Alveolar and Bronchial Nitric Oxide Parameters in Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
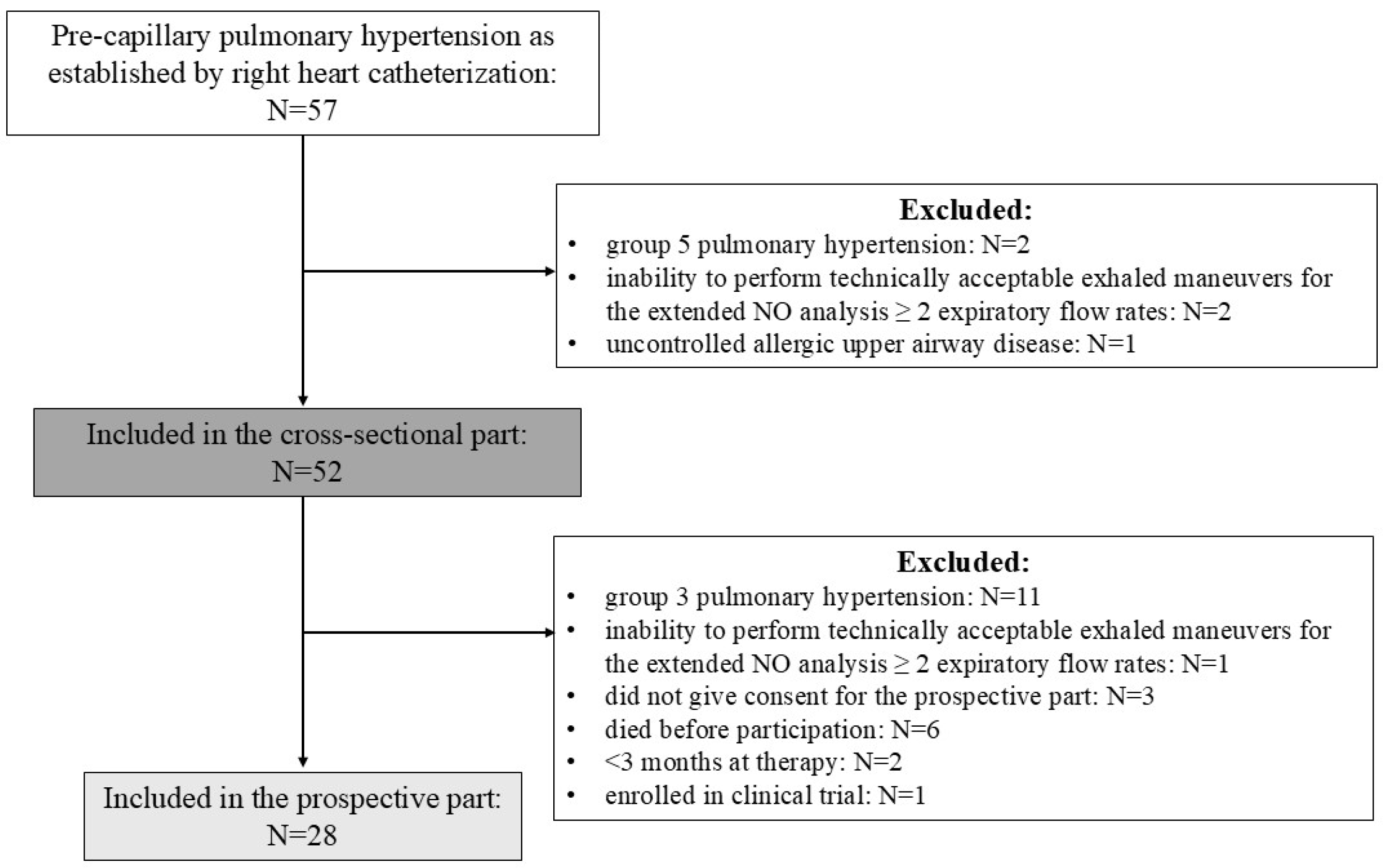
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Enrolment of Subjects
2.3. Clinical Assessment and Data Collection
2.4. Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
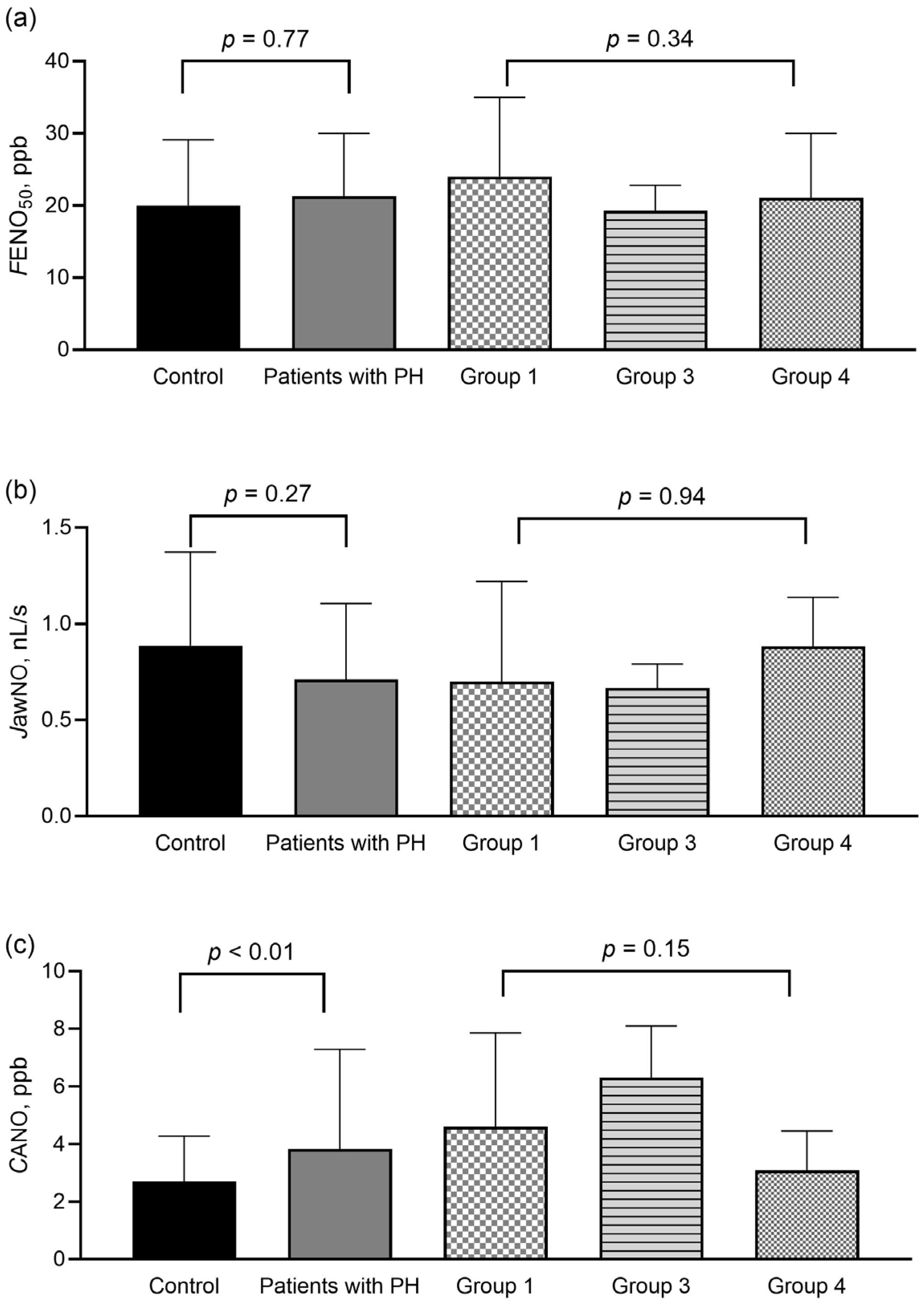
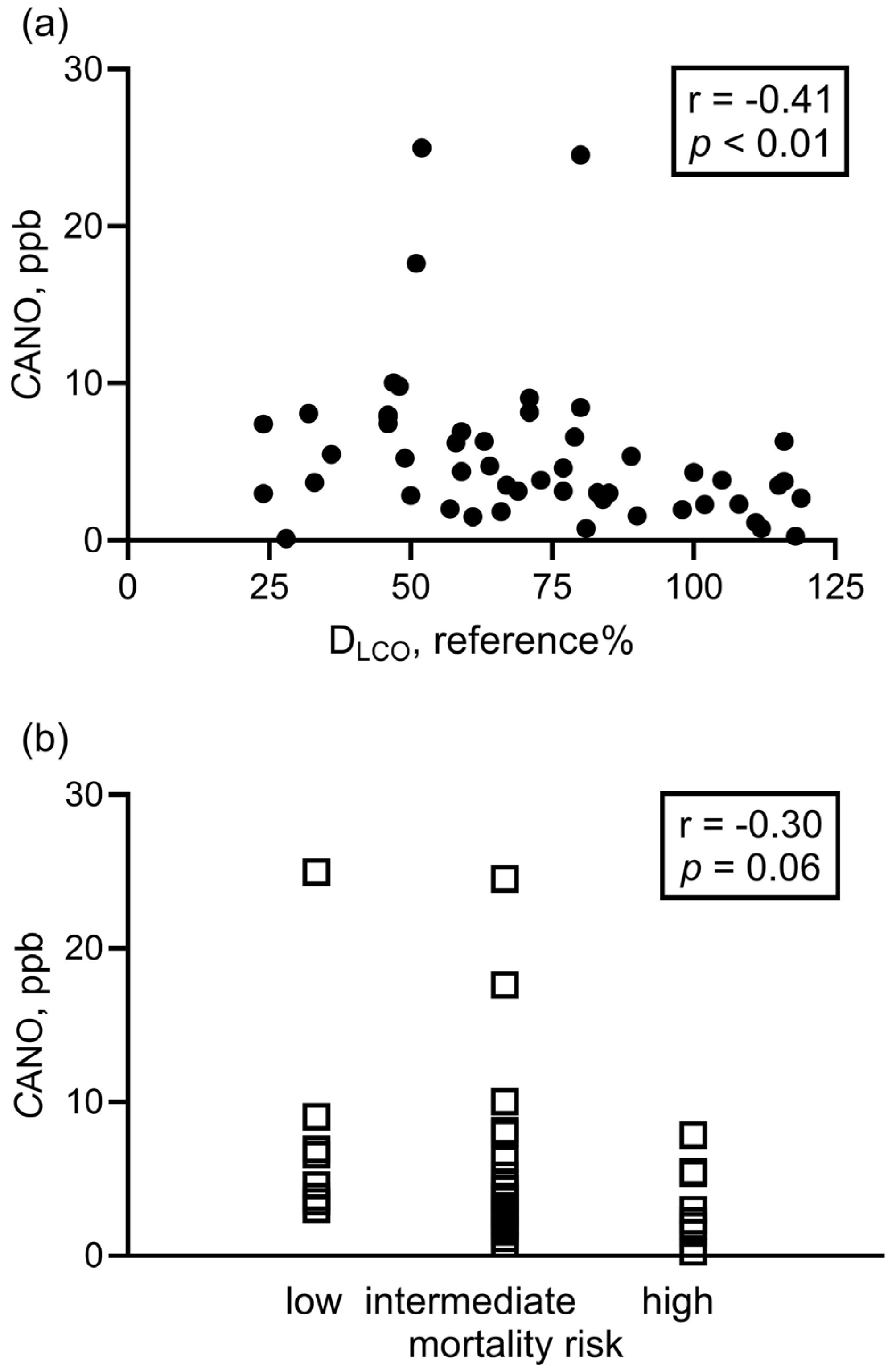
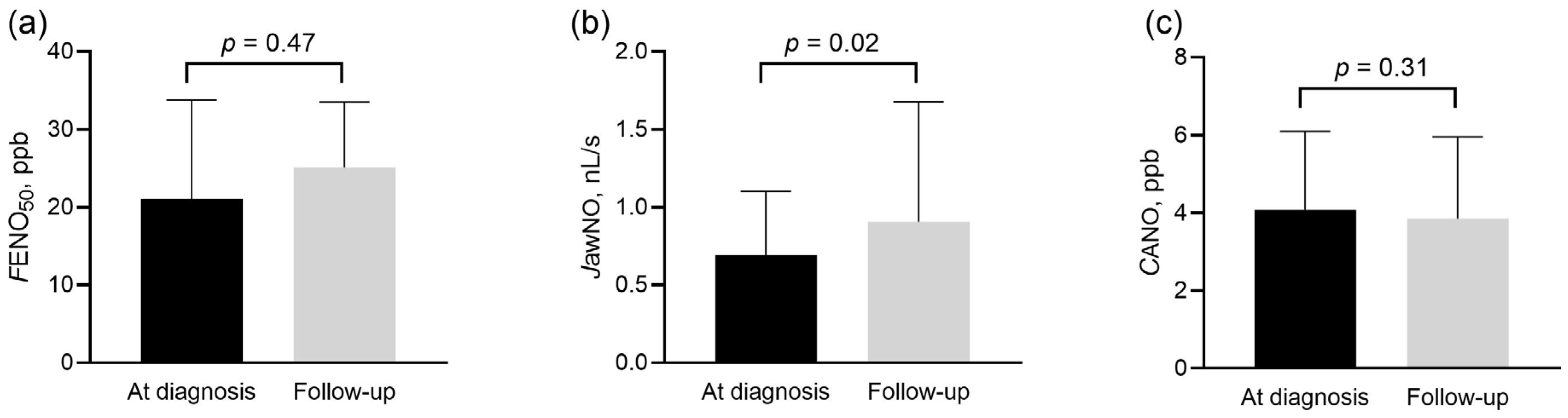
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Exhaled NO Parameters at Diagnosis and Associations with Clinical Indicators
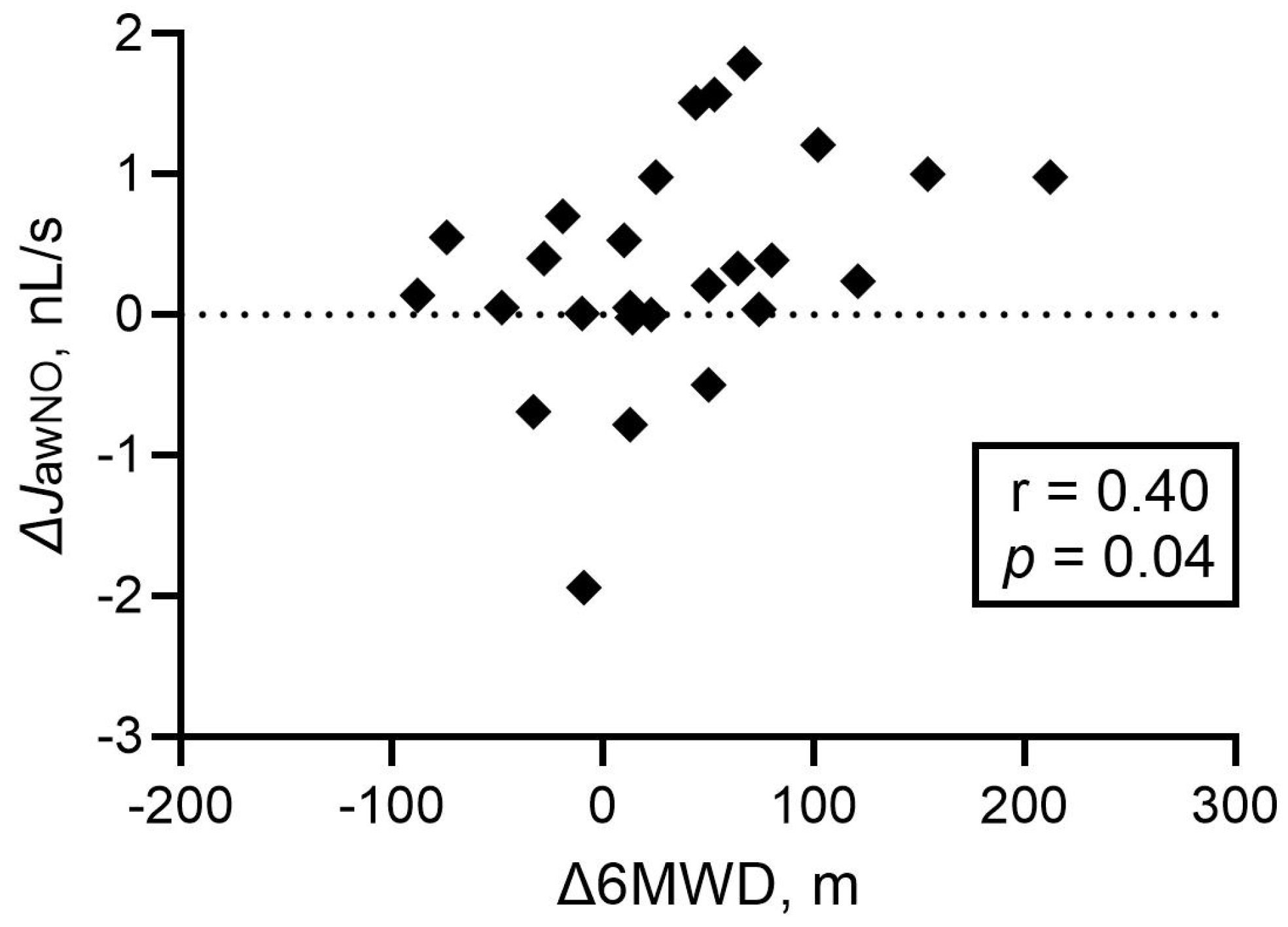
3.3. Exhaled NO Parameters at Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| CANO | Alveolar nitric oxide concentration |
| JawNO | Total bronchial flux of nitric oxide |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| RHC | Right heart catheterization |
| sGC | Soluble guanylate cyclase |
| cGMP | Cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| eNOS | Endothelial NO synthase |
| FENO50 | Fractional exhaled NO concentrations at 50 mL/s exhalation flow rate |
| mPAP | Mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| PAWP | Pulmonary artery wedge pressure |
| PVR | Pulmonary vascular resistance |
| CTEPH | Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide |
| DLCO | Diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide |
| 6MWD | 6 min walk distance |
| WHO-FC | World Health Organization Functional Class |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| L | Liter |
| N | Number |
| NA | Not applicable |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| TAPSE | Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion |
| RV-PA | Right ventricle-pulmonary artery |
| sPAP | Systolic pulmonary arterial pressure |
| SvO2 | Mixed venous oxygen saturation |
