A Comparative Review on Dry Ice Production Methods: Challenges, Sustainability and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Dry Ice and Its Applications
2.1. Properties of Dry Ice
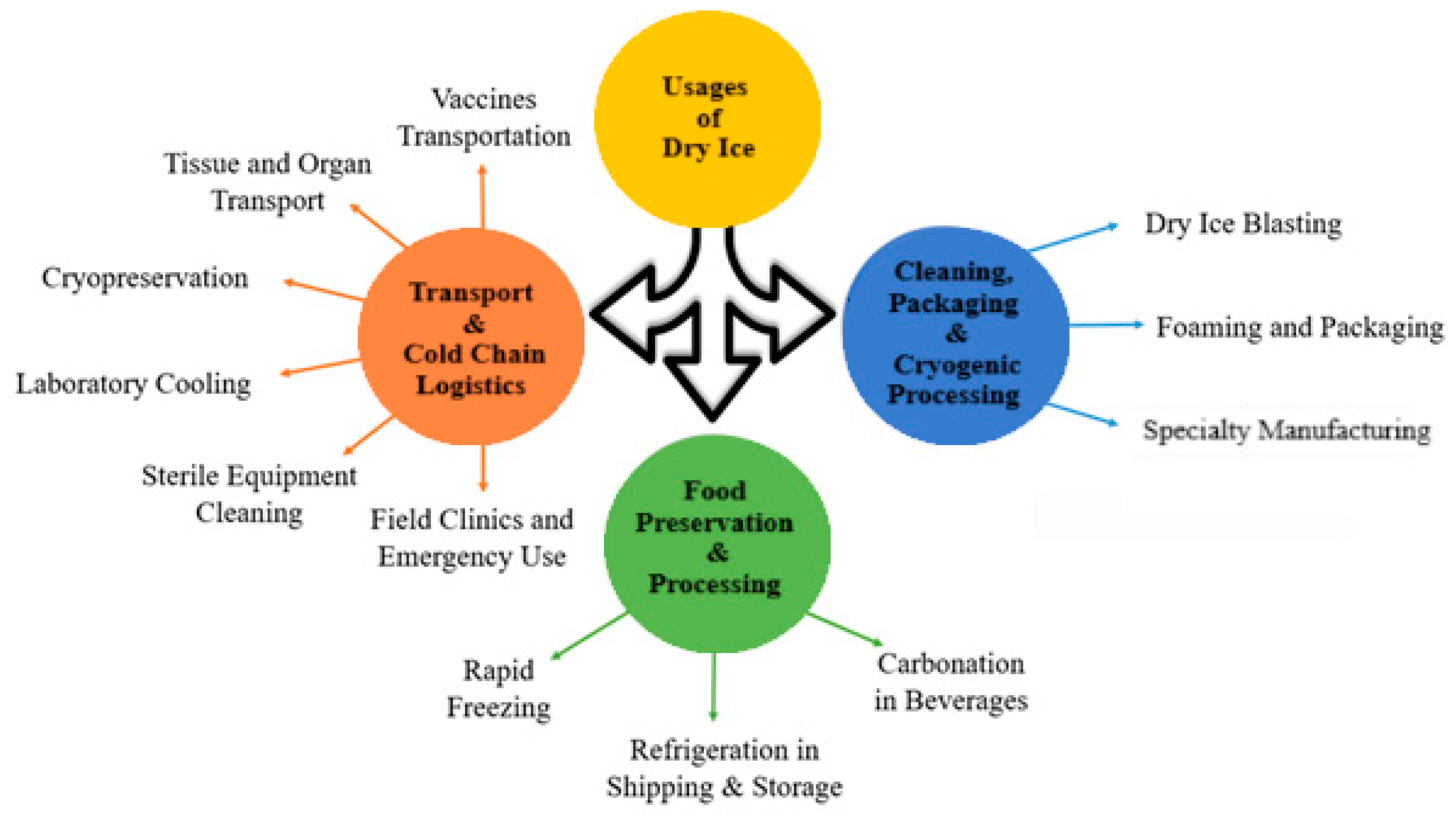
2.2. Applications Across Industries
2.2.1. Dry Ice in Transport and Cold Chain Logistics
2.2.2. Dry Ice for Food Preservation and Processing
2.2.3. Dry Ice for Cleaning, Packaging, and Cryogenic Processing
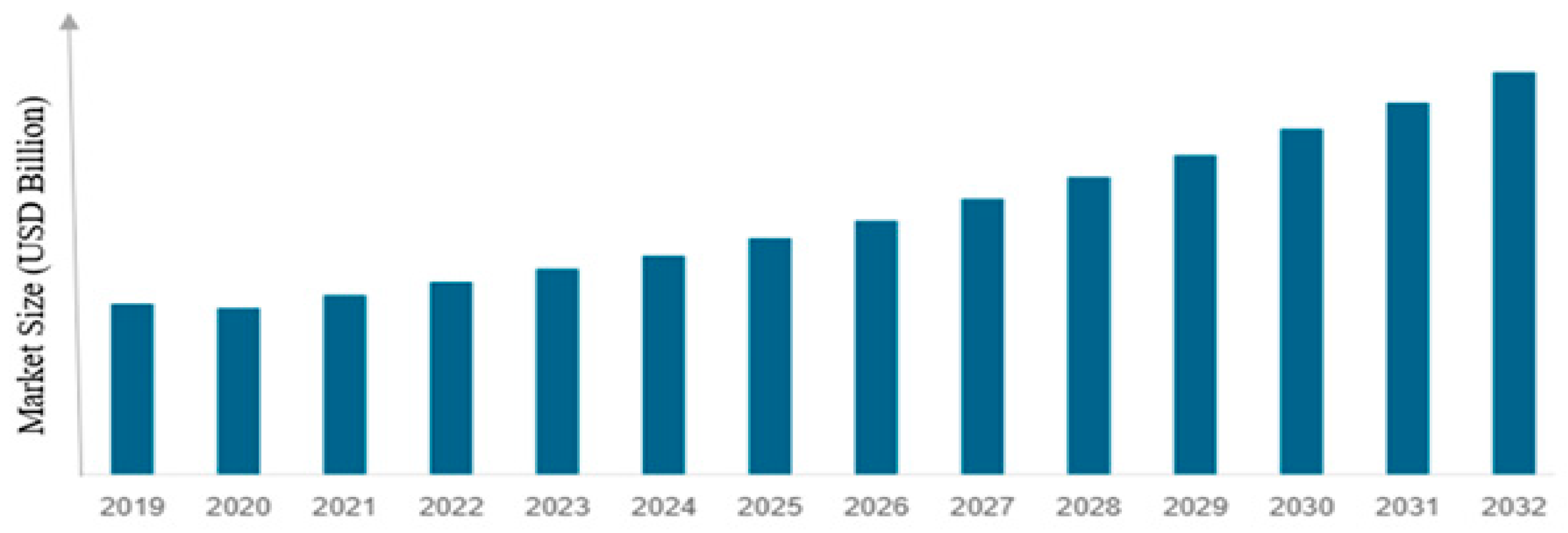
2.3. Global Market and Trends
Economic Relevance
2.4. Carbon Dioxide Sources for Dry Ice Production
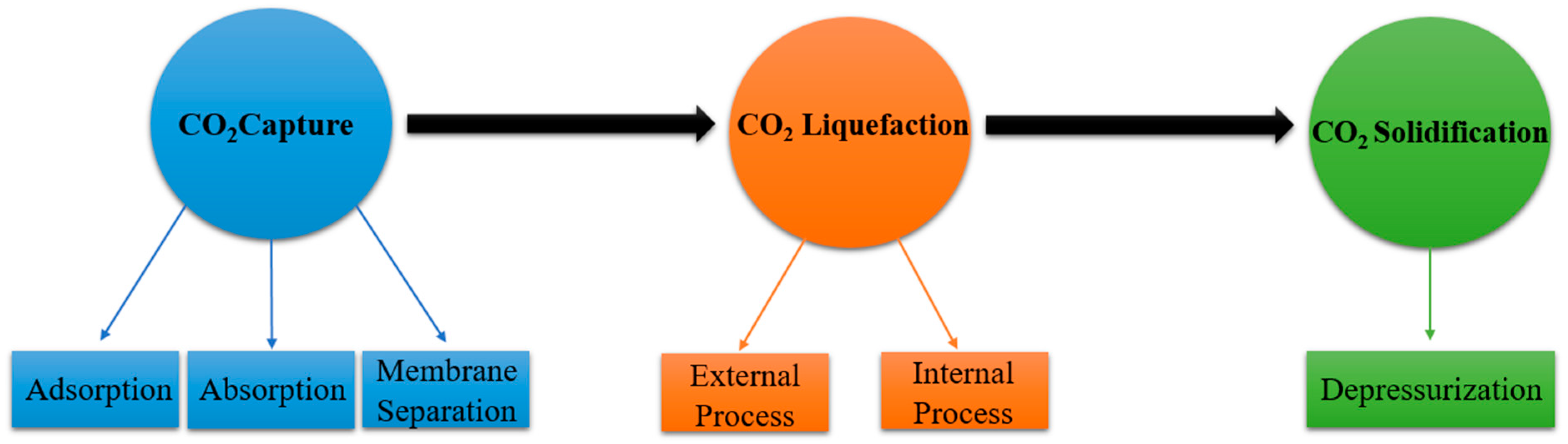
3. Dry Ice Production Pathways
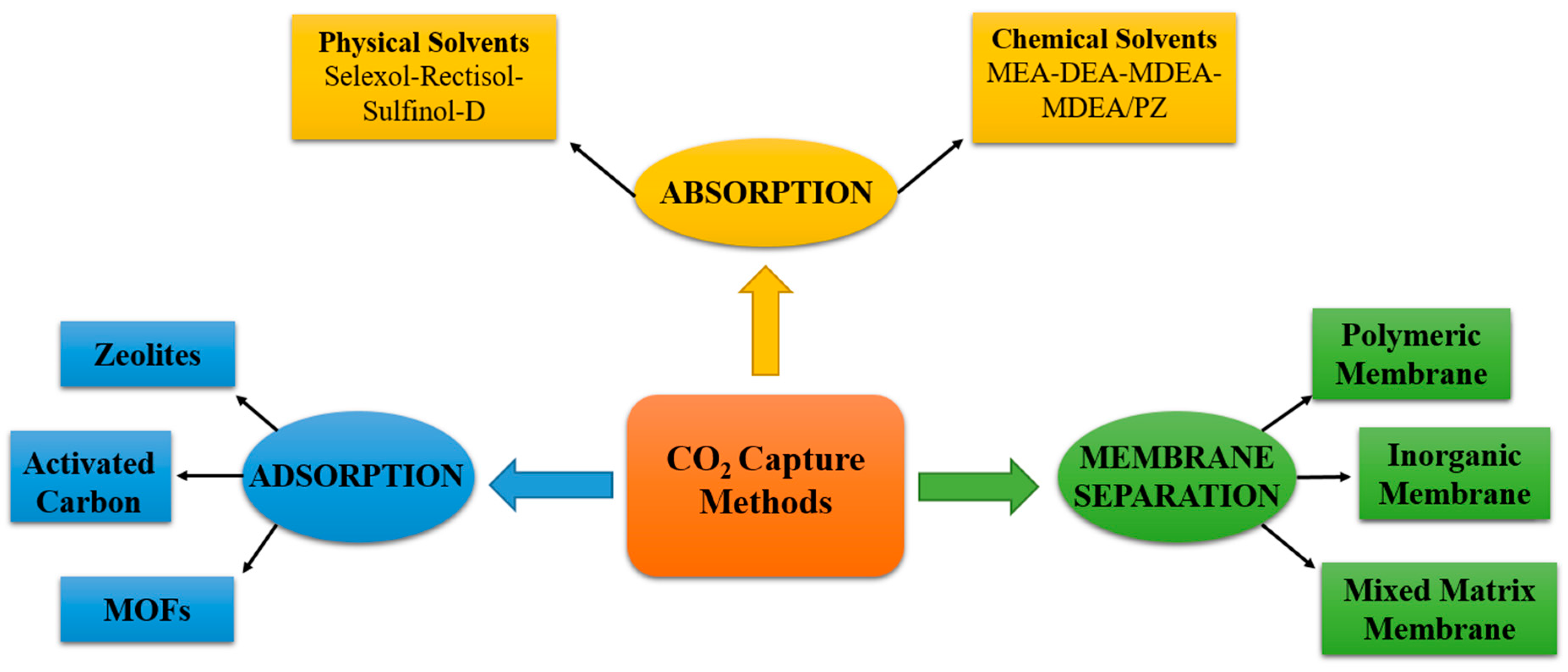
3.1. Carbon Dioxide Capture Methods
3.1.1. Adsorption
Types of Adsorbents
Comparison of Common Adsorbents for CO2 Capture
Adsorption and Desorption
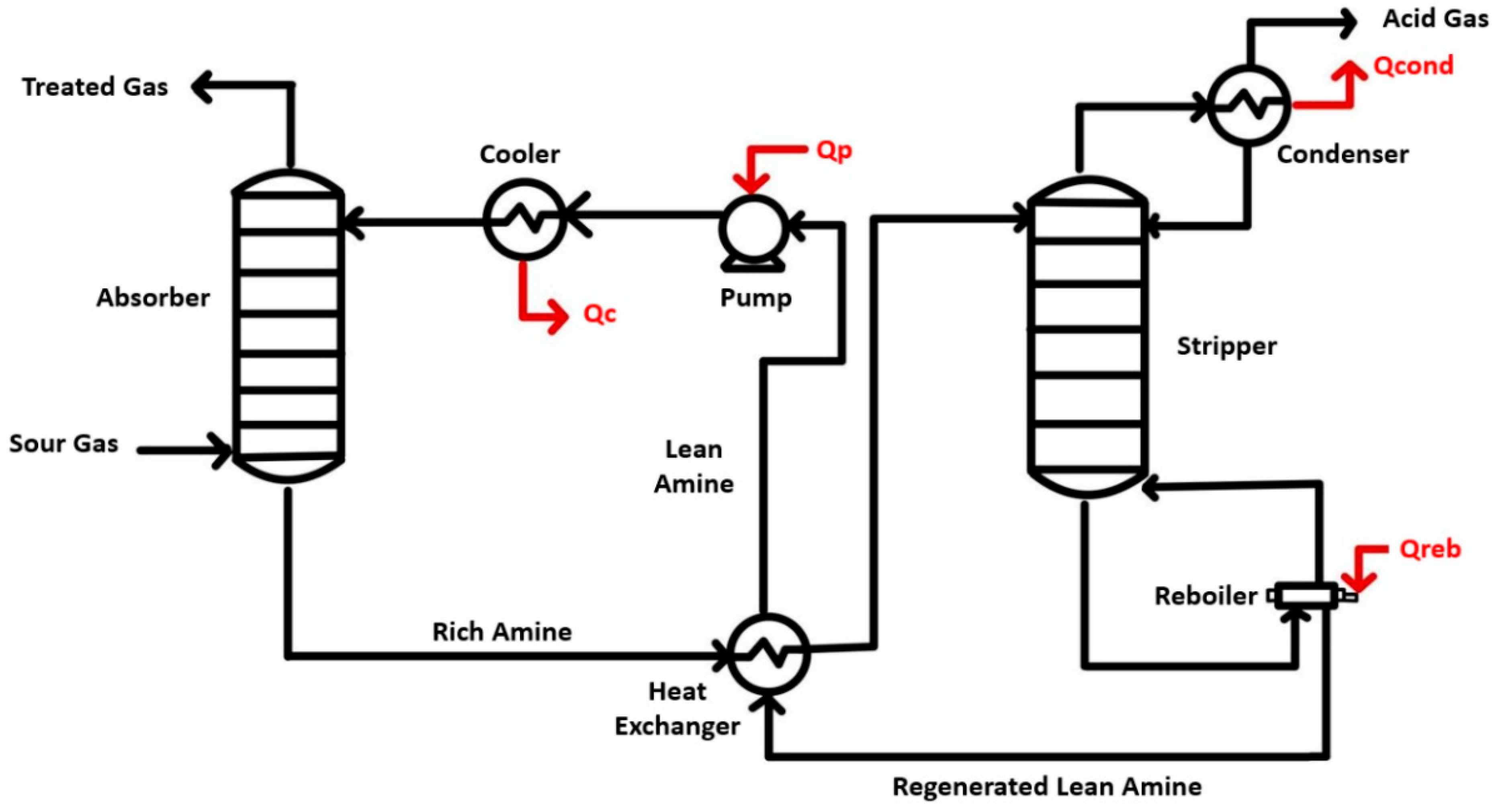
3.1.2. Absorption
Types of Absorbents
- Comparison of Common Chemical Solvents for CO2 Capture
- Comparison of Common Physical Solvents for CO2 Capture
Evaluating Chemical and Physical Solvents for CO2 Capture
Adsorption and Desorption
3.1.3. Membrane Separation
Types of Membranes
Comparison of Common Membranes for CO2 Capture
3.1.4. Evaluation of Chemical, Physical, and Membrane Methods for CO2 Capture
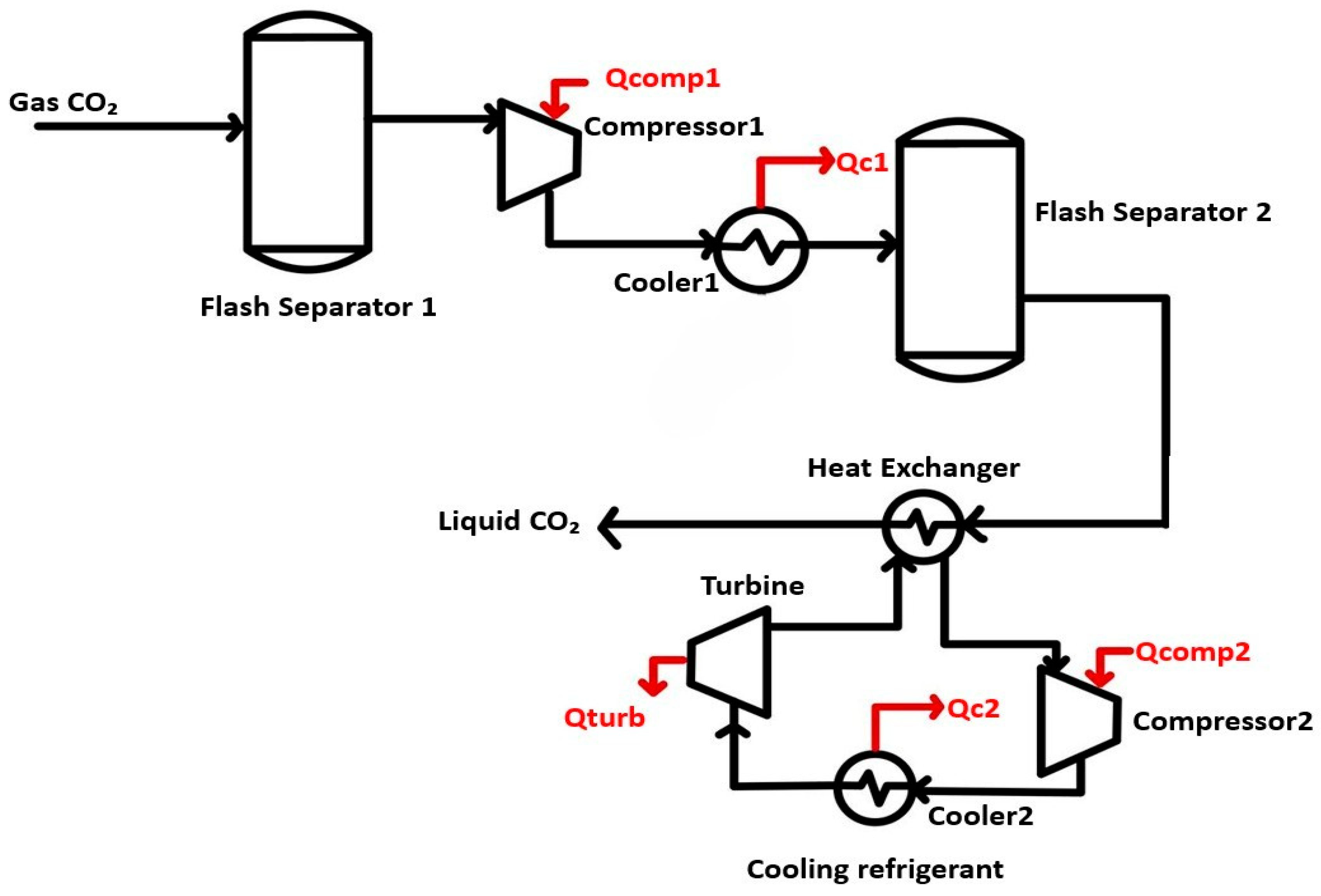
3.2. Carbon Dioxide Liquefaction
3.2.1. External Liquefaction Cycle
Comparison of Common Refrigerants Used in CO2 External Liquefaction
3.2.2. Internal Liquefaction Cycle
3.2.3. Comparison of Common Refrigerants Used in CO2 Internal Liquefaction
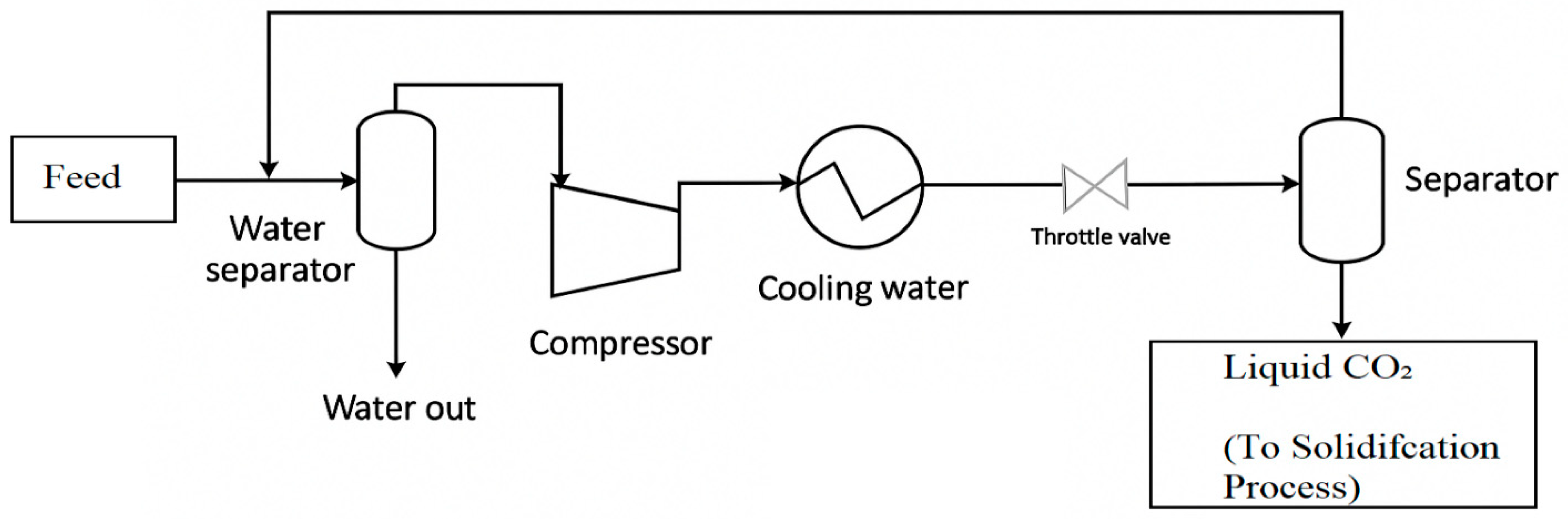
3.3. Carbon Dioxide Solidification
4. Key Challenges in Dry Ice Production
4.1. Technical Challenges
4.2. Economic Barriers
4.3. Environmental Impact
4.4. Operational and Safety Concerns
5. Sustainability Considerations
5.1. Environmental Sustainability and Circular Economy
5.2. Green Technologies
5.3. Policy Drivers and Regulation
6. Innovations and Future Perspectives
Technological Breakthroughs and Renewable Energy Integration
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| CCS | Carbon Capture and Storage |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease of 2019 |
| LN2 | Liquid Nitrogen |
| CAGR | Compound Annual Growth Rate |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA Molecules |
| IQF | Individual Quick Freezing |
| tcf | Trillion Cubic Feet |
| CH4 | Methane |
| C2H6 | Ethane |
| C3H8 | Propane |
| i-C4H10 | Isobutane |
| n-C4H10 | Butane |
| i-C5H12 | Isopentane |
| n-C5H12 | Pentane |
| n-C6H12 | Cyclohexane |
| n-C7H16 | Heptane |
| N2 | Nitrogen |
| H2O | Water |
| MOF | Metal–Organic Framework |
| TSA | Temperature Swing Absorption |
| PSA | Pressure Swing Absorption |
| MEA | Monoethanolamine |
| DEA | Diethanolamine |
| MDEA | Methyldiethanolamine |
| H2S | Hydrogen Sulfide |
| MMM | Mixed Matrix Membrane |
| R-134a | 1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane |
| BP | Boiling Point |
| GWP | Global Warming Potential |
| GWI | Global Warming Impact |
| ODP | Ozone Depletion Potential |
| LCO2 | Liquid Carbon Dioxide |
| PR-EOS | Peng-Robinson Equation of State |
| PZ | Piperazine |
References
