Synthetic Methods of Sugar Amino Acids and Their Application in the Development of Cyclic Peptide Therapeutics
Abstract
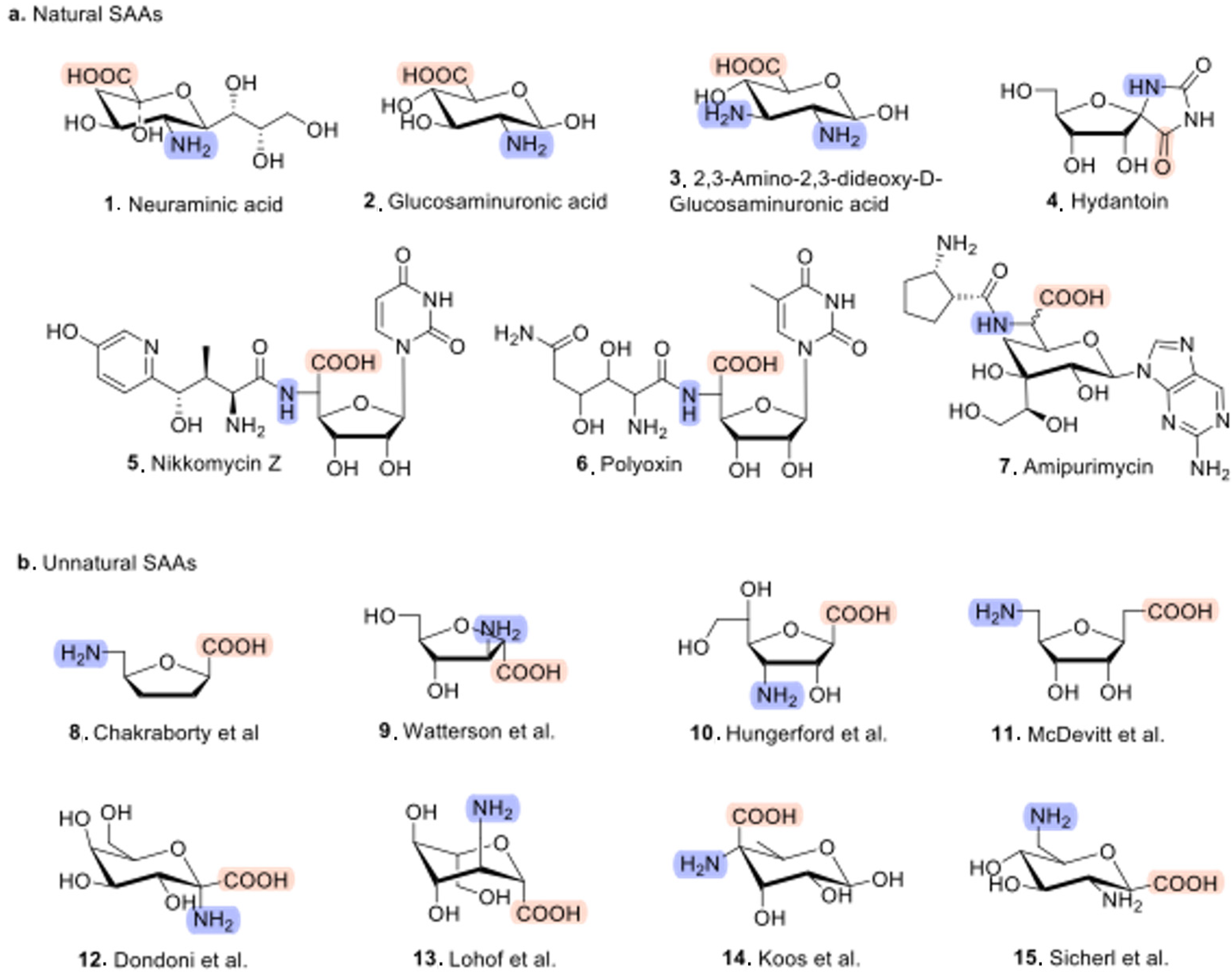
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis Methods of Sugar Amino Acids
2.1. Traditional Synthesis Methods of Sugar Amino Acids
2.2. Synthesis of Novel Sugar Amino Acids
2.2.1. Synthesis of Furan and Pyran SAA
- Synthesis of Furan δ-SAA
- 2.