| ppb | Particles per billion |
| PDE5i | Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor |
| ERA | Endothelin receptor antagonist |
| Δ | Difference between values at follow-up and diagnosis |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| nNOS | Neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnweber, T.; Schneider, E.M.; Nairz, M.; Theurl, I.; Weiss, G.; Tymoszuk, P.; Loffler-Ragg, J. Risk assessment in precapillary pulmonary hypertension: A comparative analysis. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienn, M.; Gertz, R.J.; Gerhardt, F.; Kroger, J.R.; Zaytoun, H.; Reimer, R.P.; Kaplan, A.; Wissmuller, M.; Kovacs, G.; Rosenkranz, S.; et al. CT-derived lung vessel morphology correlates with prognostic markers in precapillary pulmonary hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2024, 43, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, F. The cGMP system: Components and function. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lazar, Z.; Meszaros, M.; Bikov, A. The Nitric Oxide Pathway in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Pathomechanism, Biomarkers and Drug Targets. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 7168–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benza, R.L.; Grunig, E.; Sandner, P.; Stasch, J.P.; Simonneau, G. The nitric oxide-soluble guanylate cyclase-cGMP pathway in pulmonary hypertension: From PDE5 to soluble guanylate cyclase. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 230183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klinger, J.R.; Kadowitz, P.J. The Nitric Oxide Pathway in Pulmonary Vascular Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, S71–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindicci, C.; Ito, K.; Torre, O.; Barnes, P.J.; Kharitonov, S.A. Effects of aminoguanidine, an inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase, on nitric oxide production and its metabolites in healthy control subjects, healthy smokers, and COPD patients. Chest 2009, 135, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Cailes, J.B.; Black, C.M.; du Bois, R.M.; Barnes, P.J. Decreased nitric oxide in the exhaled air of patients with systemic sclerosis with pulmonary hypertension. Thorax 1997, 52, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammad, M.; Folkerts, G.; Kashani, B.S.; Naghan, P.A.; Dastenae, Z.H.; Khoundabi, B.; Garssen, J.; Mortaz, E.; Adcock, I.M. Exhaled nitric oxide is not a biomarker for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension or for treatment efficacy. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Girgis, R.E.; Champion, H.C.; Diette, G.B.; Johns, R.A.; Permutt, S.; Sylvester, J.T. Decreased exhaled nitric oxide in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Response to bosentan therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Mathai, S.C.; Hummers, L.K.; Shah, A.A.; Wigley, F.M.; Lechtzin, N.; Hassoun, P.M.; Girgis, R.E. Exhaled nitric oxide in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis. Pulm. Circ. 2016, 6, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovschi, A.; Henrohn, D.; Eriksson, A.; Lundberg, J.O.; Alving, K.; Wikström, G. Increased plasma and salivary nitrite and decreased bronchial contribution to exhaled NO in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Manamegent and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: 2025 Report. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/ (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Lazar, Z.; Kelemen, A.; Galffy, G.; Losonczy, G.; Horvath, I.; Bikov, A. Central and peripheral airway nitric oxide in patients with stable and exacerbated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Breath. Res. 2018, 12, 036017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, Z.; Horvath, P.; Puskas, R.; Galffy, G.; Losonczy, G.; Horvath, I.; Bikov, A. A suitable protocol for measuring alveolar nitric oxide in asthma with differing severity to assess peripheral airways inflammation. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Barnes, P.J.; Loukides, S.; Sterk, P.J.; Hogman, M.; Olin, A.C.; Amann, A.; Antus, B.; Baraldi, E.; Bikov, A.; et al. A European Respiratory Society technical standard: Exhaled biomarkers in lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic, S.; European Respiratory, S. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukias, N.M.; George, S.C. A two-compartment model of pulmonary nitric oxide exchange dynamics. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, P.; Bargagli, E.; Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Pieroni, M.; Fontana, G.A.; Sestini, P.; Refin, R.M. Extended Exhaled Nitric Oxide Analysis in Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, R.E.; Gugnani, M.K.; Abrams, J.; Mayes, M.D. Partitioning of alveolar and conducting airway nitric oxide in scleroderma lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, J.R.; Abman, S.H.; Gladwin, M.T. Nitric oxide deficiency and endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaid, A.; Saleh, D. Reduced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, T.; Stiller, B.; McPhaden, A.R.; Wadsworth, R.M. Nitric oxide synthases in infants and children with pulmonary hypertension and congenital heart disease. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweik, R.A.; Laskowski, D.; Abu-Soud, H.M.; Kaneko, F.; Hutte, R.; Stuehr, D.J.; Erzurum, S.C. Nitric oxide synthesis in the lung. Regulation by oxygen through a kinetic mechanism. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumpanakis, D.; Karagiannis, K.; Paredi, P.; Bikov, A.; Bonifazi, M.; Lota, H.K.; Kalsi, H.; Minelli, C.; Dikaios, N.; Kastis, G.A.; et al. Contribution of Peripheral Airways Dysfunction to Poor Quality of Life in Sarcoidosis. Chest 2025, 168, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.U.; Mellemkjaer, S.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Bendstrup, E.; Simonsen, U.; Hilberg, O. Diagnostic and prognostic role of biomarkers for pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, N.O.; Bingol, Z.; Kiyan, E.; Karaayvaz, E.B.; Bilge, A.K.; Issever, H.; Okumus, G. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurement in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Follow-Up Study. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 24, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, M.; Dweik, R.A.; Laskowski, D.; Arroliga, A.C.; Erzurum, S.C. High levels of nitric oxide in individuals with pulmonary hypertension receiving epoprostenol therapy. Lung 2001, 179, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Fukuo, K.; Nakahashi, T.; Hata, S.; Morimoto, S.; Ogihara, T. cGMP upregulates nitric oxide synthase expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 1995, 25, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, M.; Jahn, H.U.; Seybold, J.; Neurohr, C.; Barnes, P.J.; Hippenstiel, S.; Kraemer, H.J.; Suttorp, N. Identification and function of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csósza, G.; Valkó, L.; Dinya, E.; Losonczy, G.; Müller, V.; Lázár, Z.; Karlócai, K. Right Ventricular Stroke Work Index in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Retrospective Observational Study. Pulm. Circ. 2024, 