- Prajapati, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Dayal, P.; Gairola, A.; Borate, R.B.; Srivastava, R. The role of carbon in life’s blueprint and carbon cycle understanding earth’s essential cycling system: Benefits and harms to our planet. AgriSustain. Int. J. 2023, 1, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Caramanna, G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Vega, F.; Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Vilches Arenas, L.F.; Navarrete, B. Carbon capture and utilization technologies: A literature review and recent advances. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 1403–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, D.; Bhattacharya, R.; Kaur, T.; Pandya, R.; Sarkar, A.; Ray, A.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, A.; Ghosh, P.; Chemudupati, R.I. Innovative approaches for carbon capture and storage as crucial measures for emission reduction within industrial sectors. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkarem, A.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R. Development of CO2 liquefaction cycles for CO2 sequestration. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 33–34, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, C.; Ozturkoglu, Y. Investigating the performance of the sustainable cold supply chain in the pharmaceutical industry. Int. J. Pharm. Healthc. Mark. 2022, 16, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines on the International Packaging and Shipping of Vaccines, 6th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- INTELSIUS. COVID-19 Vaccine Transport: The Role of Dry Ice. Available online: https://intelsius.com/news/covid-19-vaccine-role-dry-ice/ (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Bagwan, N.S.; Gevaers, R.; Dewulf, W. Cooling Technologies in Cooled Supply Chains. About the Suitability and Sustainability of Dry Ice as a Cooling Medium. An Exhaustive Review. In Advances in Resilient and Sustainable Transport; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 274–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiat, I.; Al-Ansari, T. A review of carbon capture and utilisation as a CO2 abatement opportunity within the EWF nexus. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 45, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigato, F.; Woodley, J.M.; Alvarado-Morales, M. Modeling the effect of CO2 limitation in continuous fermentation for biosuccinic acid production. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 79, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenath, S.; Sam, A.A. Hybrid membrane-cryogenic CO2 capture technologies: A mini-review. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1167024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Kitamura, Y.; Li, S. Energy analysis of the cryogenic CO2 capture process based on Stirling coolers. Energy 2014, 65, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, Q.; Deng, S.; Li, H.; Kitamura, Y. Cryogenic-based CO2 capture technologies: State-of-the-art developments and current challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y. Study on a novel process for CO2 compression and liquefaction integrated with the refrigeration process: A novel process for CO2 compression and liquefaction. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, S.; Borho, I.; Jung, J.; Schmidt, M.S. Review: CO2 capturing methods of the last two decades. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 8087–8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Vanderwal, C.D. Lessons Learned: Asphyxiation Hazard Associated with Dry Ice. ACS Chem. Health Saf. 2023, 30, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, E.; Raouf, F.; Alyani, S.J.; Kardan, A.; Moghaddam, A.M. Carbon dioxide capture and utilization in post-combustion: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 14351–14382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CO2METER. Dry Ice Dangers, Uses, and Safety Best Practices. Available online: https://www.co2meter.com/blogs/news/dry-ice-dangers-uses-safety-best-practices (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhao, N. Application of CO2 in the preservation of temperature-sensitive biological products. J. CO2 Util. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chu, X.; Zheng, J. A combined experimental-mathematical study on the kinetics of dry ice sublimation under different airflow velocities and blowing modes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 258, 124567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purandare, A.; Verbruggen, W.; Vanapalli, S. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the dry ice sublimation temperature for varying far-field pressure and CO2 concentration. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 148, 107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J. Thermodynamic analysis of CO2 sublimation cooling for rapid freezing applications. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 424–431. [Google Scholar]
- Saiduzzaman; Konstantinov, V.A.; Andersson, O. Thermal Conductivity of Solid Carbon Dioxide. Int. J. Thermophys. 2025, 46, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Evaluation of insulated dry ice containers for extended low-temperature storage in cold chain logistics. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 38, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhang, G.-Y. Effect of dry ice as admixture on engineering properties of alkali-activated slag: Setting time, strength, and sustainability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Exactly is Dry Ice? We Have the Answer! DRY ICE ENERGY. Available online: https://dryiceenergy.com/en/what-is-dry-ice/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Study on CO2 solid-gas sublimation characteristics for cold chain logistics applications. J. CO2 Util. 2023, 22, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- nexAir. Dry Ice Applications in Healthcare: Ensuring Safe Transport of Medical Supplies. Available online: https://www.nexair.com/learning-center/dry-ice-applications-in-healthcare-ensuring-safe-transport-of-medical-supplies/ (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- DRY ICE CORP. Innovative Applications of Dry Ice in the Medical Industry (Part 2). Available online: https://www.dryicecorp.com/many-uses-of-dry-ice/innovative-applications-of-dry-ice-in-the-medical-industry-part-2/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- nexAir. How nexAir’s Dry Ice Solutions Improve Food Safety and Quality Control. Available online: https://www.nexair.com/learning-center/how-nexairs-dry-ice-solutions-improve-food-safety-and-quality-control/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Reliant Dry Ice. The Ultimate Guide to Shipping Perishable Foods with Dry Ice. Available online: https://www.reliantdryice.com/post/the-ultimate-guide-to-shipping-perishable-foods-with-dry-ice (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- nexAir. Carbonated Beverage Production: Dry Ice Applications in Drink Carbonation. Available online: https://www.nexair.com/learning-center/carbonated-beverage-production-dry-ice-applications-in-drink-carbonation/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Zhou, R.; Du, C.; Chen, B. Experimental study on the cleaning performance of dry ice blasting for industrial equipment. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 38, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Máša, V.; Horňák, D.; Petrilák, D. Industrial use of dry ice blasting in surface cleaning. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzido, A.; Krawczyk, P. Abrasive Technologies with Dry Ice as a Blasting Medium—Review. Energies 2023, 16, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reliant Dry Ice. Innovative Uses of Dry Ice in Food Processing. Available online: https://www.reliantdryice.com/post/innovative-uses-of-dry-ice-in-food-processing (accessed on 13 June 2024).
