Abstract
The appearance of spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in the so-called type-II multiferroic materials has received a lot of attention. The nature and mechanisms of such polarization were intensively studied using perovskite rare-earth manganites, RMnO3, as model systems. Later, multiferroic properties were discovered in some RFeO3 perovskites and possibly in some RCrO3 perovskites. However, R2NiMnO6 double perovskites have ferromagnetic structures that do not break the inversion symmetry. It was found recently that more complex magnetic structures are realized in A-site-ordered quadruple perovskites, RMn3Ni2Mn2O12. Therefore, they have the potential to be multiferroics. In this work, dielectric properties in magnetic fields up to 9 T were investigated for such perovskites as RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Ce to Ho and for BiMn3Ni2Mn2O12. The samples with R = Bi, Ce, and Nd showed no dielectric anomalies at all magnetic fields, and the dielectric constant decreases with decreasing temperature. The samples with R = Sm to Ho showed qualitatively different behavior when the dielectric constant started increasing with decreasing temperature below certain temperatures close to the magnetic ordering temperatures, TN. This difference could suggest different magnetic ground states. The samples with R = Eu, Dy, and Ho still showed no anomalies on the dielectric constant. On the other hand, peaks emerged at TN on the dielectric constant in the R = Sm sample from about 2 T up to the maximum available field of 9 T. The Gd sample showed peaks on dielectric constant at TN between about 1 T and 7 T. Transition temperatures increase with increasing magnetic fields for R = Sm and decrease for R = Gd. These findings suggest the presence of magnetic-field-induced multiferroic states in the R = Sm and Gd samples with intermediate ionic radii. Dielectric properties at different magnetic fields are also reported for Lu2NiMnO6 for comparison.
1. Introduction
The appearance of spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in the so-called type-II multiferroic materials has received a lot of attention in the literature [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Because ferroelectric polarization appears as a result of a magnetic ordering, there is a strong magnetoelectric coupling in such materials, allowing for the control of ferroelectric polarization via a magnetic field and vice versa [8,9]. The nature and mechanisms of such polarization were intensively studied using perovskite-structure rare-earth (R) manganites, RMnO3, as model systems [10,11,12,13]. Only some members of the RMnO3 family with specific magnetic structures develop spin-induced ferroelectric polarization, for example, in RMnO3 (R = Tb to Dy) with modulated sinusoidal/spiral antiferromagnetic (AFM) ordering and in RMnO3 (R = Ho to Lu) with the so-called E-type magnetic ordering. Multiferroic properties were discovered in some RFeO3 perovskites [14,15,16,17,18,19,20] and possibly in some RCrO3 perovskites [21,22,23]. While the multiferroic properties of RFeO3 at very low temperatures, where they are caused by additional magnetic orderings of the R3+ sublattice, are well established [14,15,16], the existence of ferroelectric polarization at higher temperatures in RFeO3 and RCrO3 is still under debate [18,19,24].
All R2NiMnO6 double perovskites [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41] have simple ferromagnetic (FM) structures (in the first approximation), which do not break inversion centers and do not produce spin-induced ferroelectric polarization. Nevertheless, there are a few reports with claims of spin-induced ferroelectric properties in R2NiMnO6 double perovskites [25,26]. However, such claims were not confirmed [27], and therefore, they are still controversial. The use of cations smaller than Lu3+ (rXIII(Lu3+) = 0.977 Å [42]) at the R sites (such as Sc3+ with rXIII(Sc3+) = 0.870 Å and In3+ with rXIII(In3+) = 0.92 Å [42]) further reduces Ni–O–Mn bond angles in the R2NiMnO6 series, weakens the strength of direct FM Ni–Mn exchange interactions, and stabilizes complex AFM structures. For example, Sc2NiMnO6 demonstrates two AFM transitions [43]. The dielectric constant of Sc2NiMnO6 starts increasing with decreasing temperature when approaching TN1 = 35 K and shows a sharp drop below TN2 = 17 K. On the other hand, pyroelectric current measurements did not show the development of spin-induced ferroelectric polarization [43]. One AFM transition with an incommensurate structure was found in In2NiMnO6 at TN = 26 K [44,45], and this compound shows spin-induced ferroelectric polarization [45]. Ferroelectric polarization is suppressed by magnetic fields above 6 T. The dielectric constant of In2NiMnO6 basically decreases with decreasing temperature between 5 K and 300 K, and a sharp peak is only observed at TN [45]. It turned out that Lu2NiMnO6 is located near a phase boundary between FM and AFM states on the phase diagram of the R2NiMnO6 double perovskites, and a moderate pressure can induce a transition from an FM state to an incommensurate AFM state [35].
The R2NiMnO6 family of B-site-ordered double perovskites was recently extended further to a subfamily of A-site-ordered quadruple perovskites [46,47,48,49,50,51] with the composition of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Bi [52], La [53,54], Ce [52], Nd [55], Sm [55], Gd [55], Dy [55], and Ho [52]. RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 behaves differently from R2NiMnO6. For example, LaMn3Ni2Mn2O12 has two magnetic transitions at TN = 46 K and TC = 34 K [53] (similar to Sc2NiMnO6 and in comparison with other members of the R2NiMnO6 family (R = La to Lu)). Complex magnetic structures are realized in LaMn3Ni2Mn2O12 [53]. NdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 already shows one magnetic transition at TN = 26 K [55]. Net FM components are developed at the ground states of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = La and Nd. On the other hand, AFM ground states are basically realized in RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Sm to Ho. Complex AFM ground states are promising for the realization of spin-induced ferroelectric polarization. However, detailed dielectric studies of the RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 perovskites have not been performed yet.
Therefore, in this work, we investigated nearly all members of the RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 family by performing detailed measurements of dielectric constant in different magnetic fields up to 9 T. While no dielectric constant anomalies were found at a zero magnetic field in all samples, peaks emerge in the dielectric constant in the R = Sm and Gd samples in intermediate ranges of the magnetic field. These observations suggest the presence of magnetic-field-induced multiferroic states in the R = Sm and Gd samples. Basic physical properties of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 and dielectric properties at different magnetic fields for Lu2NiMnO6 are also reported for comparison.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. R = Bi, Ce, and Nd
Temperature dependence of dielectric constant and loss tangent of BiMn3Ni2Mn2O12 in different magnetic fields is shown in Figure 1. Very weak effects of magnetic fields on dielectric constant values were observed in agreement with the reported weak effects of magnetic fields on specific heat values [52]. No dielectric constant anomalies were observed at TN = 36 K [52] of BiMn3Ni2Mn2O12.