14, e12433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Cooper, B.G.; Jensen, R.; Kendrick, A.; MacIntyre, N.R.; Thompson, B.R.; Wanger, J. 2017 ERS/ATS Standards for Single-Breath Carbon Monoxide Uptake in the Lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control Subjects | Patients with Pre-Capillary PH | p-Value | Patients with Pre-Capillary PH | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Group 3 | Group 4 | |||||
| N | 27 | 52 | 23 | 11 | 18 | ||
| Male, N (%) | 12 (44) | 26 (50) | 0.81 | 10 (44%) | 9 (82%) | 7 (39%) | 0.06 |
| Age, years | 54 ± 10 | 58 ± 15 | 0.27 | 55 ± 15 | 65 ± 11 | 56 ± 16 | 0.18 |
| Never/former/current smoker, N | 15/10/2 | 40/11/1 | 0.12 | 18/4/1 | 6/5/0 | 16/2/0 | 0.16 |
| Pack-years | 26 (13–47) | 30 (20–40) | 0.60 | 30 (15–32) | 40 (30–63) | 17 (10–21) | 0.07 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 28.0 ± 6.0 | 29.0 ± 6.9 | 0.50 | 28.8 ± 6.2 | 27.0 ± 6.4 | 30.8 ± 7.8 | 0.28 |
| Inhaled therapy, N (%) | NA | NA | |||||
| Inhaled corticosteroid | 0 | 7 (13) | 2 (9) | 3 (27) | 2 (11) | ||
| Long-acting beta2-agonist | 2 (7) | 8 (15) | 3 (13) | 3 (27) | 1 (6) | ||
| Long-acting anticholinergic | 4 (15) | 6 (12) | 2 (9) | 3 (27) | 0 | ||
| Systemic corticosteroid use, N (%) | 0 | 6 (12) | 0.09 | 0 | 5 (45) | 1 (6) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory comorbidities, N (%) | 0.92 | <0.001 | |||||
| Bronchial asthma | 1 (4) | 3 (6) | 1 (4) | 0 | 2 (11) | ||
| COPD | 4 (15) | 6 (12) | 2 (9) | 4 (36) | 0 | ||
| ILD | 4 (15) | 7 (13) | 0 | 7 (64) | 0 | ||
| OSA | 0 | 1 (2) | 0 | 1 (9) | 0 | ||
| FVC, L | 3.60 ± 0.74 | 3.23 ± 1.26 | 0.17 | 3.22 ± 1.11 | 2.38 ± 0.77 ## | 3.77 ± 1.40 | 0.01 |
| FVC, % reference | 96 ± 13 | 92 ± 14 | 0.06 | 91 ± 21 | 64 ± 20 ** ### | 97 ± 19 | <0.001 |
| FEV1, L | 2.77 ± 0.63 | 2.33 ± 0.93 | 0.10 | 2.45 ± 0.87 | 1.78 ± 0.49 ## | 2.83 ± 1.00 | <0.01 |