- Reliant Dry Ice. Multiple Applications of Dry Ice in Food Manufacturing. Available online: https://www.reliantdryice.com/post/multiple-applications-of-dry-ice-in-food-manufacturing (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Robinson, A.; ShipScience. How to Safely Ship Food with Dry Ice. Available online: https://www.shipscience.com/how-to-safely-ship-food-with-dry-ice-2debe/ (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Li, H.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of dry ice blasting for cleaning sensitive electronic and optical components. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, O.I.-F.; Liu, C.-H.; Wang, K.; Borrego-Marin, E.; Li, H.; Alawadhi, A.H.; Navarro, J.A.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Water-Enhanced Direct Air Capture of Carbon Dioxide in Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cao, K.A.; Cao, K.L.A.; Abdillah, O.B.; Septiani, E.L.; Hirano, T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Ogi, T. Correlation between Pore Characteristics and High-Performance Carbon Dioxide Capture of Sustainable Porous Carbon Derived from Kraft Lignin and Potassium Carbonate. Energy Fuels 2025, 39, 6372–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Xu, J. Cryogenic CO2 treatment of metallic materials for improved machinability and microstructural refinement. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.; Ren, J.; Ben Matellini, D. The Development of a Cold-Chain-Packaging Risk Management Model Based on Fuzzy Bayesian Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dry Ice Market Size: Growth, Trends, and Forecast (2025–2034). Zion Market Research, May 22, 1015. Available online: https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/report/dry-ice-market (accessed on 18 July 2025).
- Sparavigna, A.C. Freezers, Dry Ice and Phase-Change Materials for Cold Chain Equipment in Ultra Low Temperature Logistics. SSRN Electron. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Ren, J.; Ben Matellini, D.; Ouyang, W. A Comprehensive Review of Modern Cold Chain Shipping Solutions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solakivi, T.; Kiiski, T.; Ojala, L. The impact of ice class on the economics of wet and dry bulk shipping in the Arctic waters. Marit. Policy Manag. 2018, 45, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, C. Cold chain transportation energy conservation and emission reduction based on phase change materials under dual-carbon background: A review. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.A.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Comparing CO2 Storage and Utilization: Enhancing Sustainability through Renewable Energy Integration. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Salazar, M.A.; Kirsten, T.; Prchlik, L. Review of the operational flexibility and emissions of gas- and coal-fired power plants in a future with growing renewables. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.; Enciso, S.; Tena, C.; Jorba, O.; Dellaert, S.; van der Gon, H.D.; García-Pando, C.P. A global catalogue of CO2 emissions and co-emitted species from power plants, including high-resolution vertical and temporal profiles. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 337–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, B.; Valencia, J.; Northrop, P.; Mart, C. Controlled Freeze Zone™ for developing sour gas reserves. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; Yang, M.-W.; Zhuang, Z.-Y.; Lin, P.-W.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yang, H.-S.; Chou, C.-T. CO2 Capture from Flue Gas of a Coal-Fired Power Plant Using Three-Bed PSA Process. Energies 2021, 14, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, K.; Mullick, A.; Ali, A.; Kargupta, K.; Ganguly, S. Cryogenic carbon dioxide separation from natural gas: A review based on conventional and novel emerging technologies. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 453–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA Greenhouse Gas R; D Programme. Impact of Impurities on CO2 Capture, Transport and Storage; PH4/32; IEA GREENHOUSE GAS R&D PROGRAMME: Cheltenham, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Burgers, W.; Northrop, P.; Kheshgi, H.; Valencia, J. Worldwide development potential for sour gas. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneesh, A.M.; Sam, A.A. A mini-review on cryogenic carbon capture technology by desublimation: Theoretical and modeling aspects. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1167099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufford, T.; Smart, S.; Watson, G.; Graham, B.; Boxall, J.; da Costa, J.D.; May, E. The removal of CO2 and N2 from natural gas: A review of conventional and emerging process technologies. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 94–95, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, P.; Psarras, P.; Wilcox, J. CO2 capture from the industry sector. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 63, 146–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünveren, E.E.; Monkul, B.Ö.; Sarıoğlan, Ş.; Karademir, N.; Alper, E. Solid amine sorbents for CO2 capture by chemical adsorption: A review. Petroleum 2017, 3, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, B.; Gorbounov, M.; Soltani, S.M. Influence of surface modification on selective CO2 adsorption: A technical review on mechanisms and methods. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 312, 110751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Miccio, F.; Ammendola, P. Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide for Post-combustion Capture: A Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 12845–12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, J.; Garcia, G.; Balsamo, M.; Zhou, M.; Mouzon, J. Microchannel zeolite 13X adsorbent with high CO2 separation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Botella, E.; Valencia, S.; Rey, F. Zeolites in Adsorption Processes: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17647–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Perez-Botella, E.; Palomar, J. Impact of humidity on CO2 capture performance of zeolite-based adsorbents. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 28, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Chang, L.; Xie, K. Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide on Activated Carbon. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2006, 15, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.L.; Luna, F.M.T.; Silva, I.J.; de Azevedo, D.C.; Grande, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Moreira, R.F. Carbon dioxide–nitrogen separation through adsorption on activated carbon in a fixed bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniarasu, R.; Rathore, S.K.; Murugan, S. Biomass-based activated carbon for CO2 adsorption—A review. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 1674–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoneef, M.M.; Jedli, H.; Mbarek, M. Experimental study of CO2 adsorption using activated carbon. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 065602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, A.A.; Othman, M.R.; Kim, J. A review on application of activated carbons for carbon dioxide capture: Present performance, preparation, and surface modification for further improvement. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43329–43364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, K.; Rogow, D.L.; Mason, J.A.; McDonald, T.M.; Bloch, E.D.; Herm, Z.R.; Bae, T.-H.; Long, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Capture in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 724–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, Z.I.; Lim, K.L.; Teh, L.P. Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and their Applications in CO2Adsorption and Conversion. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202200572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lucier, B.E.; Boyle, P.D.; Huang, Y. Understanding the Fascinating Origins of CO2 Adsorption and Dynamics in MOFs. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 5829–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, T.; Abnisa, F.; Daud, W.M.A.W. A review on production of metal organic frameworks (MOF) for CO2 adsorption. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 707, 135090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.; Phan, A.; Wang, B.; Knobler, C.; Furukawa, H.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. High-Throughput Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks and Application to CO2 Capture. Science 2008, 319, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cao, X.; Lv, D.; Cheng, F. Hydrophobic metal–organic framework UiO-66-(CF3)2/PIM-1 mixed-matrix membranes for stable CO2/N2 separation under high humidity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, S.K.; Varghese, A.M.; Kuppireddy, S.; Al Wahedi, Y.; AlHajaj, A.; Karanikolos, G.N.; Dumée, L.F. MOF@MOF core-shell hybrid adsorbents with controlled water vapor affinity towards enhanced and steady CO2 capture in moist conditions. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2025, 14, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, J. Hydrophobic Metal–Organic Frameworks: Assessment, Construction, and Diverse Applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1901758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.S.; Park, S.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, M.; Choi, D.S.; Choe, J.H.; Hong, C.S. Moisture-tolerant diamine-appended metal–organic framework composites for effective indoor CO2 capture through facile spray coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, H.J.; Ghaemi, A.; Shahhosseini, S. Improving CO2 adsorption efficiency of an amine-modified MOF-808 through the synthesis of its graphene oxide composites. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizkardes, A.K.; Wang, P.; Hoffman, J.; Budhathoki, S.; Hopkinson, D. Amine-functionalized porous organic polymers for carbon dioxide capture. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 6668–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardane, R.V.; Shen, M.-S.; Fisher, E.P.; Losch, J. Adsorption of CO2 on Zeolites at Moderate Temperatures. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreisbach, F.; Staudt, R.; Keller, J. High Pressure Adsorption Data of Methane, Nitrogen, Carbon Dioxide and their Binary and Ternary Mixtures on Activated Carbon. Adsorption 1999, 5, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cui, X.; Ma, J.; Li, R. Adsorption of carbon dioxide on alkali-modified zeolite 13X adsorbents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2007, 1, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, N.S.; Rajendran, A. Measurement of competitive CO2 and N2 adsorption on Zeolite 13X for post-combustion CO2 capture. Adsorption 2019, 25, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkarem, A.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Alhashim, H. Comparative analysis of CO2 adsorption on activated carbon and zeolite 13X under humid conditions. J. CO2 Util. 2016, 15, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Garshasbi, V.; Jahangiri, M.; Anbia, M. Equilibrium CO2 adsorption on zeolite 13X prepared from natural clays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streb, A.; Mazzotti, M. Adsorption for efficient low carbon hydrogen production: Part 1—Adsorption equilibrium and breakthrough studies for H2/CO2/CH4 on zeolite 13X. Adsorption 2021, 27, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmahini, A.H.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Friedrich, D.; Brandani, S.; Sarkisov, L. Performance-based screening of porous materials for carbon capture. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, S. Temperature swing adsorption for CO2 capture: Thermal design and management on adsorption bed with single-tube/three-tube internal heat exchanger. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 199, 117538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, A.A.; Naji, S.Z. Comparison study of activators performance for MDEA solution of acid gases capturing from natural gas: Simulation-based on a real plant. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaoha, C.; Odoh, K.; Ikpatt, E.; Orji, R.; Idem, R. Process simulation, parametric sensitivity analysis and ANFIS modeling of CO2 capture from natural gas using aqueous MDEA–PZ blend solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5588–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lawal, A.; Stephenson, P.; Sidders, J.; Ramshaw, C. Post-combustion CO2 capture with chemical absorption: A state-of-the-art review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.E.P.; González, À.; Llorens, J.; Bonet, J. Investigating best available technique for CO2 chemical absorption: Solvent selection based on empirical surrogate model and exergy loss. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 24, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Andino, J.M. A Review of Materials for Carbon Dioxide Capture. Catalysts 2025, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.Z.; Maulud, A.S.; Bustam, M.A.; Suleman, H.; Halim, H.N.A.; Shariff, A.M. Packed column modelling and experimental evaluation for CO2 absorption using MDEA solution at high pressure and high CO2 concentrations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 88, 103829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H.; Yi, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X. A review of CO2 catalytic regeneration research based on MEA solution. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1257218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Eslick, J.C.; Miller, D.C.; Kitchin, J.R. Comparisons of amine solvents for post-combustion CO2 capture: A multi-objective analysis approach. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2013, 18, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, R.M.; Lock, S.S.M.; Hussein, N.; Shahid, M.Z.; Farooqi, A.S. Simulation of Natural Gas Treatment for Acid Gas Removal Using the Ternary Blend of MDEA, AEEA, and NMP. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hemmati, A.; Rashidi, H. Industrial CO2 absorption into methyldiethanolamine/piperazine in place of monoethanolamine in the absorption column. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 142, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.N.; Hailegiorgis, S.M.; Man, Z.; Garg, S.; Shariff, A.M.; Farrukh, S.; Ayoub, M.; Ghaedi, H. High-pressure absorption study of CO2 in aqueous N -methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) and MDEA-piperazine (PZ)-1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate [bmim][OTf] hybrid solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavini, T.; Ali, M.-D.; Muhammad, W. Economic evaluation of Selexol—Based CO2 capture process for a cement plant using post—Combustion technology. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sukor, N.R.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Isa, F.M. Techno-Economic Analysis of CO2 Capture Technologies in Offshore Natural Gas Field: Implications to Carbon Capture and Storage in Malaysia. Processes 2020, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetaki, Z.; Brandani, P.; Brandani, S.; Ahn, H. Process simulation of a dual-stage Selexol process for 95% carbon capture efficiency at an integrated gasification combined cycle power plant. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2015, 39, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Song, D. Conceptual design, optimization and thermodynamic analysis of a CO2 capture process based on Rectisol. Energy 2022, 244, 122566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Martelli, E.; Marechal, F.; Consonni, S. Review, modeling, Heat Integration, and improved schemes of Rectisol®-based processes for CO2 capture. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 70, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, T.N.; Wang, M. Role of solvents in CO2 capture processes: The review of selection and design methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulfinol. National Energy Technology Laboratory. Available online: https://www.netl.doe.gov/research/coal/energy-systems/gasification/gasifipedia/sulfinol (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Ma, Y.; Liao, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Ji, D.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, D. Comparative Investigation of Different CO2 Capture Technologies for Coal to Ethylene Glycol Process. Processes 2021, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I.; Hoadley, A.F.; Mahajani, S.M.; Ganesh, A. Multi-objective optimisation of a Rectisol™ process for carbon capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 119, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Gani, R.; Zhou, T. Comparative Economic Analysis of Physical, Chemical, and Hybrid Absorption Processes for Carbon Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Yun, J.; Shao, L. Modeling and validation of carbon dioxide absorption in aqueous solution of piperazine + methyldiethanolamine by PC-SAFT and E-NRTL models in a packed bed pilot plant: Study of kinetics and thermodynamics. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, C.; Pérez-Calvo, J.-F.; van der Spek, M.; Mazzotti, M. Optimal design of an MDEA CO2 capture plant for low-carbon hydrogen production—A rigorous process optimization approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Ardali, S.M.; Hazrati-Kalbibaki, M.; Fattahi, M.; Lezsovits, F. Multi-objective optimization of post combustion CO2 capture using methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) and piperazine (PZ) bi-solvent. Energy 2020, 211, 119035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhasakul, S.; Ku, H.-M.; Douglas, P.L. A simulation model of a CO2 absorption process with methyldiethanolamine solvent and piperazine as an activator. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2013, 15, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, L.; Danilović, D.; Karović-Maričić, V.; Leković, B.; Crnogorac, M. Application of membrane technology for separation CO2 from natural gas. Podzemn. Rad. 2020, 36, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ho, W.S. Recent Progress in the Engineering of Polymeric Membranes for CO2 Capture from Flue Gas. Membranes 2020, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.R.A.; Jeong, H.-K. Recent advances on mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation: Opportunities and engineering challenges. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ho, W.S.W. Polymeric membranes for CO2 separation and capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 628, 119244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Membrane materials targeting carbon capture and utilization. Adv. Membr. 2022, 2, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.R.T.; Ambrosi, A.; Di Luccio, M.; Hotza, D. Membranes for separation of CO2/CH4 at harsh conditions. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 98, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wei, J.; Ma, Y.; Deng, J.; Yi, S.; Wang, B.; Deng, L.; Jiang, X.; Dai, Z. Facilitated transport membranes for CO2/CH4 separation–State of the art. Adv. Membr. 2022, 2, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera-Titus, M. Porous Inorganic Membranes for CO2 Capture: Present and Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1413–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Lv, Y.; Tan, T. Facile manufacture of COF-based mixed matrix membranes for efficient CO2 separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, J.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Nasir, N.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z. 110th Anniversary: Mixed Matrix Membranes with Fillers of Intrinsic Nanopores for Gas Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7706–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; Li, S.W.; Xiao, Y.C.; Shao, L. CO2–selective mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) containing graphene oxide (GO) for enhancing sustainable CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2017, 56, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.S.Q.; Hansen, N.; Motadayen, M.; Lock, N.; Henriksen, M.L.; Quinson, J. A Review of Metal-Organic Frameworks and Polymers in Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2 Capture. Chemistry 2024, 155–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; He, N.; Yao, Y.; Ma, A.; Zhang, E.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, X. Mixed matrix membranes for gas separations: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 152912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, R.; Wu, H. Efficient CO2 Capture by Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanosheets as Fillers To Fabricate Multi-Permselective Mixed Matrix Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5528–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, E.; Suk, H.D.; Ponnamma, D.; Hassan, M.K.; Hawari, A.; Alshammari, B.A.; Al-Ejji, M. Exploring 3D Printing and Electrospinning Technologies for Advanced Porous Membrane Fabrication: A Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 70032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, X.Y.D.; Lee, J.J.C.; Wu, W.-Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Bu, J. Advancements in CO2 capture by absorption and adsorption: A comprehensive review. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 81, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojsilović, K.; Božović, N.; Stojanović, S.; Damjanović-Vasilić, L.; Serdechnova, M.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Stojadinović, S.; Vasilić, R. Zeolite-containing photocatalysts immobilized on aluminum support by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Nasiri, M.; Asl, A.H. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Piperazine on Carbon Dioxide Loading in N-Methyl Diethanolamine Aqueous Solutions and Water/Oil Microemulsions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2024, 69, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam Khan, B.; Ullah, A.; Saleem, M.W.; Khan, A.N.; Faiq, M.; Haris, M. Energy Minimization in Piperazine Promoted MDEA-Based CO2 Capture Process. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z.; Fu, W.; Kung, C.-W.; Shang, J. Development of zeolite adsorbents for CO2 separation in achieving carbon neutrality. npj Mater. Sustain. 2024, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Clarizia, G.; Jansen, J.C. CO2 removal from natural gas by membranes: A review of the application and comparison with other technologies. J. CO2 Util. 2016, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, P.; Wang, K.; Adu, E.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P. The optimization and thermodynamic and economic estimation analysis for CO2 compression-liquefaction process of CCUS system using LNG cold energy. Energy 2021, 236, 121376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyon, K.; Mehrpooya, M.; Hajinezhad, A. Comparison of different CO2 liquefaction processes and exergoeconomic evaluation of integrated CO2 liquefaction and absorption refrigeration system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 211, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetenhall, B.; Aghajani, H.; Chalmers, H.; Benson, S.D.; Ferrari, M.-C.; Li, J.M.; Race, J.; Singh, P.; Davison, J. Impact of CO2 impurity on CO2 compression, liquefaction and transportation. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 2764–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, A.A.A.; Saaid, I.M.; Yusof, M.A.M.; Husein, N.; Zaidin, M.F.; Sabil, K.M. Physical and chemical effect of impurities in carbon capture, utilisation and storage. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2023, 13, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, L.A.; Gilardi, M.; Giudici, F.; Spatolisano, E. New Solvents for CO2 and H2S Removal from Gaseous Streams. Energies 2021, 14, 6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Sun, X.; Hou, C.; Xu, R.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z. Simulation of H2S and CO2 removal from IGCC syngas by cryogenic distillation. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J. Design and optimization of external CO2 liquefaction processes using refrigerants for energy-efficient CO2 capture. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 39, 101169. [Google Scholar]