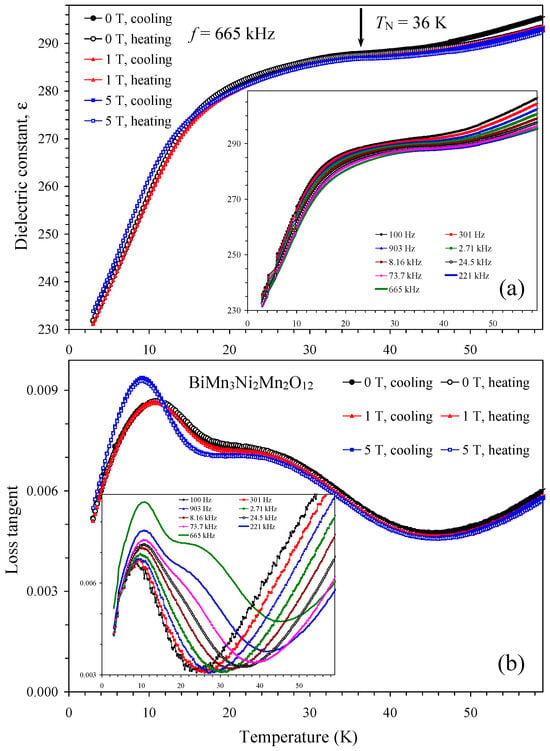
Figure 1.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of BiMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 1, and 5 T on cooling and heating. The inset shows the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant at different frequencies at H = 0 T (on cooling). The arrow shows a magnetic transition temperature [52]. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of BiMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 1, and 5 T on cooling and heating. The inset shows the temperature dependence of the loss tangent at different frequencies at H = 0 T (on cooling).
The temperature dependence of the dielectric constant and loss tangent of CeMn3Ni2Mn2O12 (Figure 2) and NdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 (Figure 3 and Figure S1) were qualitatively similar. The dielectric constant slightly decreased with decreasing temperature, and weak effects of magnetic fields on dielectric constant values were observed below about 60 K. Loss tangent of both samples showed broad anomalies below about 15 K (at the frequency of 665 kHz). No dielectric constant anomalies were observed at their magnetic transition temperatures of 27 K and 33 K (for R = Ce [52]) and 26 K (for R = Nd [55]). In dielectric insulator materials without any ferroelectric or ferroelectric-like transitions, the dielectric constant is usually temperature independent or slightly decreases with decreasing temperature. Therefore, the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant of the R = Ce and Nd samples is typical for ordinary insulators.
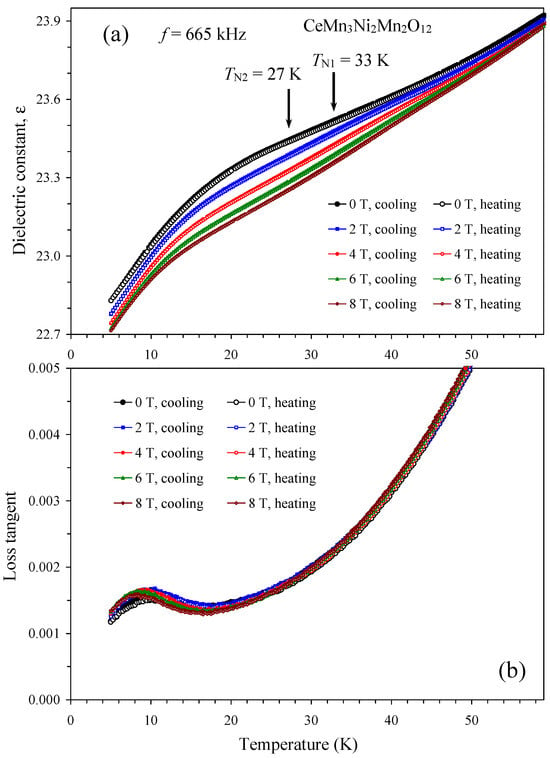
Figure 2.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of CeMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating. Arrows show magnetic transition temperatures [52]. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of CeMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating.
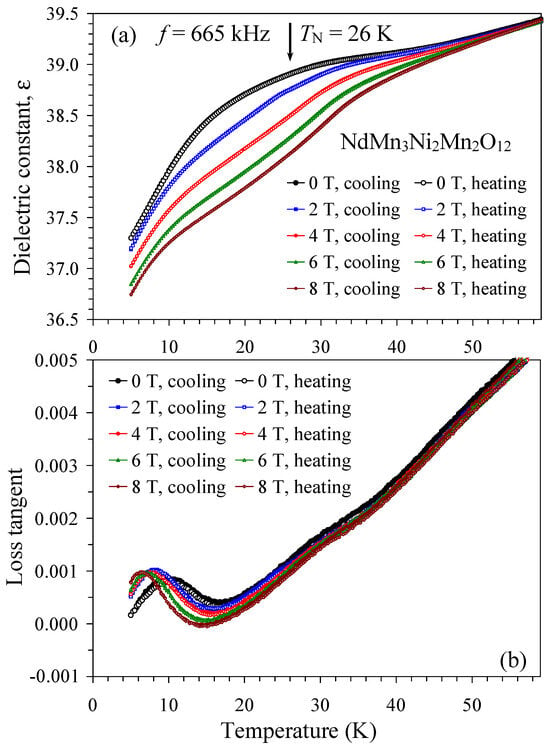
Figure 3.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of NdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating. The arrow shows a magnetic transition temperature [55]. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of NdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating.
2.2. R = Sm
The temperature dependence of the dielectric constant of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Sm to Ho was qualitatively different from that of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Bi, Ce, and Nd because the dielectric constant started increasing with decreasing temperature below about 30–40 K. The increase of the dielectric constant suggests the development of polar correlations. This change in the behavior of the dielectric constant also correlates with the changes in the magnetic properties because net FM components were observed at the ground states of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Ce and Nd, while AFM ground states are basically realized in RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Sm to Ho. This change in the behavior of the dielectric constant could reflect different magnetic structures.
The dielectric constant and loss tangent of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 are shown in Figure 4 and Figures S2–S4. At H = 0 T, the dielectric constant and loss tangent of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 showed no detectable anomalies. However, at H = 2 T, a small kink appears on the dielectric constant, and a peak is visible on the loss tangent near TN = 23 K. At higher magnetic fields (4–8 T), a small kink on the dielectric constant transforms to a small peak. Peaks on both dielectric constant and loss tangent are moving to higher temperatures with increasing magnetic field in agreement with the similar shift of specific heat anomalies (Figure 5a), confirming their common magnetic origin. Peaks on loss tangent were observed at 20.5 K (at 2 T), 21.5 K (at 4 T), 23.0 K (at 6 T), 24.5 K (at 8 T), and 25.2 K (at 9 T). Almost no hysteresis in the peak positions was observed during cooling and heating. Therefore, the appearance of peaks on both dielectric constant and loss tangent at magnetic fields of 2–9 T suggests the development of spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at such magnetic fields.
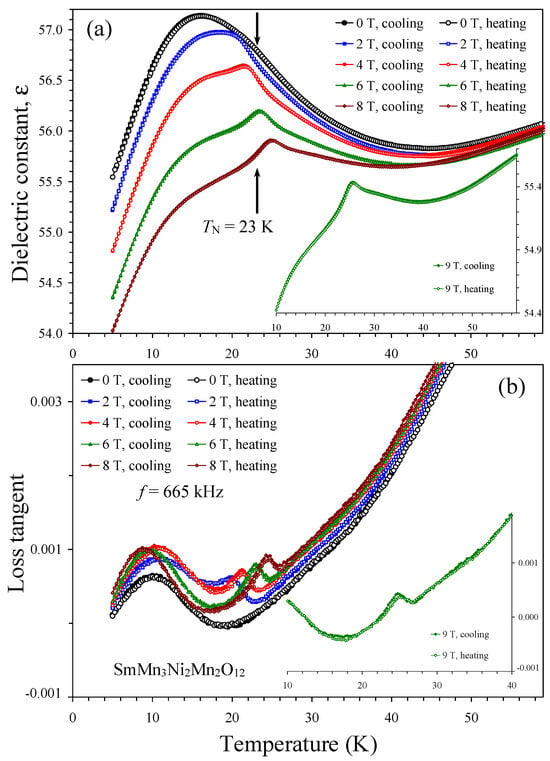
Figure 4.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating. The arrow shows a magnetic transition temperature at H = 0 T [55]. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating. The insets show data at a magnetic field of 9 T.
