Extraction and Chromatographic Approaches for Coumarin, Furocoumarin, and Polymethoxyflavone Characterization in Foods
Abstract
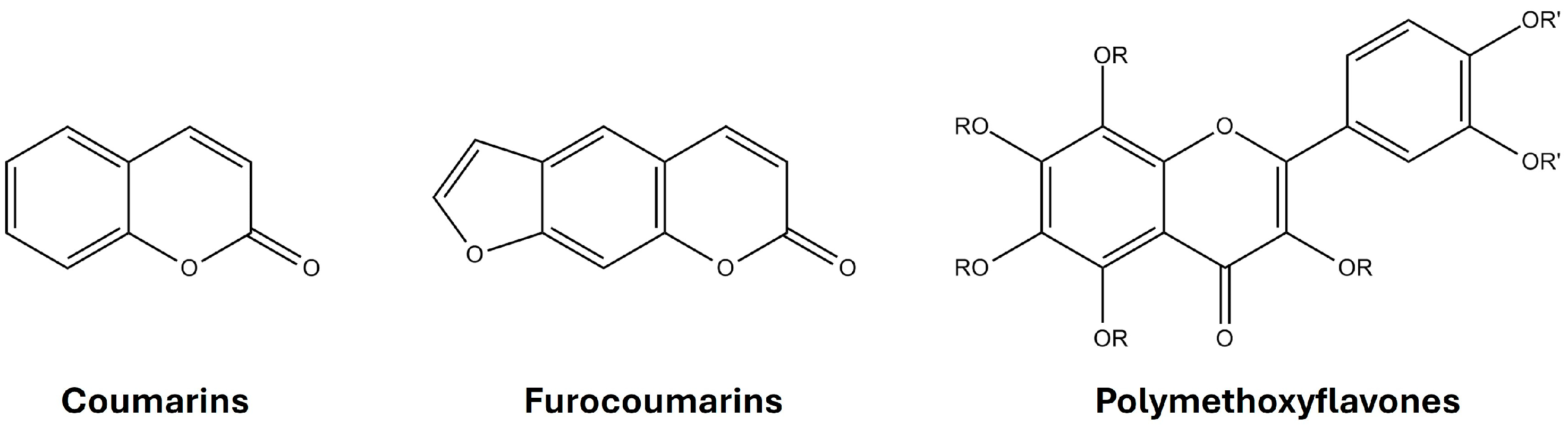
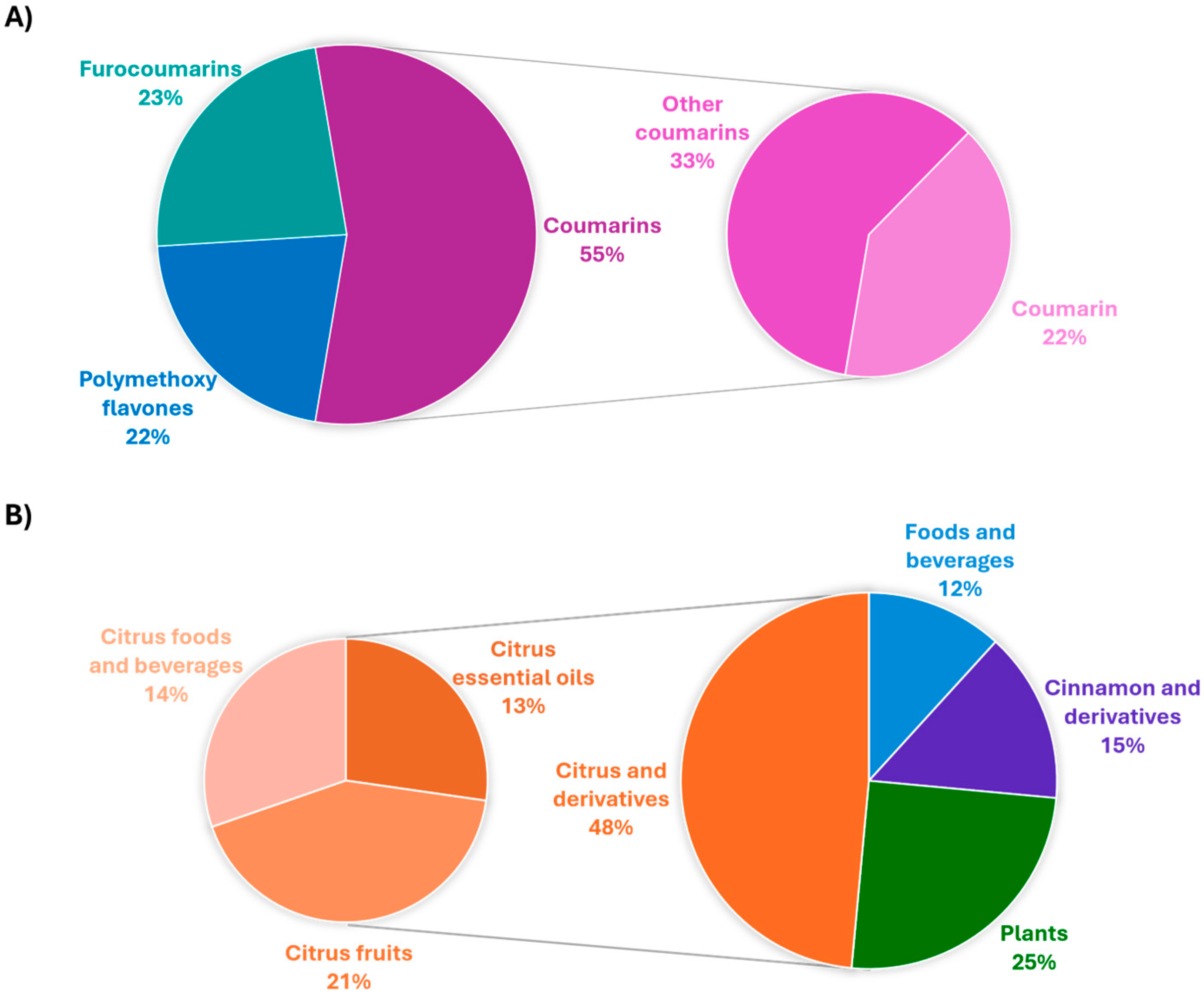
1. Introduction
Paper Selection
2. Extraction Methods
2.1. UAE
2.2. SLE
2.3. LLE
2.4. SPE
2.5. QuEChERS
2.6. SFE
2.7. Miscellanea
| Samples | OHCs | Extraction | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cachaças | Two Cs: 4-methylumbelliferone, coumarin | Filtration | HPLC-DAD | [29] |
| Wines and spirits | Six Cs: esculetin, scopoletin, fraxetin, umbelliferone, 4-methylumbelliferone, coumarin | Dilution | HPLC-HRMS | [30] |
| Citrus essential oils | Fifteen FCs: psoralen, bergapten, xanthotoxin, isopimpinellin, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, byakangelicol, byakangelicin, heraclenin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, bergamottin, imperatorin, isoimperatorin, phellopterin, and epoxybergamottin | Dilution | HPTLC | [31] |
| Cold-pressed Citrus essential oils | Ten Cs: aurapten, citropten, epoxyaurapten, herniarin, isomerazin, meranzin, meranzin hydrate, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin, 5-isopentenyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin, osthol; 15 FCs: bergamottin, bergapten, byakangelicin, byakangelicol, cnidicin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, isoimperatorin, isopimpinellin, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, phellopterin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, epoxybergamottin hydrate; 5 PMFs: nobiletin, sinensetin, tangeretin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, heptamethoxyflavone | Dilution | SFC-QqQ- MS/MS | [32] |
| Cold-pressed Citrus essential oils, Citrus-flavoured juices and beverages | Eigth Cs: coumarin, herniarin, meranzin, meranzin hydrate, citropten, epoxyaurapten, auraptene, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxy-coumarin; 21 FCs: 8-methoxypsoralen, byakangelicin, psoralen, oxypeucedanin hydrate, angelicin, isopimpinellin, heraclenin, oxypeucedanin, bergapten, byakangelicol, isobergapten, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, imperatorin, trioxalen, phellopterin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, isoimperatorin, cnidicin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, bergamottin; seven PMFs: sinensetin, nobiletin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 5-O-demethylnobiletin, tangeretin, gardenin A, gardenin B | Dilution | HPLC-QqQ- MS/MS | [33] |
| Mandarin essential oil | Five PMFs: tangeretin, nobiletin, sinensetin, tetra-O-methyl scutellarein, heptamethoxyflavone | Dilution | HPLC-PDA-MS | [34] |
| Cold-pressed Citrus essential oils | Nine Cs: coumarin, meranzin hydrate, herniarin, citropten, meranzin, isomeranzin, aurapten, epoxyaurapten, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 19 FCs: byakangelicin, 8-methoxypsoralen, psoralen, angelicin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, isopimpinellin, heraclenin, bergapten, isobergapten, byakangelicol, oxypeucedanin, imperatorin, phellopterin, cnidilin, isoimperatorin, epoxybergamottin, cnidicin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, bergamottin; seven PMFs: sinensetin, nobiletin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, tangeretin, 5-O-demethylnobiletin, gardenin A, gardenin B | Dilution | HPLC-PDA | [35] |
| Extra-virgin olive oils flavoured with aromatic plants | Four Cs: citropten, herniarin, meranzin, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 11 FCs: bergamottin, bergapten, byakangelicol, cnidicin, cnidilin, isoimperatorin, isopimpinellin, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, phellopterin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen; seven PMFs: gardenin A, gardenin B, nobiletin, sinensetin, tangeretin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 5-O-demethylnobiletin | Dilution | HPLC-MS/MS | [36] |
| Citrus essential oils | Two Cs: citropten, herniarin; 16 FCs: bergapten, psoralen, xanthotoxin, bergamottin, epoxybergamottin, byakangelicol, byakangelicin, isopimpinellin, imperatorin, isoimperatorin, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, heraclenin, phellopterin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, angelicin | Dilution | UHPLC-TOF- MS | [37] |
| Bergamot essential oil | Untargeted compounds | Dilution | Ambient MS | [38] |
| Citrus sinensis oil | Eight PMFs: sinensetin, hexamethoxyflavone, tetramethyl-O-isoscutellarein, nobiletin, tetramethyl-O-scutellarein, heptamethoxyflavone, 5-demethylnobiletin, tangeretin | Dilution | HPLC-DAD | [39] |
| Citrus essential oils | Ten Cs: meranzin hydrate, herniarin, citropten, meranzin, isomeranzin, epoxyaurapten, osthol, 5-isopentenyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin, aurapten, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 15 FCs: byakangelicin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, isopimpinellin, bergapten, byakangelicol, oxypeucedanin, isoimperatorin, imperatorin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, 5-(isopent-2′-eniloxy)-8-(2′,3′-epoxy)-isopentenyloxypsoralen, cnidicin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, 5-geranyloxy-8-methoxypsoralen, bergamottin; six PMFs: sinensetin, hexamethoxyflavone, nobiletin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, heptamethoxyflavone, tangeretin | Dilution | NanoUPLC- UV/EI-MS | [40] |