- Liquid Ammonia Price Per Kg. World. 2025. Available online: https://www.indexbox.io/search/liquid-ammonia-price-per-kg/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Morales-Fuentes, A.; Ramírez-Hernández, H.; Méndez-Díaz, S.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Sánchez-Cruz, F.; Silva-Romero, J.; García-Lara, H. Experimental study on the operating characteristics of a display refrigerator phasing out R134a to R1234yf. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 130, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Propylene Glycol Market 2025. World–Propylene Glycol (Propane-1,2-Diol)–Market Analysis, Forecast, Size, Trends and Insights. World. 2025. Available online: https://www.indexbox.io/store/world-propylene-glycol-propane-12-diol-market-analysis-forecast-size-trends-and-insights/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Øi, L.E.; Eldrup, N.; Adhikari, U.; Bentsen, M.H.; Badalge, J.L.; Yang, S. Simulation and Cost Comparison of CO2 Liquefaction. Energy Procedia 2016, 86, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Haider, J.; Lim, H. Carbon capture and liquefaction from methane steam reforming unit: 4E’s analysis (Energy, Exergy, Economic, and Environmental). Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Morosuk, T. Exergetic and Economic Evaluation of CO2 Liquefaction Processes. Energies 2021, 14, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, H. Thermodynamic and economic analysis of refrigerants in CO2 liquefaction processes. J. CO2 Util 2018, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Qiao, H.; Xu, G. Performance evaluation of refrigerants for external CO2 liquefaction with focus on ammonia’s thermodynamic advantages. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 46, 101469. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Pei, P.; Lu, Y.; Yi, L.; Shi, Y. Simulation and experiment for oxygen-enriched combustion engine using liquid oxygen to solidify CO2. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 29, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Tsang, D.C.; Li, J.-S.; Yeung, T.L.; Ding, S.; Poon, C.S. Green remediation of contaminated sediment by stabilization/solidification with industrial by-products and CO2 utilization. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.; Tamvada, S.; Shirdade, N.; Saneie, N.; Lolla, V.Y.; Batheyrameshbapu, V.; Anand, S. Increased solidification delays fragmentation and suppresses rebound of impacting drops. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.03801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogdu, F.; Hafner, K.; Altin, O.; Karatas, O.; Boz, Z.; Welt, B.A. Dry ice sublimation: A computational study with experimental validation for the effects of geometry. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e17496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Industrial Gases Association AISBL. Environmental Impacts of Carbon Dioxide and Dry Ice Production; Doc 111/23; European Industrial Gases Association AISBL: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Wang, Z.; Bhatti, U.H.; Fan, X. Recent progress in carbon dioxide capture technologies: A review. Clean Energy Sci. Technol. 2023, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dry Ice Market Size And Share Analysis—Growth Trends and Forecasts (2025–2032). CMI7684, February 2025. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/dry-ice-market (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- How Dry Ice Technology Can Create Sustainability in Modern Companies. TECH, September 2022. Available online: https://fineeng.eu/how-dry-ice-technology-can-create-sustainability-in-modern-companies/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Fu, L.; Ren, Z.; Si, W.; Ma, Q.; Huang, W.; Liao, K.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, P. Research progress on CO2 capture and utilization technology. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 66, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.T.; Fairweather, M.; Pourkashanian, M.; Woolley, R.M. The range and level of impurities in CO2 streams from different carbon capture sources. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2015, 36, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip, K.; Oduniyi, I.B. Low-Cost, Energy-Efficient and Carbon-Saving Dry Ice Air Conditioning System–A Possible By-Product of a Novel and Highly Cost-Effective Carbon Capture Technology. Glob. J. 2022, 22, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Asgharian, H.; Iov, F.; Nielsen, M.P.; Liso, V.; Burt, S.; Baxter, L. Analysis of cryogenic CO2 capture technology integrated with Water-Ammonia Absorption refrigeration cycle for CO2 capture and separation in cement plants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, H.O.; Alexander, T.; Alton, A.; Condon, C.; de Haas, E.; Galbiati, C.; Goretti, A.; Hohmann, T.; Ianni, A.; Kendiziora, C.; et al. First Commissioning of a Cryogenic Distillation Column for Low Radioactivity Underground Argon. arXiv 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadola, A.; Patel, V.; Potdar, S.; Mallick, S. Technology Scouting—Carbon Capture: From Today’s to Novel Technologies; Concawe: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, E.S.; Davison, J.E.; Herzog, H.J. The cost of CO2 capture and storage. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2015, 40, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CO2 Liquefaction: The Economics? Thunder Said Energy. Available online: https://thundersaidenergy.com/downloads/co2-liquefaction-the-economics/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Hughes, S.; Zoelle, A. Cost of Capturing CO2 from Industrial Sources; National Energy Technology Laboratory: Albany, OR, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.; Ruiz, J.; Sanchez, P. Assessment of methane emissions during CO2 capture in natural gas processing plants. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 32, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- UNECE. About Methane Management. Available online: https://unece.org/sustainable-energy/about-methane-management (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Mullen, D.; Braakhuis, L.; Knuutila, H.K.; Gibbins, J.; Lucquiaud, M. Monoethanolamine Degradation Rates in Post-combustion CO2 Capture Plants with the Capture of 100% of the Added CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 13677–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Life-cycle assessment of CO2 capture and solidification for dry ice production: Energy use and emissions. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 36, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Park, J. Safety assessment of high-pressure CO2 systems in cryogenic processes for CO2 capture and utilization. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 30, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Messer. Safety Data Sheet Carbon Dioxide (Solid); RS-CO2-018C; Messer: Bad Soden, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Evaluating Safety in CO2 Systems; International Institute of Ammonia Refrigeration (IIAR): Alexandria, VA, USA, June 2023. Available online: https://www.iiar.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Chadwell, J.L.; Blundon, C.; Anderson, C. Incidents Associated with Oil and Gas Operations. Available online: http://www.mms.gov (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Kooi, E.; Manuel, H.; Mud, M.; Bellamy, L. Fifteen years of incident analysis: Causes, consequences, and other characteristics of incidents with hazardous substances at major hazard companies in the period 2004–2018. RIVM 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiat, I.; Banu, A.; Bicer, Y.; Amhamed, A.I.; Al-Ansari, T. Circularity within carbon capture networks: A review of capture and utilization technologies. J. CO2 Util. 2025, 95, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Jiang, T.; Rao, C. Review of Policy Framework for the Development of Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q. Comparison of the environmental impact of typical packaging systems for food cold chain express based on life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 430, 139756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarhan, L.M.; Alayyar, A.S.; Alqahtani, N.B.; Khdary, N.H. Circular Carbon Economy (CCE): A Way to Invest CO2 and Protect the Environment, a Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. CCUS in the Transition to Net-Zero Emissions. 2020. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/ccus-in-clean-energy-transitions (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Pan, M.; Zhao, H.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Bao, G. A Review of the Cascade Refrigeration System. Energies 2020, 13, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik, E.; Kosowski, P.; Stopa, J. Cryogenic liquefaction and separation of CO2 using nitrogen removal unit cold energy. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 131, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechelmann, R.-H.; Seevers, J.-P.; Otte, A.; Sponer, J.; Stark, M. Renewable Energy Integration for Steam Supply of Industrial Processes—A Food Processing Case Study. Energies 2020, 13, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, M.; El-Maghraby, R.M.; Fathy, M. Evaluation of variable speed drives to improve energy efficiency and reduce gas emissions: Case study. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2023, 29, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Climate Action EU ETS. 2025. Available online: https://climate.ec.europa.eu/eu-action/eu-emissions-trading-system-eu-ets_en (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- PRIMER: 45Q Tax Credit for Carbon Capture Projects. 2023. Available online: https://carboncapturecoalition.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Volcovici, V. Senate bill would raise value of tax credit to use captured CO2 to produce more oil. Reuters, 20 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Anyebe, A.P.; Yeboah, O.K.K.; Bakinson, O.I.; Adeyinka, T.Y.; Okafor, F.C. Optimizing Carbon Capture Efficiency through AI-Driven Process Automation for Enhancing Predictive Maintenance and CO2 Sequestration in Oil and Gas Facilities. Am. J. Environ. Clim. 2024, 3, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylani, V.; Busaeri, N.; Radjasa, O.K.; Hiron, N.; Mutiara, F. Comprehensive Review of Carbon Capture Technologies for Climate Change Mitigation. Indones. J. Energy 2025, 8, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, H.M. Learnings from Delivering a Modular, Industrial-Scale Carbon Capture Plant for the Waste-to-Energy Industry. Capturi, March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Acampora, L.; Grilletta, S.; Costa, G. The Integration of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) in Waste-to-Energy Plants: A Review. Energies 2025, 18, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Wong, D.A.; Yang, J. Recent Advances in Polymer-Inorganic Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2 Separation. Polymers 2021, 13, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, M.; Zadehahmadi, F.; Sadiq, M.M.; Sutton, A.L.; Mahdavi, H.; Hill, M.R. Challenges and solutions to the scale-up of porous materials. Commun. Mater. 2024, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, V.H.U.; Tamba, J.S.; Eze, M.C.; Okafor, W.O.; Bawor, F.H. Integration of carbon capture utilization and storage into sustainable energy policies in Africa: The case of Liberia. Oxf. Open Energy 2024, 3, oiae011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.M. Study shows AI could revolutionise carbon capture systems. Power Technology, January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Modular CO2 Purification and Liquefaction Plants. Linde. Available online: https://www.linde-engineering.com/products-and-services/process-plants/co2-plants/co2-purification-and-liquefaction/modular-co2-plants (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- POET—Portland Completes Construction On Renewable CO2 Addition. Advanced Biofuels USA, January 2022.
- Liu, Z.; Shi, S.; Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Tan, T.; Nielsen, J. Opportunities of CO2-based biorefineries for production of fuels and chemicals. Green Carbon 2023, 1, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clean, Renewable Bio-CO2 for Dry Ice. Poet. 2023. Available online: https://poet.com/co2 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Dry Ice Corp. The Latest Trends in Dry Ice Technology. Available online: https://www.dryicecorp.com/the-science-of-dry-ice/the-latest-trends-in-dry-ice-technology/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Innovative Applications of Dry Ice in BioTech Production. Reliant Dry Ice, August 2024.
- Dry Ice Semiconductor Cleaning. Cold Jet. Available online: https://www.coldjet.com/dry-ice-blasting/industries/semiconductor-equipment-cleaning/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).