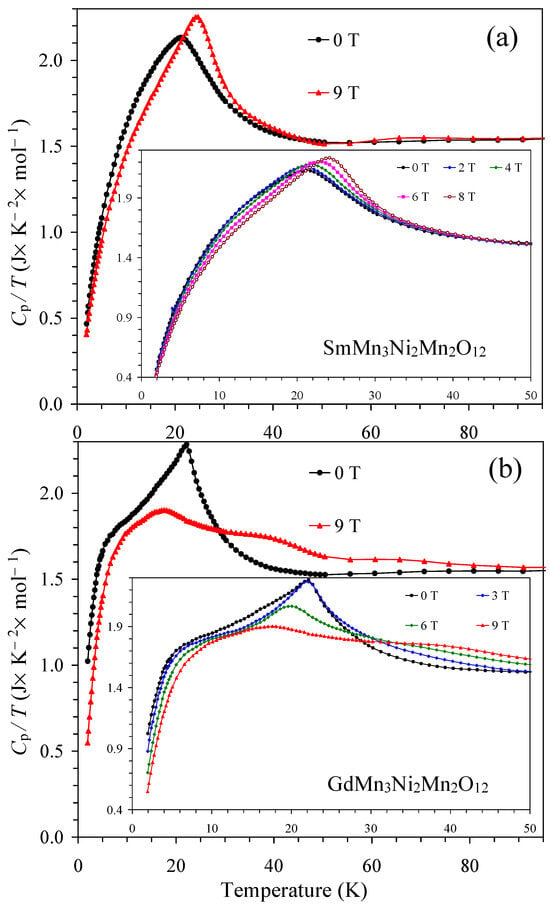
Figure 5.
(a) Cp/T vs. T curves of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 measured at H = 0 and 9 T on cooling. The inset shows Cp/T vs. T curves at H = 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T. (b) Cp/T vs. T curves of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 measured at H = 0 and 9 T on cooling. The inset shows Cp/T vs. T curves at H = 0, 3, 6, and 9 T.
2.3. R = Eu
As EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 has not been reported yet, we start with the basic characterization of this compound by other methods. EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 crystallized in a cubic structure of the A-site-ordered quadruple perovskite family [46,47,48,49,50,51] with a = 7.3430(1) Å. The quality of the standard laboratory X-ray diffraction data (with a measurement speed of 3°/min) did not allow detection of superstructure reflections related to (partial) ordering of Ni2+ and Mn4+ cations and, therefore, to assign the Im-3 or Pn-3 space groups. Therefore, we measured X-ray diffraction data with a speed of 0.1°/min between 38° and 44° and could detect a very weak (311) superstructure reflection. This fact suggests that there is a partial ordering of Ni2+ and Mn4+ cations, and the space group is Pn-3, similar to some other members of the RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 family [55]. Laboratory X-ray diffraction data also showed the presence of some amounts of (Eu1−xMnx)MnO3 impurity (space group Pnma with a = 5.5357 Å, b = 7.5834 Å, c = 5.3196 Å; about 6.7 wt. %) and NiO impurity (space group R-3m with a = 2.9597 Å and c = 7.2374 Å; about 2.5 wt. %). The (Eu1−xMnx)MnO3 impurity has a ferrimagnetic transition near 140 K.
Temperature dependence of specific heat and magnetic susceptibilities of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 is shown in Figure 6. Specific heat data clearly showed the presence of one magnetic transition at TN = 33 K; the specific heat anomaly was slightly dependent on magnetic fields. χ vs. T curves showed a very small kink at TN = 33 K. On the other hand, differential dχT/dT vs. T curves allowed detecting the magnetic anomaly more clearly (the inset of Figure 6b). At high temperatures, inverse magnetic susceptibilities followed the Curie–Weiss law (Figure S5), and the obtained Curie–Weiss parameters (using the 7 T FCC curve in a temperature range of 250–350 K) were μeff = 11.216μB (the experimental effective magnetic moment) and θ = +0.1 K (the Curie–Weiss temperature). The μeff value was close to the expected calculated value of μcalc = 11.382μB (taking 3.4μB for Eu3+ [56]).
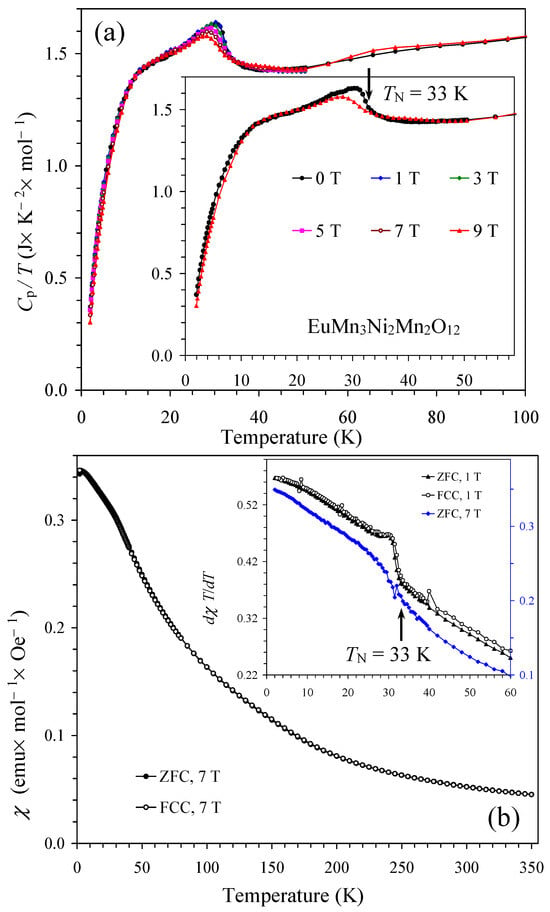
Figure 6.
(a) Cp/T vs. T curves of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 measured at H = 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 T on cooling. The inset shows Cp/T vs. T curves at H = 0 and 9 T. The arrow shows a magnetic transition temperature. (b) ZFC (filled symbols) and FCC (empty symbols) dc magnetic susceptibility curves (χ = M/H) of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 measured at H = 7 T. The inset shows ZFC and FCC dχT/dT vs. T curves at H = 1 T and 7 T.