| Cinnamomum cassia Blume bark | One C: coumarin | UAE | HPLC-DAD | [41] |
| Cinnamon flavoring powders | One C: coumarin | UAE | HPLC-UV | [42] |
| Cinnamon powders and sticks | One C: coumarin | UAE | HPLC-UV | [43] |
| Cinnamon, tea, breakfast cereal, milk rice, cinnamon bun | One C: coumarin | UAE | HPTLC | [44] |
| Citrus australasica L. peel and pulp | One C: coumarin | UAE | HPLC-QTOF- MS/MS | [45] |
| Juices, beverages, jams, bakery products flavored with Citrus and cinnamon | Nine Cs: coumarin, aurapten, citropten, epoxyaurapten, herniarin, isomerazin, meranzin, meranzin hydrate, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 15 FCs: 8-methoxypsoralen, bergamottin, bergapten, byakangelicin, byakangelicol, cnidicin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, isoimperatorin, isopimpinellin, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, phellopterin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, psoralen; four PMFs: nobiletin, sinensetin, tangeretin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein | UAE LLE | SFC-QqQ- MS/MS | [46] |
| Citrus-flavored beverages and jams | Eight Cs: aurapten, citropten, epoxyaurapten, herniarin, isomeranzin, meranzin, meranzin hydrate, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 20 FCs: angelicin, bergamottin, bergapten, byakangelicin, byakangelicol, cnidicin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, heraclenin, imperatorin, isobergapten, isoimperatorin, isopimpinellin, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, phellopterin, psoralen, trioxsalen, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen; Seven PMFs: gardenin A, gardenin B, nobiletin, sinensetin, tangeretin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 5-O-demethylnobiletin | UAE LLE | HPLC-MS/MS | [47] |
| Pummelo fruits | Four Cs: umbelliferone, scoparone, limettin, isomeranzin; eight FCs: psoralen, bergaptol, xanthotoxin, bergapten, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, imperatorin, isoimperatorin, 6′,7′-epoxybergamottin; eight PMFs: eupatorin-5-methylether, sinensetin, 3′,4′,5,5′,6,7-heptamethoxyflavone, nobiletin, 5-hydroxy-7,8,4′-trimethoxyflavone, tangeretin, 5-hydroxy-3′,4′,7-trimethoxyflavone, 5-hydroxy-3,7,3′,4′-tetramethoxyflavone | UAE | UHPLC-QqQ- MS/MS | [48] |
| Satsuma mandarin peels and pulp | Eight Cs: umbelliferone, isomeranzin, scoparone, meranzin hydrate, limettin, scopoletin, aurapten, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 11 FCs: bergaptol, psoralen, isopsoralen, xanthotoxin, bergapten, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, imperatorin, isoimperatorin, 6′,7′-epoxybergamottin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, bergamottin; nine PMFs: 5-hydroxy-7,8,4′-trimethoxyflavone, eupatorin-5-methylether, 5,7,3′,4′-tetramethoxyflavone, 5,3′-dihydroxy-3,6,7,4′-tetramethoxyflavone, 5-demethylnobiletin, 3′,4′,5,5′,6,7-hexamethoxyflavone, sinensetin, tangeretin, nobiletin | UAE | HPLC-QqQ- MS | [49] |
| Artemisia annua | Two Cs: scopolin, scopoletin | UAE | HPLC-DAD | [50] |
| Heracleum sphondylium L. and Aesculus hippocastanum L. | Six Cs: coumarin, scoparone, isoscopoletin, esculin, esculetin, umbelliferone; six FCs: xanthotoxin, byakangelicin, isopimpinellin, bergapten, phellopterin, xanthotoxol | UAE | MEKC | [51] |
| Shiranuhi fruit and peels | One PMF: tetramethyl-O-scutellarein | SLE | MPLC | [53] |
| Melilotus officinalis L. and propolis | Nine Cs: esculin, daphnetin, fraxetin, umbelliferone, 4-methylumbelliferone, 4-hydroxycoumarin, scoparone, coumarin, herniarin | SLE | UHPLC-UV- FLD | [54] |
| Sweet clover herb, hay, and spoiled hay | Three Cs: dicumarol, coumarin and 4-hydroxycoumarin | SLE | HPLC-DAD | [55] |
| Citrus fruits | One PMF: nobiletin | SLE | HPLC-UV | [56] |
| Citrus peels | Thirteen Cs: trihydroxycoumarin hexoside, trihydroxycoumarin hexoside isomer, methoxy-trihydroxycoumarin hexoside, methoxy-trihydroxycoumarin hexoside isomer, methoxy-umbelliferone-hexoside, methoxy-trihydroxycoumarin hexoside isomer, dimethoxy-umbelliferone hexoside, benzyl-methyl-cyclohexanecarboxylateumbelliferone pentoside, umbelliferone, hydroxy-trimethoxy-methylchromen-4-one, allyloxy-dimethylcoumarin, aurapten, aurapten isomer; one FC: epoxybergamottin; seven PMFs: tetrahydroxy-dimethoxyflavone, dihydroxy-dimethoxyflavone, dihydroxy-trimethoxyflavone, dihydroxy-trimethoxyflavone isomer, dihydroxy-methoxyflavanone, dihydroxy-tetramethoxyflavone, hydroxy-pentamethoxyflavone | SLE | UPLC-QTOF- MS/MS | [57] |
| Vanilla extracts | One C: coumarin | SLE | MID-FTIR | [58] |
| Citrus sinensis peels | Six PMFs: 8-hydroxy-3,4′,5,6,7-pentamethoxyflavone, 5-hydroxy-6,7,8,3′,4′-pentamethoxyflavone, tangeretin, nobiletin, 3-methoxynobiletin, 7-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy-3, 4′-methylenedioxyflavone | SLE | TLC | [59] |