| Property | Value | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Sublimation Point | −78.5 °C at 1 atm | Allows for direct solid-to-gas transition. |
| Latent Heat of Sublimation | 571 kJ/kg | High energy absorption for effective cooling. |
| Density (Solid) | 1560 kg/m3 | Compact cooling material. |
| Specific Heat (Solid) | 0.85 J/(g·K) | Limited heat absorption in solid form. |
| Triple Point | −56.6 °C, 5.18 atm | Only above this pressure can CO2 be liquid. |
| Vapor Pressure | 5.1 atm at −56.6 °C | Requires high pressure to stay liquid. |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.16 W/(m·K) | Low conductivity, allowing for prolonged cooling. |
| Application | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccines Transportation | Control temperature during transport | Maintains extremely low temperatures for sensitive vaccines, such as mRNA vaccines, ensuring effectiveness during shipping [30]. |
| Organ Preservation | Viability conservation during transport | Keeps tissues, organs and blood samples at low temperatures to avoid degradation during transport for transplant or medical analysis [30]. |
| Cryosurgery | Long-term storage of biological samples | Freezes and stores biological samples like tissues, cells and DNA, preserving them for medical use or research [20,21]. |
| Application | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Storage | Rapid freezing | -Used for flash freezing perishable items like meats and seafood to preserve freshness, texture, and nutrition [32,33]. -Helps prevent large ice crystals, inhibits microbial growth, preserves flavor, and supports IQF systems [22,28]. |
| Preservation During Transit | Refrigeration in shipping | -Maintains appropriate temperatures during transport for items like meat and dairy [23]. -Avoids residue, works without power, and reduces spoilage [23,29]. |
| Carbonation | Beverage carbonation | -Creates carbonation by sublimating CO2 into the liquid, increasing dissolved CO2 content and forming fizziness [34]. -Displaces oxygen in the beverage, preserving flavor and preventing oxidation, producing visual fog for sensory appeal [34]. |
| Application | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Blasting | Non-abrasive surface cleaning | -Removes contaminants from machinery, equipment, and surfaces without leaving any residue [36]. -Pellets sublimate on contact, embrittling and detaching contaminants [25,26]. |
| Foaming and packaging | Expanded-foam production and cold packaging | -Employed in the production of expanded foam materials. -Ensures structural stability and insulation performance and creates inert packaging environments for sensitive goods [45]. |
| Shrink fitting (Cryogenic Processing) | Material hardening and precise assembly | Hardens materials like metals and plastics and enables shrink fitting by cooling components for tighter tolerances [15]. |
| Parameters | Coal Power Plants | Natural Gas Reserves |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Flow Rate | High, depending on plant capacity (1–3 Mt CO2/year, 70% of global flow) [58]. | High, depending on the reserve (0.5–10+ Mt CO2/year, 25% of global flow) [58]. |
| CO2 Fraction in Stream | 10–15% [58]. | Can reach up to 50% in sour gas reserves [58]. |
| CO2 Concentration | Low (10–15% due to mixing with nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases) [58]. | High (20–50%, especially in sour gas reserves) [58]. |
| Pressure | Low (near atmospheric in flue gas, 0.1 MPa) [54]. | High (>10 MPa, particularly in sour gas reserves) [54]. |
| Impurities | Includes nitrogen (75–80%), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulates (10–15%) [54]. | H2S (up to 20%), hydrocarbons (10–30%), and water vapor (5–10%) [54]. |
| Yield | Moderate to high with post-combustion capture system (50–85% recovery) [54]. | High, specifically in sour gas reserves (90–95% recovery) [54]. |
| Property | Zeolites (13X) | Activated Carbon | MOFs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Selectivity | High (80–90%) [86]. | Moderate (60–70%) [56,57]. | High (tunable, 85–95%) [61,62]. |
| CO2 Adsorption Capacity | High (5–6 mmol/g) [86]. | Moderate to high (3–5 mmol/g) [56,57]. | Very high (8–10 mmol/g) [74]. |
| Operating Pressure | High pressure (30–70 bar) [66,67]. | Flexible (10–50 bar) [70]. | High pressure (20–50 bar) [61,63]. |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (>600 °C) [65,67]. | Moderate to high (400–500 °C) [57,58]. | Moderate (300–400 °C) [61,63]. |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent [77,78,80]. | Moderate [57,58]. | Moderate to poor [61,63]. |
| Regeneration Energy | Moderate (500–800 kJ/kg) [87]. | Low (300–500 kJ/kg) [71]. | Moderate to high (800–1000 kJ/kg) [76]. |
| Cost | Low to Moderate (5–10 $/kg) [66,67]. | Low (3–7 $/kg) [71]. | High (20–50 $/kg) [75,76]. |
| Industrial Maturity | Well-established [89]. | Well-established [58,59,60]. | Emerging [62,63,64]. |
| Suitability for Natural Gas | Excellent [65,66,67]. | Good [57,58,59]. | Limited (due to stability) [61,62,63]. |
| Environmental Impact | Low (Reusable, minimal waste) [65,67]. | Low (Widely available, renewable potential) [57,59]. | Moderate (Complex disposal and energy intensive synthesis) [74,75]. |
| Optimal Operating Conditions | Dry gas streams, high CO2 concentration, high flow rate [84]. | Humid environments, moderate pressure, low to moderate flow rate [85]. | Dry, low-temperature, high-pressure systems; best under controlled conditions [73]. |
| Parameter | MEA | DEA | MDEA | Blended Amines (MDEA + Piperazine) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction Rate with CO2 | High (1.2–1.5 kmol/m3. S) [62,63]. | Moderate (0.6–0.8 kmol/m3. S) [62,63]. | Low (0.2–0.3 kmol/m3. S) [62,63]. | Moderate to High (0.8–1.2 kmol/m3. S) [61,62,63]. |
| CO2 Loading Capacity | Moderate (0.4–0.5 mol CO2/mol MEA) [62,63]. | Moderate (0.4–0.5 mol CO2/mol DEA) [94]. | High (0.8–1 mol CO2/mol MDEA) [61,62,63]. | High (1–1.2 mol CO2/mol blended amine) [62,63]. |
| Energy for Regeneration | High (4–4.5 MJ/kg CO2) [98]. | Moderate (3–3.5 MJ/kg CO2) [61,62]. | Low (2–2.5 MJ/kg CO2) [94]. | Low to Moderate (2.5–3 MJ/kg CO2) [98]. |
| Resistance to Degradation | Low (30%) [94]. | Moderate (60–70%) [94]. | High (85–90%) [62,63]. | High (85–90%) [62,63]. |
| Corrosion Risk | High (70–80%) [94]. | Moderate (50–60%) [94]. | Low (20–30%) [94]. | Low to Moderate (25–35%) [62,63]. |
| Cost | Low (1–2 $/kg) [101]. | Moderate (2–4 $/kg) [101]. | Moderate (2–5 $/kg) [63,64]. | Moderate to High (4–6 $/kg) [63,64]. |
| Industrial Application | Suitable for low-pressure gas [63,64]. | Suitable for moderate loads [101]. | Ideal for high-pressure gas [101]. | Suitable for most scenarios [63,64,102]. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate (High regeneration energy and potential waste) [101]. | Moderate (Improved stability over MEA) [62,63]. | Low (Minimal degradation, lower waste disposal) [63,64]. | Moderate (Might require solvent management) [62,63]. |
| Criteria | Sulfinol-D | Selexol | Rectisol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Selectivity | High (90–95%) -Selective chemical and physical interaction with CO2 [65,66]. | Moderate (70–80%) -May absorb impurities [104]. | High (85–90%) [107]. |
| CO2 Capture Efficiency | High (85–90%) -Effective for acid gas removal [65,66]. | Moderate to High (75–85%) -Efficient at high pressures [104]. | Moderate to High (75–85%) -Effective for high-pressure, low-temperature streams [68,69]. |
| Operating Pressure | Moderate to High (10–60 bar) -Versatile under natural gas conditions [106]. | High (20–70 bar) -Performs best at high pressures [66,67]. | High (20–70 bar) -Designed for high-pressure and cryogenic conditions [108]. |
| Operating Temperature | Ambient (25–50 °C) -Limited cooling required [66,67]. | Ambient to moderate cooling (10–40 °C) [66,67]. | Low -Requires cryogenic conditions (−40 to −70 °C) [108]. |
| Regeneration Process | Thermal regeneration (1.8–2.5 MJ/kg CO2) -Heat required for CO2 release [105]. | Pressure swing (1.5–2 MJ/kg CO2) -Reducing pressure to release CO2 [106]. | Pressure and temperature swing -Cryogenic heating needed (4–5 MJ/kg CO2) [112]. |
| Energy Requirements | Moderate Due to mix of chemical and physical interactions (1.8–2.5 MJ/kg CO2) [65,66]. | Low to Moderate (1.5–2.5 MJ/kg CO2) [105]. | High Due to cryogenic cooling and heating (4–5 MJ/kg CO2) [69,70]. |
| Hydrocarbon Co-Adsorption | Moderate (10–15%) [106]. | Potentially high (20–30%) -Hydrocarbons may dissolve in the solvent [65,66]. | Low (5–10%) [107]. |
| Purity of Captured CO2 | High (90–95%) -Reliable for pure CO2 streams [66,67]. | Moderate (70–85%) -Impurities may need further purification [65,66,67]. | Moderate to High (85–95%) [68,69]. |
| Operating Cost | Moderate (40–55 $/ton CO2) -Balanced performance and maintenance costs [67,68]. | Low to Moderate (30–50 $/ton CO2) -May require post-treatment [106]. | High (60–100 $/ton CO2) -Expensive cryogenic setup and energy demand [68,70]. |
| Solvent Stability | High (85–90%) -Effective for repeated cycles, minimal degradation [104]. | High (90–95%) [65,66]. | High (90–95%) [108]. |
| Suitability for Low CO2 Concentration | High -Effective across a range of CO2 concentrations [105]. | Moderate -Best at higher CO2 concentrations [104]. | Moderate -Best at higher CO2 concentrations [69,70]. |
| Criteria | Chemical Solvents | Physical Solvents |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
| |
| Disadvantages |
|
| Aspect | Polymeric Membranes | Inorganic Membranes | Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selectivity | Moderate (40–60%) [75,76,77]. | High (80–95%) [124]. | High (75–90%) [81,83]. |
| Permeability | Moderate (100–500 Barrer) -Balance between diffusion and solubility [121]. | High (500–2000 Barrer) -Depends on pore structure [78,79]. | High (400–1500 Barrer) -Improved by embedded fillers [126]. |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (80–120 °C) -Sensitive to high temperatures [76,77]. | High (200–600 °C) [124]. | Moderate (120–200 °C) [127]. |
| Chemical Stability | Prone to degradation (60–80%) [76,77]. | High (90–95%) -Corrosion-resistant [124]. | Improved (80–90%) -Depends on filler compatibility [128]. |
| Cost | Low (50–100 $/m2) -Affordable and scalable [119]. | High (200–500 $/m2) -Expensive materials and fabrication [125]. | Moderate (100–250 $/m2) -Balance between polymeric and inorganic [82,83]. |
| Operational Flexibility | High (85–95%) [75,77]. | Low (50–70%) (brittle) [78,79]. | Moderate (70–85%) [81,83]. |
