High-Fat, High-Calorie Breast Milk in Women with Overweight or Obesity and Its Association with Maternal Serum Insulin Concentration and Triglycerides Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Maternal Characteristics
3.2. Milk Composition
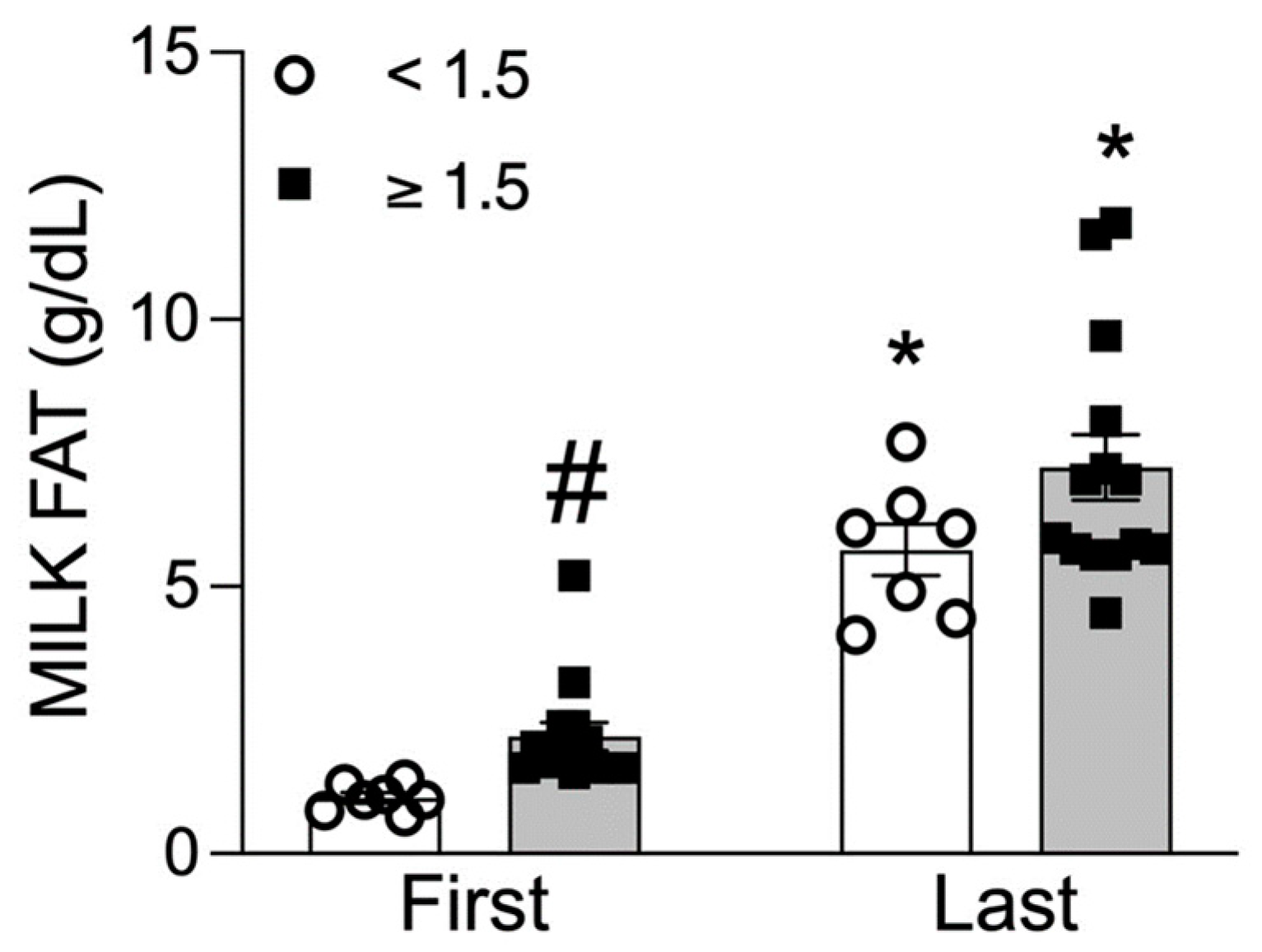
3.3. Lipid Analysis
3.4. Maternal Serum Factors and Milk Triglycerides (TG)
3.5. Low versus High Milk Fat Content
3.6. Infant Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Severe Obesity among Adults Aged 20 and Over: United States, 1960–1962 through 2017–2018. In Health E-Stats; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, F.K.; Celis-Morales, C.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Parra-Soto, S.L.; Lewsey, J.; Mackay, D.; Pell, J.P. Changes over 15 years in the contribution of adiposity and smoking to deaths in England and Scotland. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkner, B.; Cossrow, N.D.F.H. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and obesity-associated hypertension in the racial ethnic minorities of the United States. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kit, B.K.; Kuklina, E.; Carroll, M.D.; Ostchega, Y.; Freedman, D.S.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of and trends in dyslipidemia and blood pressure among US children and adolescents, 1999–2012. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Kit, B.; Carroll, M. Abnormal Cholesterol among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 2011–2014. In NCHS Data Brief; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Despres, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2016 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaeel, A.; Weems, S.; McClendon, M.; Morales, F.E. Interventions Aimed at Decreasing Obesity in Hispanic Children in the First 1000 Days: A Systematic Review. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2018, 20, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.M.; Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Freedman, D.S.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity and Severe Obesity Prevalence in US Youth and Adults by Sex and Age, 2007–2008 to 2015–2016. JAMA 2018, 319, 1723–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauerslev, M.; Narang, T.; Gray, N.; Samuels, T.A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Childhood obesity on the rise during COVID-19: A request for global leaders to change the trajectory. Obesity 2022, 30, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.S.; Chumlea, W.C. Tracking of body mass index in children in relation to overweight in adulthood. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 145s–148s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, J.K.; Power, C.; Cole, T.J. Child to adult body mass index in the 1958 British birth cohort: Associations with parental obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 1997, 77, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Whelton, P.K.; Xi, B.; Krousel-Wood, M.; Bazzano, L.; He, J.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Rate of change in body mass index at different ages during childhood and adult obesity risk. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, B.A.; Edmunds, L.S.; Stratton, H.H.; Pruzek, R.M. Rapid infant weight gain predicts childhood overweight. Obesity 2006, 14, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Girard, M. Early determinants of overweight at 4.5 years in a population-based longitudinal study. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stettler, N.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Katz, S.H.; Zemel, B.S.; Stallings, V.A. Rapid weight gain during infancy and obesity in young adulthood in a cohort of African Americans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, P.R.; O’Brien, M.; Houts, R.; Bradley, R.; Belsky, J.; Crosnoe, R.; Friedman, S.; Mei, Z.; Susman, E.J. Identifying risk for obesity in early childhood. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e594–e601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.K.; Ahmed, M.L.; Emmett, P.M.; Preece, M.A.; Dunger, D.B. Association between postnatal catch-up growth and obesity in childhood: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2000, 320, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stettler, N.; Zemel, B.S.; Kumanyika, S.; Stallings, V.A. Infant weight gain and childhood overweight status in a multicenter, cohort study. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, R.C. Predicting preschooler obesity at birth: The role of maternal obesity in early pregnancy. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e29–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenthal, D.B.; Maiden, K.; Rao, A.; West, D.W.; Gidding, S.S.; Bartoshesky, L.; Carterette, B.; Ross, J.; Strobino, D. Independent relation of maternal prenatal factors to early childhood obesity in the offspring. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 121, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.B.; Darbinian, J.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Markman, M.A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Ferrara, A.; Hedderson, M.M. Maternal gestational weight gain and offspring risk for childhood overweight or obesity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 259.E1–259.E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Taveras, E.M.; Kleinman, K.P.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Gillman, M.W. Gestational weight gain and child adiposity at age 3 years. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 196, 322.e1–322.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesel, J.C.; Eckhardt, C.L.; Day, N.L.; Brooks, M.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Bodnar, L.M. Is gestational weight gain associated with offspring obesity at 36 months? Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bider-Canfield, Z.; Martinez, M.P.; Wang, X.; Yu, W.; Bautista, M.P.; Brookey, J.; Page, K.A.; Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H. Maternal obesity, gestational diabetes, breastfeeding and childhood overweight at age 2 years. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.; Ross, M.G. Maternal-infant nutrition and development programming of offspring appetite and obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78 (Suppl. S2), 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.; Ferrini, M.G.; Han, G.; Narwani, K.; Ross, M.G. Maternal High Fat Diet Programs Male Mice Offspring Hyperphagia and Obesity: Mechanism of Increased Appetite Neurons via Altered Neurogenic Factors and Nutrient Sensor AMPK. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstey, E.H.; Chen, J.; Elam-Evans, L.D.; Perrine, C.G. Racial and Geographic Differences in Breastfeeding—United States, 2011–2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauregard, J.L.; Hamner, H.C.; Chen, J.; Avila-Rodriguez, W.; Elam-Evans, L.D.; Perrine, C.G. Racial Disparities in Breastfeeding Initiation and Duration among U.S. Infants Born in 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress in increasing breastfeeding and reducing racial/ethnic differences—United States, 2000–2008 births. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lapillonne, A.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Embleton, N.; Fewtrell, M.; Fidler Mis, N.; Gerasimidis, K.; Hojsak, I.; Hulst, J.; Indrio, F.; et al. Feeding the Late and Moderately Preterm Infant: A Position Paper of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Haschke, F.; Haiden, N.; Detzel, P.; Yarnoff, B.; Allaire, B.; Haschke-Becher, E. Feeding patterns during the first 2 years and health outcome. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 62 (Suppl. S3), 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.; Ey, J.; Holberg, C.J.; Wright, A.L.; Martinez, F.D.; Taussig, L.M. Exclusive breast-feeding for at least 4 months protects against otitis media. Pediatrics 1993, 91, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.L.; Holberg, C.J.; Martinez, F.D.; Morgan, W.J.; Taussig, L.M. Breast feeding and lower respiratory tract illness in the first year of life. Group Health Medical Associates. BMJ 1989, 299, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, D.; Steer, C.D.; Northstone, K.; Emmett, P.M. Effects on childhood body habitus of feeding large volumes of cow or formula milk compared with breastfeeding in the latter part of infancy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Ni, Z.; Hao, L.; Yang, N.; Yang, X. Early feeding of larger volumes of formula milk is associated with greater body weight or overweight in later infancy. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leghi, G.E.; Netting, M.J.; Middleton, P.F.