| Citrus-flavored beers | Seven Cs: aurapten, citropten, epoxyaurapten, herniarin, isomeranzin, meranzin hydrate, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 16 FCs: angelicin, bergamottin, bergapten, byakangelicin, byakangelicol, cnidicin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, heraclenin, isoimperatorin, isopimpinellin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, phellopterin, psoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen, 8-geranyloxypsoralen; seven PMFs: gardenin A, gardenin B, nobiletin, sinensetin, tangeretin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 5-O-methylnobiletin | LLE | HPLC-MS/MS | [60] |
| Citrus and herbliquors | Eight Cs: coumarin, herniarin, meranzin, meranzin hydrate, citropten, epoxyaurapten, auraptene, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxy-coumarin; 21 FCs: 8-methoxypsoralen, byakangelicin, psoralen, oxypeucedanin hydrate, angelicin, isopimpinellin, heraclenin, oxypeucedanin, bergapten, byakangelicol, isobergapten, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, imperatorin, trioxalen, phellopterin, cnidilin, epoxybergamottin, isoimperatorin, cnidicin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, bergamottin; seven PMFs: sinensetin, nobiletin, tetra-O-methylscutellarein, 5-O-demethylnobiletin, tangeretin, gardenin A, gardenin B | LLE | HPLC-QqQ- MS/MS | [61] |
| Citrus juices | Five Cs: scopoletin, citropten, meranzin, isomeranzin, osthol; 6 FCs: bergaptol, bergapten, oxypeucedanin, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, epoxybergamottin, bergamottin; four PMFs: sinensetin, nobiletin, heptamethoxyflavone, tangeretin | SPE | HPLC-PDA- FLD | [62] |
| Citrus juices | Twelve Cs: scopoletin, umbelliferone, herniarin, meranzin, isomeranzin, meranzin hydrate, citropten, auraptenol, marmin, osthol, aurapten, 5-geranoxy-7-methoxycoumarin; 16 FCs: heraclenol, bergaptol, oxypeucedanin hydrate, byakangelicin, bergapten, heraclenin, isosinensetin, byakangelicol, oxypeucedanin, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, imperatorin, phellopterin, isoimperatorin, 6′,7′-epoxybergamottin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, bergamottin; eight PMFs: sinensetin, tetramethyl-O-isoscutellarein, nobiletin, tetramethyl-O-scutellarein, heptamethoxyflavone, tangeretin, 5-demethylnobiletin, 5-demethyltangeretin | SPE | HPLC-PDA- FLD | [63] |
| Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima peels | Three PMFs: nobiletin, tangeretin, 5-demethylnobiletin | SPE | HSCCC | [64] |
| Sweet clover herb, hay, and spoiled hay | One C: dicoumarol | SPE | HPLC-DAD | [65] |
| Tokaj wine | Six Cs: esculin, coumarin, herniarin, 4-methylumbelliferone, scoparone, scopoletin | SPE | HPLC-DAD- FLD | [66] |
| Cinnamon foods and plants (lavender, chamomile, archangel) | Three Cs: coumarin, 7-hydroxycoumarin, 7-methoxycoumarin | SPE | HPLC-DAD | [67] |
| Soft drink, biscuits, sesame paste | Six Cs: coumarin, 7-methoxycoumarin, 7-methylcoumarin, 7-diethylaminocoumarin, pyranocoumarin, 3,3′-carbonylbis (7-diethylaminocoumarin) | SPE | HPLC-MS/MS | [68] |
| Tsoureki, cinnamon biscuit, panettone | One C: coumarin | SPE | HPLC-DAD | [69] |
| Citrus paradisi Macf. fruit and juice | Seven FCs: bergaptol, psoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen, bergapten, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, epoxybergamottin, bergamottin | QuEChERS | UPLC-MS/MS | [70] |
| Foods and beverages, with Citrus, figs, vegetables, herbs, and spices | Seven FCs: bergaptol, psoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen, bergapten, 6′,7′-dihydroxybergamottin, epoxybergamottin, bergamottin | QuEChERS | UPLC-MS/MS | [71] |
| Cinnamon bakery products | One C: coumarin | QuEChERS | GC-MS | [72] |
| Helichrysum italicum flowers | One C: scopoletin | SFE | HPLC-UV | [73] |
| Citrus unshiu peels | One PMF: nobiletin | SFE | HPLC-UV-Vis | [75] |
| Citri reticulatae pericarpium | Three PMFs: nobiletin, 3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-heptamethoxyflavone, tangeretin | SFE | HPLC-DAD | [76] |
| Pithecellobium dulce bark | One FC: bergapten | MAE | HPLC-UV/Vis | [77] |
| Cinnamomum verum bark | One C: coumarin | Soxhlet extraction | UHPLC-QqQ- MS/MS | [78] |
| Prangos pabularia essential oil | One C: suberosin | Hydrodistillation with Clevenger | GC-FID GC-MS | [79] |
| Geijera parviflora leaves | Three Cs: osthol, scoparone, xanthyletin; one FC: isopsoralen | SLE | GC-MS | [80] |
| Cassia cinnamon, chamomile tea, Tokaj wines | Seven Cs: 6,7-dihydroxycoumarin, 7,8-dihydroxy-6-methoxycoumarin, 7-hydroxycoumarin, 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin, 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin, coumarin, 7-methoxycoumarin | on-line MISPE | HPLC-DAD | [81] |
| Matricaria chamomilla | Two Cs: herniarin, umbelliferone | Maceration | HPLC-PDA | [82] |
| Lemon and persian lime | Three Cs: herniarin, citropten, 5 geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin; eight FCs: oxypeucedanin hydrate, isopimpinellin, bergapten, bergamottin, byakangelicol, oxypeucedanin, 8-geranyloxypsoralen, 5-geranyloxy-8-methoxypsoralen | UAE LLE | HPLC-DAD | [83] |