| Commercial Availability | Widely used (90–95% adoption in industry) [119]. | Limited use (30–50% adoption) [125]. | Under development for scale-up (10–30% adoption) [127]. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate -Prone to waste generation [76,77]. | Low -Minimal waste but energy-intensive [124]. | Moderate -High energy needs [128]. |
| Criteria | Absorption | Membrane Separation | Adsorption |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Purity | High -Can reach up to 99% with MDEA + piperazine [63,64]. | Moderate (70–80%) -Requires further purification with polymeric membranes [77,78]. | High (90–95%) with zeolite 13X [58,59]. |
| Selectivity | High -Up to 95% (MDEA + piperazine) [64,65]. | Between 40 and 60% with polymeric membranes (potential hydrocarbon co-separation) [77,78]. | High (80–90%) with zeolite 13X [58,59]. |
| Operating Pressure | Moderate to High with MDEA + piperazine (10–50 bar) [64,65]. | Moderate to High with polymeric membranes (10–40 bar) [121]. | High (30–70 bar) with zeolite 13X [87]. |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate (70–80%) MDEA + piperazine [65,66]. | High (85–90%) No regeneration required with polymeric membranes [78,79]. | Moderate (70–80%) High energy for regeneration with zeolite 13X [58,59]. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and industrially proven (MDEA + piperazine) [98]. | Scalable but limited to specific setups (polymeric membranes) [121]. | Scalable but less practical for large-scale applications (zeolite 13X) [58,59]. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate (60–70%) for MDEA + piperazine [98]. | High (75–90%) Low operational costs for polymeric membranes [122]. | Moderate (65–75%) High regeneration costs for zeolite 13X [87]. |
| Industrial Maturity | Widely used and well-established (MDEA + piperazine) [63,64,65]. | Widely used (polymeric membranes) [78,79]. | Well established (zeolite 13X) [58,59]. |
| Adaptability | Effective across varying CO2 concentrations (particularly MDEA + piperazine) [63,64,65]. | Best for moderate to high pressures and bulk CO2 removal (polymeric membranes) [77,79]. | Effective for specific conditions (zeolite 13X) [57,59]. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate (solvent management required for MDEA + piperazine) [98]. | Low for polymeric membranes [77,78]. | Moderate (energy-intensive process with zeolite 13X) [87]. |
| Parameter | Ammonia (NH3) | Propane (C3H8) | R-134a (1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermodynamic Efficiency | 90–95% High cooling efficiency for liquefaction [146]. | 85–90% Effective in moderate setups [148]. | 75–85% [147]. |
| Environmental Impact | ODP:0, GWP: <1 [146]. | ODP:0, GWP: ~3 [148]. | ODP:0, GWP: ~1430 [147]. |
| Cost | 0.2–0.5 $/kg [146]. | 1–1.5 $/kg [148]. | 6–10 $/kg [147]. |
| Safety | Corrosive Requires ventilation systems [146]. | Highly flammable Safety risks in operations [148]. | Non-flammable [147]. |
| Availability | ~70% Globally used in industries [146]. | ~20% Moderately available in industries [148]. | ~10% Decreasing availability due to regulations [147]. |
| Operating Pressure | High 200–300 psi [146]. | Moderate 150–200 psi [148]. | Low 100–200 psi [147]. |
| Applications | Large scale liquefaction [146]. | General industrial processes [148]. | Small scale applications [147]. |
| Durability/Compatibility | Requires corrosion-resistant systems [146]. | Compatible with most setups [148]. | Compatible with existing systems but requires frequent servicing [147]. |
| Parameters | Internal Liquefaction | External Liquefaction |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs (Equipment + Installation) | 27.74 mill. EURO [149]. | 22.31 mill. EURO [149]. |
| Maintenance Cost | 6.75 mill. EURO/yr [149]. | 3.96 mill. EURO/yr [149]. |
| Duty | 17,918 kW [149]. | 10,044 kW [149]. |
| Refrigerant Cost | None | 0.2–0.5 $/kg (for NH3) [146]. |
| CO2 Liquefaction Prices | 9.97 $/ton [150]. | 8.77 $/ton [150]. |
| Global Warming Impacts | 0.629 kg CO2 -eq kg LCO2−1 [150]. | 0.608 kg CO2 -eq kg LCO2−1 [150]. |
| CO2 Yield | ~85–90% [140]. | ~95–98% [140]. |
| CO2 Purity | ~99.5% [140]. | ~99.8% [140]. |
| Ease of Operation | Requires specialized monitoring [151]. | Simplified due to refrigerant use [151]. |
| Flexibility | Less adaptable to varying operational needs [151]. | Highly adaptable for different setups [151]. |
| Parameter | Value/Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Capture Cost (natural gas) | $15–25 per ton | [168] |
| CO2 Capture Cost (flue gas) | $40–120 per ton | [168] |
| Capital Cost (100,000 tons/year plant) | $10.6 million | [169] |
| Energy Consumption (Liquefaction) | 112 kWh per ton CO2 | [169] |
| Cost Increase for >99% CO2 Purity | +30–40% | [170] |
| Environmental Impact | Causes | Consequences | Mitigation Measures | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methane Emissions | Sweet gas escaping absorber units | High GWP (28–36x CO2), contributes to climate change | Install methane recovery systems; regular leak detection and repair (LDAR) programs | [172] |
| Chemical Degradation of Amine Solvent | Oxidative/thermal breakdown in absorber/regenerator | Formation of toxic by-products like N-nitrosamines (carcinogenic) | Use corrosion inhibitors, limit oxygen exposure, and regularly replace degraded amine | [173] |
| CO2 Emissions from Inefficiencies | Incomplete capture, energy-intensive liquefaction | Emission of 0.3–0.5 tons CO2 per ton dry ice; decreased process sustainability | Improve capture rate >90%, integrate renewables, recycle CO2 losses | [158] |
| Concern | Cause | Consequences | Recommendations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handling of high-pressure systems | CO2 compression and storage at ≥57 bar | Explosion risk, equipment rupture, injury | Install pressure relief valves, regular inspections, operator training | [176] |
| Low-temperature CO2 storage | Solid CO2 stored below −78.5 °C | Frostbite, material embrittlement, PPE failure | Use cryo-rated materials, enforce PPE use, thermal hazard protocols | [176] |
| Integration of new tech in outdated systems | Retrofitting modern systems into legacy plants | Control failure, inefficiencies, downtime | Perform compatibility audits, phased upgrades, retrain staff | [179] |
| Inadequate emergency protocols | No drills or safety systems | Delayed leak response, safety incidents | Conduct emergency drills, develop SOPs, install CO2 detectors | [178] |
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Relevance to Circular Economy | Directly Targeted SDGs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-Loop CO2 Production System | Recycle CO2 within the plant through recovery and reuse after sublimation | Minimizes resource consumption and reduces waste | Maintains CO2 in continuous operational cycle | SDG 12, SDG 13 | [183] |
| Waste-to-Product CO2 Utilization | Capture CO2 from waste streams for use in dry ice production | Reduces overall emissions; valorizes waste | Enables upcycling of industrial emissions | SDG 12, SDG 9, SDG 13 | [183] |
| Integration with Other Industries | Partner with nearby facilities for CO2 sourcing and reuse | Saves transport costs; improves efficiency | Encourages industrial symbiosis and resource sharing | SDG 9, SDG 12, SDG 13 | [183] |
| Process Optimization and Monitoring | Use sensors and controls to track CO2 recovery and reuse rates | Enhances system reliability and conservation | Supports data-driven circular operation | SDG 12, SDG 9, SDG 13 | [181] |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Power processes with solar, wind, or other renewables | Reduces fossil energy dependence and emissions | Enables clean, renewable-driven CO2 production | SDG 7, SDG 12, SDG 13 | [184] |
| Enabling Policy and Regulation | Support via carbon pricing, carbon credits, and circular economy mandates | Strengthens business case; incentivizes action | Fosters institutional adoption of circular systems | SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 17 | [181] |
| Category | Innovation | Description | Benefits | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Breakthroughs | AI-Driven Optimization | Implementation of AI-based systems in pilot-scale carbon capture operations | Increases CO2 capture efficiency by 16.7% and reduces energy consumption by 36.3% | [199] |
| Modular Liquefaction Units | Compact CO2 liquefaction plants designed for decentralized deployment, with 100–360 t/day capacity | Allow rapid installation, improved scalability, and reduced transport-related emissions | [200] | |
| Renewable-Powered CO2 Sourcing | Dry ice facilities powered by renewable electricity and fed with bio-CO2 from ethanol production | Enables carbon-neutral dry ice generation aligned with sustainability goals | [201] | |
| AI-Controlled Operations | AI-assisted heat-rate optimization systems used in industrial power plants | Enhances energy efficiency and lower CO2 emissions by over 2% | [202] | |
| Emerging Applications | Additive Manufacturing | Usage of dry ice in 3D printing post-processing and thermal control | Enhances precision, avoids surface damage and improves cleaning methods | [205] |
| Carbon Sequestration | Solid CO2 used for transportation and injection into storage formations | Supports long-term CO2 removal and mitigates climate change | [205] | |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Utilized for cleaning delicate electronic components with no residue | Reduces risk of damage and contamination during production | [206] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assaf, J.C.; Issa, C.; Flouty, T.; El Marji, L.; Nakad, M. A Comparative Review on Dry Ice Production Methods: Challenges, Sustainability and Future Directions. Processes 2025, 13, 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092848
Assaf JC, Issa C, Flouty T, El Marji L, Nakad M. A Comparative Review on Dry Ice Production Methods: Challenges, Sustainability and Future Directions. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092848
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssaf, Jean Claude, Christina Issa, Tony Flouty, Lea El Marji, and Mantoura Nakad. 2025. "A Comparative Review on Dry Ice Production Methods: Challenges, Sustainability and Future Directions" Processes 13, no. 9: 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092848
APA StyleAssaf, J. C., Issa, C., Flouty, T., El Marji, L., & Nakad, M. (2025). A Comparative Review on Dry Ice Production Methods: Challenges, Sustainability and Future Directions. Processes, 13(9), 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092848