- Synthesis of Pyran δ-SAA
2.2.2. Synthesis of C6-Substituted 3,4-Dideoxyfuran SAAs
2.2.3. Synthesis of Furanose Quaternary α-Amino Acids
2.2.4. Synthesis of Cis and Trans Bicyclic Sugar Amino Acids
2.2.5. Synthesis of Cis Bicyclic Sugar Amino Acids
2.2.6. Synthesis of Trans-Pyranobicyclic Sugar Amino Acids
2.3. Simple and Efficient Methods for Synthesizing Novel Amino Acids
2.3.1. Six-Step Synthesis of Sugar Amino Acid Analogs
2.3.2. Three-Step Synthesis of Novel 2-C-Branch SAAs
3. Structure-Function Relationships in SAA-Containing Peptides
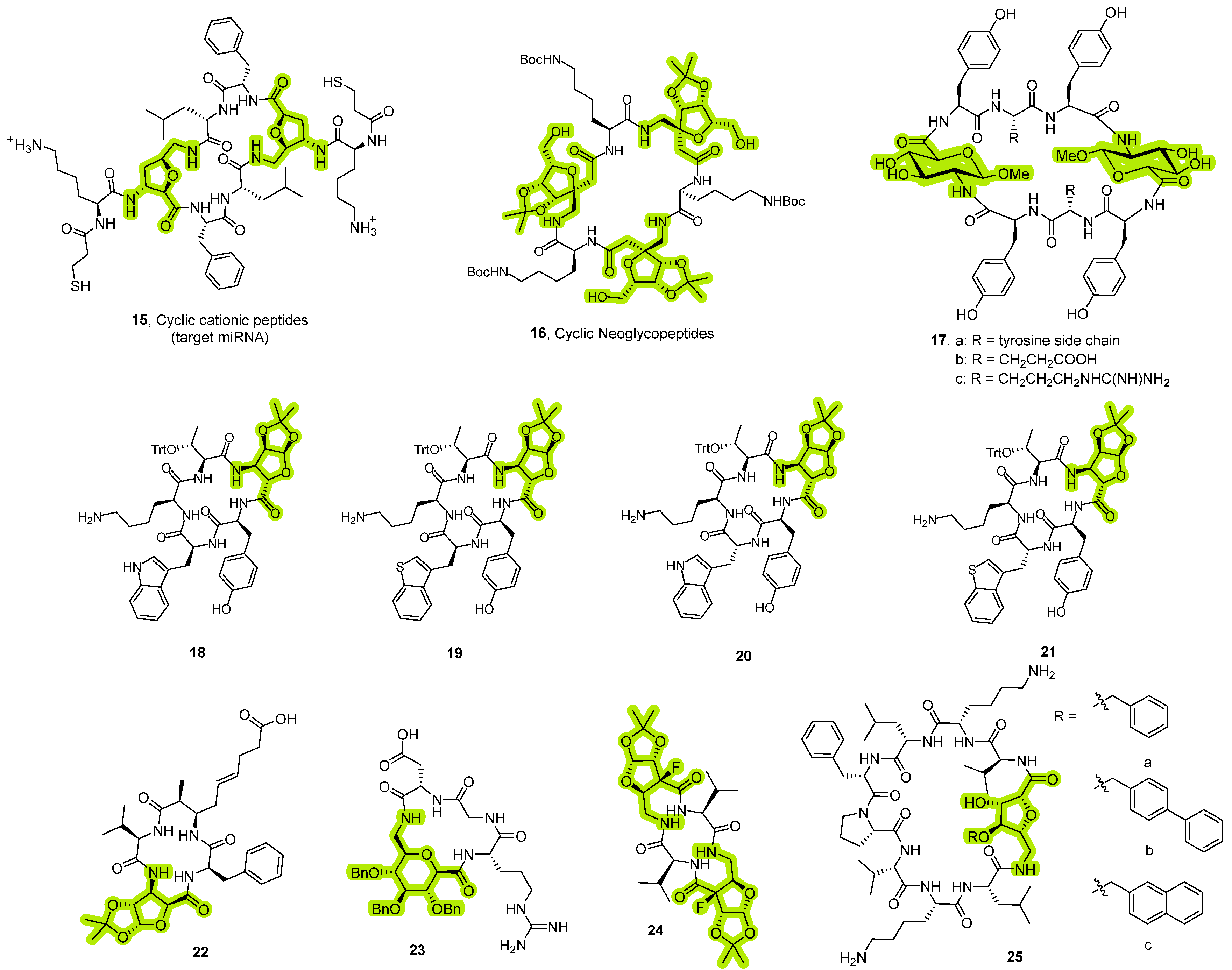
3.1. Conformational Impact of SAA Incorporation
- β-Turn Stabilization
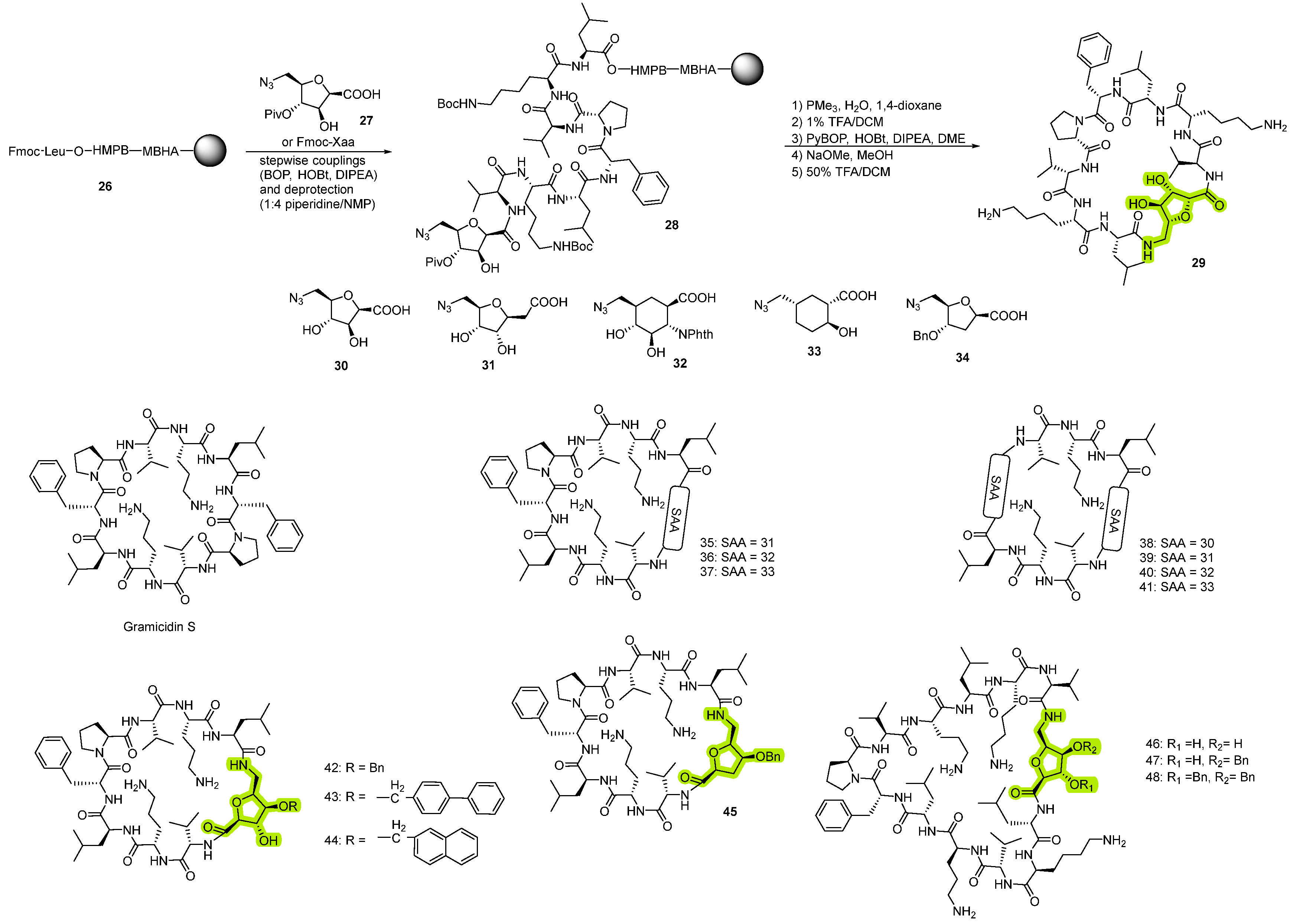
Case Study: Gramicidin S Analogs
- 2.
- Helical Induction
3.2. Application of SAA
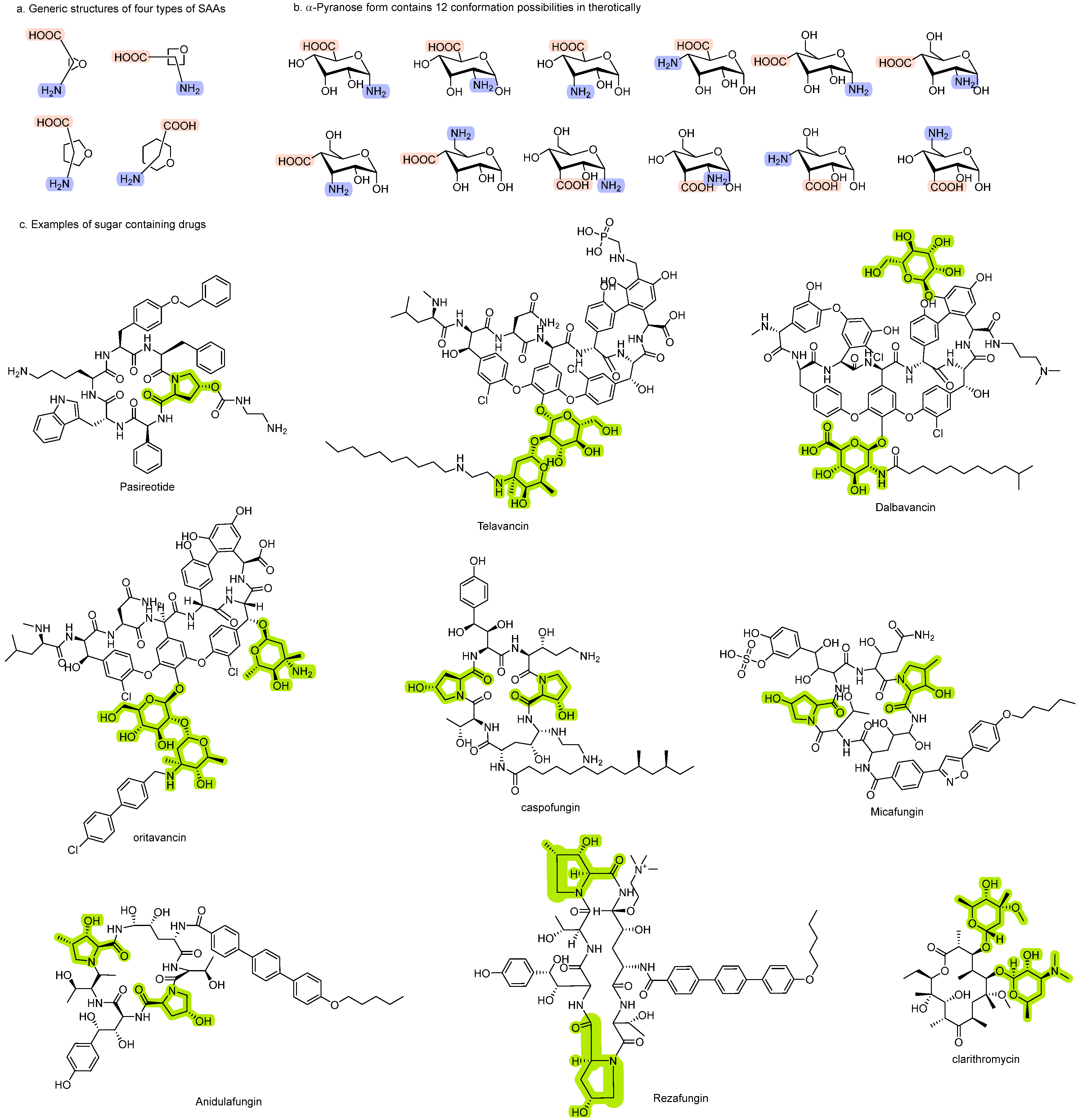
3.2.1. Glycomimetic and Peptidomimetic Functions of SAA
Glycomimetics
Peptidomimetics
- Linear Peptidomimetics
- 2.
- Cyclic Peptides
- 3.
- Mixed Oligomers
3.2.2. Synthesis of Cyclic Peptides Containing SAA
3.3. Synthesis of Cyclic Peptides Containing δ-Glycine Amino Acids
3.4. Synthesis of Chiral Macrocyclic Glycopeptides via Ring-Closing Metathesis
3.5. SAA Insertion to Enhance Hydrophilicity
3.6. Application of Sugars–Amino Acids–Nucleotides
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAAs | sugar amino acids |
References
- Baschang, G. Muramylpeptides and Lipopeptides: Studies towards Immunostimulants. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 6331–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, K.C.; Sarva, J.; Subhash, G. Sugar Amino Acid Based Scaffolds—Novel Peptidomimetics and Their Potential in Combinatorial Synthesis. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2002, 5, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyns, K.; Kiessling, G.; Lindenberg, W.; Paulsen, H. D-Galaktosaminuronsäure (2-Amino-2-desoxy-D-galakturonsäure) als Baustein des Vi-Antigens. Chem. Ber. 1959, 92, 2435–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wede, J.; Volk, F.-J.; Frahm, A.W. Carbocyclic α-Amino Acids: Asymmetric Strecker Synthesis of 2-Alkylated 1-Aminocyclopentanecarboxylic Acids. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2000, 11, 3231–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fülöp, F. Alicyclic β-Amino Acids: Useful Synthons in Drug Research. Farmaco 2000, 55, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelo, F.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Marrot, J.; Rauter, A.P.; Sinaÿ, P.; Blériot, Y. Stereochemical Assignment and First Synthesis of the Core of Miharamycin Antibiotics. Chem.-Eur. J. 2008, 14, 10066–10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernecki, S.; Franco, S.; Horns, S.; Valéry, J. Studies Directed towards the Synthesis of Miharamycin B. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 4003–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Feng, C.; Chen, Y.; Tan, H. Novel Polyoxins Generated by Heterologous Expression of the Polyoxin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster in the sanN-Inactivated Mutant of Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Tian, Y.; Tan, H. Selectively Improving Nikkomycin Z Production by Blocking the Imidazolone Biosynthetic Pathway of Nikkomycin X and Uracil Feeding in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risséeuw, M.; Overhand, M.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Simone, M.I. A Compendium of Cyclic Sugar Amino Acids and Their Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Nitrogen Analogues. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 613–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risséeuw, M.D.P.; Overhand, M.