| Angelica dahurica roots | Two Cs: osthol, umbelliferone; six FCs: angelicin, imperatorin, xanthotoxin, isoimperatorin, oxypeucedanin, xanthotoxol | UAE | SFC-PDA | [84] |
| Ammi visnaga (L.) Lam. fruits | Five Cs: dihydrosamidin, visnadin, samidin, khellin, visnagin | UAE | SFC-PDA | [85] |
| Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson fruits | One C: osthol; one FC: imperatorin | SLE | SP-SFC- UV/Vis | [86] |
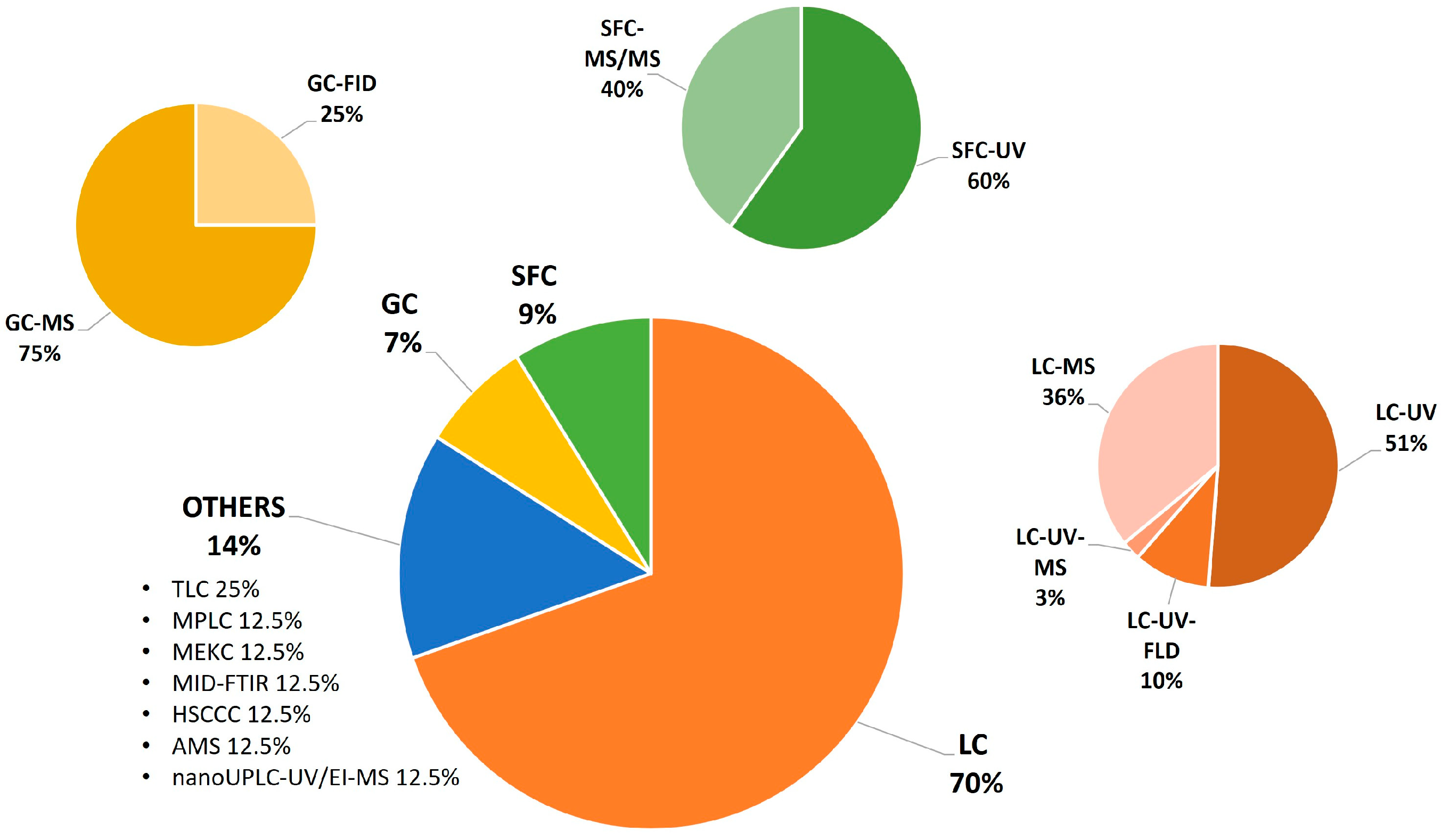
3. Analytical Methods Used to Characterize OHCs
3.1. Gas Chromatography Methods
3.2. Liquid Chromatography Methods
3.2.1. HPLC Coupled with Spectrophotometric Detectors
3.2.2. HPLC Coupled with Mass Spectrometer Detectors
3.3. Supercritical Fluid Chromatographic Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matos, M.J.; Santana, L.; Uriate, E.; Abreu, O.A.; Molina, E.; Guardado Yordi, E. Coumarins—An important class of phytochemicals. In Phytochemicals—Isolation, Characterisation and Role in Human Health; Chapter 5; Rao, A.V., Rao, L.G., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; pp. 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncar, M.; Jakovljevic, M.; Subaric, D.; Pavlic, M.; Buzjak Sluzek, V.; Cindric, I.; Molnar, M. Coumarins in food and methods of their determination. Foods 2020, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Girolamo, A.; Lippolis, V.; Pascale, M. Overview of recent liquid chromatography mass spectrometry-based methods for natural toxins detection in food products. Toxins 2022, 14, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.-H.; Feng, X.-S. Progress in pretreatment and analytical methods of coumarins: An update since 2012—A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 503–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, A.; Báidez, A.; Gómez, P.; Arcas, M.C.; Porras, I.; García-Lidón, A.; Del Río, J.A. Citrus paradisi and Citrus sinensis flavonoids: Their influence in the defence mechanism against Penicillium digitatum. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Guo, H.; Geng, F.; Zhuang, Q.; Li, H.; Wu, D. Natural sources, refined extraction, biosynthesis, metabolism, and bioactivities of dietary polymethoxyflavones (PMFs). Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Aslam, M.; Imran, M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Saeed, F.; Khursheed, T.; Umar, M.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Al Ghorab, A.H.; Alsagaby, S.A.; et al. Polymethoxyflavones: An updated review on pharmacological properties and underlying molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 866–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on Cosmetic Products (Recast). Official Journal of the European Union, L 342/59, 22 December 2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- International Fragrance Association. IFRA Standard. 48th Amendment—Citrus Oils and Other Furocoumarins Containing Essential Oils. 2015. Available online: https://ifrafragrance.org/standards/IFRA_STD48_0174.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Lake, B.G. Coumarin metabolism, toxicity and carcinogenicity: Relevance for human risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 423–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotland, T.; Paulsen, J.E.; Sanner, T.; Alexander, J.; Husøy, T. Risk assessment of coumarin using the bench mark dose (BMD) approach: Children in Norway which regularly eat oatmeal porridge with cinnamon may exceed the TDI for coumarin with several folds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Coumarin in flavourings and other food ingredients with flavouring properties-scientific opinion of the panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC). EFSA J. 2004, 6, 793. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/793 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- European Parliament. Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on flavourings and certain food ingredients with flavouring properties for use in and on foods and amending Council Regulation (EEC) No 1601/91, Regulations (EC) No 2232/96 and (EC) No 110/2008 and Directive 2000/13/EC. Official Journal of the European Union 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:354:0034:0050:en:PDF (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Heghes, S.C.; Vostinaru, O.; Mogosan, C.; Miere, D.; Iuga, C.A.; Filip, L. Safety Profile of Nutraceuticals Rich in Coumarins: An Update. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 803338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Fragrance Association. IFRA Standard. 49th Amendment—Coumarin. 2020. Available online: https://ifrafragrance.org/docs/default-source/ifra-code-of-practice-and-standards/49th-amendment/ifra-49th-amendment-(att-04)---index-of-ifra-standards.pdf?sfvrsn=6269aaf4_3 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- International Fragrance Association. IFRA Standard. 