Isothermal magnetization curves (M vs. H) showed nearly linear behavior at T = 5–200 K above about 1 T (Figure S5). The S-type shape was observed near the origin without any significant hysteresis originating from the impurity contribution with soft FM-like properties. Nearly the same S-type contribution was observed at T = 5–100 K, that is, below and above TN = 33 K of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12. On the other hand, the S-type shape near the origin disappeared at 200 K, that is, above the ferrimagnetic transition of the (Eu1−xMnx)MnO3 impurity. Therefore, the χ vs. T and M vs. H curves give evidence that a purely AFM transition takes place in EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 without any net FM-like moments.
Temperature dependence of the dielectric constant and loss tangent of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 (Figure 7) at different magnetic fields (0–8 T) showed no anomalies at TN = 33 K, suggesting the absence of any detectable (spin-induced) ferroelectric polarization.
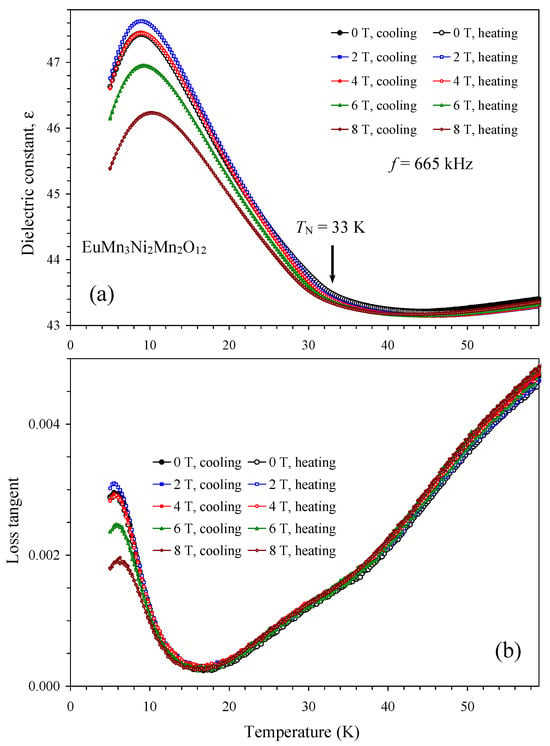
Figure 7.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating. The arrow shows a magnetic transition temperature. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating.
2.4. R = Gd
The dielectric constant of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 showed a small kink near TN = 22 K at H = 0 T (Figure 8 and Figure S6). The kink transforms to a weak peak already at H = 1 T. The most pronounced peaks on dielectric constant and loss tangent were observed at H = 5 T (Figure 8 and Figure 9). Peaks on the dielectric constant disappear at H = 8 and 9 T. Peaks on the dielectric constant clearly move to lower temperatures with increasing magnetic fields (peaks were observed at 23.2 K at 1 T, 23.0 K at 2 T, 22.5 K at 3 T, 21.5 K at 4 T, 20.5 K at 5 T, and 19.2 K at 6 T) in agreement with specific heat measurements (Figure 5b), confirming their common magnetic origin. Therefore, GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 exhibits spin-induced ferroelectric polarization at about H = 1–7 T.
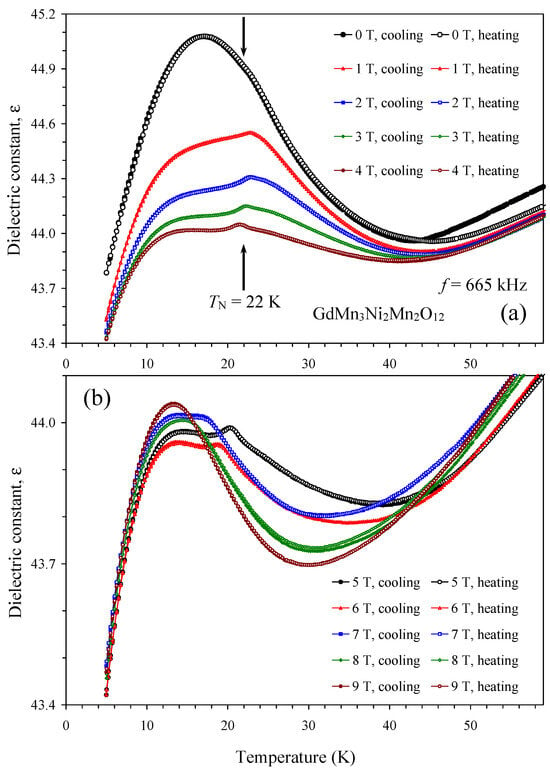
Figure 8.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 T on cooling and heating. The arrow shows a magnetic transition temperature at H = 0 T [55]. (b) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 T on cooling and heating.
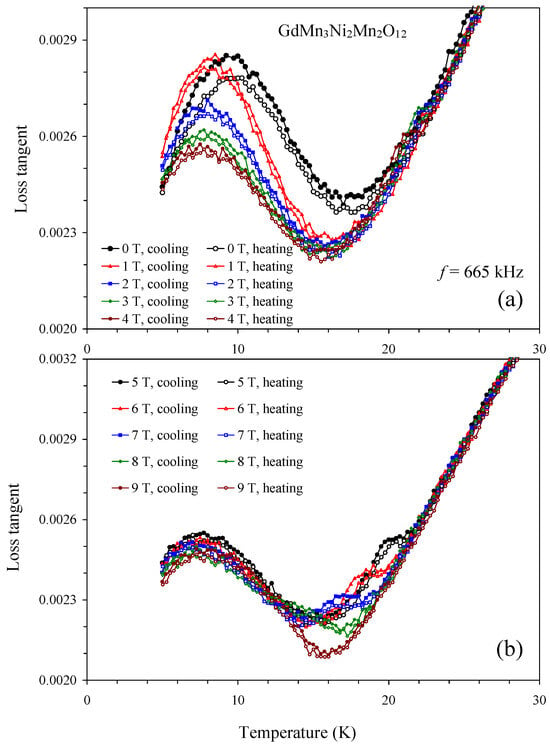
Figure 9.
(a) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 T on cooling and heating. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 T on cooling and heating.
2.5. R = Dy
The temperature dependence of the dielectric constant and loss tangent of DyMn3Ni2Mn2O12 between H = 0 T and H = 8 T (Figure 10) was close to those of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 (Figure 6). No anomalies were observed at the magnetic transition temperatures of 36 K and 10 K [55].
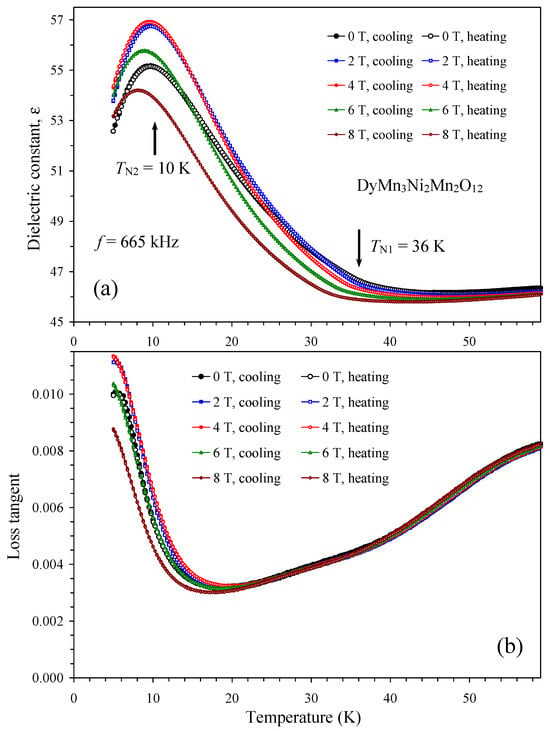
Figure 10.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of DyMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating. The arrows show the magnetic transition temperatures at H = 0 T [55]. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of DyMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 T on cooling and heating.
