magnes. Res. 1991, 4, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Yatabe, M.S.; Yatabe, J.; Takano, K.; Murakami, Y.; Sakuta, R.; Abe, S.; Sanada, H.; Kimura, J.; Watanabe, T. Effects of a high-sodium diet on renal tubule Ca2+ transporter and claudin expression in Wistar-Kyoto rats. BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, C.Y.; Britton, F.; Peterson, R.; Ward, D.; Northcutt, C.; Breslau, N.A.; McGuire, J.; Sakhaee, K.; Bush, S.; Nicar, M.; et al. Ambulatory evaluation of nephrolithiasis: Classification, clinical presentation and diagnostic criteria. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, S.; Rodgers, A.L. Idiopathic calcium oxalate urolithiasis: Risk factors and conservative treatment. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 345, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, C.Y.; Kaplan, R.; Bone, H.; Townsend, J.; Waters, O. A simple test for the diagnosis of absorptive, resorptive and renal hypercalciurias. N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, L.C. Observations on the analysis of ten thousand urinary calculi. J. Urol. 1962, 88, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.N.; Curhan, G.C. Fructose consumption and the risk of kidney stones. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coe, F.L. Hyperuricosuric calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int. 1978, 13, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martillo, M.A.; Nazzal, L.; Crittenden, D.B. The crystallization of monosodium urate. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, R.; Xiang, Y.B.; Elasy, T.; Xu, W.H.; Cai, H.; Cai, Q.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.O. Purine-rich foods, protein intake, and the prevalence of hyperuricemia: The Shanghai Men’s Health Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, W.G.; Heyburn, P.J.; Peacock, M.; Hanes, F.A.; Swaminathan, R. The effect of high animal protein intake on the risk of calcium stone-formation in the urinary tract. Clin. Sci. 1979, 57, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, I.H.; Palella, T.D.; Kelley, W.N. Hyperuricemia: A marker for cell energy crisis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutchik, S.D.; Resnick, M.I. Cystine calculi: Diagnosis and management. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 24, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Agarwal, M.M.; Sharma, S. Medical therapy for calculus disease. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkin, M.E.; Preminger, G.M. Demystifying the medical management of nephrolithiasis. Rev. Urol. 2011, 13, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.M.; Singh, S.K.; Mavuduru, R.; Mandal, A.K. Preventive fluid and dietary therapy for urolithiasis: An appraisal of strength, controversies and lacunae of current literature. Indian J. Urol. 2011, 27, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerman, J.M.; Assimos, D.G. Hypocitraturia: Pathophysiology and medical management. Rev. Urol. 2009, 11, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.D.A.; Donzele, J.L.; de Oliveira Silva, F.C.; de Oliveira, R.F.M.; de Abreu, M.L.T.; Saraiva, A.; Haese, D.; Kill, J.L. Levels of digestible methionine+ cystine in diets for high genetic potential barrows from 95 to 125 kg. Rev. Bras. Zootech. 2011, 40, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worcester, E.M.; Coe, F.L.; Evan, A.P.; Parks, J.H. Reduced renal function and benefits of treatment in cystinuria vs other forms of nephrolithiasis. BJU Int. 2006, 97, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, Z.; Monga, M. Medical and dietary therapy for kidney stone prevention. Korean J. Urol. 2014, 55, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noce, A.; Vidiri, M.F.; Marrone, G.; Moriconi, E.; Bocedi, A.; Capria, A.; Rovella, V.; Ricci, G.; De Lorenzo, A.; Di Daniele, N. Is low-protein diet a possible risk factor of malnutrition in chronic kidney disease patients? Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Laville, M. Low Protein Diets for CHRONIC kidney Disease in Non Diabetic Adults; The Cochrane Library: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, V.; Kopple, J.D.; Wang, X.; Beck, G.J.; Collins, A.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Greene, T.; Levey, A.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Effect of a very low protein diet on outcomes: Long term follow-up of the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of protein energy wasting in non dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: Reconciling low protein intake with nutritional therapy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, E. Management of acute renal failure. Injury 2005, 1, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Rule, A.D.; Krambeck, A.E.; Lieske, J.C. Chronic kidney disease in kidney stone formers. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Appel, L.J.; Anderson, C.A.; Miller, E.R. Effect of a high-protein diet on kidney function in healthy adults: Results from the Omni Heart trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadeja, Y.P.; Kher, V. Protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease: An update with focus on nutritional interventions to improve outcomes. Indian J. Endocr. Metab. 2012, 16, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avesani, C.M.; Kamimura, M.A.; Cuppari, L. Energy expenditure in chronic kidney disease patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Bross, R.; Shapiro, B.B.; Morrison, G.; Kopple, J.D. Dietary energy requirements in relatively healthy maintenance hemodialysis patients estimated from long-term metabolic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, M.A.; Kawachi, I.; Berkman, L.F.; Subramanian, S.V. Is economic growth associated with reduction in child under nutrition in India? PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1000424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, C.M.J. Significance of diet in chronic kidney disease. J. Nephropharmacol. 2013, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoletti, R.; Cai, T.; Mondaini, N.; Melone, F.; Travaglini, F.; Carini, M.; Rizzo, M. Epidemiology and risk factors in urolithiasis. Urol. Int. 2007, 79 (Suppl. 1), 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, J.A.; Johnson, R.J.; Mazzali, M.; Beshensky, A.M.; Stietz, S.; Giachelli, C.; Liaw, L.; Alpers, C.E.; Couser, W.G.; Kleinman, J.G.; et al. Osteopontin is a critical inhibitor of calcium oxalate crystal formation and retention in renal tubules. JASN 2003, 14, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).