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Muhlhausler, A.B.S. The impact of maternal obesity on human milk macronutrient composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, J.K.C.; Casavale, K.O.; Li, Y.; Hopperton, K.E.; Chakrabarti, S.; Hines, E.P.; Brooks, S.P.J.; Bondy, G.S.; MacFarlane, A.J.; Weiler, H.A.; et al. Perspective: Human Milk Composition and Related Data for National Health and Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 2098–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Lerma, J.; Selma-Royo, M.; Hervas, D.; Yang, B.; Intonen, L.; González, S.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Linderborg, K.M.; Collado, M.C. Breast Milk Lipidome Is Associated with Maternal Diet and Infants’ Growth. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 854786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, F.; Ye, M.; Hu, P.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Association between dietary fatty acid patterns based on principal component analysis and fatty acid compositions of serum and breast milk in lactating mothers in Nanjing, China. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8704–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.G.; Kobayashi, K.; Han, G.; Desai, M. Modulation of Milk and Lipid Synthesis and Secretion in a 3-Dimensional Mouse Mammary Epithelial Cell Culture Model: Effects of Palmitate and Orlistat. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaniqueli, D.; Oliosa, P.R.; Neves, F.S.; Pani, V.O.; Martins, C.R.; de Souza Peçanha, M.A.; Barbosa, M.C.R.; de Faria, E.R.; de Oliveira Alvim, R.; Mill, J.G. Ponderal index classifies obesity in children and adolescents more accurately than body mass index z-scores. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 86, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh-Wargo, S.; Valentic, J.; Khaira, S.; Super, D.M.; Collin, M. Human Milk Analysis Using Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.Y.; Williams, K.J.; Su, B.; Bensinger, S.J. Profiling of mouse macrophage lipidome using direct infusion shotgun mass spectrometry. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Bettcher, L.F.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Hornburg, D.; Pearson, M.J.; Blomberg, N.; Giera, M.; Snyder, M.P.; Raftery, D.; Bensinger, S.J.; et al. A DMS Shotgun Lipidomics Workflow Application to Facilitate High-Throughput, Comprehensive Lipidomics. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2021, 32, 2655–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenness, R. The composition of human milk. Semin. Perinatol. 1979, 3, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.G.; Ferris, A.M.; Lammi-Keefe, C.J.; Henderson, R.A. Lipids of bovine and human milks: A comparison. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzikowska, A.; Czerwonogrodzka-Senczyna, A.; Weker, H.; Wesołowska, A. Correlation between human milk composition and maternal nutritional status. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2018, 69, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.H.; Akhtar, N.A.; Robertson, A.D.; Ahmed, M.G. Lactational capacity of marginally nourished mothers: Relationships between maternal nutritional status and quantity and proximate composition of milk. Pediatrics 1986, 78, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.M.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Vickers, M.H.; Devaraj, S.; Huang, F.; Pang, W.W.; Godfrey, K.M.; Chan, S.Y.; Thakkar, S.K.; Cutfield, W.S. A nutritional supplement taken during preconception and pregnancy influences human milk macronutrients in women with overweight/obesity and gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1282376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, W.B., 3rd; Canolty, N.L.; Aitchison, J.M.; Dunkley, W.L. Influence of sampling on fatty acid composition of human milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1978, 31, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Nishida, Y.; Taki, M.; Murase, M.; Mukai, Y.; Itabashi, K.; Debari, K.; Iiyama, A. Is increased fat content of hindmilk due to the size or the number of milk fat globules? Int. Breastfeed. J. 2009, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, H.; Kato, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Tamura, M.; Ohto, N.T.; Nagao, S.; Hirose, J. Comprehensive Analysis of Lipid Composition in Human Foremilk and Hindmilk. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, M.V.Q.; Grant, M.; Lanigan, J.; Singhal, A. Does human milk composition predict later risk of obesity? A systematic review. BMC Nutr. 2023, 9, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.G.; Desai, M. Developmental programming of appetite/satiety. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64 (Suppl. S1), 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peto, R.; Whitlock, G.; Jha, P. Effects of obesity and smoking on U.S. life expectancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Mi, J.; Duan, J.L.; Yan, S.J.; Cheng, H.; Hou, D.Q.; Zhao, X.Y. Familial clustering of obesity and the role of lifestyle factors among children in Beijing. Zhonghua Yu Fang. Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 43, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burke, V.; Beilin, L.J.; Dunbar, D. Family lifestyle and parental body mass index as predictors of body mass index in Australian children: A longitudinal study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksvytis, A.; Stakisaitis, D. Impact of obesity on lipid profiles in middle-aged women. Medicina 2004, 40, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Bays, H.E.; Toth, P.P.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Abate, N.; Aronne, L.J.; Brown, W.V.; Gonzalez-Campoy, J.M.; Jones, S.R.; Kumar, R.; La Forge, R.; et al. Obesity, adiposity, and dyslipidemia: A consensus statement from the National Lipid Association. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013, 7, 304–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franssen, R.; Monajemi, H.; Stroes, E.S.; Kastelein, J.J. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 95, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Dang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X.; Yu, H. Changes in serum TG levels during pregnancy and their association with postpartum hypertriglyceridemia: A population-based prospective cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, M.J.; Siimes, M.A.; Perheentupa, J.; Salmenperä, L.; Miettinen, T.A. Serum cholesterol and lipoprotein concentrations in mothers during and after prolonged exclusive lactation. Metabolism 1992, 41, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Sunehag, A.L.; Haymond, M.W. De novo synthesis of milk triglycerides in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E838–E847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Sunehag, A.L.; Haymond, M.W. Effect of dietary macronutrient composition under moderate hypocaloric intake on maternal adaptation during lactation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.C.; Picciano, M.F. Regulation of milk lipid secretion and composition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S. Mechanism of chain length determination in biosynthesis of milk fatty acids. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, S.; Dewey, K.; Novotny, R.; Stang, J.; Taveras, E.; Kleinman, R.; Raghavan, R.; Nevins, J.; Scinto-Madonich, S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Dietary Patterns During Lactation and Human Milk Composition and Quantity: A NESR Systematic Review. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 5, 815. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, E.; Yang, N.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Leghi, G.E.; Netting, M.J.; Elmes, M.J.; Langley-Evans, S.C. Acute changes to breast milk composition following consumption of high-fat and high-sugar meals. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2021, 17, e13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Q.; Liu, W.; Zeng, T.; Chen, X.; Luo, T.; Deng, Z. Effect of Different Dietary Patterns on Macronutrient Composition in Human Breast Milk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keikha, M.; Bahreynian, M.; Saleki, M.; Kelishadi, R. Macro- and Micronutrients of Human Milk Composition: Are They Related to Maternal Diet? A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keikha, M.; Shayan-Moghadam, R.; Bahreynian, M.; Kelishadi, R. Nutritional supplements and mother’s milk composition: A systematic review of interventional studies. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2021, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Components of human breast milk: From macronutrient to microbiome and microRNA. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnol, A.F.; Loizeau, M.; Girard, J. Insulin receptor activity and insulin sensitivity in mammary gland of lactating rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, E828–E834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Lapidot, S.A.; Phair, R.D.; Parks, E.J. Insulin activation of plasma nonesterified fatty acid uptake in metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.; Martín-Hidalgo, A.; Herrera, E. Insulin-induced up-regulation of lipoprotein lipase messenger ribonucleic acid and activity in mammary gland. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Makker, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G.; Hong, X.; Aziz, K.B.; Wang, X. Maternal and fetal factors affecting cord plasma leptin and adiponectin levels and their ratio in preterm and term newborns: New insight on fetal origins of metabolic dysfunction. Precis. Nutr. 2022, 1, e00013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feuermann, Y.; Mabjeesh, S.J.; Shamay, A. Leptin affects prolactin action on milk protein and fat synthesis in the bovine mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2941–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.C.; McFadden, T.B.; Forsyth, I. Hormonal regulation of mammary differentiation and milk secretion. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2002, 7, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, T.; Yonekura, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hagino, A.; Katoh, K.; Obara, Y. Effects of long-chain fatty acids on cytosolic triacylglycerol accumulation and lipid droplet formation in primary cultured bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butts, C.A.; Hedderley, D.I.; Herath, T.D.; Paturi, G.; Glyn-Jones, S.; Wiens, F.; Stahl, B.; Gopal, P. Human Milk Composition and Dietary Intakes of Breastfeeding Women of Different Ethnicity from the Manawatu-Wanganui Region of New Zealand. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.L.; Chelvi, S.K.T.; Lim, S.L.; Chen, Y.; Tan, E.A.; Pai, N.N.; Gong, Y.H.; Foo, J.; Rauff, M.; Chong, Y.S. The influence of maternal ethnic group and diet on breast milk fatty acid composition. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2010, 39, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.R.; de Castro, L.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Sañudo, A.; Marcacine, K.O.; Amir, L.H.; Ross, M.G.; Coca, K.P. Breastfeeding Practices and Problems among Obese Women Compared with Nonobese Women in a Brazilian Hospital. Women’s Health Rep. 2021, 2, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, R.; Steegers, E.A.; Duijts, L.; Felix, J.F.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W. Childhood cardiometabolic outcomes of maternal obesity during pregnancy: The Generation R Study. Hypertension 2014, 63, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, P.P.; Lysakowski, T.Y.; Engstrom, J.L.; Kavanaugh, K.L.; Mangurten, H.H. The accuracy of test weighing for preterm infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1990, 10, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lemes, S.F.; de Souza, A.C.P.; Payolla, T.B.; Versutti, M.D.; de Fátima da Silva Ramalho, A.; Mendes-da-Silva, C.; Souza, C.M.; Milanski, M.; Torsoni, A.S.; Torsoni, M.A. Maternal Consumption of High-fat Diet in Mice Alters Hypothalamic Notch Pathway, NPY Cell Population and Food Intake in Offspring. Neuroscience 2018, 371, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larnkjær, A.; Ong, K.K.; Carlsen, E.M.; Ejlerskov, K.T.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F. The Influence of Maternal Obesity and Breastfeeding on Infant Appetite- and Growth-Related Hormone Concentrations: The SKOT Cohort Studies. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2018, 90, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrish, I.; Sindi, A.; Sakalidis, V.S.; Lai, C.T.; McEachran, J.L.; Tint, M.T.; Perrella, S.L.; Nicol, M.P.; Gridneva, Z.; Geddes, D.T. Relationships between the Intakes of Human Milk Components and Body Composition of Breastfed Infants: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikniaz, L.; Jr Mahdavi, R.; Arefhoesseini, S.R.; Sowti Khiabani, M. Association between fat content of breast milk and maternal nutritional status and infants’ weight in Tabriz, Iran. Malays. J. Nutr. 2009, 15, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, C.F.; Hohman, E.E.; Birch, L.L.; Paul, I.M.; Savage, J.S. INSIGHT responsive parenting intervention effects on child appetite and maternal feeding practices through age 3 years. Appetite 2021, 159, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Normal (BMI 18.9–24.9) n = 9 | OW/OB (BMI ≥ 25) n = 13 | p-Value OW/OB vs. Normal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 29.8 ± 2.6 | 29 ± 1.9 | NS |