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Simone, M.I. A Compendium of Sugar Amino Acids (SAA): Scaffolds, Peptide- and Glyco-Mimetics. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2007, 18, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Y. Post-Modification of Amino Acids and Peptides for the Rapid Synthesis of C-Glycoamino Acids and C-Glycopeptides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202201036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruner, S.A.W.; Locardi, E.; Lohof, E.; Kessler, H. Carbohydrate-Based Mimetics in Drug Design: Sugar Amino Acids and Carbohydrate Scaffolds. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondoni, A.; Marra, A. Methods for Anomeric Carbon-Linked and Fused Sugar Amino Acid Synthesis: The Gateway to Artificial Glycopeptides. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 4395–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmid, V.G.; Duong, K.H.Y.; Horváth, D.; Ferentzi, K.; Farkas, V.; Perczel, A. Application of Sugar Amino Acids: Flow Chemistry Used for α/β-Chimera Synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 6071–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soengas, R.G.; Silva, S. Spirocyclic Nucleosides in Medicinal Chemistry: An Overview. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soengas, R.G.; Estévez, A.M.; Estévez, J.C.; Estévez, R.J. An Overview on the Synthesis of Furanoid and Pyranoid Sugar α- and β-Amino Acids and Related Aminocycloalkanecarboxylic Acids from Carbohydrates. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2011, 14, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichard, C.J.F.; Mitchell, E.P.; Wormald, M.R.; Watson, K.A.; Johnson, L.N.; Zographos, S.E.; Koutra, D.D.; Oikonomakos, N.G.; Fleet, G.W.J. Potent Inhibition of Glycogen Phosphorylase by a Spirohydantoin of Glucopyranose: First Pyranose Analogues of Hydantocidin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburrini, A.; Colombo, C.; Bernardi, A. Design and Synthesis of Glycomimetics: Recent Advances. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 495–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschmann, R.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Pietranico, S.; Leahy, E.M.; Salvino, J.; Arison, B.; Cichy, M.A.; Spoors, P.G.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Sprengeler, P.A.; et al. De Novo Design and Synthesis of Somatostatin Non-Peptide Peptidomimetics Utilizing β-d-Glucose as a Novel Scaffolding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 12550–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.D. β-d-Allose: From D-Glucose by Oxidation of 1,2:5,6-Di-O-isopropylidene-α-d-glucofuranose and Reduction of 1,2:5,6-Di-O-isopropylidene-α-d-ribo-hexofuranos-3-ulose. In General Carbohydrate Method; Whistler, R.L., BeMiller, J.N., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Mondal, D.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Synthesis of Glucose-Templated Lysine Analogs and Incorporation into the Antimicrobial Dipeptide Sequence kW-OBn. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Goldschmid, V.G.; Pintér, I.; Farkas, V.; Perczel, A. α/β-Chimera Peptide Synthesis with Cyclic β-Sugar Amino Acids: An Efficient Coupling Protocol. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Pimpalpalle, T.M.; Linker, T.; Yin, J. Study on the Synthesis of Novel Sugar Amino Acids. Acta Chim. Sin. 2015, 73, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Sudhakar, G. Synthesis of C6-Substituted 3,4-Dideoxy Furanoid Sugar Amino Acids. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2005, 16, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Bera, S.; Mondal, D. Synthesis of Conformationally Rigid Sugar-Fused Lactones and Sugar α-Amino Acids. Tetrahedron 2023, 146, 133646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulueta, M.M.L.; Zhong, Y.-Q.; Hung, S.-C. Synthesis of l-Hexoses and Their Related Biomolecules. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3275–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miriyala, B.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Williamson, J.S. Chemoselective Reductive Alkylation of Ammonia with Carbonyl Compounds: Synthesis of Primary and Symmetrical Secondary Amines. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paryzek, Z.; Skiera, I. Synthesis and Cleavage of Lactones and Thiolactones: Applications in Organic Synthesis. A Review. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2007, 39, 203–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplander, K.; Hidestål, O.; Katebzadeh, K.; Lindström, U.M. A Green and Facile Route to γ- and δ-Lactones via Efficient Pinner-Cyclization of Hydroxynitriles in Water. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kandiyal, P.S.; Shukla, P.K.; Ampapathi, R.S.; Chakraborty, T.K. Conformational Studies of Glycosylated Cyclic Oligomers of Furanoid Sugar Amino Acids. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5671–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risséeuw, M.D.P.; Grotenbreg, G.M.; Witte, M.D.; Tuin, A.W.; Leeuwenburgh, M.A.; Van der Marel, G.A.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Overhand, M. The Synthesis of cis- and trans-Fused Bicyclic Sugar Amino Acids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2006, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.D.; Smith, M.D.; Marquess, D.G.; Claridge, T.D.W.; Brittain, D.E.A.; Fleet, G.W.J. From Sequencamers to Foldamers? Tetrameric Furanose Carbopeptoids from cis- and trans-5-Aminomethyl-tetrahydrofuran-2-carboxylates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Withers, S.G. Syntheses of the 3- and 4-Thio Analogues of 4-Nitrophenyl 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-β-d-gluco- and galactopyranoside. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2212–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.-Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.-X.; Rademacher, C.; Zou, X.P.; Zheng, H.N.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.L.; Linker, T.; Yin, J. Synthesis and Conformational Analysis of Linear Homo- and Heterooligomers from Novel 2-C-Branched Sugar Amino Acids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruner, S.A.W.; Truffault, V.; Voll, G.; Locardi, E.; Stöckle, M.; Kessler, H. Design, Synthesis, and NMR Structure of Linear and Cyclic Oligomers Containing Novel Furanoid Sugar Amino Acids. Chem.-Eur. J. 2002, 8, 4365–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellman, S.H. Foldamers: A Manifesto. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, D.F.; Gessier, F.; Noti, C.; Kast, P.; Seebach, D. Probing the Proteolytic Stability of β-Peptides Containing α-Fluoro- and α-Hydroxy-β-amino Acids. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frackenpohl, J.; Arvidsson, P.I.; Schreiber, J.V.; Seebach, D. The Outstanding Biological Stability of β- and γ-Peptides toward Proteolytic Enzymes: An In Vitro Investigation with Fifteen Peptidases. ChemBioChem 2001, 2, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, O.M.; Kim, S.; Welch, B.D.; Hodsdon, M.E.; Kay, M.S.; Schepartz, A. Inhibiting HIV Fusion with a β-Peptide Foldamer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13126–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritzer, J.A.; Stephens, O.M.; Guarracino, D.A.; Reznik, S.K.; Schepartz, A. β-Peptides as Inhibitors of Protein–Protein Interactions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; DeGrado, W.F. De Novo Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Antimicrobial β-Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7553–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gademann, K.; Kimmerlin, T.; Hoyer, D.; Seebach, D. Peptide Folding Induces High and Selective Affinity of a Linear and Small β-Peptide to the Human Somatostatin Receptor 4. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gademann, K.; Seebach, D. Synthesis of Cyclo-β-tripeptides and Their Biological in vitro Evaluation as Antiproliferatives against the Growth of Human Cancer Cell Lines. Helv. Chim. Acta 2001, 84, 2924–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.; Reddy, G.B.; Rao, C.L. Titanium tetrachloride mediated reductive ring opening of C-aryl pseudoglycals. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanas, C.; de la Torre, B.G.; Fernández-Reyes, M.; Santiveri, C.M.; Jiménez, M.A.; Rivas, L.; Jiménez, A.I.; Andreu, D.; Cativiela, C. Sequence Inversion and Phenylalanine Surrogates at the β-Turn Enhance the Antibiotic Activity of Gramicidin S. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4119–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotenbreg, G.M.; Buizert, A.E.M.; Llamas-Saiz, A.L.; Spalburg, E.; van Hooft, P.A.; de Neeling, A.J.; Noort, D.; van Raaij, M.J.; van der Marel, G.A.; Overkleeft, H.S.; et al. β-Turn Modified Gramicidin S Analogues Containing Arylated Sugar Amino Acids Display Antimicrobial and Hemolytic Activity Comparable to the Natural Product. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7559–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Forgó, P.; Stine, K.J.; D’Souza, V.T. Methods for Selective Modifications of Cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1977–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Roy, S.; Koley, D.; Dutta, S.K.; Kunwar, A.C. Conformational Analysis of Some C2-Symmetric Cyclic Peptides Containing Tetrahydrofuran Amino Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6240–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhara, Y.; Izumi, M.; Ichikawa, M.; Penno, M.B.; Ichikawa, Y. Peptide-Sugar Hybrids: Like Peptide, Like Oligosaccharide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 7167–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughin, C.; Masson, G.; Zhu, J. Rapid Synthesis of Cyclodepsipeptides Containing a Sugar Amino Acid or a Sugar Amino Alcohol by a Sequence of a Multicomponent Reaction and Acid-Mediated Macrocyclization. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A. Synthesis of Chiral Macrocyclic Sugar–Peptide Hybrids by Ring-Closing Metathesis Approach. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3038–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, T.; Kita, K. Gramicidin S and Polymyxins: The Revival of Cationic Cyclic Peptide Antibiotics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3821–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.A. Medicinal Significance of Naturally Occurring Cyclotetrapeptides. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 70, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkov, T.; Roberts, K.D.; Li, J. Rediscovering the Octapeptins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, W.; Briner, U.; Doepfner, W.; Haller, R.; Huguenin, R.; Marbach, P.; Petcher, T.J.; Pless. SMS 201–995: A Very Potent and Selective Octapeptide Analogue of Somatostatin with Prolonged Action. Life Sci. 1982, 31, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Huang, X.; Wong, C.