2.6. R = Ho
Temperature dependence of dielectric constant and loss tangent of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 between 0 T and 9 T is shown on Figure 11 and Figure 12. Both dielectric constant and loss tangent showed small peaks near 36 K; this temperature matches with the magnetic transition temperature of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 [52], which was unambiguously determined with specific heat and magnetization measurements [52]. On the other hand, this temperature is also close to the magnetic and ferroelectric transition temperature of the HoMn2O5 impurity [57,58,59,60], which shows very strong and sharp anomalies on both dielectric constant and loss tangent [57,58,59]. The positions and intensities of the peaks remained nearly the same in all magnetic fields in HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12; and there was small hysteresis in the positions of the peaks on cooling and heating. Exactly the same behavior was observed in HoMn2O5 [57,58,59]. On the other hand, no hysteresis was observed on the temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibilities of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 [52] (we note that almost no anomalies were observed on magnetic susceptibilities of HoMn2O5 [59,60]). Therefore, we believe that there is a high probability that the observed anomalies on dielectric constant and loss tangent are caused by the HoMn2O5 impurity even though its amount was quite small (about 3 weight % [52]). Therefore, the intrinsic dielectric constant and loss tangent of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 are very close to those of DyMn3Ni2Mn2O12; that is, there are no detectable anomalies at the magnetic transition temperature between 0 T and 9 T.
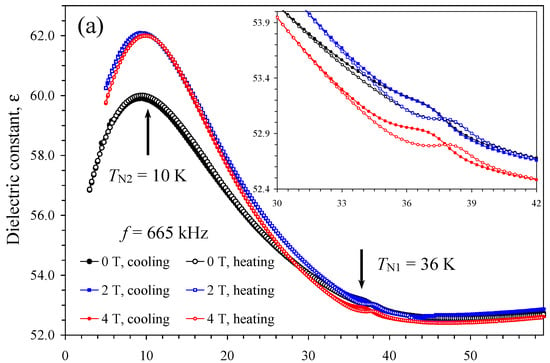
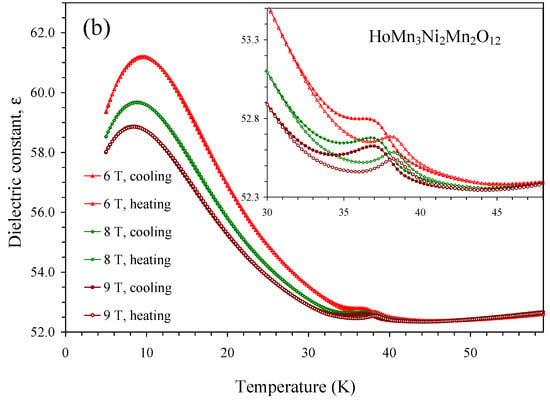
Figure 11.
(a) Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, and 4 T on cooling and heating. The arrows show the magnetic transition temperatures [52]. (b) Temperature dependence of the dielectric constant of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 6, 8, and 9 T on cooling and heating. The insets show magnified parts.
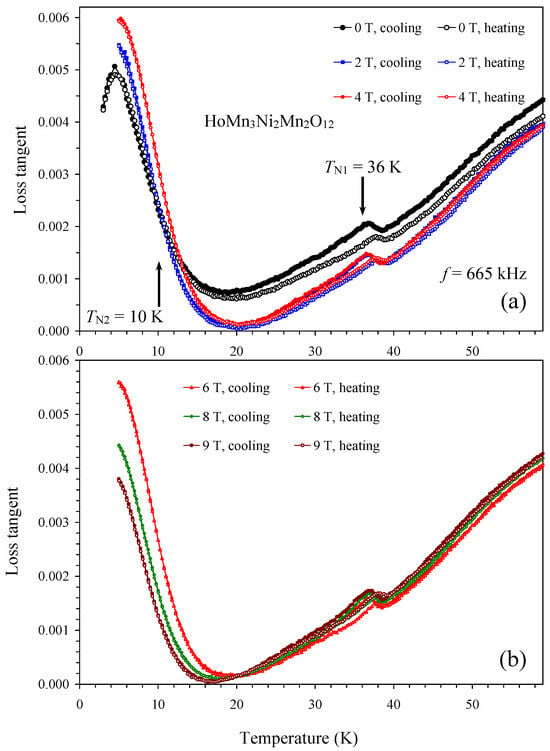
Figure 12.
(a) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 0, 2, and 4 T on cooling and heating. The arrows show the magnetic transition temperatures [52]. (b) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of HoMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 6, 8, and 9 T on cooling and heating.
2.7. Lu2NiMnO6
For comparison, we report here the dielectric properties of one member of the R2NiMnO6 family with the smallest R3+ cation of R = Lu. Specific heat measurements confirmed the presence of one FM transition at TC = 41 K (the inset of Figure 13b and Figure S7). Dielectric properties of different members of the R2NiMnO6 family were reported in the literature [39,40], and no dielectric anomalies were usually observed. On the other hand, very detailed studies in the vicinity of TC demonstrated very weak kink-like anomalies at TC [25,36]; however, effects of magnetic fields have not been studied. Temperature dependence of the dielectric constant and loss tangent of our Lu2NiMnO6 sample, prepared by a high-pressure high-temperature method at 6 GPa, is shown in Figure 13. At H = 0 T, we observed a very weak kink-like anomaly at TC similar to the previous reports [25,36]. The kink-like anomaly could originate from magnetostriction effects because Lu2NiMnO6 is a ferromagnet [61,62]. High magnetic fields smeared kink-like anomalies; for example, at H = 7 T and 9 T, no visible dielectric anomalies were detected near TC. Therefore, Lu2NiMnO6 does not develop ferroelectric polarization between 0 T and 9 T. The dielectric constant decreases with decreasing temperature between 3 K and 300 K, as for ordinary insulators/dielectrics.
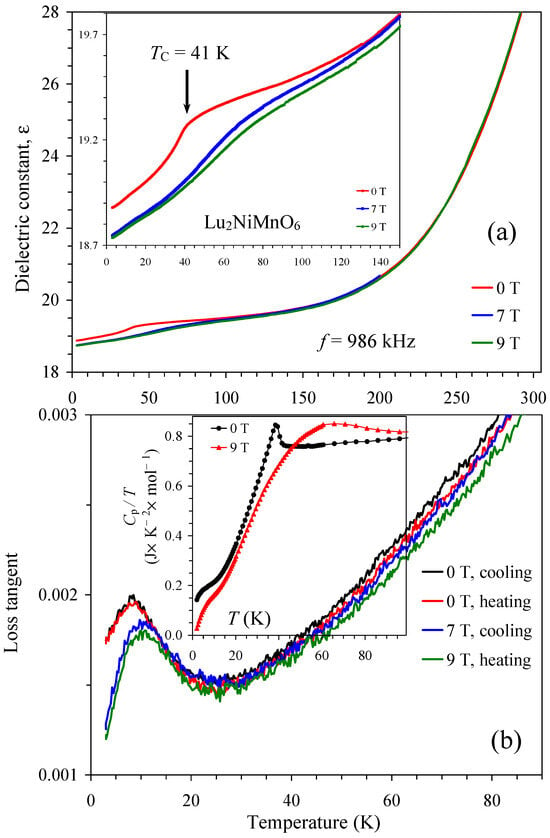
Figure 13.