| BMI | 21.2 ± 0.6 | 31.9 ± 1.6 * | p < 0.001 |
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 85.0 ± 3.3 | 84.4 ± 2.5 | NS |
| Serum Insulin (µIU/mL) | 8.4 ± 2.0 | 17.6 ± 3.4 | p < 0.04 |
| * HOMA IR | 1.87 ± 0.54 | 2.87 ± 0.70 | p = 0.083 |
| Serum Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 98.6 ± 20.2 | 101.5 ± 18.9 | NS |
| Serum Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 205.3 ± 14.1 | 185.6 ± 10.0 | NS |
| Serum LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 124.4 ± 11.3 | 108.8 ± 8.6 | NS |
| Serum HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 61.2 ± 5.9 | 56.9 ± 3.3 | NS |
| Serum Non-HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 144.1 ± 11.9 | 128.7 ± 9.5 | NS |
| Cholesterol/HDL Ratio | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.2 | NS |
| Serum Leptin (ng/mL) | 11.4 ± 2.5 | 32.7 ± 8.9 * | p < 0.001 |
| Serum Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | NS |
| Total Milk Volume (mL) | 80 ± 12 | 88 ± 7 | NS |
| Milk | First Sample (1st Sample) | Middle (4th Sample) | Middle (6th Sample) | Last (8th Sample) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | OW/OB | Normal | OW/OB | Normal | OW/OB | Normal | OW/OB | |
| Crude Protein (g/dL) | 1.17 ± 0.04 | 1.16 ± 0.04 | 1.17 ± 0.05 | 1.13 ± 0.05 | 1.13 ± 0.02 | 1.14 ± 0.05 | 1.12 ± 0.05 | 1.12 ± 0.04 |
| True Protein (g/dL) | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 0.90 ± 0.04 |
| Carbohydrate (g/dL) | 8.51 ± 0.06 | 8.61 ± 0.09 | 8.46 ± 0.07 | 8.55 ± 0.12 | 8.47 ± 0.05 | 8.55 ± 0.10 | 8.41 ± 0.06 | 8.50 ± 0.12 |
| Solids (g/dL) | 11.3 ± 0.22 | 12.0 ± 0.35 | 12.4 ± 0.4 | 13.0 ± 0.4 | 12.7 ± 0.4 | 13.6 ± 0.5 | 15.6 ± 0.6 | 17.1 ± 0.8 |
| Normal (BMI 18.9–24.9) n = 9 | OW/OB (BMI ≥ 25) n = 13 | p-Value OW/OB vs. Normal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 6 | 4 | |
| Female | 3 | 7 | |
| Birth Weight (g) | 3235 ± 145 | 3413 ± 95 | p = 0.0677 |
| Birth Height (cm) | 50.7 ± 0.7 | 50.2 ± 0.6 | NS |
| Ponderal Index ^ (Birth) | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | p = 0.0573 |
| Body Weight at Visit (g) | 5032 ± 48 | 5058 ± 38 | NS |
| Length at Visit (cm) | 56.7 ± 0.7 | 56.5 ± 0.5 | NS |
| Milk Intake per Feed (mL) | 64.5 ± 6.4 | 90.0 ± 13.6 | p < 0.05 |
| Milk Intake (mL/kg body weight) | 12.3 ± 1.2 | 17.6 ± 2.6 | p < 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ross, M.G.; Kavasery, M.P.; Cervantes, M.K.; Han, G.; Horta, B.; Coca, K.P.; Costa, S.O.; Desai, M. High-Fat, High-Calorie Breast Milk in Women with Overweight or Obesity and Its Association with Maternal Serum Insulin Concentration and Triglycerides Levels. Children 2024, 11, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020141
Ross MG, Kavasery MP, Cervantes MK, Han G, Horta B, Coca KP, Costa SO, Desai M. High-Fat, High-Calorie Breast Milk in Women with Overweight or Obesity and Its Association with Maternal Serum Insulin Concentration and Triglycerides Levels. Children. 2024; 11(2):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020141
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoss, Michael G., Manasa P. Kavasery, MacKenzie K. Cervantes, Guang Han, Bernardo Horta, Kelly P. Coca, Suleyma O. Costa, and Mina Desai. 2024. "High-Fat, High-Calorie Breast Milk in Women with Overweight or Obesity and Its Association with Maternal Serum Insulin Concentration and Triglycerides Levels" Children 11, no. 2: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020141
APA StyleRoss, M. G., Kavasery, M. P., Cervantes, M. K., Han, G., Horta, B., Coca, K. P., Costa, S. O., & Desai, M. (2024). High-Fat, High-Calorie Breast Milk in Women with Overweight or Obesity and Its Association with Maternal Serum Insulin Concentration and Triglycerides Levels. Children, 11(2), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020141