-H. Design and Synthesis of Cyclic Sialyl Lewis X Mimetics: A Remarkable Enhancement of Inhibition by Pre-organizing All Essential Functional Groups. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 9499–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Sun, X.; Bienaymé, H.; Zhu, J. Activation of a Terminal Carboxylic Acid by an Internal Oxazole: A Novel Synthesis of Macrocyclodepsipeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6700–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughin, C.; Zhao, G.; Bienaymé, H.; Zhu, J. 5-Aminooxazole as an Internal Traceless Activator of C-Terminal Carboxylic Acid: Rapid Access to Diversely Functionalized Cyclodepsipeptides. Chem.-Eur. J. 2006, 12, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bililign, T.; Griffith, B.R.; Thorson, J.S. Structure, activity, synthesis and biosynthesis of aryl-C-glycosides. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 742–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaara, M.; Fox, J.; Loidl, G.; Siikanen, O.; Apajalahti, J.; Hansen, F.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M.; Vaara, T. Novel Polymyxin Derivatives Carrying Only Three Positive Charges Are Effective Antibacterial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mándity, I.M.; Fülöp, F. An Overview of Peptide and Peptoid Foldamers in Medicinal Chemistry. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrele, C.; Martinek, T.A.; Reiser, O.; Berlicki, Ł. Peptides Containing β-Amino Acid Patterns: Challenges and Successes in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9718–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Claridge, T.D.W.; Davies, S.G.; Ling, K.B.; Odell, B.; Rees, T.L.; Roberts, P.M.; Russell, A.J.; Smith, A.D.; Smith, L.J.; et al. A Systematic Study of the Solid-State and Solution-Phase Conformational Preferences of β-Peptides Derived from C(3)-Alkyl-Substituted Transpentacin Derivatives. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 69–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beke, T.; Csizmadia, I.G.; Perczel, A. On the Flexibility of β-Peptides. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Vankar, Y.D. Selective Deprotection of Terminal Isopropylidene Acetals and Trityl Ethers Using HClO4-Supported on Silica Gel. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetényi, A.; Tóth, G.K.; Somlai, C.; Vass, E.; Martinek, T.A.; Fülöp, F. Stabilisation of Peptide Foldamers in an Aqueous Medium by Incorporation of Azapeptide Building Blocks. Chem.-Eur. J. 2009, 15, 10736–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Csordás, B.; Zsoldos-Mády, V.; Pintér, I.; Farkas, V.; Perczel, A. C-3 Epimers of Sugar Amino Acids as Foldameric Building Blocks: Improved Synthesis, Useful Derivatives, Coupling Strategies. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordás, B.; Nagy, A.; Harmat, V.; Zsoldos-Mády, V.; Leveles, I.; Pintér, I.; Farkas, V.; Perczel, A. Origin of Problems Related to Staudinger Reduction in Carbopeptoid Syntheses. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, K.H.Y.; Goldschmidt, G.; Pintér, I.; Perczel, A. Synthesis of Chimera Oligopeptide Including Furanoid β-Sugar Amino Acid Derivatives with Free OHs: Mild but Successful Removal of the 1,2-O-Isopropylidene from the Building Block. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vembaiyan, K.; Pearcey, J.A.; Bhasin, M.; Lowary, T.L.; Zou, W. Synthesis of Sugar-Amino Acid-Nucleosides as Potential Glycosyltransferase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Agard, N.J.; Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. A Strain-Promoted [3+2] Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition for Covalent Modification of Biomolecules in Living Systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15046–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compain, P.; Martin, O.R. Carbohydrate Mimetics-Based Glycosyltransferase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carchon, G.; Chrétien, F.; Chapleur, Y. Toward Partial Fucosyl Transferase Transition-State Analogues: Methylene Sulfono Sulfonamide as Surrogate of Pyrophosphate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 5715–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carchon, G.; Chrétien, F.; Delannoy, P.; Verbert, A.; Chapleur, Y. Synthesis of a Non-Charged Analogue of Guanosyldiphosphofucose. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 8821–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Steensma, D.H.; Takaoka, Y.; Yun, J.W.; Kajimoto, T.; Wong, C.H. A Search for Pyrophosphate Mimics for the Development of Substrates and Inhibitors of Glycosyltransferases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, N.L.; Zheng, R.B.; Pearcey, J.; Zhou, R.; Completo, G.C.; Lowary, T.L. Development of a Coupled Spectrophotometric Assay for GlfT2, a Bifunctional Mycobacterial Galactofuranosyltransferase. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method Name | Starting Materials | Key Steps | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Method | Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, glucosamine, galactose) | Introduction of amino group via azides, cyanides, or nitromethane; introduction of carboxyl group via selective oxidation, Wittig reaction, or carbon dioxide | Basic method applicable for synthesizing various sugar amino acids |
| Synthesis of Furan and Pyran SAA | Furan alcohols, pyran alcohols, etc. | TEMPO oxidation, Curtius rearrangement, protection and deprotection | Synthesis of sugar amino acids with post-translational modifications for drug design and biological applications |
| Synthesis of Furan δ-SAA | Furan alcohols | TEMPO oxidation, Curtius rearrangement, Boc protection, deprotection | Synthesis of δ-sugar amino acids with furan structures |
| Synthesis of Pyran δ-SAA | Methyl 3,7-anhydro-4,5,6-tri-O-benzyl-2-deoxy-D-gulo-D-glycerate | Curtius rearrangement, saponification | Synthesis of δ-sugar amino acids with pyran structures |
| Synthesis of Chiral 3,4-Dideoxyfuran SAA with Various Alkyl Substitutions at C6 | Chiral N,N-dibenzylamino aldehyde, glyceraldehyde acetone | Lithium acetylide reaction, addition, reduction, protection, sulfonation, cyclization, oxidation | Introduction of a stereocenter at the C6 position to construct multifunctional units |
| Synthesis of Furanose Quaternary α-Amino Acids | 1,2:5,6-di-O-isopropylidene-α-D-glucopyranose | Ammoniation, oxidation, reduction, protection, hydrolysis, cyclization | Synthesis of furanose quaternary α-amino acids with amine and acid functional groups at the C3 position |
| Synthesis of Cis Bicyclic Sugar Amino Acids | 3,4,6-tri-O-benzyl-D-glucuronic acid | Epoxidation, α-C-glycosidation, partial reduction, alkylation, ring-closing metathesis | Introduction of additional conformations through Petasis olefination and ring-closing metathesis |
| Synthesis of Trans-Pyranobicyclic Sugar Amino Acids | Acetylene α-glycoside | Epimerization, partial reduction, alkylation, Petasis olefination, ring-closing metathesis | Introduction of additional conformations through Petasis olefination and ring-closing metathesis |
| Six-Step Synthesis of Sugar Amino Acid Analogs | 3,4,6-O-triacetyl-D-glucal, 3,4,6-O-triacetyl-D-galactal | Free radical addition, decarboxylation, deacetylation, iodination, azide substitution, one-pot reductive amination | High-yield synthesis of sugar amino acid analogs based on natural amino acids |