| FEV1, % reference | 90 ± 16 | 82 ± 22 | 0.09 | 84 ± 17 | 61 ± 20 ** ### | 93 ± 21 | <0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | 0.78 ± 0.13 | 0.76 ± 0.10 | 0.66 | 0.76 ± 0.10 | 0.78 ± 0.13 | 0.76 ± 0.08 | 0.92 |
| DLCO, % reference | 87 ± 19 N = 8 | 72 ± 2 | NA | 77 ± 30 | 47 ± 19 ** # | 82 ± 16 | <0.01 |
| 6MWD, m | 465 ± 76 N = 8 | 350 ± 137 | NA | 366 ± 125 | 252 ± 101 # | 388 ± 148 | 0.02 |
| Total N = 52 | Group 1 N = 23 | Group 3 N = 11 | Group 4 N = 18 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mPAP, mmHg | 46 (37–54) | 52 (39–59) | 44 (36–49) | 44 (37–52) | 0.21 |
| PVR, Wood Unit | 8.5 (5.8–12.5) | 9.8 (5.9–14.7) | 9.8 (5.7–12.1) | 7.6 (4.6–10.0) | 0.22 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 8 (6–11) | 8 (7–11) | 8 (5–10) | 10 (6–14) | 0.57 |
| Right atrial pressure, mmHg | 10 (4–15) | 9 (3–13) | 6 (2–13) | 14 (6–19) | 0.11 |
| Cardiac index, L/min/m2 | 2.1 (1.9–2.7) | 1.9 (1.7–2.8) | 2.2 (2.0–2.7) | 2.1 (1.9–2.7) | 0.58 |
| Stroke volume index, mL/m2 | 28 (23–36) | 28 (21–37) | 28 (22–36) | 27 (24–33) | 0.70 |
| SvO2, % | 66 (62–69) N = 42 | 66 (61–70) N = 21 | 67 (63–69) N = 9 | 65 (62–68) N = 12 | 0.86 |
| TAPSE, mm | 17 (13–20) | 14 (11–20) | 18 (13–19) | 20 (16–22) | 0.13 |
| Estimated sPAP, mmHg | 74 (59–93) | 86 (65–94) | 79 (63–96) | 62 (41–89) | 0.07 |
| TAPSE/estimated sPAP, mm/mmHg | 0.22 (0.14–0.34) | 0.16 (0.12–0.29) | 0.20 (0.14–0.29) | 0.32 (0.22–0.49) * | 0.02 |
| RV-PA uncoupling, N (%) | 37 (71) | 18 (78) | 10 (91) | 9 (50) | 0.04 |
| Right atrial area, cm2 | 25 (18–31) | 26 (21–31) | 26 (21–32) | 21 (17–30) | 0.46 |
| WHO functional classes, N (%) | 0.01 | ||||
| I or II | 10 (19) | 2 (9) | 0 | 8 (44) | |
| III | 38 (73) | 20 (87) | 10 (91) | 8 (44) | |