Temperature dependence of (a) dielectric constant and (b) loss tangent at one frequency of 986 kHz in Lu2NiMnO6 at H = 0, 7, and 9 T in different temperature ranges. The inset in the panel (a) shows details below 150 K, where the arrow shows a ferromagnetic transition temperature. The inset in the panel (b) shows Cp/T vs. T curves of Lu2NiMnO6 at H = 0 and 9 T.
3. Materials and Methods
RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 samples with R = Bi, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, and Ho were prepared from stoichiometric mixtures of Bi2O3 (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.9999%), CeO2 (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.99%), R2O3 (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.9%), Mn2O3 (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.99%), MnO2 (Alfa Aesar, Ward Hill, MA, USA, 99.99%), and NiO (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.9%). Single-phase Mn2O3 was prepared from a commercial MnO2 chemical (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.99%) by annealing in air at 923 K for 24 h. The synthesis was performed at about 6 GPa and at about 1500 K for 2 h in sealed Au capsules using a belt-type HP instrument. After annealing at 1500 K, the samples were cooled down to room temperature by turning off the heating current, and the pressure was slowly released.
The Lu2NiMnO6 sample was prepared from stoichiometric mixtures of Lu2O3 (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.9%), MnO2 (Alfa Aesar, Ward Hill, MA, USA, 99.99%), and NiO (Rare Metallic Co., Tokyo, Japan, 99.9%) by the high-pressure high-temperature method at about 6 GPa and at about 1700 K for 2 h in a sealed Pt capsule. We note that the oxygen content and purity of MnO2 (Alfa Aesar, Ward Hill, MA, USA, 99.99%) were confirmed before its use by the thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray powder diffraction. The refined lattice parameters of Lu2NiMnO6 (space group P21/n with a = 5.1490(1) Å, b = 5.5123(1) Å, c = 7.4073(1) Å, and β = 90.441(1)°) were close to the reported values [35].
X-ray powder diffraction data of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 were collected at room temperature on a MiniFlex600-C diffractometer (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) using CuKα radiation (a 2θ range of 10–120°, a step width of 0.02°, and a scan speed of 3°/min; and a 2θ range of 38–44°, a step width of 0.02°, and a scan speed of 0.1 °/min) (Figure S8). The Rietveld analysis of all X-ray powder diffraction data was performed using the RIETAN-2000 program [63]. The crystallographic characterization of other samples was reported in [52,55].
Magnetic measurements of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 were performed on SQUID magnetometers (Quantum Design MPMS3, San Diego, CA, USA) between 2 K and 350 K (and between 330 K and 750 K) in applied fields of 0.01 T, 1 T, and 7 T under both zero-field-cooled (ZFC) and field-cooled on cooling (FCC) conditions. Magnetic-field dependence was measured at different temperatures between −7 T and +7 T. Specific heat, Cp, of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 was measured on cooling from 100 K to 2 K at different magnetic fields from 0 T to 9 T by a pulse relaxation method using a commercial calorimeter (Quantum Design PPMS, San Diego, CA, USA).
Dielectric properties were measured using an Alpha-A High Performance Frequency Analyzer (NOVOCONTROL Technologies, Montabaur, Germany) on cooling and heating in a temperature range between 3–5 K and 70–300 K and a frequency range from 100 Hz to 665 kHz (or 986 kHz) at different magnetic fields from 0 T to 9 T. Pieces of pellets were used in all magnetic, specific heat, and dielectric measurements.
4. Conclusions
Dielectric properties of the A-site-ordered quadruple perovskites, RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Bi, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, and Ho, were investigated at different magnetic fields between 0 T and 9 T. A principal difference in the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant was observed for R = Bi, Ce, and Nd and for R = Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, and Ho. The dielectric constant of the former group decreases with decreasing temperature down to the lowest temperature. The dielectric constant of the latter group starts increasing with decreasing temperature when approaching magnetic transition temperatures, suggesting different magnetic ground states. Peak-like anomalies were found on dielectric constant and loss tangent in intermediate magnetic-field ranges for the R = Sm and Gd samples, suggesting the existence of “hidden” [64] magnetic-field-induced multiferroic states. Physical properties of a new compound, EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12, were also investigated with specific heat and magnetization measurements. Dielectric properties of Lu2NiMnO6 at different magnetic fields are reported for comparison.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics13100315/s1. Figure S1: Temperature dependence of (a) dielectric constant and (b) loss tangent of NdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at different frequencies from 100 Hz to 665 kHz. Measurements were performed on cooling at H = 0 T; Figure S2: Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at different frequencies from 100 Hz to 665 kHz. Measurements were performed on cooling at (a) H = 0 T and at (b) H = 8 T; Figure S3: Temperature dependence of loss tangent of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at different frequencies from 100 Hz to 665 kHz. Measurements were performed on cooling at (a) H = 0 T and at (b) H = 8 T; Figure S4: Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of (a) 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 T and (b) 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 T on cooling and heating. Different measurements (from Figure 4 in the main text and from Figures S2 and S3) are reported. Temperature dependence of loss tangent of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of (c) 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 T and (d) only at 0 and 1 T (to emphasize the absence of anomalies) on cooling and heating. (e) Temperature dependence of loss tangent of SmMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at one frequency of 665 kHz and different magnetic fields of 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 T; Figure S5: (a) M vs. H curves of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at T = 5 K, 20 K, 40 K, 60 K, 100 K, and 200 K. The inset shows a magnified part of the M vs. H curves at T = 5 K and 20 K. (b) M vs. H curves of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at T = 5 K and 20 K, below its TN = 33 K. The S-type shape of the M vs. H curves near the origin comes from a contribution from the ferrimagnetic impurity (Eu1−xMnx)MnO3 (space group Pnma); otherwise, the M vs. H curves were linear without hysteresis. (c) Inverse magnetic susceptibilities of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 measured at magnetic fields of H = 100 Oe, 10 kOe, and 70 kOe in the low-temperature (LT) region of 2–350 K and in the high-temperature (HT) region of 330–750 K. Red lines show the Curie–Weiss fittings of the LT and HT data at H = 70 kOe; fitting parameters are shown on this figure. The anomaly near 140 K on the LT region originates from the ferrimagnetic impurity (Eu1−xMnx)MnO3. A very weak anomaly near 400 K, seen on the HT data at H = 100 Oe, could originate from traces of NiMnO3 impurity observed in some other samples of RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Bi, Ce, and Ho. Magnetic measurements showed that the amount of a possible NiMnO3 impurity was very small, well below the detection limit of laboratory X-ray diffraction; Figure S6: Temperature dependence of dielectric constant of GdMn3Ni2Mn2O12 at different frequencies from 100 Hz to 665 kHz. Measurements were performed on heating at (a) H = 0 T and at (b) H = 5 T; Figure S7: Cp/T vs. T curves of Lu2NiMnO6 at different magnetic fields of H = 0, 0.2, 1, 2, 3, 5, and 9 T. Measurements were performed on cooling; Figure S8: (a) Experimental (black crosses), calculated (red line), and difference (blue line at the bottom) room-temperature laboratory X-ray powder diffraction patterns of EuMn3Ni2Mn2O12 (space group Pn−3) in a 2θ range of 16° and 120°. The tick marks show possible Bragg reflection positions for the main phase (brown), (Eu1−xMnx)MnO3 impurity (blue), and NiO impurity (green) (from top to bottom). (b) A magnified part of the experimental and calculated patterns in a 2θ range of 38° and 44°, emphasizing the presence of the (311) reflection from the (partial) B-site ordering. The data between 38° and 44° were measured with a speed of 0.1°/min and scaled to match with other data (panel (a)) measured with a speed of 3°/min; because of scaling, the background on panel (b) was not fitted well.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.B.; methodology, A.A.B.; validation, A.A.B.; formal analysis, A.A.B.; investigation, A.A.B., R.L., and K.Y.; resources, K.Y.; data curation, A.A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.B.; writing—review and editing, A.A.B.; supervision, A.A.B. and K.Y.; project administration, A.A.B.; funding acquisition, K.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. JP25K01657) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in this study are openly available on Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17131358.