49th Amendment—Citrus Oils and Other Furocoumarins Containing Essential Oils. 2020. Available online: https://ifrafragrance.org/standards/IFRA_STD_089.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Elmusa, F.; Elmusa, M. Mini-review on coumarins: Sources, biosynthesis, bioactivity, extraction and toxicology. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2024, 11, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, G.; Pinto, M.I.; Noronha, J.P.; Burrows, H.D. Analysis of food by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with coulometric detection and related techniques: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4113–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Alves, S.; Lourenco, S.; Fernandes, T.A.; Canas, S. Coumarins in spirit beverages: Sources, quantification, and their involvement in quality, authenticity and food safety. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.-H.; Zhang, J.-W.; Feng, X.-S. Supercritical fluid chromatography—A technical overview and its applications in medicinal plant analysis: An update covering 2012–2018. Analyst 2019, 144, 5324–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzera, M.; Zwerger, M. Analysis of natural products by SFC—Applications from 2015 to 2021. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulaev, V.; Isaac, G. Supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry—A metabolomics perspective. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1092, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepthi, G.; Mahathi, T.; Madhavi Latha, T.; Laya, G.; Lavanya, N.; Mamatha, S.; Lokesh, V. Review on the usefulness of advanced chromatographic analytical methods for determination of herbal molecules. Int. J. Drug Del. Nonotech. 2023, 13, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sherma, J.; Rabel, F. A review of thin layer chromatography methods for determination of authenticity of foods and dietary supplements. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2018, 41, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrianidi, A. A classification of liquid chromatography mass spectrometry techniques for evaluation of chemical composition and quality control of traditional medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Rigano, F.; Arigò, A.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Coumarins, psoralens and polymethoxyflavones in cold-pressed Citrus essential oils: A review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2021, 33, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFRA. IFRA Analytical Method—Quantitative Determination of Furocoumarins by HPLC-DAD. 2013. Available online: https://ifrafragrance.org/docs/default-source/guidelines/il958-12-04-2013-(att01)-quantitative-determination-of-furocoumarins-by-hplc-dad.pdf?sfvrsn=79de4d02_2 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Nowak, P.M.; Koscielniak, P. What color is your method? Adaptation of the RGB additive color model to analytical method evaluation. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10343–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, W.D.; Cardoso, M.G.; Nelson, D.L. Cachaça stored in casks newly constructed of oak (Quercus sp.), amburana (Amburana cearensis), jatoba (Hymenaeae carbouril), balsam (Myroxylon peruiferum) and peroba (Paratecoma peroba): Alcohol content, phenol composition, colour intensity and dry extract. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstel, D.; Gautier, E.; Marchal, A. Role of Oak Coumarins in the Taste of Wines and Spirits: Identification, Quantitation, and Sensory Contribution through Perceptive Interactions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7434–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Borgne, E.; Cicchetti, E.; Bertrand, T. HPTLC methods for qualitative and quantitative analysis of selected furocoumarins in essential oils. Flavour Fragr. J. 2017, 32, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigò, A.; Russo, M.; Testa Camillo, M.R.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Zoccali, M. Supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry of oxygen heterocyclic compounds in Citrus essential oils. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4821–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cafeo, G.; Russo, M.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, P. Quantitative analysis of oxygen heterocyclic compounds using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry, method development and environmental assessment. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Rigano, F.; Arigò, A.; Sciarrone, D.; Calabrò, M.L.; Farnetti, S.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Rapid isolation, reliable characterization, and water solubility improvement of polymethoxyflavones from cold-pressed mandarin essential oil. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arigò, A.; Rigano, F.; Micalizzi, G.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Oxygen heterocyclic compound screening in Citrus essential oils by linear retention index approach applied to liquid chromatography coupled to photodiode array detector. Flavour Fragr. J. 2019, 34, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, E.; Russo, M.; Cucinotta, L.; El Majdoub, Y.O.; Testa Camillo, M.R.; De Grazia, G.; Arigò, A.; Sciarrone, D.