| IV | 4 (8) | 1 (4) | 1 (9) | 2 (12) | |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 1676 (433–3297) | 2161 (455–3461) | 2202 (645–4107) | 785 (169–2778) | 0.28 |
| Diagnosis | Follow-Up | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WHO functional classes, N | <0.001 | ||
| I or II | 10 | 21 | |
| III | 16 | 7 | |
| IV | 2 | 0 | |
| 6MWD, m N = 26 | 403 ± 123 | 435 ± 123 | 0.02 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 881 (282–2667) | 517 (220–1636) | 0.03 |
| Four-strata risk category | <0.01 | ||
| Low | 5 | 10 | |
| Intermediate low risk | 9 | 13 | |
| Intermediate high risk | 13 | 2 | |
| High risk | 1 | 3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Csoma, B.; Szűcs, G.; Bikov, A.; Rozgonyi, Z.D.; Nagy, A.; Matics, Z.; Müller, V.; Karlócai, K.; Csósza, G.; Lázár, Z. Alveolar and Bronchial Nitric Oxide Parameters in Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122957
Csoma B, Szűcs G, Bikov A, Rozgonyi ZD, Nagy A, Matics Z, Müller V, Karlócai K, Csósza G, Lázár Z. Alveolar and Bronchial Nitric Oxide Parameters in Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(12):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122957
Chicago/Turabian StyleCsoma, Balázs, Gergő Szűcs, András Bikov, Zsolt Dezső Rozgonyi, Alexandra Nagy, Zsombor Matics, Veronika Müller, Kristóf Karlócai, Györgyi Csósza, and Zsófia Lázár. 2025. "Alveolar and Bronchial Nitric Oxide Parameters in Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension" Biomedicines 13, no. 12: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122957
APA StyleCsoma, B., Szűcs, G., Bikov, A., Rozgonyi, Z. D., Nagy, A., Matics, Z., Müller, V., Karlócai, K., Csósza, G., & Lázár, Z. (2025). Alveolar and Bronchial Nitric Oxide Parameters in Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension. Biomedicines, 13(12), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13122957