Acknowledgments
MANA was supported by the World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI), MEXT, Japan.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Schmid, H. Multi-ferroic magnetoelectrics. Ferroelectrics 1994, 162, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerenstein, W.; Mathur, N.; Scott, J.F. Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 2006, 442, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomskii, D.I. Multiferroics: Different ways to combine magnetism and ferroelectricity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 306, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.-W.; Mostovoy, M. Multiferroics: A magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomskii, D. Classifying multiferroics: Mechanisms and effects. Physics 2009, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokura, Y.; Seki, S.; Nagaosa, N. Multiferroics of spin origin. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2014, 77, 076501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, M.; Lottermoser, T.; Meier, D.; Trassin, M. The evolution of multiferroics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, J.T.; Trassin, M.; Ashraf, K.; Gajek, M.; He, Q.; Yang, S.Y.; Nikonov, D.E.; Chu, Y.; Salahuddin, H.S.; Ramesh, R. Electric-field-induced magnetization reversal in a ferromagnet-multiferroic heterostructure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 217202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueland, B.G.; Lynn, J.W.; Laver, M.; Choi, Y.J.; Cheong, S.-W. Origin of electric-field-induced magnetization in multiferroic HoMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 147204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Goto, T.; Shintani, H.; Ishizaka, K.; Arima, T.; Tokura, Y. Magnetic control of ferroelectric polarization. Nature 2003, 426, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzelmann, M.; Harris, A.B.; Jonas, S.; Broholm, C.; Schefer, J.; Kim, S.B.; Zhang, C.L.; Cheong, S.-W.; Vajk, O.P.; Lynn, J.W. Magnetic inversion symmetry breaking and ferroelectricity in TbMnO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 087206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomjakushin, V.Y.; Kenzelmann, M.; Dönni, A.; Harris, A.B.; Nakajima, T.; Mitsuda, S.; Tachibana, M.; Keller, L.; Mesot, J.; Kitazawa, H.; et al. Evidence for large electric polarization from collinear magnetism in TmMnO3. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 043019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dönni, A.; Nakajima, T.; Mitsuda, S.; Tachibana, M.; Kitazawa, H.; Pomjakushin, V.; Keller, L.; Niedermayer, C.; Scaramucci, A.; et al. E-type noncollinear magnetic ordering in multiferroic o-LuMnO3. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Iguchi, S.; Arima, T.; Tokura, Y. Magnetic-field-induced ferroelectric state in DyFeO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 097205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Taguchi, Y.; Arima, T.H.; Tokura, Y. Electric-field-induced generation and reversal of ferromagnetic moment in ferrites. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, E.; Cano, A. Non-collinear magnetism in multiferroic perovskites. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, Y.K.; Park, J.H.; Oak, M.-A.; Jang, H.M.; Son, J.Y.; Scott, J.F. Spin-canting-induced improper ferroelectricity and spontaneous magnetization reversal in SmFeO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 117201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.D.; Terada, N.; Radaelli, P.G. Comment on “Spin-canting-induced improper ferroelectricity and spontaneous magnetization reversal in SmFeO3”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 219701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-Y.; Drees, Y.; Fernández-Díaz, M.T.; Zhao, L.; Vasylechko, L.; Sheptyakov, D.; Bell, A.M.T.; Pi, T.W.; Lin, H.-J.; Wu, M.-K.; et al. k = 0 magnetic structure and absence of ferroelectricity in SmFeO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 217203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswaran, B.; Sanyal, D.; Chakrabarti, M.; Sundarayya, Y.; Sundaresan, A.; Rao, C.N.R. Interplay of 4f-3d magnetism and ferroelectricity in DyFeO3. EPL 2013, 101, 17001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Sundaresan, A.; Rao, C.N.R. Novel features of multiferroic and magnetoelectric ferrites and chromites exhibiting magnetically driven ferroelectricity. Mater. Horiz. 2014, 1, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.N.P.; Teixeira, R.C.; Moreira, R.P.; Correia, J.G.; Araújo, J.P.; Lopes, A.M.L. Local inhomogeneous state in multiferroic SmCrO3. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvezdin, A.K.; Gareeva, Z.V.; Chen, X.M. Multiferroic order parameters in rhombic antiferromagnets RCrO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2021, 33, 385801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Gonjal, J.; Schmidt, R.; Romero, J.-J.; Ávila, D.; Amador, U.; Morán, E. Microwave-assisted synthesis, microstructure, and physical properties of rare-earth chromites. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Ge, L.; Wang, S.; Yuan, H.; Feng, S. Hydrothermal synthesis and multiferroic properties of Y2NiMnO6. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50969–50974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gu, L.; Lu, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J. Magnetism-driven ferroelectricity in double perovskite Y2NiMnO6. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13260–13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhalil, H.; Nair, H.S.; Kumar, C.M.N.; Strydom, A.M.; Elizabeth, S. Ferromagnetism and the effect of free charge carriers on electric polarization in the double perovskite Y2NiMnO6. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 214426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Benítez, J.; Martínez-Lope, M.J.; Alonso, J.A.; García-Muñoz, J.L. Magnetic and structural features of the NdNi1−xMnxO3 perovskite series investigated by neutron diffraction. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 226001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retuerto, M.; Muñoz, Á.; Martínez-Lope, M.J.; Alonso, J.A.; Mompeán, F.J.; Fernández-Díaz, M.T.; Sánchez-Benítez, J. Magnetic interactions in the double perovskites R2NiMnO6 (R = Tb, Ho, Er, Tm) investigated by neutron diffraction. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 10890–10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, R.J.; Fillman, R.; Whitaker, H.; Nag, A.; Tiwari, R.M.; Ramanujachary, K.V.; Gopalakrishnan, J.; Lofland, S.E. An investigation of structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of R2NiMnO6 (R = rare earth, Y). Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Kumar, S.; Patra, N.; Bhattacharya, D.; Jha, S.N.; Basaula, D.R.; Bhatt, S.; Khan, M.; Liu, S.-W.; Biring, S.; et al. Role of antisite disorder, rare-earth size, and superexchange angle on band gap, Curie temperature, and magnetization of R2NiMnO6 double perovskites. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, K.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Nishimori, N.; Satoh, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Mizoguchi, M. Magnetic properties of REMe0.5Mn0.5O3 (RE = rare earth element, Me = Ni, Co). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 67, 4218–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.V.; Glazkova, I.S.; Akulenko, A.A.; Sergueev, I.; Chumakov, A.I.; Yi, W.; Belik, A.A.; Presniakov, I.A. 61Ni nuclear forward scattering study of magnetic hyperfine interactions in double perovskites A2NiMnO6 (A = Sc, In, Tl). J. Phys. Chem. 2019, 123, 23628–23634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Khalyavin, D.D.; Manuel, P.; Blake, J.; Orlandi, F.; Yi, W.; Belik, A.A. Colossal magnetoresistance in the insulating ferromagnetic double perovskites Tl2NiMnO6: A neutron diffraction study. Acta Mater. 2019, 173, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, N.; Colin, C.V.; Qureshi, N.; Hansen, T.; Matsubayashi, K.; Uwatoko, Y.; Belik, A.A. Pressure-induced incommensurate antiferromagnetic order in a ferromagnetic B-site ordered double-perovskite Lu2NiMnO6. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 094412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, L.; Yuan, H. B-site ordering, magnetic and dielectric properties of hydrothermally synthesized Lu2NiMnO6. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, S.; Saha, S.; Dutta, A.; Murthy, J.K.; Venimadhav, A.; Shannigrahi, S.; Sinha, T.P. Magnetic ordering and conduction mechanism of different electroactive regions in Lu2NiMnO6. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 134102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, T.L.; Cao, J.J.; Yan, S.M.; Fang, Y.; Han, Z.D.; Qian, B.; Jiang, X.F.; Wang, D.H. Critical behavior and magnetocaloric effect in the multiferroic double perovskite Lu2NiMnO6. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katari, V.; Babu, P.D.; Mishra, S.K.; Mittal, R.; Bevara, S.; Achary, S.N.; Deshpande, S.K.; Tyagi, A.K. Effect of preparation conditions on magnetic and dielectric properties of Y2MMnO6 (M = Co, Ni). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarla, D.C.; Jyothinagaram, K.M.; Das, A.K.; Adyam, V. Dielectric and magnetodielectric properties of R2NiMnO6 (R = Nd, Eu, Gd, Dy, and Y). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 2858–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, Z.Z.; Yuan, L.; Ti, R.X.; Wu, H.R.; Yuan, H.M. Double perovskites R2NiMnO6 with small R3+ cations: Magnetic interactions tuned by R3+ ionic radius and the role of orbital ordering. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1039, 182997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystall. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Princep, A.J.; Guo, Y.F.; Johnson, R.D.; Khalyavin, D.D.; Manuel, P.; Senyshyn, A.; Presniakov, I.A.; Sobolev, A.V.; Matsushita, Y.; et al. Sc2NiMnO6: A double-perovskite with a magnetodielectric response driven by multiple magnetic orders. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 8012–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Liang, Q.F.; Matsushita, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Belik, A.A. High-pressure synthesis, crystal structure, and properties of In2NiMnO6 with antiferromagnetic order and field-induced phase transition. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 14108–14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, N.; Khalyavin, D.D.; Manuel, P.; Yi, W.; Suzuki, H.S.; Tsujii, N.; Imanaka, Y.; Belik, A.A. Ferroelectricity induced by ferriaxial crystal rotation and spin helicity in a B-site-ordered double-perovskite multiferroic In2NiMnO6. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 104413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’ev, A.N.; Volkova, O.S. New functional materials AC3B4O12 (Review). Low Temp. Phys. 2007, 33, 895–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y. A-site ordered quadruple perovskite oxides AA′3B4O12. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 078108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, I. Novel catalytic properties of quadruple perovskites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belik, A.A.; Johnson, R.D.; Khalyavin, D.D. The rich physics of A-site-ordered quadruple perovskite manganites AMn7O12. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 15458–15472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solana-Madruga, E.; Arevalo-Lopez, A.M. High-pressure A-site manganites: Structures and magnetic properties. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 315, 123470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhu, X.H. Research progress on quadruple perovskite oxides. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 9510–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belik, A.A. A site-ordered quadruple perovskites, RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Bi, Ce, and Ho, with different degrees of B site ordering. Molecules 2025, 30, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.Y.; Liu, M.; Dai, J.H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Cao, H.; Cruz, C.D.; Chen, C.T.; Xu, Y.; Shen, X.; et al. LaMn3Ni2Mn2O12: An A-and B-site ordered quadruple perovskite with A-site tuning orthogonal spin ordering. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8988–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, C.-E.; Cheng, C.; Chen, X.R. A–B-intersite-dependent magnetic order and electronic structure of LaMn3Ni2Mn2O12: A first-principles study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belik, A.A.; Liu, R.; Tanaka, M.; Yamaura, K. B-site-ordered and disordered structures in A-site-ordered quadruple perovskites RMn3Ni2Mn2O12 with R = Nd, Sm, Gd, and Dy. Molecules 2024, 29, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, C.; McEuen, P. Introduction to Solid State Physics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama, D.; Miyasaka, S.; Tokura, Y. Magnetic-field-induced polarization and depolarization in HoMn2O5 and ErMn2O5. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 064421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailova, B.; Gospodinov, M.M.; Güttler, B.; Yen, F.; Litvinchuk, A.P.; Iliev, M.N. Temperature-dependent Raman spectra of HoMn2O5 and TbMn2O5. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 172301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulov, I.; Nizhankovskii, V.I.; Lovchinov, V.; Dimitrov, D.; Apostolov, A. Colossal magnetostriction effect in HoMn2O5. Eur. Phys. J. B 2006, 52, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzankov, D.; Skumryev, V.; Aroyo, M.; Puzniak, R.; Kuz’min, M.D.; Mikhov, M. Magnetic anisotropy of multiferroic HoMn2O5 single crystal. Solid State Commun. 2008, 147, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, M.; Bagri, A.; Barlettani, D.; Teather, E.; Squillante, L.; de Souza, M.; Pontes, R.B.; Silva, A.G.; Mori, T.J.A.; Perry, R.; et al. Magnetostriction as the origin of the magnetodielectric effect in La2CoMnO6. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2025, 9, 094403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Ghosh, A.; Mahendiran, R. Giant magnetostriction in La2CoMnO6 synthesized by microwave irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 022403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, F.; Ikeda, T. A Rietveld-analysis program RIETAN-98 and its applications to zeolites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2000, 321–324, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sundaresan, A. Unveiling a hidden multiferroic state under magnetic fields in BaHoFeO4. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 184420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).