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, P. Quality Evaluation of Flavoured Extra-Virgin Olive Oils According to Their Chemical Composition. Food Anal. Methods 2023, 16, 1313–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, J.; Liberto, E.; Beolor, J.C.; Brevard, H.; Bicchi, C.; Rubiolo, P. Oxygenated heterocyclic compounds to differentiate Citrus spp. essential oils through metabolomic strategies. Food Chem. 2016, 206, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, D.; Di Donna, L.; Mazzotti, F.; Tagarelli, A.; Napoli, A.; Furia, E.; Sindona, G. Rapid discrimination of bergamot essential oil by paper spray mass spectrometry and chemometric analysis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.J.; Tan, X.; Zhai, Y.L.; Wang, Q.; Gao, F.J.; Liu, G.L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H. Prophylactic Effects of Polymethoxyflavone-Rich Orange Peel Oil on Nω-Nitro-L-Arginine-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigano, F.; Russo, M.; Arigò, A.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Combining linear retention index and electron ionization mass spectrometry for a reliable identification in nano liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1610, 460581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, R.; Al-Zehouri, J. Determination of coumarin in methanol extract of cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia Blume) using reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 726–729. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Liu, W.; Babajanian, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, P.; Swanson, G. Development and Validation of a UPLC-DAD Method for Quantitative Analysis of Coumarin, trans-Cinnamic Acid, trans-Cinnamaldehyde, and Eugenol in Encapsulated Cinnamon Flavoring Powder. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pages-Rebull, J.; Sagristà, G.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Application of HPLC-UV combined with chemometrics for the detection and quantification of ‘true cinnamon’ adulteration. Talanta 2024, 271, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, S.; Winheim, L.; Morlock, G.E. Planar chromatographic screening and quantification of coumarin in food, confirmed by mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, R.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Rai, D.K. Comprehensive Characterization and Quantification of Antioxidant Compounds in Finger Lime (Citrus australasica L.) by HPLC-QTof-MS and UPLC-MS/MS. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafeo, G.; Satira, A.; Russo, M.; Mondello, M.; Dugo, P. Determination of Oxygen Heterocyclic Compounds in Foods Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigò, A.; Rigano, F.; Russo, M.; Trovato, E.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Dietary Intake of Coumarins and Furocoumarins through Citrus Beverages: A Detailed Estimation by a HPLC-MS/MS Method Combined with the Linear Retention Index System. Foods 2021, 10, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Guo, P.M.; Pang, W.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Jiao, B.N.; Kilmartin, P.A. A rapid UHPLC-QqQ-MS/MS method for the simultaneous qualitation and quantitation of coumarins, furocoumarins, flavonoids, phenolic acids in pummelo fruits. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Pang, W.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiao, B. A rapid UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS method for targeted screening and quantitative analysis of secondary metabolites in satsuma mandarin. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Yu, P.; Wang, M.; Qiu, F. Phytochemical analysis and geographic assessment of flavonoids, coumarins and sesquiterpenes in Artemisia annua L. based on HPLC-DAD quantification and LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS confirmation. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresler, S.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Kováčik, J.; Kubrak, T.; Strzemski, M.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Rysiak, A.; Sowa, I. Separation and determination of coumarins including furanocoumarins using micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. Talanta 2018, 187, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priego-Capote, F. Solid—Liquid extraction techniques. In Analytical Sample Preparation with Nano- and Other High-Performance Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.M.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, J.E.; An, H.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Hyun, C.; Lee, N.H. Tetramethyl-O-scutellarin isolated from peels of immature Shiranuhi fruit exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machyňáková, A.; Hroboňová, K. Simultaneous determination of coumarin derivatives in natural samples by ultra high performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 56, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hroboňová, K.; Sádecká, J.; Čižmárik, J. HPLC separation and determination of dicoumarol and other simple coumarins in sweet clover. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2018, 17, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayek, N.M.; el-Shazly, A.H.; Abdel-Monem, A.R.; Moussa, M.Y.; Abd-Elwahab, S.M.; El-Tanbouly, N.D. Comparative study of the hypocholesterolemic, antidiabetic effects of four agro-waste Citrus peels cultivars and their HPLC standardization. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayek, N.M.; Farag, M.A.; Abdel Monem, A.R.; Moussa, M.Y.; Abd-Elwahab, S.M.; El-Tanbouly, N.D. Comparative Metabolite Profiling of Four Citrus Peel Cultivars via Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight-Mass Spectrometry and Multivariate Data Analyses. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2019, 57, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ley, C.M.; Hernández-Martínez, D.M.; Osorio-Revilla, G.; Tapia-Ochoategui, A.P.; Dávila-Ortiz, G.; Gallardo-Velázquez, T. Prediction of coumarin and ethyl vanillin in pure vanilla extracts using MID-FTIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Talanta 2019, 197, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul Naser, A.; Younis, E.; El-Feky, A.; Elbatanony, M.; Hamed, M. Management of Citrus sinensis peels for protection and treatment against gastric ulcer induced by ethanol in rats. Biomarkers 2020, 25, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovato, E.; Arigò, A.; Vento, F.; Micalizzi, G.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Influence of Citrus Flavor Addition in Brewing Process: Characterization of the Volatile and Non-Volatile Profile to Prevent Frauds and Adulterations. Separations 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafeo, G.; Salerno, T.M.G.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, P.; Russo, M. Miniaturized extraction, fast and sustainable chromatographic approach for determination of oxygen heterocyclic compounds in alcoholic beverages. Green Anal. Chem. 2024, 10, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.J.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Hung, W.L.; Rouseff, R.L. Determination of citrus juice coumarins, furanocoumarins and methoxylated flavones using solid phase extraction and HPLC with photodiode array and fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rouseff, R.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, H. Comprehensive identification and distribution pattern of 37 oxygenated heterocyclic compounds in commercially important citrus juices. LWT 2021, 152, 112351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zang, W.; Ji, S.; Cao, J.; Sun, C. Three Polymethoxyflavones Purified from Ougan (Citrus reticulata Cv. Suavissima) Inhibited LPS-Induced NO Elevation in the Neuroglia BV-2 Cell Line via the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrobonová, K.; Machynáková, A.; Cizmárik, J. Determination of dicoumarol in Melilotus officinalis L. by using molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1539, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hroboňová, K.; Sádecká, J. Coumarins content in wine: Application of HPLC, fluorescence spectrometry, and chemometric approach. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machynakova, A.; Hrobonova, K. Preparation and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective extraction of coumarins from food and plant samples. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.M.; Li, Y.L.; Xu, X.L.; Chen, F.M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D. Application of urea-based magnetic covalent organic framework as sorbent for the determination of coumarin and its derivatives in food samples combined with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiouri, N.P.; Ampatzi, N.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Samanidou, V.F. Development of a capsule phase microextraction methodology for the selective determination of coumarin in foodstuff analyzed by HPLC-DAD. Adv. Sample Prep. 2022, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, K.; Vance, T.M.; Perkins, C.; Provatas, A.; Wu, S.; Qureshi, A.; Cho, E.; Chun, O.K. Development of a comprehensive analytical method for furanocoumarins in grapefruit and their metabolites in plasma and urine using UPLC-MS/MS: A preliminary study. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melough, M.M.; Lee, S.G.; Cho, E.; Kim, K.; Provatas, A.A.; Perkins, C.; Park, M.K.; Qureshi, A.; Chun, O.K. Identification and Quantitation of Furocoumarins in Popularly Consumed Foods in the U.S. Using QuEChERS Extraction Coupled with UPLC-MS/MS Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5049–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, F.; Müller, C.; Stöckelhuber, M.; Bracher, F. Determination of coumarin in seasonal bakery products using QuEChERS and GC-MS. Pharm.-Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 72, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokić, S.; Rajić, M.; Bilić, B.; Molnar, M. Supercritical Extraction of Scopoletin from Helichrysum italicum (Roth) G. Don Flowers. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brondz, I.; Sedunov, B.; Sivaraman, N. Influence of Modifiers on Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) and Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE), Part I. Int. J. Anal. Mass Spectrom. Chromatogr. 2017, 5, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oba, C.; Ota, M.; Nomura, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Takito, J.; Sato, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Inomata, H. Extraction of nobiletin from Citrus unshiu peels by supercritical fluid and its CRE-mediated transcriptional activity. Phytomedicine 2017, 27, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.; Lv, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, S. Supercritical fluid CO2 extraction of three polymethoxyflavones from Citri reticulatae pericarpium and subsequent preparative separation by continuous high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1124, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katekhaye, S.D.; Laddha, K.S. Microwave-assisted Extraction and RP-HPLC Quantification of Bergapten from Pithecellobium dulce. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 78, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, R.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, B.; Rameshkumar, K.B. Quantification of coumarin and related phenolics in cinnamon samples from south India using UHPLC-ESI-QqQLIT-MS/MS method. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanca, N.; Tsikolia, M.; Ozek, G.; Ozek, T.; Ali, A.; Bernier, U.R.; Duran, A.; Baser, K.H.C.; Khan, I.A. The Identification of Suberosin from Prangos pabularia Essential Oil and Its Mosquito Activity against Aedes aegypti. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2016, 10, 311–325. [Google Scholar]
- Sadgrove, N.J.; Lyddiard, D.; Jones, G.L. Bioactive volatiles from Geijera parviflora Lindl. (Rutaceae): Evidence for coumarin chemotypes. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1125, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machynáková, A.; Lhotská, I.; Hrobonová, K.; Satínsky, D. On-line coupling of molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction with liquid chromatography for the fast determination of coumarins from complex samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, M.; Mendešević, N.; Šubarić, D.; Banjari, I.; Jokić, S. Comparison of various techniques for the extraction of umbelliferone and herniarin in Matricaria chamomilla processing fractions. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungen, M.; Lotz, P.; Patz, C.D.; Steingass, C.B.; Schweiggert, R. Coumarins, psoralens, and quantitative 1H-NMR spectroscopy for authentication of lemon (Citrus limon [L.] Burm.f.) and Persian lime (Citrus × latifolia [Yu.Tanaka] Tanaka) juices. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.T. Supercritical fluid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4925–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, I.; Murauer, A.; Ganzera, M. Determination of coumarins in the roots of Angelica dahurica by supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winderl, B.; Schwaiger, S.; Ganzera, M. Fast and improved separation of major coumarins in Ammi visnaga (L.) Lam. by supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmaster, A.P.; Owen, N.; Brussaux, S.; Brevard, H.; Hiserodt, R.; Leijs, H.; Bast, N.; Weber, B.; Loesing, G.; Sherlock, A.; et al. Quantification of selected furocoumarins by high-performance liquid chromatography and UV-detection: Capabilities and limits. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1257, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, A.; Li, A.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R. Isolation and purification of osthole and imperatorin from Fructus cnidii by semi-preparative supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cafeo, G.; Irrera, E.; Russo, M.; Dugo, P. Extraction and Chromatographic Approaches for Coumarin, Furocoumarin, and Polymethoxyflavone Characterization in Foods. Foods 2024, 13, 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162517
Cafeo G, Irrera E, Russo M, Dugo P. Extraction and Chromatographic Approaches for Coumarin, Furocoumarin, and Polymethoxyflavone Characterization in Foods. Foods. 2024; 13(16):2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162517
Chicago/Turabian StyleCafeo, Giovanna, Elisa Irrera, Marina Russo, and Paola Dugo. 2024. "Extraction and Chromatographic Approaches for Coumarin, Furocoumarin, and Polymethoxyflavone Characterization in Foods" Foods 13, no. 16: 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162517
APA StyleCafeo, G., Irrera, E., Russo, M., & Dugo, P. (2024). Extraction and Chromatographic Approaches for Coumarin, Furocoumarin, and Polymethoxyflavone Characterization in Foods. Foods, 13(16), 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162517