| Three-Step Synthesis of Novel 2-C-Branch Sugar Amino Acids | 2-deoxy-2-C-nitromethyl pyranoside | Hydrogenation, protection, TEMPO/NaOCl oxidation | Efficient synthesis of 2-C-branch sugar amino acids |
| Application Area | Specific Application | Detailed Description |
|---|---|---|
| Glycomimetic and Peptidomimetic | Glycomimetic | SAA served as a template for the early synthetic SAAs that mimic oligosaccharide structures. Early research focused on the synthesis of SAA oligomers in this context. |
| Linear Peptidomimetic | Although SAA65 does not inhibit the active site of the proteasome, the synthesis method provides ideas for the development of new proteasome inhibitors. | |
| Cyclic Peptide | Novel cationic antimicrobial peptides based on SAA exhibit antibacterial activity against a variety of bacteria; gramicidin S analogs containing arylated SAA have great antibacterial potential; cyclic peptides containing specific amino acids show great potential in ligand recognition and binding. | |
| Mixed Oligomer | The β-amino acids derived from it can inhibit cell adhesion and tumor cell invasion. | |
| Synthesis of Cyclic Peptides | Synthesis of Cyclic Neoglycopeptides with γ-Glycine Amino Acids | A hybrid macrocyclic structure with dual reactive groups was constructed. However, it is difficult to synthesize and purify, and the lactone ring will be transformed during the reaction. |
| Synthesis of Cyclic Peptides Containing δ-Glycine Amino Acids | δ-Glycine amino acids and tyrosine form the macrocycle. Some of these macrocycles can interact with specific purine derivatives and have the potential to be used as artificial receptors. | |
| Synthesis of Chiral Macrocyclic Glycopeptides via Ring-Closing Metathesis | This technology was used to synthesize various cyclic glycopeptide hybrids, which contain isopropyl-protected furanose sugar rings. | |
| SAA Insertion to Enhance Hydrophilicity | Introducing SAA improves the hydrophobicity of oligopeptides containing β-amino acids. The Duong team established a relevant deprotection method. | |
| Application of Sugars-Amino Acids-Nucleotides | Glycosyltransferase Inhibitor | Amino acids were used to replace the diphosphate moiety of sugar nucleotides. SAANs containing tryptophan and histidine have moderate inhibitory effects, but SAANs have poor permeability. |
| Application | Target | Lead Compound | Activity (IC50/MIC) | Selectivity | Development Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | Bacterial membrane | SAA-GS-3 | 1.8 μg/mL | >55.6 | Preclinical |
| Anticancer | SSTR2/5 | SAA-SST-14 | 0.8 nM | >100 | Preclinical |
| Anticancer | αvβ3 integrin | SAA-RGD-1 | 3.2 nM | >50 | Preclinical |
| Anti-inflammatory | P-selectin | SAA-sLeX-2 | 85 nM | >25 | Research |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, C.; Wang, D. Synthetic Methods of Sugar Amino Acids and Their Application in the Development of Cyclic Peptide Therapeutics. Processes 2025, 13, 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092849
Bao C, Wang D. Synthetic Methods of Sugar Amino Acids and Their Application in the Development of Cyclic Peptide Therapeutics. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092849
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Chengcheng, and Dekai Wang. 2025. "Synthetic Methods of Sugar Amino Acids and Their Application in the Development of Cyclic Peptide Therapeutics" Processes 13, no. 9: 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092849
APA StyleBao, C., & Wang, D. (2025). Synthetic Methods of Sugar Amino Acids and Their Application in the Development of Cyclic Peptide Therapeutics. Processes, 13(9), 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092849







